目录
1 进入情境
生日,朋友送了一堆弹珠,有大有小;我想找出自己的幸运数字8对应的那颗弹珠。有什么办法呢?
- 排序,然后从头数到第八个。
- 找八次,每次找到最小的后,放到一边。
比较一下哪个好?
- 排序很烦,因为朋友送了我
一卡车弹珠,而我只想要第八个,工作量太大,不实际。 - 找八次,每次都要从一车里找最小的,也很累。好在朋友附赠了一个魔法道具——金字塔。
1-1 金字塔道具
就是把一车弹珠从金字塔的头上倒入,按下开关,最小的弹珠就被放到金字塔的塔尖了。这样反复取走头顶的最小弹珠、再按,八次之后就能拿到幸运弹珠了!
金字塔还有其他的俗名,像小顶堆、隐式二叉堆、斐波那契堆和其他堆,效果是一样的。
效率 O(KlgN)
1-2 感觉还不够
取了八次,得到的是前八个有序的弹珠,但前七个我都不想要,能不能一步到位,直接跳过前面步骤,直接找出我要的第八颗弹珠呢?
比如,更加NB的魔法道具?
就是你啦,妙蛙种子!……不好意思串台了。闪烁着金色光芒的传说中的厨具——万能筛子!!!
1-3 万能筛子

正经的筛子是一种带孔的网,大于孔的会被留住筛子里,小于孔的会掉下去。如上所示,孔的大小是固定的。
神奇筛子就厉害了,允许控制孔的大小。试想,假如凭直觉估到了第八颗弹珠的大小,设为孔径,只需把一车弹珠往筛子上这么哗哗一倒,筛出十来颗弹珠,岂不是爽歪歪。可能眼睛一扫就出结果,这多快!
1-4 怎么用呢
为了方便说清楚,假设我们要找第K颗弹珠,默认是从小到大的次序。
- 随机选一颗弹珠pivot作为孔洞的大小,筛一筛,之后得到两部分,筛子里剩下大A颗,筛子外出现小b颗。
- 看
幸运弹珠在哪一堆里,若K< 小b,说明幸运弹珠就在筛子外的小珠子里,回到第一步继续选第K颗; - 若K等于小b,说明说明
幸运弹珠就是pivot,找到了! - 若K> 小b,说明
幸运弹珠还在筛子里,调整孔的大小,继续筛里面的弹珠。注意,因为这次已经找到了前 小b颗,所以接下来只需要回到第一步找第(K- 小b)颗弹珠。
性能 O(N)
2 代码实现
2-1 伪代码描述
Top(k,A,l,r)表示在数组A[l,r]中查找第k小的数。Partitio(A,l,r):以首元素A[l]为枢纽pivot,将数组A分为两部分,小于枢纽的放前面,大于枢纽的放后面,结束后返回枢纽的正确下标L=2。如下图所示,A[l,L]是已经满足不大于枢纽的部分。
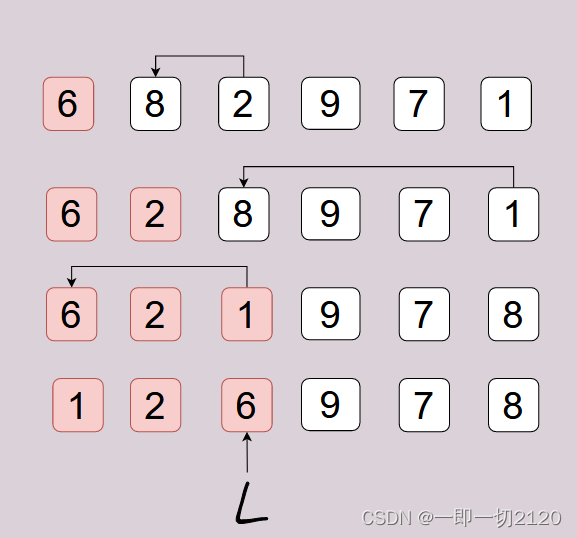
function Top(k,A,l,r):
Exchange A[l] <--> A[Random(l,r)] #随机选一个元素作为pivot放到起点位置
p <- Partition(A,l,r)# 按首元素划分,返回pivot的数组下标p
nth <- p-l+1 #pivot 在当前范围的数组中是第nth个
if nth == k then
return A[p]
if k < nth then
return Top(k,A,l,p-1)
return Top(k-nth,A,p+1,r)
function Partitio(A,l,r):
pivot <- A[l]
L <- l
for R <- l+1 to r do
if not (pivot < A[R]) then # 发现一个逆序的数
L<- L+1 # 首个可交换的大于枢纽的值的下标
Exchange A[L]<-->A[R]
Exchange A[L]<-->A[l]# 把枢纽值放到分界线上
return L
2-2 完整实例c++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include<cstdlib> //rand() 获取随机数
using namespace std;
#define see(x) cout << x << endl
#define see2(x, y) cout << (x) <<"\t"<< (y) << endl
class Solution
{
using Array=vector<int> ;
public:
int topKth(int kth,Array &A,int l,int r){//修改数组要传入引用
if(l>r) return -1; //检查下标的合法性
if(l==r&&kth==1) return A[l]; //只有一个数,可能会对0取余
swap(A[l],A[rand() % (r-l)+l]);
int p=partition(A,l,r);//小堆 枢纽 大堆中枢纽的下标
int ith=p-l+1;
if(ith==kth) return A[p];
if(ith>kth) return topKth(kth,A,l,p-1);//在小堆A[l,p-1]里找
return topKth(kth-ith,A,p+1,r);//在大的堆A[p+1,r]里找
}
int partition(Array &A,int l,int r){
int pivot=A[l];
int R,L=l;
for(R=l+1;R<=r;++R){
if(!(pivot<A[R])){//!优先级高于<
swap(A[++L],A[R]);
}
}
swap(A[L],A[l]);//注意复位
return L;
}
};
void test()
{
vector<int> A{6,8,2,9,7,1};
vector<int> sortedA{1,2,6,7,8,9};
Solution sol;
//test partition()
// sol.partition(A,0,5);
// for(auto& x:A){
// see(x);
// }
bool pass=true;
for (size_t ith = 1; ith <= A.size(); ++ith)
{
int now=sol.topKth(ith,A,0,5);
// see2(ith,now);
if(sortedA[ith-1]!= now)//idx+1=ith
{
pass=false;
break;
}
}
if (pass)
{
see("Accept!!!");
}
else
{
see("something error.");
}
