一、基础知识
什么是rip
动态路由协议 RIP(Routing Information Protocol)是一种距离向量(distance-vector)型的内部网关协议(Interior Gateway Protocol,IGP),旨在用于小型网络或中小型企业网络中。RIP最初在RFC 1058中定义,后续版本在RFC 2453中进行了更新
rip的优点
- 简单易于配置和实现:RIP的配置相对简单,适合初学者和小型网络的使用。
- 低资源消耗:RIP使用较少的计算资源和带宽,适用于较慢的网络连接。
- 支持跳数限制:RIP使用跳数(hops)作为路由选择的度量标准,可以限制路由到达目标的最大跳数,避免出现无限循环的问题。
rip的缺点
- 慢速收敛:由于RIP使用固定的时间间隔来发送路由更新信息,网络发生变化时,收敛(convergence)速度较慢,可能导致一段时间内网络不稳定。
- 不适合大型网络:RIP在大型复杂网络中不适用,因为rip最大跳数为15,当要经过16跳才能到达某个节点时,rip将其视为不可达。且其收敛速度慢且对网络拓扑变化敏感。
- 跳数限制局限性:RIP使用跳数作为度量标准,忽略了网络中链路的带宽、延迟等因素,导致可能选择非最优路径。
rip协议的两个版本version 1和version 2
区别:
- V1不携带子网掩码--不支持子网划分、子网汇总;V2携带子网掩码--支持子网划分、子网汇总
- V1广播更新--255.255.255.255 V2组播更新 --224.0.0.9
- V2支持手工认证 -- 保障更新安全
- v1不支持身份验证,v2支持身份验证,管理员可为v2开启认证模式并设置基本的密码来确保传播的路由信息是加密的
<aside> 💡 相邻的两个路由器运行的rip版本必须一致
</aside>
关于rip的配置命令(以华为ensp路由器为例)
基础配置
开启rip协议:[r1]rip 1 数字1代表rip进程号,默认为1
指定rip的版本:version 2/1 rip有两个版本,分别为version 1和version 2
宣告路由器接口所在主类: network 1.0.0.0 无论是version 1还是version 2,在宣告的时候只能使用接口ip地址所在的主类来进行宣告,比如某接口的IP地址是192.168.25.3,该ip地址是C类地址,则宣告192.168.25.0 即可
<aside> 💡 宣告主类的作用:rip协议会将连接在路由器上的处于宣告网段内的接口激活,激活状态即rip会通过该接口传递rip路由信息包
</aside>
进阶配置
rip的手工认证:
RIPv2(Routing Information Protocol Version 2)支持手工认证,这是一种简单的身份验证机制,用于确保只有授权的路由器可以交换路由信息。手工认证使用共享的密码(也称为密钥)来验证邻居路由器之间的合法性,并且会对传输的路由信息按照指定的哈希算法进行加密。
配置在与邻居直连的接口上即可
[r1]interface g0/0/1
[r1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]rip authentication-mode md5 usual 123456 #指定使用md5算法加密,口令设置为123456
邻居之间的两个接口的秘钥的加密算法以及口令必须完全一致
rip的手工汇总
在RIP(Routing Information Protocol)中,rip **summary-address <**汇总地址**> <**点分十进制掩码**>** 是一种用于汇总路由信息的命令。它的作用是将多个具体的子网路由信息合并成一个汇总路由,从而减少路由表的规模和节省路由器的处理资源。汇总路由是指代表多个具体子网的单个路由。
注意这里一定要使用点分十进制掩码,这样的设计让你算得更明白
作用和优势:
- 路由表规模优化:当一个路由器连接到多个具体子网时,它可能会学习到许多具体的子网路由信息,导致路由表的规模变得很大。使用**
summary-address**命令可以将这些具体子网汇总成一个较大的网络,从而显著减少路由表中的条目数量,节省路由器内存和处理资源。 - 减少路由更新的数量:RIP使用周期性的路由更新来传播路由信息,当路由表非常庞大时,这些更新的数量可能会很大,导致网络流量增加。通过使用汇总路由,可以将路由更新的数量减少到只传播汇总路由的更新信息,从而减少了网络中的路由信息交换。
- 防止路由表过度膨胀:在某些情况下,网络可能经历频繁的拓扑变化,例如,大量的具体子网路由可能在短时间内变得不稳定。使用汇总路由可以稳定路由表,防止路由表因瞬时的拓扑变化而过度膨胀。
rip的接口沉默
[r1-rip-1]silent-interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0
