1.三角测量
triangulation.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp>
// #include "extra.h" // used in opencv2
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void find_feature_matches (
const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2,
std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1,
std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2,
std::vector< DMatch >& matches );
void pose_estimation_2d2d (
const std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1,
const std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2,
const std::vector< DMatch >& matches,
Mat& R, Mat& t );
void triangulation (
const vector<KeyPoint>& keypoint_1,
const vector<KeyPoint>& keypoint_2,
const std::vector< DMatch >& matches,
const Mat& R, const Mat& t,
vector<Point3d>& points
);
// 像素坐标转相机归一化坐标
Point2f pixel2cam( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K );
int main ( int argc, char** argv )
{
if ( argc != 3 )
{
cout<<"usage: triangulation img1 img2"<<endl;
return 1;
}
//-- 读取图像
Mat img_1 = imread ( argv[1], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR );
Mat img_2 = imread ( argv[2], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR );
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
vector<DMatch> matches;
find_feature_matches ( img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches );
cout<<"一共找到了"<<matches.size() <<"组匹配点"<<endl;
//-- 估计两张图像间运动
Mat R,t;
pose_estimation_2d2d ( keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches, R, t );
//-- 三角化
vector<Point3d> points;
triangulation( keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches, R, t, points );
//-- 验证三角化点与特征点的重投影关系
Mat K = ( Mat_<double> ( 3,3 ) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1 );
for ( int i=0; i<matches.size(); i++ )
{
Point2d pt1_cam = pixel2cam( keypoints_1[ matches[i].queryIdx ].pt, K );
Point2d pt1_cam_3d(
points[i].x/points[i].z,
points[i].y/points[i].z
);
cout<<"point in the first camera frame: "<<pt1_cam<<endl;
cout<<"point projected from 3D "<<pt1_cam_3d<<", d="<<points[i].z<<endl;
// 第二个图
Point2f pt2_cam = pixel2cam( keypoints_2[ matches[i].trainIdx ].pt, K );
Mat pt2_trans = R*( Mat_<double>(3,1) << points[i].x, points[i].y, points[i].z ) + t;
pt2_trans /= pt2_trans.at<double>(2,0);
cout<<"point in the second camera frame: "<<pt2_cam<<endl;
cout<<"point reprojected from second frame: "<<pt2_trans.t()<<endl;
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
void find_feature_matches ( const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2,
std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1,
std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2,
std::vector< DMatch >& matches )
{
//-- 初始化
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
// used in OpenCV3
Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create();
Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create();
// use this if you are in OpenCV2
// Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" );
// Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" );
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming");
//-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置
detector->detect ( img_1,keypoints_1 );
detector->detect ( img_2,keypoints_2 );
//-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子
descriptor->compute ( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
descriptor->compute ( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离
vector<DMatch> match;
// BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING );
matcher->match ( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match );
//-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选
double min_dist=10000, max_dist=0;
//找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离
for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = match[i].distance;
if ( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if ( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
printf ( "-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist );
printf ( "-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist );
//当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限.
for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if ( match[i].distance <= max ( 2*min_dist, 30.0 ) )
{
matches.push_back ( match[i] );
}
}
}
void pose_estimation_2d2d (
const std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1,
const std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2,
const std::vector< DMatch >& matches,
Mat& R, Mat& t )
{
// 相机内参,TUM Freiburg2
Mat K = ( Mat_<double> ( 3,3 ) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1 );
//-- 把匹配点转换为vector<Point2f>的形式
vector<Point2f> points1;
vector<Point2f> points2;
for ( int i = 0; i < ( int ) matches.size(); i++ )
{
points1.push_back ( keypoints_1[matches[i].queryIdx].pt );
points2.push_back ( keypoints_2[matches[i].trainIdx].pt );
}
//-- 计算基础矩阵
Mat fundamental_matrix;
fundamental_matrix = findFundamentalMat ( points1, points2, CV_FM_8POINT );
cout<<"fundamental_matrix is "<<endl<< fundamental_matrix<<endl;
//-- 计算本质矩阵
Point2d principal_point ( 325.1, 249.7 ); //相机主点, TUM dataset标定值
int focal_length = 521; //相机焦距, TUM dataset标定值
Mat essential_matrix;
essential_matrix = findEssentialMat ( points1, points2, focal_length, principal_point );
cout<<"essential_matrix is "<<endl<< essential_matrix<<endl;
//-- 计算单应矩阵
Mat homography_matrix;
homography_matrix = findHomography ( points1, points2, RANSAC, 3 );
cout<<"homography_matrix is "<<endl<<homography_matrix<<endl;
//-- 从本质矩阵中恢复旋转和平移信息.
