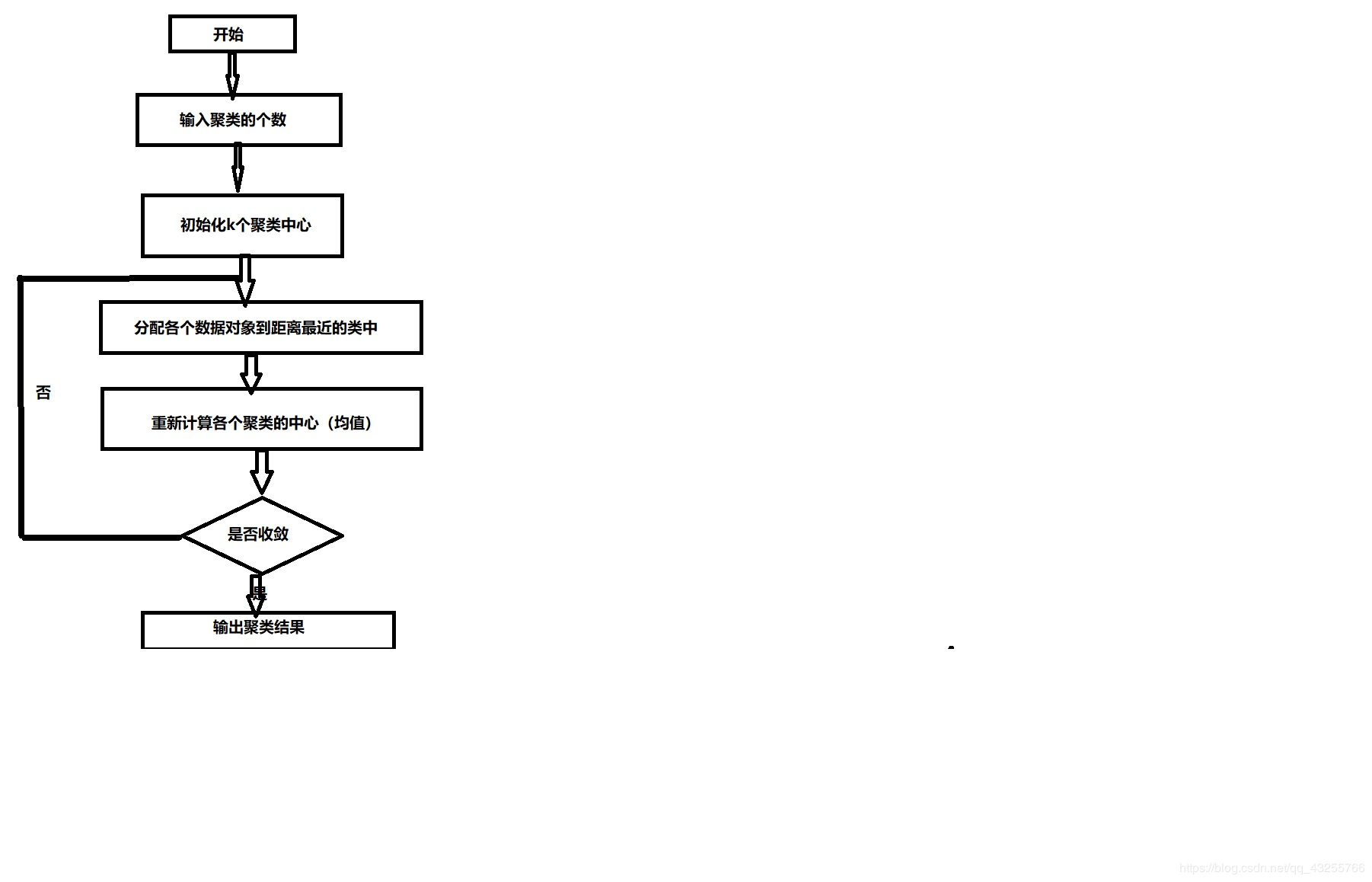
1 principle
- There are several points.
- Initialize K center randomly.(K is the number of kinds you want to classify)
- Calculate distance between each elements and these centers. The element belongs to a center which distance is the smallest. In other words, the element is the most similar to this given center.
