前言
标签分配也是影响目标检测AP的一个重要因素,仅是训练技巧,不会增加推理耗时。例如ATSS就采用自适应正负样本分配的方式带来2%的无痛涨点。最近也是好奇这些标签分配具体是怎么做的,故记录目前学习到的4种算法。代码目前基本上没啥详细注释(因为是直接抄来的),后续会精读加注释。
一、论文链接
ATSS
SimOTA(YOLOX)
taskAligned(TOOD)
o2f
二、ATSS
原理介绍
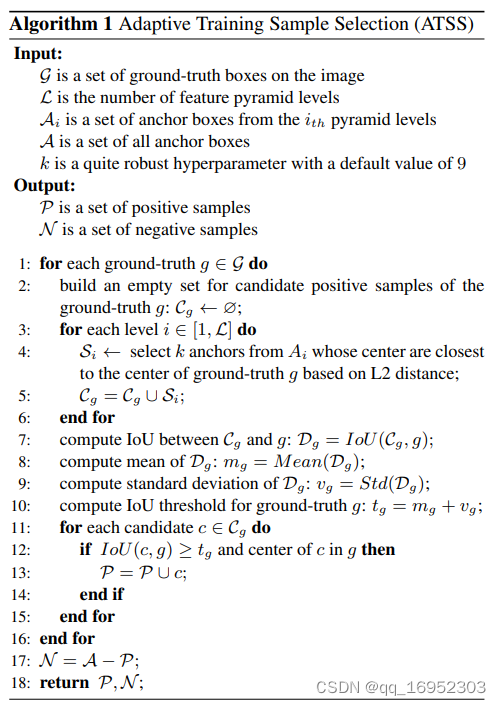
直接上ATSS标签分配算法步骤,用人话说就是:
- 对于每一个GT,根据中心距离最近的原则,每个FPN层选择k个anchor,假如是4个FPN层,那一共会到4k个
- 计算GT和k个anchor之间的IOUs
- 求IOUs的均值和均方差,mean、std
- 将均值和均方差相加的和作为IOU阈值
- 将IOU高于阈值的挑出来作为正样本
算法就是这么简单,却很有效果。以IOU均值和方差之和作为均值的好处在于:若IOU都很高,此时均值也较高,说明匹配的都挺好的,所以IOU阈值应该较高;若IOU差异大,此时IOU的方差就会大,就会出现一些匹配的比较好,还有一些匹配的比较差,此时加上方差就会把匹配的差的去掉。IOU方差有利于确定哪几个FPN层来预测目标,如下图所示:
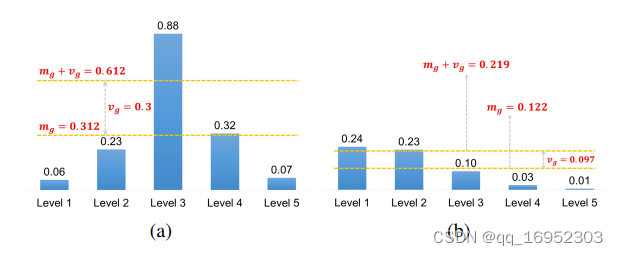
(a)的方差比较高,均值加方差,此时只有level3的被保留了,(b)的方差就比较低,1、2都可适配。
代码
抄自PaddleDetection
# Copyright (c) 2021 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import numpy as np
import paddle
import paddle.nn as nn
import paddle.nn.functional as F
from ppdet.core.workspace import register
from ..bbox_utils import iou_similarity, batch_iou_similarity
from ..bbox_utils import bbox_center
from .utils import (check_points_inside_bboxes, compute_max_iou_anchor,
compute_max_iou_gt)
__all__ = ['ATSSAssigner']
@register
class ATSSAssigner(nn.Layer):
"""Bridging the Gap Between Anchor-based and Anchor-free Detection
via Adaptive Training Sample Selection
"""
__shared__ = ['num_classes']
def __init__(self,
topk=9,
num_classes=80,
force_gt_matching=False,
eps=1e-9):
super(ATSSAssigner, self).__init__()
self.topk = topk
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.force_gt_matching = force_gt_matching
self.eps = eps
def _gather_topk_pyramid(self, gt2anchor_distances, num_anchors_list,
pad_gt_mask):
gt2anchor_distances_list = paddle.split(
gt2anchor_distances, num_anchors_list, axis=-1)
num_anchors_index = np.cumsum(num_anchors_list).tolist()
num_anchors_index = [0, ] + num_anchors_index[:-1]
is_in_topk_list = []
topk_idxs_list = []
for distances, anchors_index in zip(gt2anchor_distances_list,
num_anchors_index):
num_anchors = distances.shape[-1]
_, topk_idxs = paddle.topk(
distances, self.topk, axis=-1, largest=False)
topk_idxs_list.append(topk_idxs + anchors_index)
is_in_topk = F.one_hot(topk_idxs, num_anchors).sum(
axis=-2).astype(gt2anchor_distances.dtype)
is_in_topk_list.append(is_in_topk * pad_gt_mask)
is_in_topk_list = paddle.concat(is_in_topk_list, axis=-1)
topk_idxs_list = paddle.concat(topk_idxs_list, axis=-1)
return is_in_topk_list, topk_idxs_list
@paddle.no_grad()
def forward(self,
anchor_bboxes,
num_anchors_list,
gt_labels,
gt_bboxes,
pad_gt_mask,
bg_index,
gt_scores=None,
pred_bboxes=None):
r"""This code is based on
https://github.com/fcjian/TOOD/blob/master/mmdet/core/bbox/assigners/atss_assigner.py
The assignment is done in following steps
1. compute iou between all bbox (bbox of all pyramid levels) and gt
2. compute center distance between all bbox and gt
3. on each pyramid level, for each gt, select k bbox whose center
are closest to the gt center, so we total select k*l bbox as
candidates for each gt