recoverPose ( essential_matrix, points1, points2, R, t, focal_length, principal_point );
cout<<"R is "<<endl<<R<<endl;
cout<<"t is "<<endl<<t<<endl;
}
void triangulation (
const vector< KeyPoint >& keypoint_1,
const vector< KeyPoint >& keypoint_2,
const std::vector< DMatch >& matches,
const Mat& R, const Mat& t,
vector< Point3d >& points )
{
Mat T1 = (Mat_<float> (3,4) <<
1,0,0,0,
0,1,0,0,
0,0,1,0);
Mat T2 = (Mat_<float> (3,4) <<
R.at<double>(0,0), R.at<double>(0,1), R.at<double>(0,2), t.at<double>(0,0),
R.at<double>(1,0), R.at<double>(1,1), R.at<double>(1,2), t.at<double>(1,0),
R.at<double>(2,0), R.at<double>(2,1), R.at<double>(2,2), t.at<double>(2,0)
);
Mat K = ( Mat_<double> ( 3,3 ) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1 );
vector<Point2f> pts_1, pts_2;
for ( DMatch m:matches )
{
// 将像素坐标转换至相机坐标
pts_1.push_back ( pixel2cam( keypoint_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K) );
pts_2.push_back ( pixel2cam( keypoint_2[m.trainIdx].pt, K) );
}
Mat pts_4d;
cv::triangulatePoints( T1, T2, pts_1, pts_2, pts_4d );
// 转换成非齐次坐标
for ( int i=0; i<pts_4d.cols; i++ )
{
Mat x = pts_4d.col(i);
x /= x.at<float>(3,0); // 归一化
Point3d p (
x.at<float>(0,0),
x.at<float>(1,0),
x.at<float>(2,0)
);
points.push_back( p );
}
}
Point2f pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K )
{
return Point2f
(
( p.x - K.at<double>(0,2) ) / K.at<double>(0,0),
( p.y - K.at<double>(1,2) ) / K.at<double>(1,1)
);
}
cmakelist.cpp
注意opencv路径是安装时那个安装包的路径~
cmake_minimum_required( VERSION 2.8 )
project( imageBasics )
# 添加c++ 11标准支持
set( CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11" )
# 寻找OpenCV库
set(OpenCV_DIR /media/ufo/存储/qq下载的/ufoo/opencv-3.4.1/)
find_package( OpenCV 3 REQUIRED )
# 添加头文件
include_directories( ${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS} )
add_executable( triangulation triangulation.cpp )
# 链接OpenCV库
target_link_libraries( triangulation ${OpenCV_LIBS} )
编译:
使用develop导入对应的文件夹,build:
下载安装develop直接用apt-get快一些~
sudo apt-get install kdevelop

运行:
./build/triangulation 0.png 1.png
效果:

2.pnp
pose_estimation_3d2d.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/csparse/linear_solver_csparse.h>
#include <g2o/types/sba/types_six_dof_expmap.h>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void find_feature_matches (
const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2,
std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1,
std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2,
std::vector< DMatch >& matches );
// 像素坐标转相机归一化坐标
Point2d pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K );
void bundleAdjustment (
const vector<Point3f> points_3d,
const vector<Point2f> points_2d,
const Mat& K,
Mat& R, Mat& t
);
int main ( int argc, char** argv )
{
if ( argc != 5 )
{
cout<<"usage: pose_estimation_3d2d img1 img2 depth1 depth2"<<endl;
return 1;
}
//-- 读取图像
Mat img_1 = imread ( argv[1], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR );
Mat img_2 = imread ( argv[2], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR );
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
vector<DMatch> matches;
find_feature_matches ( img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches );
cout<<"一共找到了"<<matches.size() <<"组匹配点"<<endl;
// 建立3D点
Mat d1 = imread ( argv[3], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED ); // 深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像
Mat K = ( Mat_<double> ( 3,3 ) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1 );
vector<Point3f> pts_3d;
vector<Point2f> pts_2d;
for ( DMatch m:matches )
{
ushort d = d1.ptr<unsigned short> (int ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.y )) [ int ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.x ) ];
if ( d == 0 ) // bad depth
continue;
float dd = d/5000.0;
Point2d p1 = pixel2cam ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K );
