①观察灰度分布来描述一幅图像成为空间域,观察图像变化的频率被成为频域。
②频域分析:低频对应区域的图像强度变化缓慢,高频对应的变化快。低通滤波器去除了图像的高频部分,高通滤波器去除了图像的低频部分。
(1)低通滤波
①栗子:
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
int main()
{
// Read input image
cv::Mat image= cv::imread("boldt.jpg",0);
if (!image.data)
return 0;
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Original Image");
cv::imshow("Original Image",image);
// Blur the image with a mean filter
cv::Mat result;
cv::blur(image,result,cv::Size(5,5));
// Display the blurred image
cv::namedWindow("Mean filtered Image");
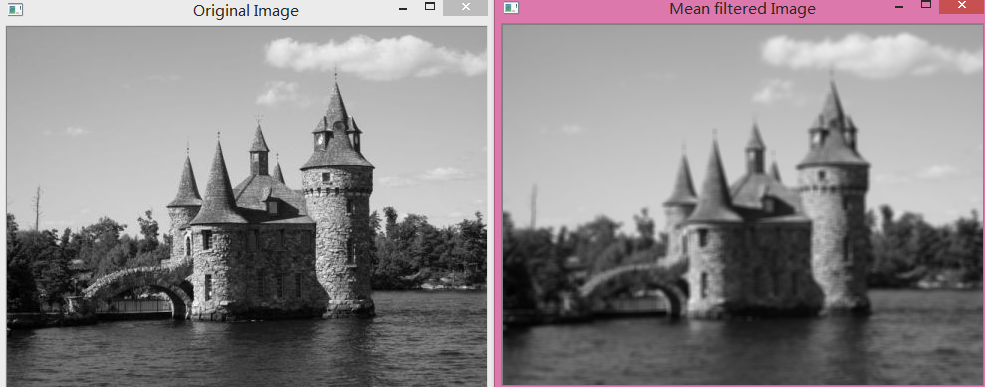
cv::imshow("Mean filtered Image",result);结果:每个像素变为相邻像素的平均值, 快速的强度变化转化为平缓的过度
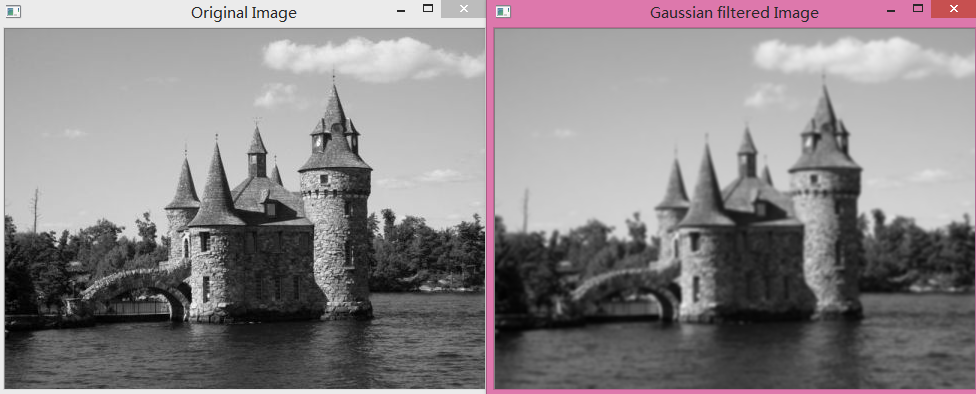
②栗子:近的像素添加更多的权重。:高斯滤波器
cv::GaussianBlur(image,result,cv::Size(5,5),1.5);(2)中值滤波 :非线性滤波
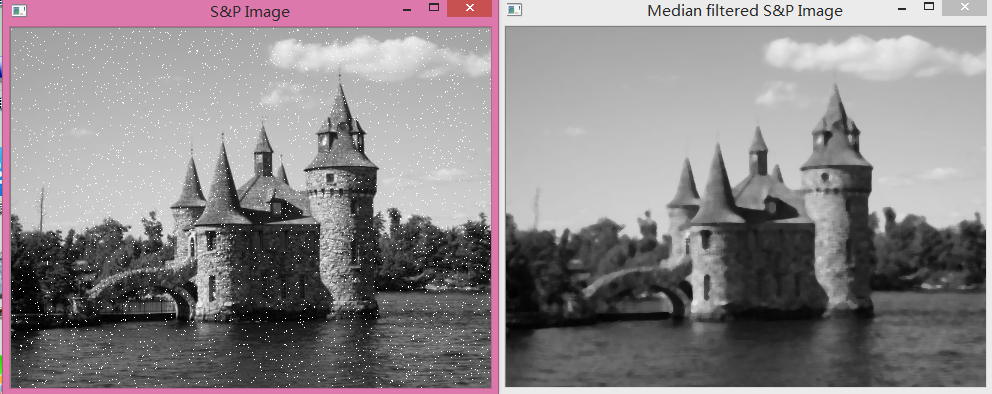
有效去除椒盐噪点
cv::medianBlur(image,result,5);(3)方向滤波(Sobel)
强调图像中的高频分量,使用高通滤波器进行边缘检测。
Sobel算子是一种经典的边缘检测线性滤波器,可被认为是图像在垂直和水平方向变化的测量。
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>








 本文介绍了图像处理中的滤波技术,包括低通滤波器(如平均滤波和高斯滤波)用于平滑图像,中值滤波用于去除椒盐噪声,以及Sobel算子作为高通滤波器用于边缘检测。通过拉普拉斯变换强调图像的高频分量,揭示图像的边缘和细节。
本文介绍了图像处理中的滤波技术,包括低通滤波器(如平均滤波和高斯滤波)用于平滑图像,中值滤波用于去除椒盐噪声,以及Sobel算子作为高通滤波器用于边缘检测。通过拉普拉斯变换强调图像的高频分量,揭示图像的边缘和细节。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 5735
5735

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








