通域分析对于图像处理后面涉及到模式识别的内容来说是基础
连通区域(Connected Component)一般是指图像中具有相同像素值且位置相邻的前景像素点组成的图像区域(Region,Blob)。连通区域分析(Connected Component Analysis,Connected Component Labeling)是指将图像中的各个连通区域找出并标记。
连通区域分析是一种在CVPR和图像分析处理的众多应用领域中较为常用和基本的方法。例如:OCR识别中字符分割提取(车牌识别、文本识别、字幕识别等)、视觉跟踪中的运动前景目标分割与提取(行人入侵检测、遗留物体检测、基于视觉的车辆检测与跟踪等)、医学图像处理(感兴趣目标区域提取)、等等。也就是说,在需要将前景目标提取出来以便后续进行处理的应用场景中都能够用到连通区域分析方法,通常连通区域分析处理的对象是一张二值化后的图像。
看了几篇博客总结如下:
其中最主要的参考博客 :404了,so what? http://blog.csdn.net/icvpr/article (这是该作者的主页)
很多人转载了,给出一个转载的链接:http://blog.csdn.net/shanx_s/article/details/52860896
参考博客2:http://www.cnblogs.com/ronny/p/img_aly_01.html(博主将过程拆分讲解的很清楚)
参考博客3:http://blog.csdn.net/YU_Xianguo/article/details/49743147(两步法的一种加速版)
参考博客4:http://blog.csdn.net/menghuanxiy/article/details/45741027#reply (种子填充法的一种实现)
参考博客5:http://blog.csdn.net/augusdi/article/details/9008921(很快,代码很短,排名很高(第7))
参考博客6:http://blog.csdn.net/xjt2015/article/details/51283387 (种子填充法的实现)
理论充能任务
任务一:
二值图像,顾名思义就是图像的亮度值只有两个状态:黑(0)和白(255)。二值图像在图像分析与识别中有着举足轻重的地位,因为其模式简单,对像素在空间上的关系有着极强的表现力。在实际应用中,很多图像的分析最终都转换为二值图像的分析,比如:医学图像分析、前景检测、字符识别,形状识别。二值化+数学形态学能解决很多计算机识别工程中目标提取的问题。
二值图像分析最重要的方法就是连通区域标记,它是所有二值图像分析的基础,它通过对二值图像中白色像素(目标)的标记,让每个单独的连通区域形成一个被标识的块,进一步的我们就可以获取这些块的轮廓、外接矩形、质心、不变矩等几何参数。
任务二:
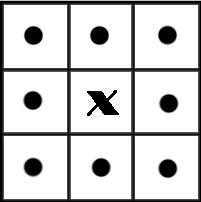
在我们讨论连通区域标记的算法之前,我们先要明确什么是连通区域,怎样的像素邻接关系构成连通。在图像中,最小的单位是像素,每个像素周围有8个邻接像素,常见的邻接关系有2种:4邻接与8邻接。4邻接一共4个点,即上下左右,如下左图所示。8邻接的点一共有8个,包括了对角线位置的点,如下右图所示。
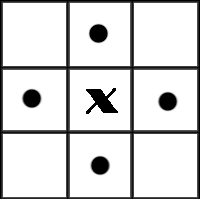
如果像素点A与B邻接,我们称A与B连通,于是我们不加证明的有如下的结论:
如果A与B连通,B与C连通,则A与C连通。
在视觉上看来,彼此连通的点形成了一个区域,而不连通的点形成了不同的区域。这样的一个所有的点彼此连通点构成的集合,我们称为一个连通区域。
下面这符图中,如果考虑4邻接,则有3个连通区域;如果考虑8邻接,则有2个连通区域。(注:图像是被放大的效果,图像正方形实际只有4个像素)
任务三:
二、连通区域分析的算法
从连通区域的定义可以知道,一个连通区域是由具有相同像素值的相邻像素组成像素集合,因此,我们就可以通过这两个条件在图像中寻找连通区域,对于找到的每个连通区域,我们赋予其一个唯一的标识(Label),以区别其他连通区域。
连通区域分析有基本的算法,也有其改进算法,本文介绍其中的两种常见算法:
1)Two-Pass法;2)Seed-Filling种子填充法;
1)Two-Pass(两遍扫描法)
两遍扫描法,正如其名,指的就是通过扫描两遍图像,就可以将图像中存在的所有连通区域找出并标记。思路:第一遍扫描时赋予每个像素位置一个label,扫描过程中同一个连通区域内的像素集合中可能会被赋予一个或多个不同label,因此需要将这些属于同一个连通区域但具有不同值的label合并,也就是记录它们之间的相等关系;第二遍扫描就是将具有相等关系的equal_labels所标记的像素归为一个连通区域并赋予一个相同的label(通常这个label是equal_labels中的最小值)。
下面给出Two-Pass算法的简单步骤:
(1)第一次扫描:
访问当前像素B(x,y),如果B(x,y) == 1:
a、如果B(x,y)的领域中像素值都为0,则赋予B(x,y)一个新的label:
label += 1, B(x,y) = label;
b、如果B(x,y)的领域中有像素值 > 1的像素Neighbors:
1)将Neighbors中的最小值赋予给B(x,y):
B(x,y) = min{Neighbors}
2)记录Neighbors中各个值(label)之间的相等关系,即这些值(label)同属同一个连通区域;
labelSet[i] = { label_m, .., label_n },labelSet[i]中的所有label都属于同一个连通区域(注:这里可以有多种实现方式,只要能够记录这些具有相等关系的label之间的关系即可)