4. get corresponding iou for the these candidates, and compute the
mean and std, set mean + std as the iou threshold
5. select these candidates whose iou are greater than or equal to
the threshold as positive
6. limit the positive sample's center in gt
7. if an anchor box is assigned to multiple gts, the one with the
highest iou will be selected.
Args:
anchor_bboxes (Tensor, float32): pre-defined anchors, shape(L, 4),
"xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax" format
num_anchors_list (List): num of anchors in each level
gt_labels (Tensor, int64|int32): Label of gt_bboxes, shape(B, n, 1)
gt_bboxes (Tensor, float32): Ground truth bboxes, shape(B, n, 4)
pad_gt_mask (Tensor, float32): 1 means bbox, 0 means no bbox, shape(B, n, 1)
bg_index (int): background index
gt_scores (Tensor|None, float32) Score of gt_bboxes,
shape(B, n, 1), if None, then it will initialize with one_hot label
pred_bboxes (Tensor, float32, optional): predicted bounding boxes, shape(B, L, 4)
Returns:
assigned_labels (Tensor): (B, L)
assigned_bboxes (Tensor): (B, L, 4)
assigned_scores (Tensor): (B, L, C), if pred_bboxes is not None, then output ious
"""
assert gt_labels.ndim == gt_bboxes.ndim and \
gt_bboxes.ndim == 3
num_anchors, _ = anchor_bboxes.shape
batch_size, num_max_boxes, _ = gt_bboxes.shape
# negative batch
if num_max_boxes == 0:
assigned_labels = paddle.full(
[batch_size, num_anchors], bg_index, dtype=gt_labels.dtype)
assigned_bboxes = paddle.zeros([batch_size, num_anchors, 4])
assigned_scores = paddle.zeros(
[batch_size, num_anchors, self.num_classes])
return assigned_labels, assigned_bboxes, assigned_scores
# 1. compute iou between gt and anchor bbox, [B, n, L]
ious = iou_similarity(gt_bboxes.reshape([-1, 4]), anchor_bboxes)
ious = ious.reshape([batch_size, -1, num_anchors])
# 2. compute center distance between all anchors and gt, [B, n, L]
gt_centers = bbox_center(gt_bboxes.reshape([-1, 4])).unsqueeze(1)
anchor_centers = bbox_center(anchor_bboxes)
gt2anchor_distances = (gt_centers - anchor_centers.unsqueeze(0)) \
.norm(2, axis=-1).reshape([batch_size, -1, num_anchors])
# 3. on each pyramid level, selecting topk closest candidates
# based on the center distance, [B, n, L]
is_in_topk, topk_idxs = self._gather_topk_pyramid(
gt2anchor_distances, num_anchors_list, pad_gt_mask)
# 4. get corresponding iou for the these candidates, and compute the
# mean and std, 5. set mean + std as the iou threshold
iou_candidates = ious * is_in_topk
iou_threshold = paddle.index_sample(
iou_candidates.flatten(stop_axis=-2),
topk_idxs.flatten(stop_axis=-2))
iou_threshold = iou_threshold.reshape([batch_size, num_max_boxes, -1])
iou_threshold = iou_threshold.mean(axis=-1, keepdim=True) + \
iou_threshold.std(axis=-1, keepdim=True)
is_in_topk = paddle.where(iou_candidates > iou_threshold, is_in_topk,
paddle.zeros_like(is_in_topk))
# 6. check the positive sample's center in gt, [B, n, L]
is_in_gts = check_points_inside_bboxes(anchor_centers, gt_bboxes)
