网络基本原理

ISO:国际标准化组织
OSI:开放系统互联结构模型
ISO/OSI模型把网络分成了若干层,每层都实现特定的功能。
ISO/OSI模型把网络表示成竖直的线,模型中的每一层次至少包含有一个协议,所以也可以说是模型中的协议是逐个叠放的。协议栈是个由竖直的层和对方的协议抽象而来。
OSI不是一个实际的物理模型,而是一个将网络协议规范化了的逻辑参考模型
网络通讯原理

TCP编程
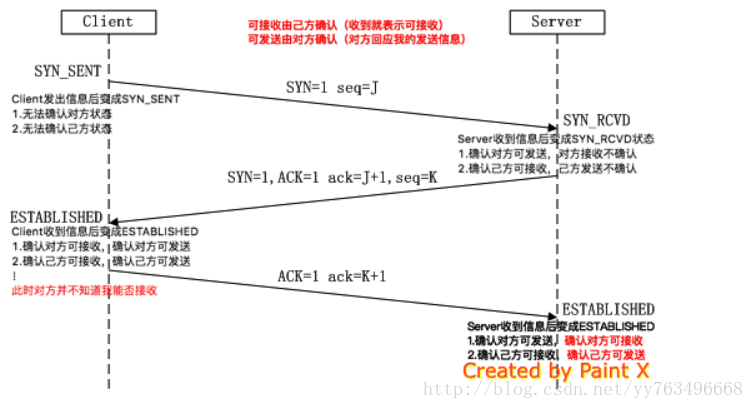
TCP协议建立连接的简图

客户端和服务器简历连接的过程
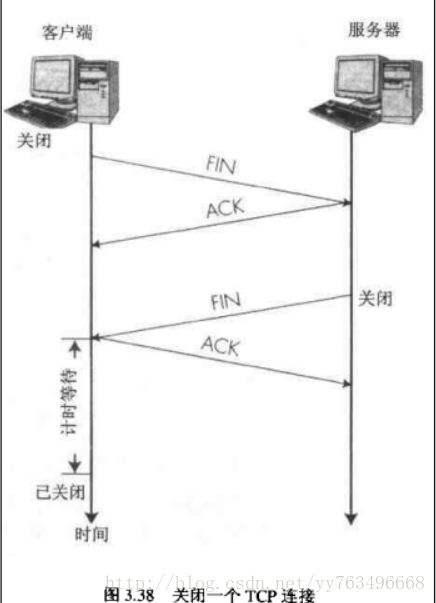
关闭TCP的四次挥手
服务端:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.IO;
using System.Threading;
namespace TcpServer
{
class Program
{
static TcpListener server;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IPAddress ip = IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1");
server = new TcpListener(ip,8111);
server.Start();
Thread th = new Thread(ReciveMsg);
th.Start();
}
static void ReciveMsg()
{
try
{
while (true)
{
TcpClient client = server.AcceptTcpClient();
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(client.GetStream());
string str = sr.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("收到来自客户端的信息是:" + str);
}
}
catch (Exception)
{
}
}
static void Send(object o)
{
TcpClient client = o as TcpClient;
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(client.GetStream());
string str = Console.ReadLine();
if (str!=null)
{
sw.WriteLine(str);
}
sw.Flush();
sw.Close();
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
客户端:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.IO;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Threading;
namespace TcpClientDemo
{
class Program
{
static TcpClient client;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
while (true)
{
client = new TcpClient("127.0.0.1", 8111);
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(client.GetStream());
string str = Console.ReadLine();
sw.WriteLine(str);
sw.Flush();
sw.Close();
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void RecMsg()
{
try
{
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(client.GetStream());
string str = string.Empty;
if ((str = sr.ReadLine())!=null)
{
Console.WriteLine("来自服务器端的信息是:" + str);
}
sr.Close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
UDP编程

