Today
• Basic Components of Code
• Types
• Conversions and Casting
• Exercises
CONSTANTS, VARIABLES, IDENTIFIERS
Reminder
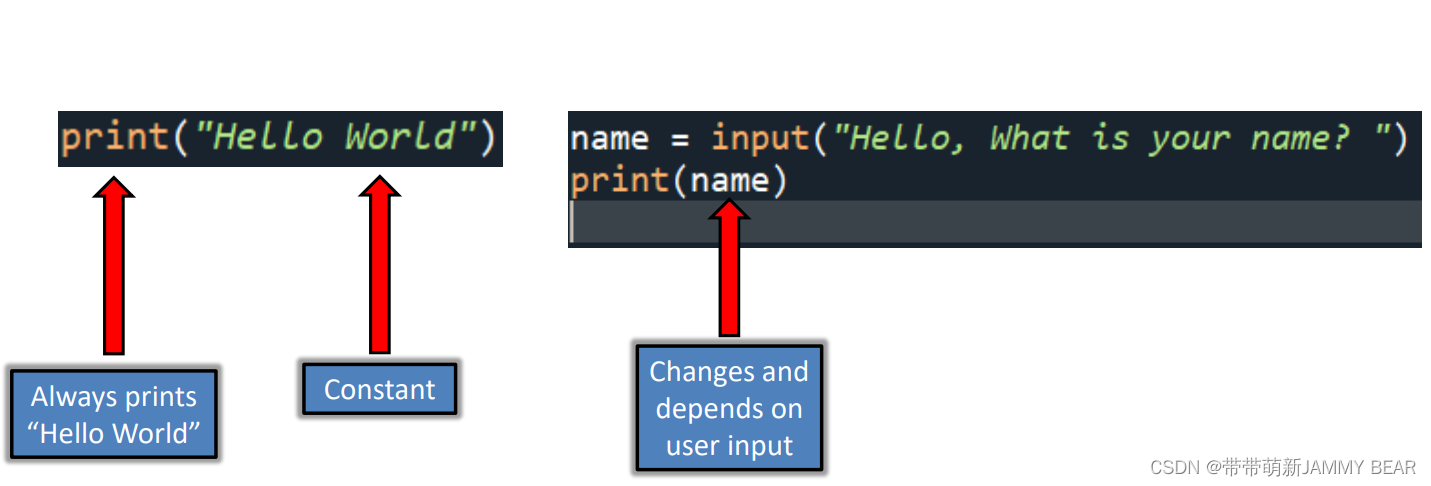
Constants 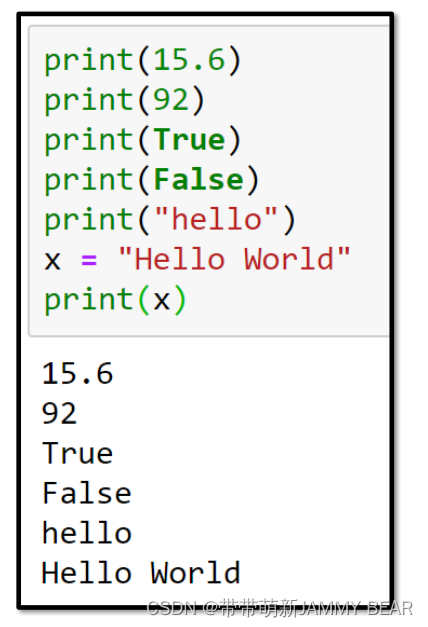
• Constants are any value:
- Numerical: 15.6, 120
- String: “Hello”, ‘bye’
- Boolean: True, False
• Can appear on their own or assigned
into a variable.
Variables
• A Variable is a cell in memory, with a given name (identifier) and value.
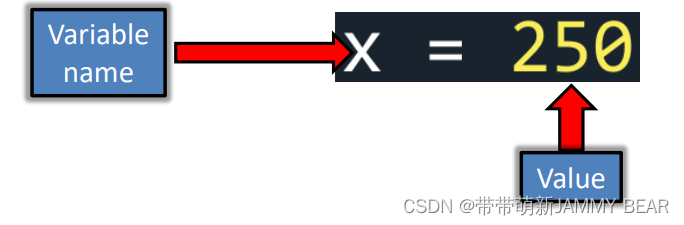
• Before we can use the variable, it must be initialized with a value.
• It is possible to update a variable by assigning a different value:

Assignment
• Assignment is made of two parts:

• How is Python performing this operation?
1. Evaluating the expression on the right side.
2. Writes the result to the variable.
• During assignment, the computer does not “solve an equation”. This is not Algebra!
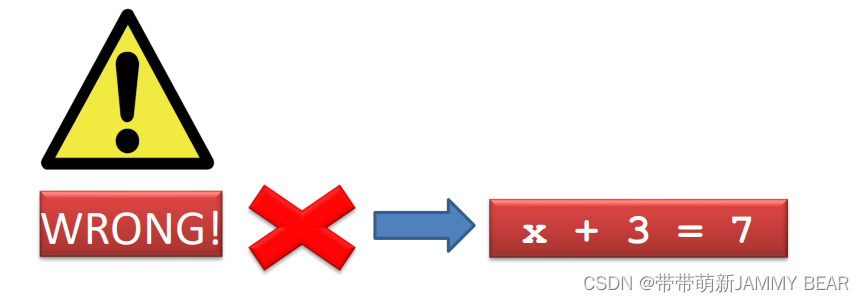

• The righthand side is evaluated first. Therefore,
• the following statement in Python is legitimate:
![]()
Identifiers
• Variable (or function) names are called Identifiers.
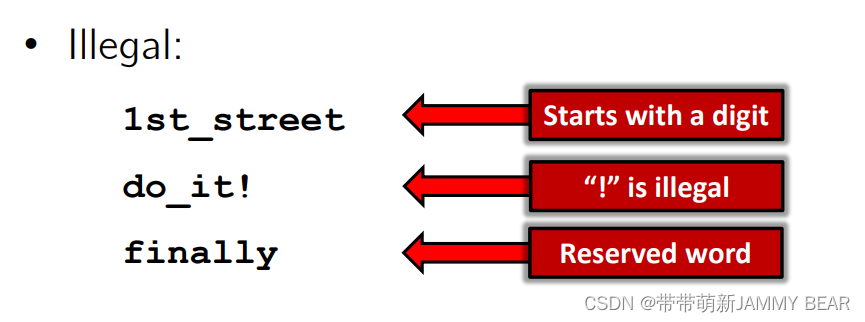
• Rules for legal identifiers in Python:
1. Only English letters (lowercase or UPPERCASE), digits or underscore (_)
2. Cannot start with a digit
3. Cannot be a reserved word
• Spyder IDE will mark a reserved word in unique color.

• Legal identifiers:
temp counter
the_one intro2cs
• The computer doesn’t care what names you choose, but you should. It is important to choose meaningful names for your variables that will aid in understanding the function of your program.
• Which example is clearer?

TYPES
Variable Types
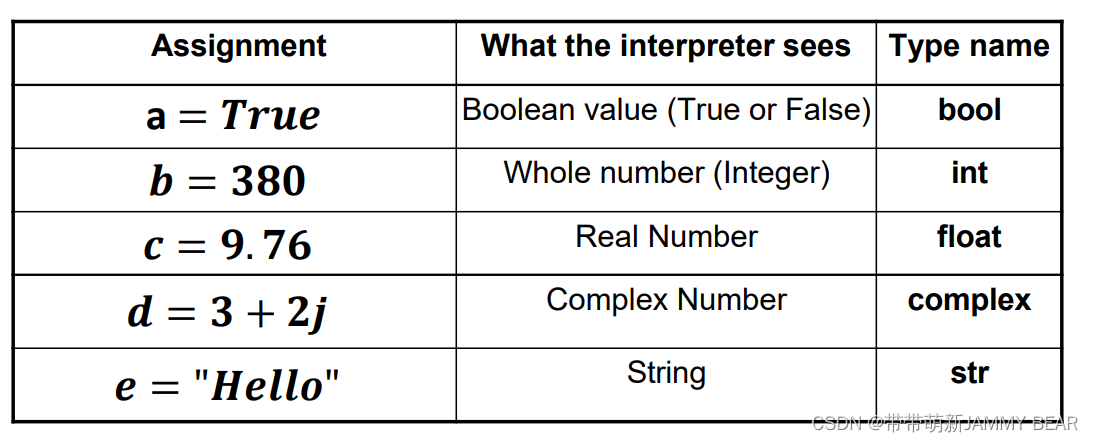
• Each variable has a Type.
• Regardless of type, a variable is stored in memory as a sequence of bits.
• The difference between types signifies how Python translates the contents of the variable to bits and back.
• These contents can vary (numbers, characters, colors, images, music….)