# select positive sample, [B, n, L]
mask_positive = is_in_topk * is_in_gts * pad_gt_mask
# 7. if an anchor box is assigned to multiple gts,
# the one with the highest iou will be selected.
mask_positive_sum = mask_positive.sum(axis=-2)
if mask_positive_sum.max() > 1:
mask_multiple_gts = (mask_positive_sum.unsqueeze(1) > 1).tile(
[1, num_max_boxes, 1])
is_max_iou = compute_max_iou_anchor(ious)
mask_positive = paddle.where(mask_multiple_gts, is_max_iou,
mask_positive)
mask_positive_sum = mask_positive.sum(axis=-2)
# 8. make sure every gt_bbox matches the anchor
if self.force_gt_matching:
is_max_iou = compute_max_iou_gt(ious) * pad_gt_mask
mask_max_iou = (is_max_iou.sum(-2, keepdim=True) == 1).tile(
[1, num_max_boxes, 1])
mask_positive = paddle.where(mask_max_iou, is_max_iou,
mask_positive)
mask_positive_sum = mask_positive.sum(axis=-2)
assigned_gt_index = mask_positive.argmax(axis=-2)
# assigned target
batch_ind = paddle.arange(
end=batch_size, dtype=gt_labels.dtype).unsqueeze(-1)
assigned_gt_index = assigned_gt_index + batch_ind * num_max_boxes
assigned_labels = paddle.gather(
gt_labels.flatten(), assigned_gt_index.flatten(), axis=0)
assigned_labels = assigned_labels.reshape([batch_size, num_anchors])
assigned_labels = paddle.where(
mask_positive_sum > 0, assigned_labels,
paddle.full_like(assigned_labels, bg_index))
assigned_bboxes = paddle.gather(
gt_bboxes.reshape([-1, 4]), assigned_gt_index.flatten(), axis=0)
assigned_bboxes = assigned_bboxes.reshape([batch_size, num_anchors, 4])
assigned_scores = F.one_hot(assigned_labels, self.num_classes + 1)
ind = list(range(self.num_classes + 1))
ind.remove(bg_index)
assigned_scores = paddle.index_select(
assigned_scores, paddle.to_tensor(ind), axis=-1)
if pred_bboxes is not None:
# assigned iou
ious = batch_iou_similarity(gt_bboxes, pred_bboxes) * mask_positive
ious = ious.max(axis=-2).unsqueeze(-1)
assigned_scores *= ious
elif gt_scores is not None:
gather_scores = paddle.gather(
gt_scores.flatten(), assigned_gt_index.flatten(), axis=0)
gather_scores = gather_scores.reshape([batch_size, num_anchors])
gather_scores = paddle.where(mask_positive_sum > 0, gather_scores,
paddle.zeros_like(gather_scores))
assigned_scores *= gather_scores.unsqueeze(-1)
return assigned_labels, assigned_bboxes, assigned_scores
SimOTA
原理介绍

盗个图,SimOTA的算法流程也极其简单,不多说了看图把。需要说明的是,前期由于模型预测不准,dynamic_k基本就为1。
代码
再次抄自PaddleDetection
# Copyright (c) 2021 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# The code is based on:
# https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/blob/master/mmdet/core/bbox/assigners/sim_ota_assigner.py
import paddle
import numpy as np
import paddle.nn.functional as F
from ppdet.modeling.losses.varifocal_loss import varifocal_loss
from ppdet.modeling.bbox_utils import batch_bbox_overlaps
from ppdet.core.workspace import register
@register
class SimOTAAssigner(object):
"""Computes matching between predictions and ground truth.