(2)第二次扫描:
访问当前像素B(x,y),如果B(x,y) > 1:
a、找到与label = B(x,y)同属相等关系的一个最小label值,赋予给B(x,y);
完成扫描后,图像中具有相同label值的像素就组成了同一个连通区域。
下面这张图动态地演示了Two-pass算法:
具体实现还是得一步一步的看代码
2)Seed Filling(种子填充法)
种子填充方法来源于计算机图形学,常用于对某个图形进行填充。思路:选取一个前景像素点作为种子,然后根据连通区域的两个基本条件(像素值相同、位置相邻)将与种子相邻的前景像素合并到同一个像素集合中,最后得到的该像素集合则为一个连通区域。
下面给出基于种子填充法的连通区域分析方法:
(1)扫描图像,直到当前像素点B(x,y) == 1:
a、将B(x,y)作为种子(像素位置),并赋予其一个label,然后将该种子相邻的所有前景像素都压入栈中;
b、弹出栈顶像素,赋予其相同的label,然后再将与该栈顶像素相邻的所有前景像素都压入栈中;
c、重复b步骤,直到栈为空;
此时,便找到了图像B中的一个连通区域,该区域内的像素值被标记为label;
(2)重复第(1)步,直到扫描结束;
扫描结束后,就可以得到图像B中所有的连通区域;
下面这张图动态地演示了Seed-Filling算法:
完整测试代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
//------------------------------【两步法新改进版】----------------------------------------------
// 对二值图像进行连通区域标记,从1开始标号
void Two_PassNew( const Mat &bwImg, Mat &labImg )
{
assert( bwImg.type()==CV_8UC1 );
labImg.create( bwImg.size(), CV_32SC1 ); //bwImg.convertTo( labImg, CV_32SC1 );
labImg = Scalar(0);
labImg.setTo( Scalar(1), bwImg );
assert( labImg.isContinuous() );
const int Rows = bwImg.rows - 1, Cols = bwImg.cols - 1;
int label = 1;
vector<int> labelSet;
labelSet.push_back(0);
labelSet.push_back(1);
//the first pass
int *data_prev = (int*)labImg.data; //0-th row : int* data_prev = labImg.ptr<int>(i-1);
int *data_cur = (int*)( labImg.data + labImg.step ); //1-st row : int* data_cur = labImg.ptr<int>(i);
for( int i = 1; i < Rows; i++ )
{
data_cur++;
data_prev++;
for( int j=1; j<Cols; j++, data_cur++, data_prev++ )
{
if( *data_cur!=1 )
continue;
int left = *(data_cur-1);
int up = *data_prev;
int neighborLabels[2];
int cnt = 0;
if( left>1 )
neighborLabels[cnt++] = left;
if( up > 1)
neighborLabels[cnt++] = up;
if( !cnt )
{
labelSet.push_back( ++label );
labelSet[label] = label;
*data_cur = label;
continue;
}
int smallestLabel = neighborLabels[0];
if( cnt==2 && neighborLabels[1]<smallestLabel )
smallestLabel = neighborLabels[1];
*data_cur = smallestLabel;
// 保存最小等价表
for( int k=0; k<cnt; k++ )
{
int tempLabel = neighborLabels[k];
int& oldSmallestLabel = labelSet[tempLabel]; //这里的&不是取地址符号,而是引用符号
if( oldSmallestLabel > smallestLabel )
{
labelSet[oldSmallestLabel] = smallestLabel;
oldSmallestLabel = smallestLabel;
}
else if( oldSmallestLabel<smallestLabel )
labelSet[smallestLabel] = oldSmallestLabel;
}
}
data_cur++;
data_prev++;
}
//更新等价队列表,将最小标号给重复区域
for( size_t i = 2; i < labelSet.size(); i++ )
{
int curLabel = labelSet[i];
int prelabel = labelSet[curLabel];
