pytorch Resnet代码实现
本文只介绍resnet的代码实现,需要对resnet有基础的了解。代码参考pytorch官方实现,删除了一些非必要的判断条件,看起来更加简洁。z再次基础上,可以根据需要加入自己需要调整的参数,比如dilation,norm_layer等.
参考
SOURCE CODE FOR TORCHVISION.MODELS.RESNET
2D ResNet50 网络结构搭建(PyTorch)
MedicalNet
网络结构


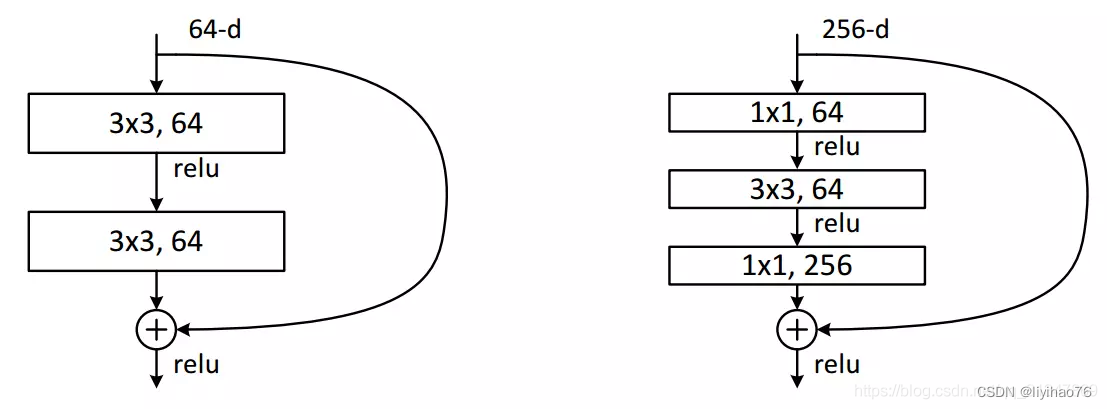
左图:BasicBlock结构,用于resnet18/34
右图: Bottleneck结构,用于resnet50/101/152
2D ResNet代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
首先是两种block的代码
#18/34
class BasicBlock_2d(nn.Module):
expansion = 1 #每一个conv的卷积核个数的倍数
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None):#downsample对应虚线残差结构
super(BasicBlock_2d, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)#BN处理
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) # 尽量使用inplace操作flag,节省显存
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x #捷径上的输出值,为了保证原始输入与卷积后的输出层叠加时维度相同
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
#50,101,152
class Bottleneck_2d(nn.Module):
'''
:param in_channel: 输入block的之前的通道数
:param out_channel: 在block中间处理的时候的通道数
out_channel*self.extention:输出的维度
:param stride:卷积步长
:param downsample:在_make_layer函数中赋值,在resnet每层链接的第一个卷积层需要改变通道 如resnet50 conv2_x输出的256降低为128 conv3_x的输入
'''
expansion = 4 #4倍,类变量,可通过类名修改
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(Bottleneck_2d, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # squeeze channels
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
# -----------------------------------------
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, bias=False, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
# -----------------------------------------
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel*self.expansion,#输出*4
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # unsqueeze channels
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel*self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
out += identity # 残差连接
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet2d(nn.Module):
"""
__init__
block: 堆叠的基本模块
block_num: 基本模块堆叠个数,是一个list,对于resnet50=[3,4,6,3]
num_classes: 全连接之后的分类特征维度
_make_layer
block: 堆叠的基本模块
channel: 每个stage中堆叠模块的第一个卷积的卷积核个数,对resnet50分别是:64,128,256,512
block_num: 当期stage堆叠block个数
stride: 默认卷积步长
"""
def __init__(self, block, blocks_num, num_classes=1000, include_top=True):#block残差结构 include_top为了之后搭建更加复杂的网络
super(ResNet2d, self).__init__()
self.include_top = include_top
self.in_channel = 64 # conv1的输出维度
self.conv1_2d = nn.Conv2d(3, self.in_channel, kernel_size=7, stride=2,
padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1_2d = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.in_channel)
self.relu_2d = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool_2d = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1) # H/2,W/2。C不变
self.layer1_2d = self._make_layer(block, 64, blocks_num[0]) # H,W不变。downsample控制的shortcut,out_channel=64x4=256
self.layer2_2d = self._make_layer(block, 128, blocks_num[1], stride=2) # H/2, W/2。downsample控制的shortcut,out_channel=128x4=512
self.layer3_2d = self._make_layer(block, 256, blocks_num[2], stride=2) # H/2, W/2。downsample控制的shortcut,out_channel=256x4=1024
self.layer4_2d = self._make_layer(block, 512, blocks_num[3], stride=2) # H/2, W/2。downsample控制的shortcut,out_channel=512x4=2048
if self.include_top:
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # output size = (1, 1)自适应
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():# 权重初始化
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
elif isinstance(m, (nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.GroupNorm)):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def _make_layer(self, block, channel, block_num, stride=1):