Args:
center_radius (int | float, optional): Ground truth center size
to judge whether a prior is in center. Default 2.5.
candidate_topk (int, optional): The candidate top-k which used to
get top-k ious to calculate dynamic-k. Default 10.
iou_weight (int | float, optional): The scale factor for regression
iou cost. Default 3.0.
cls_weight (int | float, optional): The scale factor for classification
cost. Default 1.0.
num_classes (int): The num_classes of dataset.
use_vfl (int): Whether to use varifocal_loss when calculating the cost matrix.
"""
__shared__ = ['num_classes']
def __init__(self,
center_radius=2.5,
candidate_topk=10,
iou_weight=3.0,
cls_weight=1.0,
num_classes=80,
use_vfl=True):
self.center_radius = center_radius
self.candidate_topk = candidate_topk
self.iou_weight = iou_weight
self.cls_weight = cls_weight
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.use_vfl = use_vfl
def get_in_gt_and_in_center_info(self, flatten_center_and_stride,
gt_bboxes):
num_gt = gt_bboxes.shape[0]
flatten_x = flatten_center_and_stride[:, 0].unsqueeze(1).tile(
[1, num_gt])
flatten_y = flatten_center_and_stride[:, 1].unsqueeze(1).tile(
[1, num_gt])
flatten_stride_x = flatten_center_and_stride[:, 2].unsqueeze(1).tile(
[1, num_gt])
flatten_stride_y = flatten_center_and_stride[:, 3].unsqueeze(1).tile(
[1, num_gt])
# is prior centers in gt bboxes, shape: [n_center, n_gt]
l_ = flatten_x - gt_bboxes[:, 0]
t_ = flatten_y - gt_bboxes[:, 1]
r_ = gt_bboxes[:, 2] - flatten_x
b_ = gt_bboxes[:, 3] - flatten_y
deltas = paddle.stack([l_, t_, r_, b_], axis=1)
is_in_gts = deltas.min(axis=1) > 0
is_in_gts_all = is_in_gts.sum(axis=1) > 0
# is prior centers in gt centers
gt_center_xs = (gt_bboxes[:, 0] + gt_bboxes[:, 2]) / 2.0
gt_center_ys = (gt_bboxes[:, 1] + gt_bboxes[:, 3]) / 2.0
ct_bound_l = gt_center_xs - self.center_radius * flatten_stride_x
ct_bound_t = gt_center_ys - self.center_radius * flatten_stride_y
ct_bound_r = gt_center_xs + self.center_radius * flatten_stride_x
ct_bound_b = gt_center_ys + self.center_radius * flatten_stride_y
cl_ = flatten_x - ct_bound_l
ct_ = flatten_y - ct_bound_t
cr_ = ct_bound_r - flatten_x
cb_ = ct_bound_b - flatten_y
ct_deltas = paddle.stack([cl_, ct_, cr_, cb_], axis=1)
is_in_cts = ct_deltas.min(axis=1) > 0
is_in_cts_all = is_in_cts.sum(axis=1) > 0