while( prelabel != curLabel )
{
curLabel = prelabel;
prelabel = labelSet[prelabel];
}
labelSet[i] = curLabel;
}
//second pass
data_cur = (int*)labImg.data;
for( int i = 0; i < Rows; i++ )
{
for( int j = 0; j < bwImg.cols-1; j++, data_cur++)
*data_cur = labelSet[ *data_cur ];
data_cur++;
}
}
//-------------------------------【老版两步法】-------------------------------------------
void Two_PassOld(const cv::Mat& _binImg, cv::Mat& _lableImg)
{
//connected component analysis (4-component)
//use two-pass algorithm
//1. first pass: label each foreground pixel with a label
//2. second pass: visit each labeled pixel and merge neighbor label
//
//foreground pixel: _binImg(x,y) = 1
//background pixel: _binImg(x,y) = 0
if(_binImg.empty() || _binImg.type() != CV_8UC1)
{
return;
}
// 1. first pass
_lableImg.release();
_binImg.convertTo(_lableImg, CV_32SC1 );
int label = 1; // start by 2
std::vector<int> labelSet;
labelSet.push_back(0); //background: 0
labelSet.push_back(1); //foreground: 1
int rows = _binImg.rows - 1;
int cols = _binImg.cols - 1;
for( int i = 1; i < rows; i++)
{
int* data_preRow = _lableImg.ptr<int>(i-1);
int* data_curRow = _lableImg.ptr<int>(i);
for(int j = 1; j < cols; j++)
{
if(data_curRow[j] == 1)
{
std::vector<int> neighborLabels;
neighborLabels.reserve(2); //reserve(n) 预分配n个元素的存储空间
int leftPixel = data_curRow[j-1];
int upPixel = data_preRow[j];
if( leftPixel > 1)
{
neighborLabels.push_back(leftPixel);
}
if( upPixel > 1)
{
neighborLabels.push_back(upPixel);
}
if(neighborLabels.empty())
{
labelSet.push_back(++label); //assign to a new label
data_curRow[j] = label;
labelSet[label] = label;
}
else
{
std::sort(neighborLabels.begin(),neighborLabels.end());
int smallestLabel = neighborLabels[0];
data_curRow[j] = smallestLabel;
//save equivalence
for(size_t k = 1; k < neighborLabels.size();k++)
{
int tempLabel = neighborLabels[k];
int& oldSmallestLabel = labelSet[tempLabel];
if(oldSmallestLabel > smallestLabel)
{
labelSet[oldSmallestLabel] = smallestLabel;
oldSmallestLabel = smallestLabel;
}
else if(oldSmallestLabel < smallestLabel)
{
labelSet[smallestLabel] = oldSmallestLabel;
}
}
}
}
}
}
//update equivalent labels
//assigned with the smallest label in each equivalent label set
for(size_t i = 2; i < labelSet.size();i++)
{
int curLabel = labelSet[i];
int prelabel = labelSet[curLabel];
while (prelabel != curLabel )
{
curLabel = prelabel;
prelabel = labelSet[prelabel];
}
labelSet[i] = curLabel;
}