用于将指定的接口设置为“静默”模式,从而阻止该接口上的RIP路由信息交换,目的通常是为了控制RIP协议在网络中传播路由信息的范围,从而改变RIP在特定接口上的行为。这可以有以下应用场景:
- 限制路由信息传播:在某些情况下,您可能希望限制RIP协议在特定接口上发送或接收路由更新信息,例如,阻止RIP协议跨越特定边界进入其他网络。通过在相关接口上配置**
silent-interface**命令,您可以实现对路由信息传播的控制。 - 避免冗余路由信息:如果网络中存在多个RIP实例或其他动态路由协议,您可能希望在某些接口上禁用RIP,以避免冗余的路由信息传播。
- 增强网络安全性:有时,为了增强网络的安全性,您可能希望阻止特定接口上的路由信息泄露。通过将该接口设置为静默模式,可以防止在该接口上透露网络拓扑信息。
作为网关的接口一定要设置为静默模式,因为路由器没必要和用户PC机所在的网段交换路由信息
rip的边界路由器
边界路由器(连接ISP的路由器)上定义缺省源头信息后,将自动向内网发布通告,使得内部所有路由器自动产生缺省路由指向边界路由器;若边界路由器需要缺省路由指向ISP,只能静态手工添加;
这个功能在以下场景中非常有用:
- Internet连接:当一个RIP网络连接到互联网上,但没有任何特定的路由信息时,可以使用**
default-route originate**命令将默认路由注入RIP路由表。这样,当RIP网络中的其他路由器需要发送到互联网上的目标时,它们就可以使用这个默认路由。 - 汇聚点路由:在网络设计中,有时可能需要在网络边缘设置汇聚点路由,用于将所有非本地流量汇聚到一个出口。通过在汇聚点路由器上使用**
default-route originate**命令,可以为整个网络提供一个共同的默认路由。
二、实验要求


三、实验步骤
按照下图划分好IP地址并配置好所有接口的ip地址
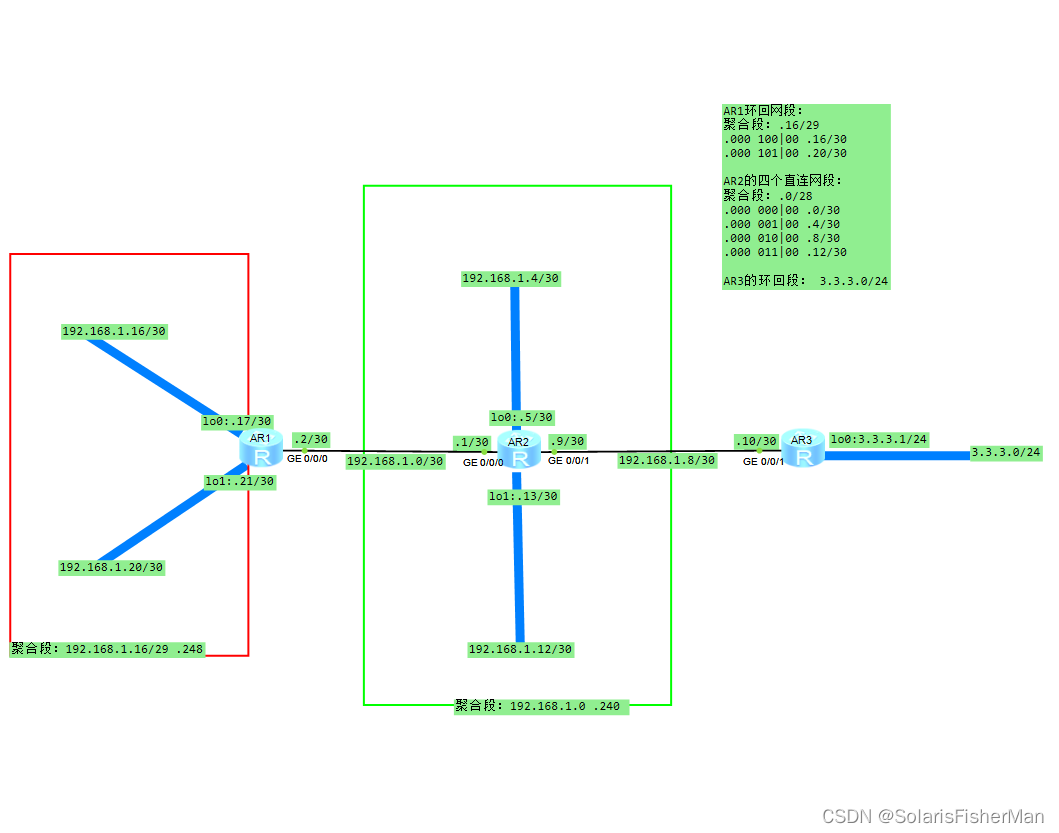

R1,R2,R3的rip配置命令如下:
<r1>system-view
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[r1]rip
[r1-rip-1]version 2
[r1-rip-1]network 192.168.1.0
[r1-rip-1]quit
[r1]interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0
[r1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]rip authentication-mode md5 usual 123456
[r1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]rip summary-address 192.168.1.16 255.255.255.248
<r2>system-view
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[r2]rip
[r2-rip-1]version 2
[r2-rip-1]network 192.168.1.0
[r2-rip-1]quit
[r2]interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/0
[r2-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]rip authentication-mode md5 usual 123456
[r2-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]rip summary-address 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.240
[r2-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]quit
[r2]interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1
[r2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]rip authentication-mode md5 usual 456789
[r2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]rip summary-address 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.240
<r3>system-view
Enter system view, return user view with Ctrl+Z.