pts_3d.push_back ( Point3f ( p1.x*dd, p1.y*dd, dd ) );
pts_2d.push_back ( keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt );
}
cout<<"3d-2d pairs: "<<pts_3d.size() <<endl;
Mat r, t;
solvePnP ( pts_3d, pts_2d, K, Mat(), r, t, false ); // 调用OpenCV 的 PnP 求解,可选择EPNP,DLS等方法
Mat R;
cv::Rodrigues ( r, R ); // r为旋转向量形式,用Rodrigues公式转换为矩阵
cout<<"R="<<endl<<R<<endl;
cout<<"t="<<endl<<t<<endl;
cout<<"calling bundle adjustment"<<endl;
bundleAdjustment ( pts_3d, pts_2d, K, R, t );
}
void find_feature_matches ( const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2,
std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1,
std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2,
std::vector< DMatch >& matches )
{
//-- 初始化
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
// used in OpenCV3
Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create();
Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create();
// use this if you are in OpenCV2
// Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" );
// Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" );
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create ( "BruteForce-Hamming" );
//-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置
detector->detect ( img_1,keypoints_1 );
detector->detect ( img_2,keypoints_2 );
//-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子
descriptor->compute ( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
descriptor->compute ( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离
vector<DMatch> match;
// BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING );
matcher->match ( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match );
//-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选
double min_dist=10000, max_dist=0;
//找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离
for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = match[i].distance;
if ( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if ( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
printf ( "-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist );
printf ( "-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist );
//当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限.
for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if ( match[i].distance <= max ( 2*min_dist, 30.0 ) )
{
matches.push_back ( match[i] );
}
}
}
Point2d pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K )
{
return Point2d
(
( p.x - K.at<double> ( 0,2 ) ) / K.at<double> ( 0,0 ),
( p.y - K.at<double> ( 1,2 ) ) / K.at<double> ( 1,1 )
);
}
void bundleAdjustment (
const vector< Point3f > points_3d,
const vector< Point2f > points_2d,
const Mat& K,
Mat& R, Mat& t )
{
// 初始化g2o
typedef g2o::BlockSolver< g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6,3> > Block; // pose 维度为 6, landmark 维度为 3
Block::LinearSolverType* linearSolver = new g2o::LinearSolverCSparse<Block::PoseMatrixType>(); // 线性方程求解器
Block* solver_ptr = new Block ( linearSolver ); // 矩阵块求解器
g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg ( solver_ptr );
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;
optimizer.setAlgorithm ( solver );
// vertex
g2o::VertexSE3Expmap* pose = new g2o::VertexSE3Expmap(); // camera pose
Eigen::Matrix3d R_mat;
R_mat <<
R.at<double> ( 0,0 ), R.at<double> ( 0,1 ), R.at<double> ( 0,2 ),
R.at<double> ( 1,0 ), R.at<double> ( 1,1 ), R.at<double> ( 1,2 ),
R.at<double> ( 2,0 ), R.at<double> ( 2,1 ), R.at<double> ( 2,2 );
pose->setId ( 0 );
pose->setEstimate ( g2o::SE3Quat (
R_mat,
Eigen::Vector3d ( t.at<double> ( 0,0 ), t.at<double> ( 1,0 ), t.at<double> ( 2,0 ) )
) );
optimizer.addVertex ( pose );
int index = 1;
for ( const Point3f p:points_3d ) // landmarks
{
g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ* point = new g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ();