//2. second pass
for( int i = 0; i < rows; i++ )
{
int *data = _lableImg.ptr<int>(i);
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++ )
{
int& pixelLabel = data[j];
pixelLabel = labelSet[pixelLabel];
}
}
}
//---------------------------------【种子填充法老版】-------------------------------
void SeedFillOld(const cv::Mat& binImg, cv::Mat& lableImg) //种子填充法
{
// 4邻接方法
if (binImg.empty() ||
binImg.type() != CV_8UC1)
{
return;
}
lableImg.release();
binImg.convertTo(lableImg, CV_32SC1);
int label = 1;
int rows = binImg.rows - 1;
int cols = binImg.cols - 1;
for (int i = 1; i < rows-1; i++)
{
int* data= lableImg.ptr<int>(i);
for (int j = 1; j < cols-1; j++)
{
if (data[j] == 1)
{
std::stack<std::pair<int,int>> neighborPixels;
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int,int>(i,j)); // 像素位置: <i,j>
++label; // 没有重复的团,开始新的标签
while (!neighborPixels.empty())
{
std::pair<int,int> curPixel = neighborPixels.top(); //如果与上一行中一个团有重合区域,则将上一行的那个团的标号赋给它
int curX = curPixel.first;
int curY = curPixel.second;
lableImg.at<int>(curX, curY) = label;
neighborPixels.pop();
if (lableImg.at<int>(curX, curY-1) == 1)
{//左边
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int,int>(curX, curY-1));
}
if (lableImg.at<int>(curX, curY+1) == 1)
{// 右边
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int,int>(curX, curY+1));
}
if (lableImg.at<int>(curX-1, curY) == 1)
{// 上边
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int,int>(curX-1, curY));
}
if (lableImg.at<int>(curX+1, curY) == 1)
{// 下边
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int,int>(curX+1, curY));
}
}
}
}
}
}
//-------------------------------------------【种子填充法新版】---------------------------
void SeedFillNew(const cv::Mat& _binImg, cv::Mat& _lableImg )
{
// connected component analysis(4-component)
// use seed filling algorithm
// 1. begin with a forgeground pixel and push its forground neighbors into a stack;
// 2. pop the pop pixel on the stack and label it with the same label until the stack is empty
//
// forground pixel: _binImg(x,y)=1
// background pixel: _binImg(x,y) = 0
if(_binImg.empty() ||
_binImg.type()!=CV_8UC1)
{
return;
}
_lableImg.release();
_binImg.convertTo(_lableImg,CV_32SC1);
int label = 0; //start by 1
int rows = _binImg.rows;
int cols = _binImg.cols;
Mat mask(rows, cols, CV_8UC1);
mask.setTo(0);
int *lableptr;
for(int i=0; i < rows; i++)
{
int* data = _lableImg.ptr<int>(i);
uchar *masKptr = mask.ptr<uchar>(i);