# in any of gts or gt centers, shape: [n_center]
is_in_gts_or_centers_all = paddle.logical_or(is_in_gts_all,
is_in_cts_all)
is_in_gts_or_centers_all_inds = paddle.nonzero(
is_in_gts_or_centers_all).squeeze(1)
# both in gts and gt centers, shape: [num_fg, num_gt]
is_in_gts_and_centers = paddle.logical_and(
paddle.gather(
is_in_gts.cast('int'), is_in_gts_or_centers_all_inds,
axis=0).cast('bool'),
paddle.gather(
is_in_cts.cast('int'), is_in_gts_or_centers_all_inds,
axis=0).cast('bool'))
return is_in_gts_or_centers_all, is_in_gts_or_centers_all_inds, is_in_gts_and_centers
def dynamic_k_matching(self, cost_matrix, pairwise_ious, num_gt):
match_matrix = np.zeros_like(cost_matrix.numpy())
# select candidate topk ious for dynamic-k calculation
topk_ious, _ = paddle.topk(pairwise_ious, self.candidate_topk, axis=0)
# calculate dynamic k for each gt
dynamic_ks = paddle.clip(topk_ious.sum(0).cast('int'), min=1)
for gt_idx in range(num_gt):
_, pos_idx = paddle.topk(
cost_matrix[:, gt_idx], k=dynamic_ks[gt_idx], largest=False)
match_matrix[:, gt_idx][pos_idx.numpy()] = 1.0
del topk_ious, dynamic_ks, pos_idx
# match points more than two gts
extra_match_gts_mask = match_matrix.sum(1) > 1
if extra_match_gts_mask.sum() > 0:
cost_matrix = cost_matrix.numpy()
cost_argmin = np.argmin(
cost_matrix[extra_match_gts_mask, :], axis=1)
match_matrix[extra_match_gts_mask, :] *= 0.0
match_matrix[extra_match_gts_mask, cost_argmin] = 1.0
# get foreground mask
match_fg_mask_inmatrix = match_matrix.sum(1) > 0
match_gt_inds_to_fg = match_matrix[match_fg_mask_inmatrix, :].argmax(1)
return match_gt_inds_to_fg, match_fg_mask_inmatrix
def get_sample(self, assign_gt_inds, gt_bboxes):
pos_inds = np.unique(np.nonzero(assign_gt_inds > 0)[0])
neg_inds = np.unique(np.nonzero(assign_gt_inds == 0)[0])
pos_assigned_gt_inds = assign_gt_inds[pos_inds] - 1
if gt_bboxes.size == 0:
# hack for index error case
assert pos_assigned_gt_inds.size == 0
pos_gt_bboxes = np.empty_like(gt_bboxes).reshape(-1, 4)
else:
if len(gt_bboxes.shape) < 2:
gt_bboxes = gt_bboxes.resize(-1, 4)
pos_gt_bboxes = gt_bboxes[pos_assigned_gt_inds, :]
return pos_inds, neg_inds, pos_gt_bboxes, pos_assigned_gt_inds
def __call__(self,
flatten_cls_pred_scores,
flatten_center_and_stride,
flatten_bboxes,
gt_bboxes,
gt_labels,
eps=1e-7):
"""Assign gt to priors using SimOTA.
TODO: add comment.
Returns:
assign_result: The assigned result.