point->setId ( index++ );
point->setEstimate ( Eigen::Vector3d ( p.x, p.y, p.z ) );
point->setMarginalized ( true ); // g2o 中必须设置 marg 参见第十讲内容
optimizer.addVertex ( point );
}
// parameter: camera intrinsics
g2o::CameraParameters* camera = new g2o::CameraParameters (
K.at<double> ( 0,0 ), Eigen::Vector2d ( K.at<double> ( 0,2 ), K.at<double> ( 1,2 ) ), 0
);
camera->setId ( 0 );
optimizer.addParameter ( camera );
// edges
index = 1;
for ( const Point2f p:points_2d )
{
g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV* edge = new g2o::EdgeProjectXYZ2UV();
edge->setId ( index );
edge->setVertex ( 0, dynamic_cast<g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ*> ( optimizer.vertex ( index ) ) );
edge->setVertex ( 1, pose );
edge->setMeasurement ( Eigen::Vector2d ( p.x, p.y ) );
edge->setParameterId ( 0,0 );
edge->setInformation ( Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity() );
optimizer.addEdge ( edge );
index++;
}
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
optimizer.setVerbose ( true );
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize ( 100 );
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>> ( t2-t1 );
cout<<"optimization costs time: "<<time_used.count() <<" seconds."<<endl;
cout<<endl<<"after optimization:"<<endl;
cout<<"T="<<endl<<Eigen::Isometry3d ( pose->estimate() ).matrix() <<endl;
}
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required( VERSION 2.8 )
project( imageBasics )
list( APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH /home/ufo/嵌入式/week12/g2o/g2o/cmake_modules )
# 添加c++ 11标准支持
set( CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11" )
# 寻找OpenCV库
set(OpenCV_DIR /media/ufo/存储/qq下载的/ufoo/opencv-3.4.1/)
set(CSparse /home/ufo/嵌入式/week12/g2o/g2oo)
find_package( OpenCV 3 REQUIRED )
find_package( CSparse REQUIRED )
include_directories( ${CSPARSE_INCLUDE_DIR} )
# 添加头文件
include_directories( ${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS} ${CSPARSE_INCLUDE_DIR})
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
include_directories("/usr/local/include/g2o/EXTERNAL/csparse")
add_executable( pose_estimation_3d2d pose_estimation_3d2d.cpp )
# 链接OpenCV库
target_link_libraries( pose_estimation_3d2d ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${G2O_LIBS} ${CSPARSE_LIBRARY})
遇到错误:
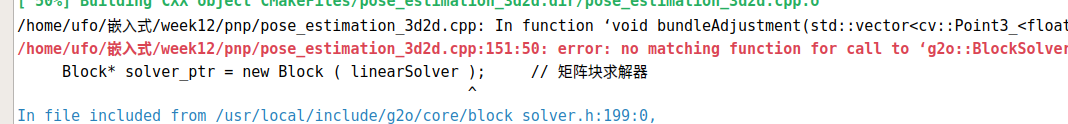
重装降级G2O~并没什么用~
可能因为cmakelist不熟悉,所以一直报错
于是参考大佬代码,没用上面那个代码,改用下面这种代码:
在cpp同级目录放一些cmake_modules:

pose_estimation_3d2d.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_unary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/csparse/linear_solver_csparse.h>
#include <g2o/types/sba/types_six_dof_expmap.h>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void find_feature_matches (
const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2,
std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1,
std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2,
std::vector< DMatch >& matches );
// 像素坐标转相机归一化坐标
Point2d pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K );
int main ( int argc, char** argv )
{
if ( argc != 4 )
{
cout<<"usage: pose_estimation_3d2d img1 img2 depth1"<<endl;
return 1;
}
//-- 读取图像
Mat img_1 = imread ( argv[1], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR );
Mat img_2 = imread ( argv[2], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR );
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
vector<DMatch> matches;
find_feature_matches ( img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches );
cout<<"一共找到了"<<matches.size() <<"组匹配点"<<endl;
// 建立3D点
Mat d1 = imread ( argv[3], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED ); // 深度图为16位无符号数,单通道图像
Mat K = ( Mat_<double> ( 3,3 ) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1 );
vector<Point3f> pts_3d;
vector<Point2f> pts_2d;
for ( DMatch m:matches )
{
