论文标题《基于深度学习的无人驾驶汽车车道跟随方法》,仅对UNET _c复现,使用pytorch
1.网络结构
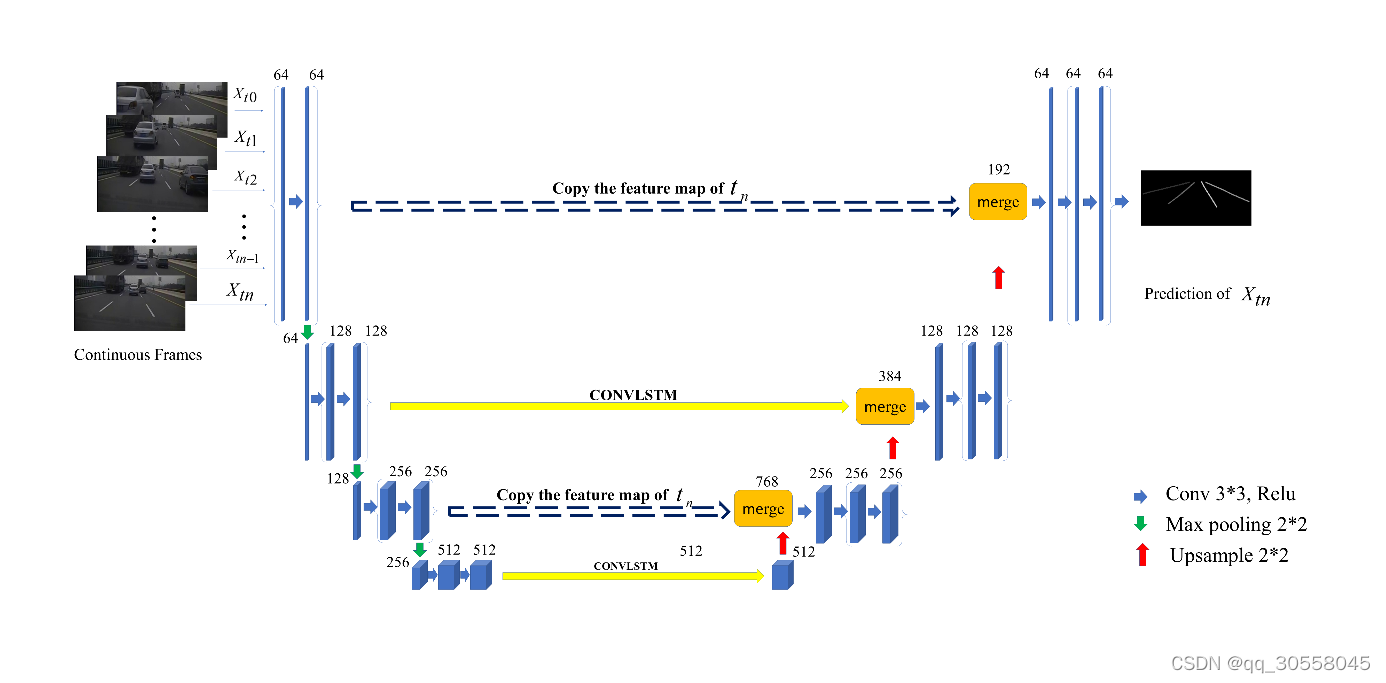
2.复现思路
基于unet模型复现,加入convlstm层block,因为使用pytorch进行组合的代码并没有,网上只有TF 的代码(convlstm2d),所以只能自己瞎写。
3.代码
3.1 convlstm
这就是网上的常见复现版本,无改动
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
class ConvLSTMCell(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, kernel_size, bias):
"""
Initialize ConvLSTM cell.
Parameters
----------
input_dim: int
Number of channels of input tensor.
hidden_dim: int
Number of channels of hidden state.
kernel_size: (int, int)
Size of the convolutional kernel.
bias: bool
Whether or not to add the bias.