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
if(data[j] == 255&&mask.at<uchar>(i,j)!=1)
{
mask.at<uchar>(i,j)=1;
std::stack<std::pair<int,int>> neighborPixels;
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int,int>(i,j)); // pixel position: <i,j>
++label; //begin with a new label
while(!neighborPixels.empty())
{
//get the top pixel on the stack and label it with the same label
std::pair<int,int> curPixel =neighborPixels.top();
int curY = curPixel.first;
int curX = curPixel.second;
_lableImg.at<int>(curY, curX) = label;
//pop the top pixel
neighborPixels.pop();
//push the 4-neighbors(foreground pixels)
if(curX-1 >= 0)
{
if(_lableImg.at<int>(curY,curX-1) == 255&&mask.at<uchar>(curY,curX-1)!=1) //leftpixel
{
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int,int>(curY,curX-1));
mask.at<uchar>(curY,curX-1)=1;
}
}
if(curX+1 <=cols-1)
{
if(_lableImg.at<int>(curY,curX+1) == 255&&mask.at<uchar>(curY,curX+1)!=1)
// right pixel
{
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int,int>(curY,curX+1));
mask.at<uchar>(curY,curX+1)=1;
}
}
if(curY-1 >= 0)
{
if(_lableImg.at<int>(curY-1,curX) == 255&&mask.at<uchar>(curY-1,curX)!=1)
// up pixel
{
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int,int>(curY-1, curX));
mask.at<uchar>(curY-1,curX)=1;
}
}
if(curY+1 <= rows-1)
{
if(_lableImg.at<int>(curY+1,curX) == 255&&mask.at<uchar>(curY+1,curX)!=1)
//down pixel
{
neighborPixels.push(std::pair<int,int>(curY+1,curX));
mask.at<uchar>(curY+1,curX)=1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
//---------------------------------【颜色标记程序】-----------------------------------
//彩色显示
cv::Scalar GetRandomColor()
{
uchar r = 255 * (rand()/(1.0 + RAND_MAX));
uchar g = 255 * (rand()/(1.0 + RAND_MAX));
uchar b = 255 * (rand()/(1.0 + RAND_MAX));
return cv::Scalar(b,g,r);
}
void LabelColor(const cv::Mat& labelImg, cv::Mat& colorLabelImg)
{
int num = 0;
if (labelImg.empty() ||
labelImg.type() != CV_32SC1)
{
return;
}
std::map<int, cv::Scalar> colors;
int rows = labelImg.rows;
int cols = labelImg.cols;
colorLabelImg.release();
colorLabelImg.create(rows, cols, CV_8UC3);
colorLabelImg = cv::Scalar::all(0);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
const int* data_src = (int*)labelImg.ptr<int>(i);
uchar* data_dst = colorLabelImg.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
int pixelValue = data_src[j];
if (pixelValue > 1)
{
if (colors.count(pixelValue) <= 0)
{
colors[pixelValue] = GetRandomColor();
num++;