ushort d = d1.ptr<unsigned short> (int ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.y )) [ int ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt.x ) ];
if ( d == 0 ) // bad depth
continue;
float dd = d/5000.0;
Point2d p1 = pixel2cam ( keypoints_1[m.queryIdx].pt, K );
pts_3d.push_back ( Point3f ( p1.x*dd, p1.y*dd, dd ) );
pts_2d.push_back ( keypoints_2[m.trainIdx].pt );
}
cout<<"3d-2d pairs: "<<pts_3d.size() <<endl;
Mat r, t;
solvePnP ( pts_3d, pts_2d, K, Mat(), r, t, false ); // 调用OpenCV 的 PnP 求解,可选择EPNP,DLS等方法
Mat R;
cv::Rodrigues ( r, R ); // r为旋转向量形式,用Rodrigues公式转换为矩阵
cout<<"R="<<endl<<R<<endl;
cout<<"t="<<endl<<t<<endl;
}
void find_feature_matches ( const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2,
std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_1,
std::vector<KeyPoint>& keypoints_2,
std::vector< DMatch >& matches )
{
//-- 初始化
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
// used in OpenCV3
Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create();
Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create();
// use this if you are in OpenCV2
// Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" );
// Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" );
Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create ( "BruteForce-Hamming" );
//-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置
detector->detect ( img_1,keypoints_1 );
detector->detect ( img_2,keypoints_2 );
//-- 第二步:根据角点位置计算 BRIEF 描述子
descriptor->compute ( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
descriptor->compute ( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- 第三步:对两幅图像中的BRIEF描述子进行匹配,使用 Hamming 距离
vector<DMatch> match;
// BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING );
matcher->match ( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match );
//-- 第四步:匹配点对筛选
double min_dist=10000, max_dist=0;
//找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离
for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = match[i].distance;
if ( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if ( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
printf ( "-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist );
printf ( "-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist );
//当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限.
for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if ( match[i].distance <= max ( 2*min_dist, 30.0 ) )
{
matches.push_back ( match[i] );
}
}
}
Point2d pixel2cam ( const Point2d& p, const Mat& K )
{
return Point2d
(
( p.x - K.at<double> ( 0,2 ) ) / K.at<double> ( 0,0 ),
( p.y - K.at<double> ( 1,2 ) ) / K.at<double> ( 1,1 )
);
}
CMakeLists.txt:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(test)
list(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake_modules)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
SET( G2O_ROOT /usr/local/include/g2o )
find_package( OpenCV REQUIRED )
find_package(Eigen3 REQUIRED)
find_package(G2O REQUIRED)
find_package( CSparse)
include_directories(
${EIGEN3_INCLUDE_DIR}
${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${G2O_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${CSPARSE_INCLUDE_DIR}
)
add_executable(pose_estimation_3d2d pose_estimation_3d2d.cpp)
target_link_libraries( pose_estimation_3d2d ${EIGEN3_LIB} ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${G2O_LIB} ${CSPARSE_LIB})
target_link_libraries(pose_estimation_3d2d g2o_core g2o_stuff)
编译
kdevelop build一下:

运行:
./build/pose_estimation_3d2d 0.png 1.png 1.png
效果:

源代码:https://github.com/2575829997/Ai-and-embedded
参考:
pnp:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_36448497/article/details/82288818
g2o:https://blog.csdn.net/slzlincent/article/details/86555166






















 2548
2548











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