"""
num_gt = gt_bboxes.shape[0]
num_bboxes = flatten_bboxes.shape[0]
if num_gt == 0 or num_bboxes == 0:
# No ground truth or boxes
label = np.ones([num_bboxes], dtype=np.int64) * self.num_classes
label_weight = np.ones([num_bboxes], dtype=np.float32)
bbox_target = np.zeros_like(flatten_center_and_stride)
return 0, label, label_weight, bbox_target
is_in_gts_or_centers_all, is_in_gts_or_centers_all_inds, is_in_boxes_and_center = self.get_in_gt_and_in_center_info(
flatten_center_and_stride, gt_bboxes)
# bboxes and scores to calculate matrix
valid_flatten_bboxes = flatten_bboxes[is_in_gts_or_centers_all_inds]
valid_cls_pred_scores = flatten_cls_pred_scores[
is_in_gts_or_centers_all_inds]
num_valid_bboxes = valid_flatten_bboxes.shape[0]
pairwise_ious = batch_bbox_overlaps(valid_flatten_bboxes,
gt_bboxes) # [num_points,num_gts]
if self.use_vfl:
gt_vfl_labels = gt_labels.squeeze(-1).unsqueeze(0).tile(
[num_valid_bboxes, 1]).reshape([-1])
valid_pred_scores = valid_cls_pred_scores.unsqueeze(1).tile(
[1, num_gt, 1]).reshape([-1, self.num_classes])
vfl_score = np.zeros(valid_pred_scores.shape)
vfl_score[np.arange(0, vfl_score.shape[0]), gt_vfl_labels.numpy(
)] = pairwise_ious.reshape([-1])
vfl_score = paddle.to_tensor(vfl_score)
losses_vfl = varifocal_loss(
valid_pred_scores, vfl_score,
use_sigmoid=False).reshape([num_valid_bboxes, num_gt])
losses_giou = batch_bbox_overlaps(
valid_flatten_bboxes, gt_bboxes, mode='giou')
cost_matrix = (
losses_vfl * self.cls_weight + losses_giou * self.iou_weight +
paddle.logical_not(is_in_boxes_and_center).cast('float32') *
100000000)
else:
iou_cost = -paddle.log(pairwise_ious + eps)
gt_onehot_label = (F.one_hot(
gt_labels.squeeze(-1).cast(paddle.int64),
flatten_cls_pred_scores.shape[-1]).cast('float32').unsqueeze(0)
.tile([num_valid_bboxes, 1, 1]))
valid_pred_scores = valid_cls_pred_scores.unsqueeze(1).tile(
[1, num_gt, 1])
cls_cost = F.binary_cross_entropy(
valid_pred_scores, gt_onehot_label, reduction='none').sum(-1)
cost_matrix = (
cls_cost * self.cls_weight + iou_cost * self.iou_weight +
paddle.logical_not(is_in_boxes_and_center).cast('float32') *
100000000)
match_gt_inds_to_fg, match_fg_mask_inmatrix = \
self.dynamic_k_matching(
cost_matrix, pairwise_ious, num_gt)
# sample and assign results
assigned_gt_inds = np.zeros([num_bboxes], dtype=np.int64)
match_fg_mask_inall = np.zeros_like(assigned_gt_inds)
match_fg_mask_inall[is_in_gts_or_centers_all.numpy(
)] = match_fg_mask_inmatrix
assigned_gt_inds[match_fg_mask_inall.astype(
np.bool)] = match_gt_inds_to_fg + 1
pos_inds, neg_inds, pos_gt_bboxes, pos_assigned_gt_inds \
= self.get_sample(assigned_gt_inds, gt_bboxes.numpy())
bbox_target = np.zeros_like(flatten_bboxes)
bbox_weight = np.zeros_like(flatten_bboxes)
label = np.ones([num_bboxes], dtype=np.int64) * self.num_classes
label_weight = np.zeros([num_bboxes], dtype=np.float32)
if len(pos_inds) > 0:
gt_labels = gt_labels.numpy()
pos_bbox_targets = pos_gt_bboxes
bbox_target[pos_inds, :] = pos_bbox_targets
bbox_weight[pos_inds, :] = 1.0
if not np.any(gt_labels):
label[pos_inds] = 0
else:
label[pos_inds] = gt_labels.squeeze(-1)[pos_assigned_gt_inds]
label_weight[pos_inds] = 1.0
if len(neg_inds) > 0:
label_weight[neg_inds] = 1.0
pos_num = max(pos_inds.size, 1)
return pos_num, label, label_weight, bbox_target
TaskAligned assigner
原理介绍
这是TOOD里面的一种方法,被用在了百度的pp-picodet中,非常强,感觉也很精妙,配合VFL loss效果很好。下面介绍一下算法步骤:
- 将iou 和 分类分数一起算一个综合分数 t = s α ∗ u β t=s^\alpha*u^\beta t=sα∗uβ
- 根据t选topK个预测框作为正样本。
- 计算新的软标签 t ′ = t / m a x t ∗ m a x u t'=t/max_t * max_u t′=t/maxt∗maxu这里对t进行了一个归一化操作,让最大值对应最大的IOU。感觉这个非常强,分类分数和IOU都并合并进了软标签。
代码
# Copyright (c) 2021 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import paddle
import paddle.nn as nn
import paddle.nn.functional as F
from ppdet.core.workspace import register
from ..bbox_utils import batch_iou_similarity
from .utils import (gather_topk_anchors, check_points_inside_bboxes,
compute_max_iou_anchor)
__all__ = ['TaskAlignedAssigner']
@register
class TaskAlignedAssigner(nn.Layer):
"""TOOD: Task-aligned One-stage Object Detection
"""
def __init__(self, topk=13, alpha=1.0, beta=6.0, eps=1e-9):
super(TaskAlignedAssigner, self).__init__()
self.topk = topk
self.alpha = alpha
self.beta = beta
self.eps = eps
@paddle.no_grad()
def forward(self,
pred_scores,
pred_bboxes,
anchor_points,
num_anchors_list,
gt_labels,
gt_bboxes,
pad_gt_mask,
bg_index,
gt_scores=None):
r"""This code is based on
https://github.com/fcjian/TOOD/blob/master/mmdet/core/bbox/assigners/task_aligned_assigner.py
The assignment is done in following steps
1. compute alignment metric between all bbox (bbox of all pyramid levels) and gt
2. select top-k bbox as candidates for each gt
3. limit the positive sample's center in gt (because the anchor-free detector
only can predict positive distance)
4. if an anchor box is assigned to multiple gts, the one with the
highest iou will be selected.
Args:
pred_scores (Tensor, float32): predicted class probability, shape(B, L, C)
pred_bboxes (Tensor, float32): predicted bounding boxes, shape(B, L, 4)
anchor_points (Tensor, float32): pre-defined anchors, shape(L, 2), "cxcy" format
num_anchors_list (List): num of anchors in each level, shape(L)
gt_labels (Tensor, int64|int32): Label of gt_bboxes, shape(B, n, 1)
gt_bboxes (Tensor, float32): Ground truth bboxes, shape(B, n, 4)
pad_gt_mask (Tensor, float32): 1 means bbox, 0 means no bbox, shape(B, n, 1)
bg_index (int): background index
gt_scores (Tensor|None, float32) Score of gt_bboxes, shape(B, n, 1)
Returns:
assigned_labels (Tensor): (B, L)
assigned_bboxes (Tensor): (B, L, 4)
assigned_scores (Tensor): (B, L, C)
"""
assert pred_scores.ndim == pred_bboxes.ndim
assert gt_labels.ndim == gt_bboxes.ndim and \
gt_bboxes.ndim == 3
batch_size, num_anchors, num_classes = pred_scores.shape
_, num_max_boxes, _ = gt_bboxes.shape
# negative batch
if num_max_boxes == 0:
assigned_labels = paddle.full(
[batch_size, num_anchors], bg_index, dtype=gt_labels.dtype)
assigned_bboxes = paddle.zeros([batch_size, num_anchors, 4])
assigned_scores = paddle.zeros(
[batch_size, num_anchors, num_classes])
return assigned_labels, assigned_bboxes, assigned_scores