• In Python, a variable type is set automatically during assignment.
• In Spyder, we can see the different variables and their type under “Variable Explorer”.
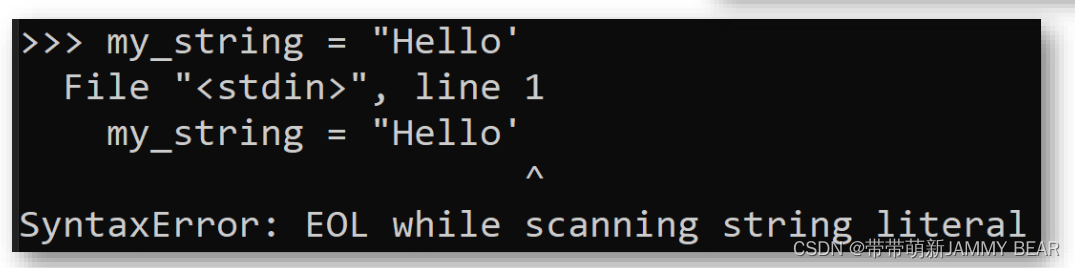
Types: String 
• Python identifies strings by double quotes and single-
quotes:
• Double Quotes: my_string = “Hello”
• Single Quotes: my_string = ‘hello’
• Must be consistent:
Type Conversion
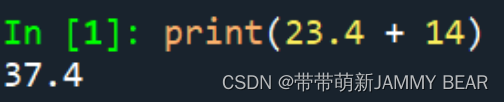
• Occasionally, we want to perform calculation on values which are stored as different types. For example, adding int with float (100 + 2.4).
• To perform such calculation, the type must be converted.
• There are two types of type conversions:
- Automatic – happens without the user’s involvement:
- Implicit – happens by implicit request (also called type casting):

Python Operators

• Operators supported by string types:
• Addition: +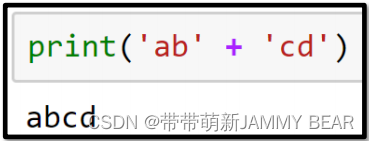
• The two operands must be strings.
• Performs concatenation of strings.
• Multiplication: *
• The two operands must be a string and an integer (the order doesn’t matter).
• Concatenates the string to itself.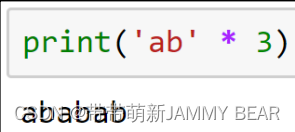
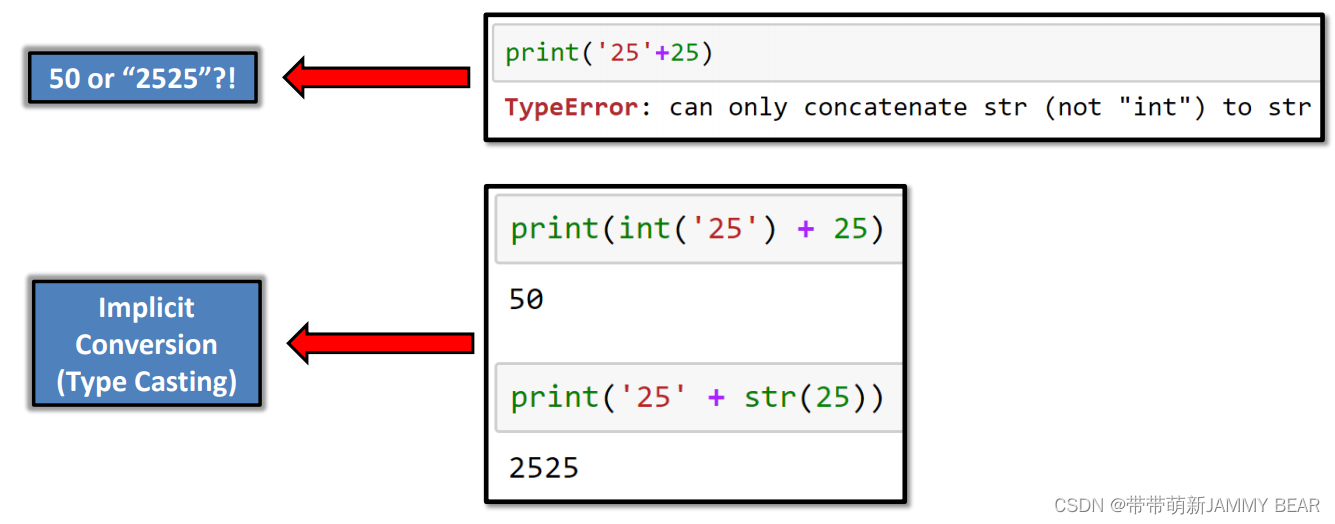
Implicit Conversion
• No automatic conversion. The computer doesn’t know which result you want!
EXERCISES
Exercise 1
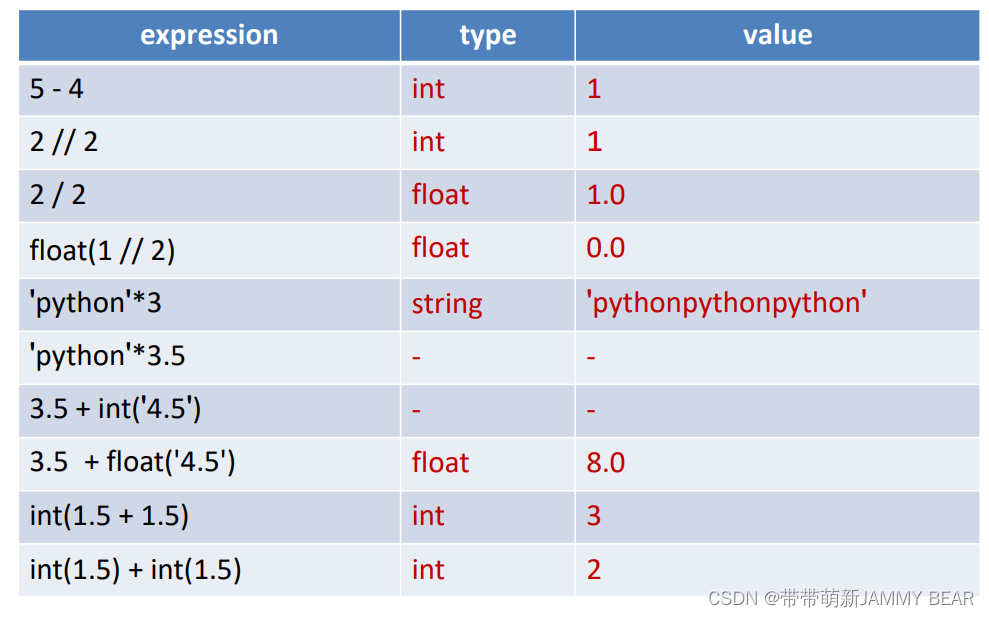
Exercise 2