}
cv::Scalar color = colors[pixelValue];
*data_dst++ = color[0];
*data_dst++ = color[1];
*data_dst++ = color[2];
}
else
{
data_dst++;
data_dst++;
data_dst++;
}
}
}
printf("color num : %d \n", num );
}
//------------------------------------------【测试主程序】-------------------------------------
int main()
{
cv::Mat binImage = cv::imread("ltc2.jpg", 0);
//cv::threshold(binImage, binImage, 50, 1, CV_THRESH_BINARY);
cv::Mat labelImg;
double time;
time= getTickCount();
//对应四种方法,需要哪一种,则调用哪一种
//Two_PassOld(binImage, labelImg);
//Two_PassNew(binImage, labelImg);
//SeedFillOld(binImage, labelImg);
//SeedFillNew(binImage, labelImg);
time = 1000*((double)getTickCount() - time)/getTickFrequency();
cout<<std::fixed<<time<<"ms"<<endl;
//彩色显示
cv::Mat colorLabelImg;
LabelColor(labelImg, colorLabelImg);
cv::imshow("colorImg", colorLabelImg);
//灰度显示
cv::Mat grayImg;
labelImg *= 10;
labelImg.convertTo(grayImg, CV_8UC1);
cv::imshow("labelImg", grayImg);
double minval, maxval;
minMaxLoc(labelImg,&minval,&maxval);
cout<<"minval"<<minval<<endl;
cout<<"maxval"<<maxval<<endl;
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
上面是一个综合代码示例,有四种方法,但是有些缺陷,表述如下:
老的两步法:速度很慢
新的两步法:速度很快 (Debug下。快了至少有10倍,与图片的大小有关系)
种子填充法无论是新的还是老的都有缺陷
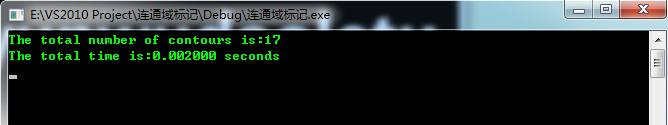
对于图一:
可以看一下几种方法的运行结果:
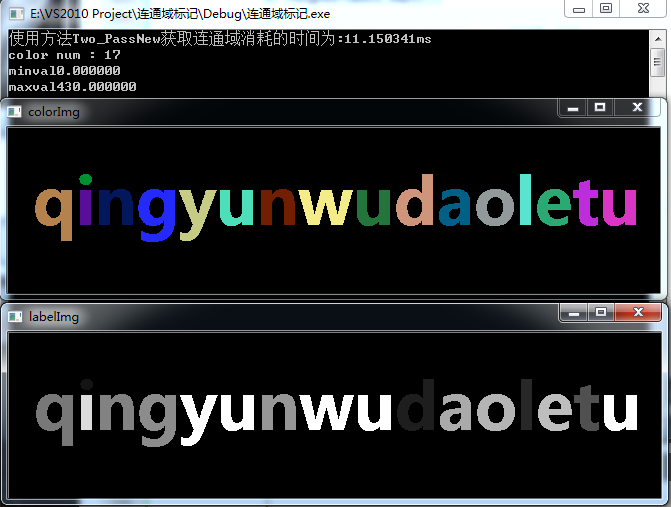
1.two_passOld
可以很明显的看出新版方法快很多
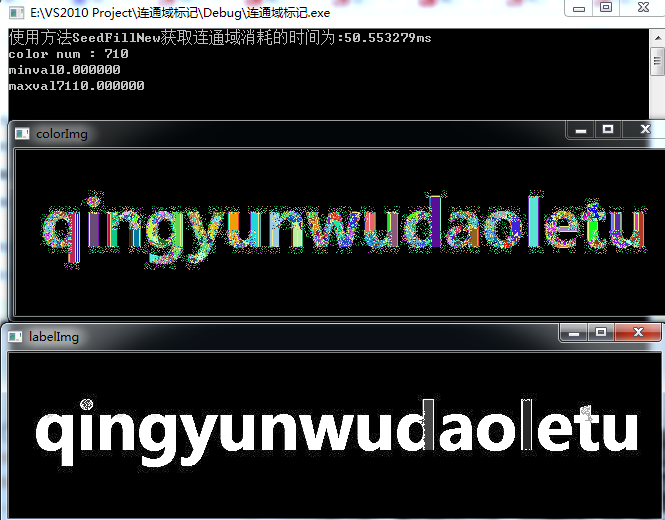
其他方法得到的图片类似,注意新版种子填充法并不能得到这样的结果,有问题。
使用新版种子填充法则需要注意屏蔽阈值化那一句语句
对于这样的图片
对于这样一张测试图:
侧视图经过matlab 的bwlabel函数测是,在4连通情况下有3087个连通域,8连通下有2471个连通域。
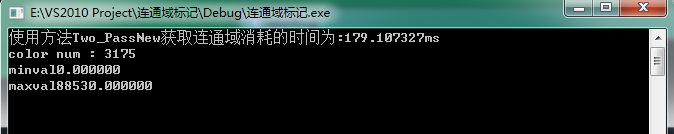
对于新版与旧版的两步法,没啥区别,就是时间上有很大差别
使用老版的种子填充法会出现边界问题,使用新版种子填充法则需要注意屏蔽阈值化那一句语句
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cv.h>
#include <highgui.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <Windows.h>
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
SetConsoleTextAttribute(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE),FOREGROUND_INTENSITY | FOREGROUND_GREEN);
IplImage* src = cvLoadImage("test.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
IplImage* dst = cvCreateImage(cvGetSize(src), 8, 3);
CvMemStorage* storage = cvCreateMemStorage(0);
CvSeq* contour = 0;
cvThreshold(src, src,120, 255, CV_THRESH_BINARY); // 二值化
cvNamedWindow("Source", 1);
cvShowImage("Source", src);
// 提取轮廓
clock_t start, finish;
start = clock();
int contour_num = cvFindContours(src, storage, &contour, sizeof(CvContour), CV_RETR_CCOMP, CV_CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE);