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
3 引申
3-1 完美的折半舍弃
- 把列表划分为若干小组,每个组最多5个元素;
- 计算每个组的中间值,得到N/5个数;
- 继续寻找中值的中值,在O(lgn)时间内得到真正的中值。
- 以此中值作为枢纽切分,每次都会舍弃一半。
总体效率 T(n)=a*lgn+b*n+T(n/2),a是求中值的中值的常系数;b是划分的常数系数,如1/5;利用主定理,可得总性能为 O(n);证明请移步使用主定理求解递归式。
伪代码说明:
function findPivot(A,l,r):
#出口
alen <- r-l+1
if alen <= 5 then
sort(A,l,r)
return A[(l+r)/2]
#切分 获得新数组B
blen <- alen / 5
for i=0 to blen-1 do
now_l <- l+5*i
now_r <- now_l+4
if now_r > r then
now_r <- r
B[i]<-findPivot(A,now_l,now_r)
#递归,中值的中值
return findPivot(B,0,blen)
C++实现
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include<algorithm>//sort()
#include<cstdlib> //rand() 获取随机数
#include<cmath> //ceil(2.3) 取不小于2.3的下一个整数
using namespace std;
#define see(x) cout << x << endl
#define see2(x, y) cout << (x) <<"\t"<< (y) << endl
class Solution
{
using Array=vector<int> ;
public:
int findPivot(Array &A,int l,int r){
int na=r-l+1;
if(na<=5){
// 也可以对A[l,r]排序,取中值
// 这里直接暴力求平均,拿和均值最接近的那个
int pivot=-1;
int sum=0;
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++) sum+=A[i];
double avg=(sum*1.0)/na;
double det=1e10;
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++) {
if(abs(A[i]-avg)<det){
det=abs(A[i]-avg);
pivot=A[i];
}
}
return pivot;
}
int nb=ceil(na/5.0);
Array B(nb,0);
for (size_t i = 0; i < nb; i++)
{
int L=l+5*i;
int R=L+4;
if(R>r) R=r;
B[i]=findPivot(A,L,R);
}
return findPivot(B,0,nb);
}
int topKth(int kth,Array &A,int l,int r){//修改数组要传入引用
if(l>r) return -1; //检查下标的合法性
if(l==r&&kth==1) return A[l]; //只有一个数
int p=partition(A,l,r);//小堆 枢纽 大堆中枢纽的下标
int ith=p-l+1;
if(ith==kth) return A[p];
if(ith>kth) return topKth(kth,A,l,p-1);//在小堆A[l,p-1]里找
return topKth(kth-ith,A,p+1,r);//在大的堆A[p+1,r]里找
}
int partition(Array &A,int l,int r){
int pivot=findPivot(A,l,r);//递归获取中位数
int L=l,R=r+1;
int pi=-1;//枢纽记录其下标
while(L<R){
while (A[L]<pivot&&(++L)<r);
while(A[--R]>pivot&&R>L);
if(L<R){
swap(A[L],A[R]);
if(A[L]==pivot) pi=L;
if(A[R]==pivot) pi=R;
}
}
swap(A[pi],A[L]);
return L;
}
};
void test()
{
vector<int> A{6,8,2,9,7,1,3,5,4,10};
Solution sol;
// test findPivot
// see(sol.findPivot(A,0,5));
// test partition
// sol.partition(A,0,A.size()-1);
// for(auto x:A){
// see(x);
// }
see(sol.topKth(9,A,0,A.size()-1));
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
3-2 找出前K小的元素(topK方法)
注意,不关心所得数据的顺序。递归思路,TopK(K,List):
- List 为空或者K是0,返回空;
- List 个数等于K,返回List;
- 按枢纽切分为筛子里的Big,筛子外的small。 如果small个数大于K,
TopK(samll,K); - 如果small的个数小于K,说明已经找到
|s|个合适的,剩下的在Big里TopK(Big,K-|s|)
3-3 O(n)效率下求中位数
已经知道数组A长度是L;
第一种情况,L是奇数,则中位数是TopKth(L/2+1,A);第二种情况,L是偶数,中位数是(topKth(L/2,A)+topKth(L/2+1,A))/2。
参考资料
《算法新解》刘新宇 2017 版
























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