"""
第一个输入参数 block 选择要使用的模块是 BasicBlock 还是 Bottleneck 类,
第二个输入参数 channel 是该模块的输出通道数,
第三个输入参数 block_num 是每个 blocks 中包含多少个 residual 子结构。
"""
downsample = None # 用于控制shorcut路的
if stride != 1 or self.in_channel != channel * block.expansion:
# 对resnet50:conv2中特征图尺寸H,W不需要下采样/2,但是通道数x4,
# 因此shortcut通道数也需要x4。对其余conv3,4,5,既要特征图尺寸H,W/2,又要shortcut维度x4
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channel, channel * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
# out_channels决定输出通道数x4,stride决定特征图尺寸H,W/2
nn.BatchNorm2d(channel * block.expansion))
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.in_channel, channel, downsample=downsample, stride=stride)) # 定义convi_x中的第一个残差块,只有第一个需要设置downsample和stride
self.in_channel = channel * block.expansion # 在下一次调用_make_layer函数的时候,self.in_channel已经x4
for _ in range(1, block_num): # 通过循环堆叠其余残差块(堆叠了剩余的block_num-1个)
layers.append(block(self.in_channel, channel))
return nn.Sequential(*layers) # '*'的作用是将list转换为非关键字参数传入
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1_2d(x)
x = self.bn1_2d(x)
x = self.relu_2d(x)
x = self.maxpool_2d(x)
x = self.layer1_2d(x)
x = self.layer2_2d(x)
x = self.layer3_2d(x)
x = self.layer4_2d(x)
if self.include_top:
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
使用resnet50进行3分类
resnet50_2d = ResNet2d(Bottleneck_2d, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=3,include_top=True)
x=torch.randn(1,3,448,448)
X=resnet50_2d(x)
print(X.shape)
# torch.Size([1, 3])
网络结构可视化
import netron
import torch.onnx
modelData ='demo.onnx' # 定义模型数据保存的路径
torch.onnx.export(resnet50_2d, x, modelData) # 将 pytorch 模型以 onnx 格式导出并保存
onnx.save(onnx.shape_inference.infer_shapes(onnx.load(modelData)), modelData)
netron.start(modelData) # 输出网络结构
2D ResNet的backbones
resnet18_2d = ResNet2d(BasicBlock_2d, [2, 2, 2, 2], include_top=False)
resnet34_2d = ResNet2d(BasicBlock_2d, [3, 4, 6, 3], include_top=False)
resnet50_2d = ResNet2d(Bottleneck_2d, [3, 4, 6, 3], include_top=False)
resnet101_2d = ResNet2d(Bottleneck_2d, [3, 4, 23, 3], include_top=False)
resnet152_2d = ResNet2d(Bottleneck_2d, [3, 8, 36, 3], include_top=False)
3D ResNet代码
3D ResNet的实现参考腾讯的MedicalNet: Med3D: Transfer Learning for 3D Medical Image Analysis.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
import math
from functools import partial
def conv3x3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, dilation=1):
# 3x3x3 convolution with padding
return nn.Conv3d(
in_planes,
out_planes,
kernel_size=3,
dilation=dilation,
stride=stride,
padding=dilation,
bias=False)
def downsample_basic_block(x, planes, stride, no_cuda=False):
out = F.avg_pool3d(x, kernel_size=1, stride=stride)
zero_pads = torch.Tensor(
out.size(0), planes - out.size(1), out.size(2), out.size(3),
out.size(4)).zero_()
if not no_cuda:
if isinstance(out.data, torch.cuda.FloatTensor):
zero_pads = zero_pads.cuda()
out = Variable(torch.cat([out.data, zero_pads], dim=1))
return out
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, dilation=1, downsample=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = conv3x3x3(inplanes, planes, stride=stride, dilation=dilation)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm3d(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3x3(planes, planes, dilation=dilation)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm3d(planes)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
self.dilation = dilation
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, dilation=1, downsample=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv3d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm3d(planes)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv3d(
planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, dilation=dilation, padding=dilation, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm3d(planes)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv3d(planes, planes * 4, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm3d(planes * 4)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
self.dilation = dilation
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet_3d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
block,
layers,
num_classes=1000,
shortcut_type='B',
no_cuda = False,
include_top=True):
super(ResNet_3d, self).__init__()
self.inplanes = 64
self.no_cuda = no_cuda
self.include_top = include_top
self.conv1 = nn.Conv3d(
1,
64,
kernel_size=7,
stride=(2, 2, 2),
padding=(3, 3, 3),
bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm3d(64)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool3d(kernel_size=(3, 3, 3), stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0], shortcut_type)
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(
block, 128, layers[1], shortcut_type, stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(
block, 256, layers[2], shortcut_type, stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(
block, 512, layers[3], shortcut_type, stride=2)
if self.include_top:
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool3d((1, 1, 1)) # output size = (1, 1)自适应
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv3d):
m.weight = nn.init.kaiming_normal(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm3d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, shortcut_type, stride=1, dilation=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
if shortcut_type == 'A':
downsample = partial(
downsample_basic_block,
planes=planes * block.expansion,
stride=stride,
no_cuda=self.no_cuda)
else:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3d(
self.inplanes,
planes * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1,
stride=stride,
bias=False), nn.BatchNorm3d(planes * block.expansion))
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride=stride, downsample=downsample))
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for i in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
if self.include_top:
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
使用3D Resnet34进行3分类
resnet34_3d = ResNet_3d(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3],shortcut_type='A',no_cuda=False,num_classes=3,include_top=True)
x=torch.randn(1,1,256,224,164)
X=resnet34_3d(x)
print(X.shape)
# torch.Size([1, 3])
使用3D Resnet50进行3分类
resnet50_3d = ResNet_3d(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3],shortcut_type='B',no_cuda=False,num_classes=3,include_top=True)
x=torch.randn(1,1,256,224,164)
X=resnet50_3d(x)
print(X.shape)
# torch.Size([1, 3])
可视化
import netron
import torch.onnx
modelData ='best.onnx' # 定义模型数据保存的路径
torch.onnx.export(resnet50_3d, x, modelData) # 将 pytorch 模型以 onnx 格式导出并保存
onnx.save(onnx.shape_inference.infer_shapes(onnx.load(modelData)), modelData)
netron.start(modelData) # 输出网络结构








 本文介绍了如何使用PyTorch实现2DResNet和3DResNet的网络结构,包括BasicBlock和Bottleneck结构,并提供了对应的代码实现。2DResNet适用于图像识别,3DResNet适用于3D医学图像分析。网络结构包括卷积、批量归一化、激活函数和残差连接等关键部分,并提供了网络结构的可视化方法。
本文介绍了如何使用PyTorch实现2DResNet和3DResNet的网络结构,包括BasicBlock和Bottleneck结构,并提供了对应的代码实现。2DResNet适用于图像识别,3DResNet适用于3D医学图像分析。网络结构包括卷积、批量归一化、激活函数和残差连接等关键部分,并提供了网络结构的可视化方法。
















 1234
1234

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