cvZero(dst); // 清空数组
CvSeq *_contour = contour;
double maxarea = 0;
double minarea = 100;
int m = 0;
for( ; contour != 0; contour = contour->h_next )
{
double tmparea = fabs(cvContourArea(contour));
if(tmparea < minarea)
{
cvSeqRemove(contour, 0); // 删除面积小于设定值的轮廓
continue;
}
CvRect aRect = cvBoundingRect( contour, 0 );
if ((aRect.width/aRect.height)<1)
{
cvSeqRemove(contour, 0); //删除宽高比例小于设定值的轮廓
continue;
}
if(tmparea > maxarea)
{
maxarea = tmparea;
}
m++;
// 创建一个色彩值
CvScalar color = CV_RGB( 0, 255, 255 );
//max_level 绘制轮廓的最大等级。如果等级为0,绘制单独的轮廓。如果为1,绘制轮廓及在其后的相同的级别下轮廓
//如果值为2,所有的轮廓。如果等级为2,绘制所有同级轮廓及所有低一级轮廓,诸此种种
//如果值为负数,函数不绘制同级轮廓,但会升序绘制直到级别为abs(max_level)-1的子轮廓
cvDrawContours(dst, contour, color, color, -1, 1, 8); //绘制外部和内部的轮廓
}
contour = _contour;
int count = 0;
for(; contour != 0; contour = contour->h_next)
{
count++;
double tmparea = fabs(cvContourArea(contour));
if (tmparea == maxarea)
{
CvScalar color = CV_RGB( 255, 0, 0);
cvDrawContours(dst, contour, color, color, -1, 1, 8);
}
}
finish = clock();
double duration;
duration = (double)(finish - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("The total number of contours is:%d \n", count);
printf("The total time is:%f seconds\n", duration);
cvNamedWindow("Components", 1);
cvShowImage("Components", dst);
cvWaitKey(0);
cvDestroyWindow("Source");
cvReleaseImage(&src);
cvDestroyWindow("Components");
cvReleaseImage(&dst);
return 0;
} 
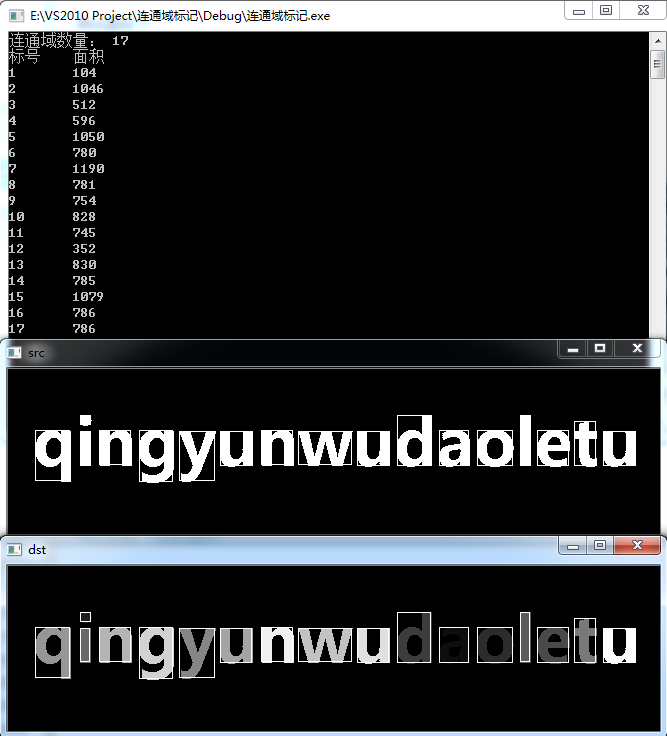
第二张比较复杂的侧视图八连通,时间如下:

#include <opencv2\opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
typedef struct _Feather
{
int label; // 连通域的label值
int area; // 连通域的面积
Rect boundingbox; // 连通域的外接矩形框
} Feather;
/*
Input:
src: 待检测连通域的二值化图像
Output:
dst: 标记后的图像
featherList: 连通域特征的清单
return:
连通域数量。
*/
int bwLabel(Mat & src, Mat & dst, vector<Feather> & featherList)
{
int rows = src.rows;
int cols = src.cols;
int labelValue = 0;
Point seed, neighbor;
stack<Point> pointStack; // 堆栈
int area = 0; // 用于计算连通域的面积
int leftBoundary = 0; // 连通域的左边界,即外接最小矩形的左边框,横坐标值,依此类推
int rightBoundary = 0;
int topBoundary = 0;
int bottomBoundary = 0;
Rect box; // 外接矩形框
Feather feather;
featherList.clear(); // 清除数组
dst.release();
dst = src.clone();
for( int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
uchar *pRow = dst.ptr<uchar>(i);
for( int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
if(pRow[j] == 255)
{
area = 0;
labelValue++; // labelValue最大为254,最小为1.