"""
super(ConvLSTMCell, self).__init__()
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.padding = kernel_size[0] // 2, kernel_size[1] // 2 # 保证在传递过程中 (h,w)不变
self.bias = bias
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.input_dim + self.hidden_dim,
out_channels=4 * self.hidden_dim, # i门,f门,o门,g门放在一起计算,然后在split开
kernel_size=self.kernel_size,
padding=self.padding,
bias=self.bias)
def forward(self, input_tensor, cur_state):
h_cur, c_cur = cur_state # 每个timestamp包含两个状态张量:h和c
print('cell h and c:', h_cur.shape, c_cur.shape)
combined = torch.cat([input_tensor, h_cur], dim=1) # concatenate along channel axis # 把输入张量与h状态张量沿通道维度串联
combined_conv = self.conv(combined) # i门,f门,o门,g门放在一起计算,然后在split开
cc_i, cc_f, cc_o, cc_g = torch.split(combined_conv, self.hidden_dim, dim=1)
i = torch.sigmoid(cc_i)
f = torch.sigmoid(cc_f)
o = torch.sigmoid(cc_o)
g = torch.tanh(cc_g)
c_next = f * c_cur + i * g # c状态张量更新
h_next = o * torch.tanh(c_next) # h状态张量更新
return h_next, c_next # 输出当前timestamp的两个状态张量
def init_hidden(self, batch_size, image_size):
"""
初始状态张量初始化.第一个timestamp的状态张量0初始化
:param batch_size:
:param image_size:
:return:
"""
height, width = image_size
init_h = torch.zeros(batch_size, self.hidden_dim, height, width, device=self.conv.weight.device)
init_c = torch.zeros(batch_size, self.hidden_dim, height, width, device=self.conv.weight.device)
return (init_h, init_c)
class ConvLSTM(nn.Module):
"""
Parameters:参数介绍
input_dim: Number of channels in input# 输入张量的通道数
hidden_dim: Number of hidden channels # h,c两个状态张量的通道数,可以是一个列表
kernel_size: Size of kernel in convolutions # 卷积核的尺寸,默认所有层的卷积核尺寸都是一样的,也可以设定不通lstm层的卷积核尺寸不同
num_layers: Number of LSTM layers stacked on each other # 卷积层的层数,需要与len(hidden_dim)相等
batch_first: Whether or not dimension 0 is the batch or not
bias: Bias or no bias in Convolution
return_all_layers: Return the list of computations for all layers # 是否返回所有lstm层的h状态
Note: Will do same padding. # 相同的卷积核尺寸,相同的padding尺寸
Input:输入介绍
A tensor of size [B, T, C, H, W] or [T, B, C, H, W]# 需要是5维的
Output:输出介绍
返回的是两个列表:layer_output_list,last_state_list
列表0:layer_output_list--单层列表,每个元素表示一层LSTM层的输出h状态,每个元素的size=[B,T,hidden_dim,H,W]
列表1:last_state_list--双层列表,每个元素是一个二元列表[h,c],表示每一层的最后一个timestamp的输出状态[h,c],h.size=c.size = [B,hidden_dim,H,W]
A tuple of two lists of length num_layers (or length 1 if return_all_layers is False).
0 - layer_output_list is the list of lists of length T of each output
1 - last_state_list is the list of last states
each element of the list is a tuple (h, c) for hidden state and memory
Example:使用示例
>> x = torch.rand((32, 10, 64, 128, 128))
>> convlstm = ConvLSTM(64, 16, 3, 1, True, True, False)
>> _, last_states = convlstm(x)
>> h = last_states[0][0] # 0 for layer index, 0 for h index
"""
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, kernel_size, num_layers,
batch_first=False, bias=True, return_all_layers=False):
super(ConvLSTM, self).__init__()
self._check_kernel_size_consistency(kernel_size)
# Make sure that both `kernel_size` and `hidden_dim` are lists having len == num_layers
kernel_size = self._extend_for_multilayer(kernel_size, num_layers) # 转为列表
hidden_dim = self._extend_for_multilayer(hidden_dim, num_layers) # 转为列表
if not len(kernel_size) == len(hidden_dim) == num_layers: # 判断一致性
raise ValueError('Inconsistent list length.')