# compute iou between gt and pred bbox, [B, n, L]
ious = batch_iou_similarity(gt_bboxes, pred_bboxes)
# gather pred bboxes class score
pred_scores = pred_scores.transpose([0, 2, 1])
batch_ind = paddle.arange(
end=batch_size, dtype=gt_labels.dtype).unsqueeze(-1)
gt_labels_ind = paddle.stack(
[batch_ind.tile([1, num_max_boxes]), gt_labels.squeeze(-1)],
axis=-1)
bbox_cls_scores = paddle.gather_nd(pred_scores, gt_labels_ind)
# compute alignment metrics, [B, n, L]
alignment_metrics = bbox_cls_scores.pow(self.alpha) * ious.pow(
self.beta)
# check the positive sample's center in gt, [B, n, L]
is_in_gts = check_points_inside_bboxes(anchor_points, gt_bboxes)
# select topk largest alignment metrics pred bbox as candidates
# for each gt, [B, n, L]
is_in_topk = gather_topk_anchors(
alignment_metrics * is_in_gts, self.topk, topk_mask=pad_gt_mask)
# select positive sample, [B, n, L]
mask_positive = is_in_topk * is_in_gts * pad_gt_mask
# if an anchor box is assigned to multiple gts,
# the one with the highest iou will be selected, [B, n, L]
mask_positive_sum = mask_positive.sum(axis=-2)
if mask_positive_sum.max() > 1:
mask_multiple_gts = (mask_positive_sum.unsqueeze(1) > 1).tile(
[1, num_max_boxes, 1])
is_max_iou = compute_max_iou_anchor(ious)
mask_positive = paddle.where(mask_multiple_gts, is_max_iou,
mask_positive)
mask_positive_sum = mask_positive.sum(axis=-2)
assigned_gt_index = mask_positive.argmax(axis=-2)
# assigned target
assigned_gt_index = assigned_gt_index + batch_ind * num_max_boxes
assigned_labels = paddle.gather(
gt_labels.flatten(), assigned_gt_index.flatten(), axis=0)
assigned_labels = assigned_labels.reshape([batch_size, num_anchors])
assigned_labels = paddle.where(
mask_positive_sum > 0, assigned_labels,
paddle.full_like(assigned_labels, bg_index))
assigned_bboxes = paddle.gather(
gt_bboxes.reshape([-1, 4]), assigned_gt_index.flatten(), axis=0)
assigned_bboxes = assigned_bboxes.reshape([batch_size, num_anchors, 4])
assigned_scores = F.one_hot(assigned_labels, num_classes + 1)
ind = list(range(num_classes + 1))
ind.remove(bg_index)
assigned_scores = paddle.index_select(
assigned_scores, paddle.to_tensor(ind), axis=-1)
# rescale alignment metrics
alignment_metrics *= mask_positive
max_metrics_per_instance = alignment_metrics.max(axis=-1, keepdim=True)
max_ious_per_instance = (ious * mask_positive).max(axis=-1,
keepdim=True)
alignment_metrics = alignment_metrics / (
max_metrics_per_instance + self.eps) * max_ious_per_instance
alignment_metrics = alignment_metrics.max(-2).unsqueeze(-1)
assigned_scores = assigned_scores * alignment_metrics
return assigned_labels, assigned_bboxes, assigned_scores
o2f用于端对端密集检测的1对少量标签分配策略
原理介绍
这是2023年CVPR(虽然我读完很怀疑。。。可能是我没体会到精妙之处),它的动机是这样的:它想去除NMS这个步骤,之所以要NMS是因为训练的时候一个GT会匹配到多个正样本,除了最正的那个正样本之外,其它的正样本都叫ambiguous sample,这些ambiguous sample作者认为一开始可以对分类loss的贡献应该随着训练的推移减少,它对应的分类标签值要逐渐降低,如下图所示:

然后它这个标签分配算法跟TOOD贼像,流程是一样的,就是计算分数的时候有差别:

然后它这个归一化的时候改了下,让ambiguous sample的标签值逐渐降低,核心就是这一点。我在TaskAligned的基础上改成了这种标签计算方式,初步效果变差,继续探索中。。。总觉得这文章说的不详细,也没多少实验。



























 188
188

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