[r3]rip
[r3-rip-1]version 2
[r3-rip-1]default-route originate
[r3-rip-1]network 192.168.1.0
[r3-rip-1]quit
[r3]interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1
[r3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]rip authentication-mode md5 usual 456789
验证全网的连通性
R1:
<r1>ping 192.168.1.5
PING 192.168.1.5: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=255 time=10 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=255 time=10 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=255 time=20 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=255 time=20 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=255 time=10 ms
--- 192.168.1.5 ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 10/14/20 ms
<r1>ping 192.168.1.10
PING 192.168.1.10: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Reply from 192.168.1.10: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=254 time=30 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.10: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=254 time=30 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.10: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=254 time=30 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.10: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=254 time=20 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.10: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=254 time=20 ms
--- 192.168.1.10 ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 20/26/30 ms
<r1>ping 3.3.3.1
PING 3.3.3.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Reply from 3.3.3.1: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=254 time=10 ms
Reply from 3.3.3.1: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=254 time=30 ms
Reply from 3.3.3.1: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=254 time=30 ms
Reply from 3.3.3.1: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=254 time=30 ms
Reply from 3.3.3.1: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=254 time=30 ms
--- 3.3.3.1 ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 10/26/30 ms
R2:
<r2>ping 192.168.1.21
PING 192.168.1.21: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Reply from 192.168.1.21: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=255 time=20 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.21: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=255 time=20 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.21: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=255 time=30 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.21: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=255 time=20 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.21: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=255 time=10 ms
--- 192.168.1.21 ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 10/20/30 ms
<r2>ping 3.3.3.1
PING 3.3.3.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Reply from 3.3.3.1: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=255 time=20 ms
Reply from 3.3.3.1: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=255 time=20 ms
Reply from 3.3.3.1: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=255 time=20 ms
Reply from 3.3.3.1: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=255 time=20 ms
Reply from 3.3.3.1: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=255 time=20 ms
--- 3.3.3.1 ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 20/20/20 ms
R3
<r3>ping 192.168.1.21
PING 192.168.1.21: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Reply from 192.168.1.21: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=254 time=30 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.21: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=254 time=30 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.21: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=254 time=40 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.21: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=254 time=30 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.21: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=254 time=30 ms
--- 192.168.1.21 ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 30/32/40 ms
<r3>ping 192.168.1.2
PING 192.168.1.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=254 time=30 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=254 time=30 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=254 time=20 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=254 time=20 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=254 time=20 ms
--- 192.168.1.2 ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 20/24/30 ms
<r3>ping 192.168.1.5
PING 192.168.1.5: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=255 time=30 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=255 time=30 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=255 time=20 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=255 time=20 ms
Reply from 192.168.1.5: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=255 time=20 ms
--- 192.168.1.5 ping statistics ---
5 packet(s) transmitted
5 packet(s) received
0.00% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max = 20/24/30 ms
R1的rip路由表
[r1]display ip routing-table protocol rip
Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Public routing table : RIP
Destinations : 2 Routes : 2
RIP routing table status : <Active>
Destinations : 2 Routes : 2
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/0 RIP 100 2 D 192.168.1.1 GigabitEthernet
0/0/0
192.168.1.0/28 RIP 100 1 D 192.168.1.1 GigabitEthernet
0/0/0
RIP routing table status : <Inactive>
Destinations : 0 Routes : 0
R2的rip路由表
<r2>display ip routing-table protocol rip
Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Public routing table : RIP
Destinations : 2 Routes : 2
RIP routing table status : <Active>
Destinations : 2 Routes : 2
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/0 RIP 100 1 D 192.168.1.10 GigabitEthernet
0/0/1
192.168.1.16/29 RIP 100 1 D 192.168.1.2 GigabitEthernet
0/0/0
RIP routing table status : <Inactive>
Destinations : 0 Routes : 0
R3的rip路由表
<r3>display ip routing-table protocol rip
Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Public routing table : RIP
Destinations : 2 Routes : 2
RIP routing table status : <Active>
Destinations : 2 Routes : 2
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface
192.168.1.0/28 RIP 100 1 D 192.168.1.9 GigabitEthernet
0/0/1
192.168.1.16/29 RIP 100 2 D 192.168.1.9 GigabitEthernet
0/0/1
RIP routing table status : <Inactive>
Destinations : 0 Routes : 0





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