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.batch_first = batch_first
self.bias = bias
self.return_all_layers = return_all_layers
cell_list = []
for i in range(0, self.num_layers): # 多层LSTM设置
# 当前LSTM层的输入维度
# if i==0:
# cur_input_dim = self.input_dim
# else:
# cur_input_dim = self.hidden_dim[i - 1]
cur_input_dim = self.input_dim if i == 0 else self.hidden_dim[i - 1] # 与上等价
cell_list.append(ConvLSTMCell(input_dim=cur_input_dim,
hidden_dim=self.hidden_dim[i],
kernel_size=self.kernel_size[i],
bias=self.bias))
self.cell_list = nn.ModuleList(cell_list) # 把定义的多个LSTM层串联成网络模型
def forward(self, input_tensor, hidden_state=None):
"""
Parameters
----------
input_tensor: 5-D Tensor either of shape (t, b, c, h, w) or (b, t, c, h, w)
hidden_state: todo
None. todo implement stateful
Returns
-------
last_state_list, layer_output
"""
if not self.batch_first:
# (t, b, c, h, w) -> (b, t, c, h, w)
input_tensor = input_tensor.permute(1, 0, 2, 3, 4)
# Implement stateful ConvLSTM
if hidden_state is not None:
raise NotImplementedError()
else:
# Since the init is done in forward. Can send image size here
b, _, _, h, w = input_tensor.size() # 自动获取 b,h,w信息
hidden_state = self._init_hidden(batch_size=b, image_size=(h, w))
layer_output_list = []
last_state_list = []
seq_len = input_tensor.size(1) # 根据输入张量获取lstm的长度
print('seq_len: ', seq_len,' start train.')
cur_layer_input = input_tensor
for layer_idx in range(self.num_layers): # 逐层计算
h, c = hidden_state[layer_idx]
output_inner = []
for t in range(seq_len): # 逐个stamp计算
h, c = self.cell_list[layer_idx](input_tensor=cur_layer_input[:, t, :, :, :], cur_state=[h, c])
# print('input tensor:',input_tensor.shape)
# print(t, '次 train h c: ', h.shape, c.shape)
output_inner.append(h) # 第 layer_idx 层的第t个stamp的输出状态
layer_output = torch.stack(output_inner, dim=1) # 第 layer_idx 层的第所有stamp的输出状态串联
cur_layer_input = layer_output # 准备第layer_idx+1层的输入张量
layer_output_list.append(layer_output) # 当前层的所有timestamp的h状态的串联
last_state_list.append([h, c]) # 当前层的最后一个stamp的输出状态的[h,c]
if not self.return_all_layers:
layer_output_list = layer_output_list[-1:]
last_state_list = last_state_list[-1:]
return layer_output_list, last_state_list
def _init_hidden(self, batch_size, image_size):
"""
所有lstm层的第一个timestamp的输入状态0初始化
:param batch_size:
:param image_size:
:return:
"""
init_states = []
for i in range(self.num_layers):
init_states.append(self.cell_list[i].init_hidden(batch_size, image_size))
return init_states
@staticmethod
def _check_kernel_size_consistency(kernel_size):
"""
检测输入的kernel_size是否符合要求,要求kernel_size的格式是list或tuple
:param kernel_size:
:return:
"""
if not (isinstance(kernel_size, tuple) or
(isinstance(kernel_size, list) and all([isinstance(elem, tuple) for elem in kernel_size]))):
raise ValueError('`kernel_size` must be tuple or list of tuples')
@staticmethod
def _extend_for_multilayer(param, num_layers):
"""
扩展到多层lstm情况
:param param:
:param num_layers:
:return:
"""
if not isinstance(param, list):
param = [param] * num_layers
return param
3.2 unet—part
unet网络的块
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class DoubleConv(nn.Module):
"""(convolution => [BN] => ReLU) * 2"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super().__init__()
self.double_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.double_conv(x)
class Down(nn.Module):
"""Downscaling with maxpool then double conv"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super().__init__()
self.maxpool_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
DoubleConv(in_channels, out_channels)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.maxpool_conv(x)
class Up(nn.Module):
"""Upscaling then double conv"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, bilinear=True):
super().__init__()
# if bilinear, use the normal convolutions to reduce the number of channels
if bilinear:
self.up = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
else:
self.up = nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels // 2, in_channels // 2, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.conv = DoubleConv(in_channels, out_channels)
def forward(self, x1, x2):
x1 = self.up(x1)
# input is CHW
print('--------up block------')
print('x1,x2 in up:\t',x1.shape,x2.shape)
diffY = torch.tensor([x2.shape[2] - x1.shape[2]])
diffX = torch.tensor([x2.shape[3] - x1.shape[3]])
x1 = F.pad(x1, [diffX // 2, diffX - diffX // 2,
diffY // 2, diffY - diffY // 2])
x = torch.cat([x2, x1], dim=1)
print('after concat channel:',x.shape)
return self.conv(x)
class OutConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(OutConv, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, x):
return self.conv(x)3.3uet_convlstm架构
这段就是自己改动的了,把(b,s,c,size)的输入,分batch加入up block 和 down blk网络训练。convlstm输入的图片的tiemstep=3,预测三帧图像,然后与target的三帧图像cat,输出。
from model.Convlstm import ConvLSTM
from model.unet_parts import *
class UNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_channels, n_classes, bilinear=True):
super(UNet, self).__init__()
self.n_channels = n_channels
self.n_classes = n_classes
self.bilinear = bilinear
self.inc = DoubleConv(n_channels, 64)
self.down1 = Down(64, 128)
self.down2 = Down(128, 256)
self.down3 = Down(256, 512)
# self.down4 = Down(512, 512)
self.cvlstm1 = ConvLSTM(128, 128, [(3, 3)], 1, True, True, False)
self.cvlstm2 = ConvLSTM(512, 512, [(3, 3)], 1, True, True, False)
self.up1 = Up(768, 256, bilinear)
self.up2 = Up(384, 128, bilinear)
# self.up3 = Up(256, 64, bilinear)
self.up3 = Up(192, 64, bilinear)
self.outc = OutConv(64, n_classes)
def forward(self, x):
b, _, _, _, _ = x.shape
x1, x2, x3, x4 = [], [], [], []
print('----------************------------\nup block:')
for i in range(b):
a = input[i, ...]