seed = Point(j, i); // Point(横坐标,纵坐标)
dst.at<uchar>(seed) = labelValue;
pointStack.push(seed);
area++;
leftBoundary = seed.x;
rightBoundary = seed.x;
topBoundary = seed.y;
bottomBoundary = seed.y;
while(!pointStack.empty())
{
neighbor = Point(seed.x+1, seed.y);
if((seed.x != (cols-1)) && (dst.at<uchar>(neighbor) == 255))
{
dst.at<uchar>(neighbor) = labelValue;
pointStack.push(neighbor);
area++;
if(rightBoundary < neighbor.x)
rightBoundary = neighbor.x;
}
neighbor = Point(seed.x, seed.y+1);
if((seed.y != (rows-1)) && (dst.at<uchar>(neighbor) == 255))
{
dst.at<uchar>(neighbor) = labelValue;
pointStack.push(neighbor);
area++;
if(bottomBoundary < neighbor.y)
bottomBoundary = neighbor.y;
}
neighbor = Point(seed.x-1, seed.y);
if((seed.x != 0) && (dst.at<uchar>(neighbor) == 255))
{
dst.at<uchar>(neighbor) = labelValue;
pointStack.push(neighbor);
area++;
if(leftBoundary > neighbor.x)
leftBoundary = neighbor.x;
}
neighbor = Point(seed.x, seed.y-1);
if((seed.y != 0) && (dst.at<uchar>(neighbor) == 255))
{
dst.at<uchar>(neighbor) = labelValue;
pointStack.push(neighbor);
area++;
if(topBoundary > neighbor.y)
topBoundary = neighbor.y;
}
seed = pointStack.top();
pointStack.pop();
}
box = Rect(leftBoundary, topBoundary, rightBoundary-leftBoundary, bottomBoundary-topBoundary);
rectangle(src, box, 255);
feather.area = area;
feather.boundingbox = box;
feather.label = labelValue;
featherList.push_back(feather);
}
}
}
return labelValue;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Mat src(imread("ltc2.jpg", 0));
if(src.empty())
exit(-1);
threshold(src, src, 127, 255, THRESH_BINARY); // 二值化图像
vector<Feather> featherList; // 存放连通域特征
Mat dst;
cout << "连通域数量: " << bwLabel(src, dst, featherList) << endl;
// 为了方便观察,可以将label“放大”
for( int i = 0; i < dst.rows; i++)
{
uchar *p = dst.ptr<uchar>(i);
for( int j = 0; j < dst.cols; j++)
{
p[j] = 30*p[j];
}
}
cout << "标号" << "\t" << "面积" << endl;
for(vector<Feather>::iterator it = featherList.begin(); it < featherList.end(); it++)
{
cout << it->label << "\t" << it->area << endl;
rectangle(dst, it->boundingbox, 255);
}
imshow("src", src);
imshow("dst", dst);
waitKey();
destroyAllWindows();
system("pause");
return 0;
}

































 4645
4645

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