Exercise 3

• Write a program that gets a number as input and returns the following number:
num = input()
num = int(num)
• Or:
num = int(input())
• Finally, we add:
num = num + 1
print(num)
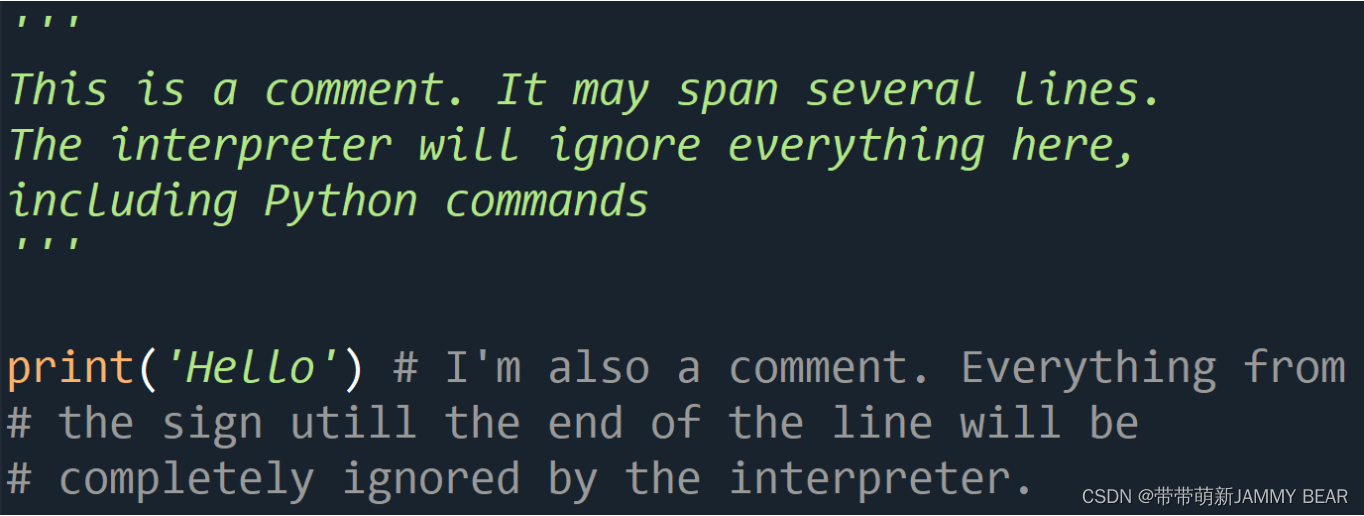
Comments and Documentation
Exercise 4
• Write a program to calculate length of hypotenuse (use Pythagoras).

























 2829
2829











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