print(f'--------第{i + 1}个batch----------')
print(f'input shape:\t', a.shape)
x1.append(self.inc(a))
print('x1 shape:\t', x1[i].shape)
x2.append(self.down1(x1[i]))
x3.append(self.down2(x2[i]))
x4.append(self.down3(x3[i]))
# x5.append(self.down4(x4[i]))
print('final batch out x4[i] shape:\t', x4[i].shape)
x1 = torch.stack(x1)
x2 = torch.stack(x2)
x3 = torch.stack(x3)
x4 = torch.stack(x4)
print('\nfinal up x4:\t', type(x4), x4.shape)
print('----------************------------\nconvlstm block:')
print('x4_target shape:\t', x4[:, -3:, ...].shape)
x2_data, x2_target = x2[:, 0:3, ...], x2[:, -3:, ...]
x2_cl_outs = self.cvlstm1(x2_data)
x4_data, x4_target = x4[:, 0:3, ...], x4[:, -3:, ...]
x4_cl_outs = self.cvlstm2(x4_data)
x4 = x4_target
b, _, _, _, _ = x4.shape
logits = []
print('----------************------------\ndown block:')
for i in range(b):
print(f'--------第{i + 1}个batch----------')
print('input x4 and conv x4:\t', x4[i, ...].shape, x4_cl_outs[0][0][i,...].shape)
x = self.up1(x4_cl_outs[0][0][i,...], x3[i, -3:, ...])
print('after featrue cat with x3:\t', x.shape)
x = self.up2(x, x2_cl_outs[0][0][i])
print('after conv cat with x2:\t', x.shape)
x = self.up3(x, x1[i, -3:, ...])
print('after feature cat with x1:', x.shape)
logits.append(self.outc(x))
logits = torch.stack(logits)
return logits
4.实例
net = UNet(n_channels=1, n_classes=1)
input = torch.randn((2, 6, 1, 512, 512))
logits = net(input)
print('result:',logits.shape)






 该博客介绍了如何使用PyTorch复现基于深度学习的无人驾驶汽车车道跟随方法,特别关注了UNet网络结构与ConvLSTM层的集成。作者首先详细阐述了ConvLSTM细胞的实现,接着展示了UNet的部分代码,包括下采样(Down)和上采样(Up)模块。最后,将这些组件整合到一个名为UNet的网络架构中,该架构能够处理时间序列输入并预测多帧图像。网络通过处理每个批次的输入图像,利用ConvLSTM进行序列建模,并通过UNet结构进行特征提取和融合,以完成车道跟随任务。
该博客介绍了如何使用PyTorch复现基于深度学习的无人驾驶汽车车道跟随方法,特别关注了UNet网络结构与ConvLSTM层的集成。作者首先详细阐述了ConvLSTM细胞的实现,接着展示了UNet的部分代码,包括下采样(Down)和上采样(Up)模块。最后,将这些组件整合到一个名为UNet的网络架构中,该架构能够处理时间序列输入并预测多帧图像。网络通过处理每个批次的输入图像,利用ConvLSTM进行序列建模,并通过UNet结构进行特征提取和融合,以完成车道跟随任务。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