- UTP简介
虽然和TCP一样也构建与IP之上,但UDP作为一种简单的、面向数据报的无连接协议,提供的是不一定可靠的传输服务。所谓的“无连接”是指在正式通信前不必与对方先建立连接,不管对方状态如何都直接发送过去。这与发送机短信非常的相似,只要发往对方的手机号就可以了,不用考虑对方手机状态。 - UDP原理
UDP将网络数据流量压缩成数据报的形式,每一个数据报用8个字节描述报头信息,剩余字节包含具体的传输数据,UDP报头很短,相对于TCP的20字节信息包含的额外开销很小,报头由4个域组成,其中每个域各占用2个字节,具体为元端口,目的端口,用户数据报长和检验和。
UDP协议使用端口号为不同的应用保留其各自的数据传输通道。UDP和TCP协议正是采用这一机制对同一时刻多种应用同时发送和接收数据实现支持。数据发送方(客户端或服务器)将UDP数据报通过源端口发送出去,而数据接收方则通过目标端口接收数据。
有的网络应用智能使用预先为其预留或注册的静态端口(如HTTP用80端口,FTP使用21端口)而另外一些网络应用则可以使用未被注册的动态端口。因为UDP报头使用两个字节(1个字节8位)存放端口号,所以端口号的有效范围从0到65535.一般来说,大于49151的端口号都代表动态端口。
UDP和TCP的区别
UDP和TCP的主要区别在是二者在如何实现信息的可靠传递方面存在不同,具体表现为以下几点:
- UDP可靠性不如TCP
TCP包含了专门的传递保证机制,当数据接收方收到发送方传来的信息时,会自动向发送方发出确认消息;发送方只有在接收到该确认消息之后才继续传递其他消息,否则将一直等待,直到收到确认信息为止。与TCP不同,UDP并不提供数据传达的保证机制。如果在发送方到接收方的传递过程中出现数据包的丢失,协议本身并不能做出任何检测或提示。因此人们把UDP称为不可靠的传输协议。 - UDP不能保证有序传输
UDP不能确保数据的发送和接收顺序。对于突发性的数据报,有可能会乱序。不过,事实上UDP的这种乱序基本上很少出现,通常只会在网络非常拥挤的情况下才有可能发生。
UDP的优势
说了这么多UDP的缺点,那使用它还有什么价值么?
从应用角度考虑,UDP相比TCP的优势,主要表现在以下几个方面。
-
UDP速度比TCP要快
-
UDP有消息边界
-
UDP可以一对多传输
服务端:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Net;
namespace UDPServer
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
UdpClient udpRec = new UdpClient(9999);
try
{
while (true)
{
IPEndPoint remoteIpEndPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Any, 0);
byte[] recBytes = udpRec.Receive(ref remoteIpEndPoint);
string returnData = Encoding.Default.GetString(recBytes);
Console.WriteLine("接收到的数据是:" + returnData);
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
finally
{
udpRec.Close();
}
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
客户端:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
namespace UDPClientDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
UdpClient client = new UdpClient("127.0.0.1", 9999);
try
{
while (true)
{
string str = Console.ReadLine();
byte[] sendBytes = Encoding.Default.GetBytes(str);
client.Send(sendBytes, sendBytes.Length);
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
finally
{
client.Close();
}
Console.Read();
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
Socket编程
Scoket TCP编程的流程图

服务端:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Net;
using System.Threading;
namespace NetWork
{
class Program
{
static Socket severSocket;
static Thread recThread;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
severSocket = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
IPAddress ip = IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1");
IPEndPoint ipPoint = new IPEndPoint(ip, 9999);
try
{
severSocket.Bind(ipPoint);
severSocket.Listen(20);
recThread = new Thread(Listen);
recThread.Start();
}
catch (SocketException se)
{
Console.WriteLine(se.Message);
}
}
static void Listen()
{
while (true)
{
Socket client = severSocket.Accept();
IPEndPoint ipEndPoint = (IPEndPoint)client.RemoteEndPoint;
string info = "客户端的ip地址是:"+ipEndPoint.Address + " 客户端的端口号:" + ipEndPoint.Port;
Thread recThread = new Thread(RecMsg);
recThread.IsBackground = true;
recThread.Start(client);
}
}
static void RecMsg(object o)
{
try
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
Socket client = o as Socket;
IPEndPoint ip = client.RemoteEndPoint as IPEndPoint;
while (true)
{
int len = client.Receive(buffer);
if (len<=0)
{
return;
}
string info = Encoding.Default.GetString(buffer,0,len);
Console.WriteLine("收到来自客户端"+ip.Address+" "+ip.Port+"的信息:"+info);
Thread sendThread = new Thread(Send);
sendThread.IsBackground = true;
sendThread.Start(client);
}
}
catch (SocketException se)
{
Console.WriteLine(se.Message);
}
}
static void Send(object o)
{
byte[] buffer = Encoding.Default.GetBytes(Console.ReadLine());
Socket sc = o as Socket;
try
{
sc.Send(buffer);
}
catch (SocketException se)
{
Console.WriteLine(se);
}
}
~Program()
{
severSocket.Disconnect(false);
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
客户端:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Threading;
namespace NetWorkClient
{
class Program
{
static Socket clientSocket;
static Thread recThread;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
clientSocket = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
IPAddress ipa = IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1");
IPEndPoint ipEndpoint = new IPEndPoint(ipa,9999);
clientSocket.Connect(ipEndpoint);
recThread = new Thread(RecMsg);
recThread.IsBackground = true;
recThread.Start();
while (true)
{
Send();
}
}
static void RecMsg()
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
while (true)
{
try
{
int len = clientSocket.Receive(buffer);
if (len<=0)
{
return;
}
string info = Encoding.Default.GetString(buffer,0,len);
Console.WriteLine("收到来自服务端的数据:"+info);
}
catch (SocketException se)
{
Console.WriteLine(se);
}
}
}
static void Send()
{
byte[] byteArr = Encoding.Default.GetBytes(Console.ReadLine());
try
{
clientSocket.Send(byteArr);
}
catch (SocketException se)
{
Console.WriteLine(se);
}
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
Scoket UDP编程的流程图






























 230
230











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