- Calculate the new centers based on Step 3.
- If the new centers are the same as the original centers, we can draw a conculsion that K-means algorithm is successful.
Using a flow chart to show above principle:
2 code(based on tensorflow)
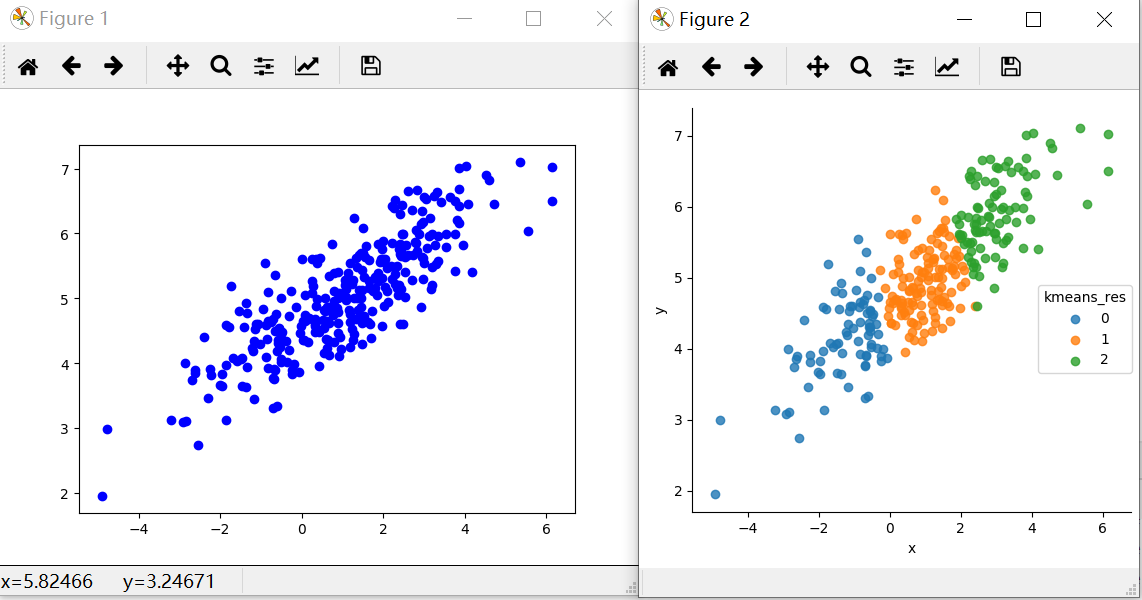
There are 300 random points, and this program will divided these points into 3 parts.
Then, use matplotlib to show the original points and the result after classification.
import numpy as np
from numpy.linalg import cholesky
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from random import shuffle
from numpy import array
def KMeansCluster(vectors, noofclusters):
"""
K-Means Clustering using TensorFlow.
`vertors`应该是一个n*k的二维的NumPy的数组,其中n代表着K维向量的数目
'noofclusters' 代表了待分的集群的数目,是一个整型值
"""
noofclusters = int(noofclusters)
assert noofclusters < len(vectors)
# 找出每个向量的维度
dim = len(vectors[0])
# 辅助随机地从可得的向量中选取中心点
vector_indices = list(range(len(vectors)))
shuffle(vector_indices)
# 计算图
# 我们创建了一个默认的计算流的图用于整个算法中,这样就保证了当函数被多次调用时,默认的图并不会被从上一次调用时留下的未使用的OPS或者Variables挤满
graph = tf.Graph()
with graph.as_default():
# 计算的会话
sess = tf.Session()
##构建基本的计算的元素
##首先我们需要保证每个中心点都会存在一个Variable矩阵
##从现有的点集合中抽取出一部分作为默认的中心点
centroids = [tf.Variable((vectors[vector_indices[i]]))for i in range(noofclusters)]
##创建一个placeholder用于存放各个中心点可能的分类的情况
centroid_value = tf.placeholder("float64", [dim])
cent_assigns = []
for centroid in centroids:
cent_assigns.append(tf.assign(centroid, centroid_value))
##对于每个独立向量的分属的类别设置为默认值0
assignments = [tf.Variable(0) for i in range(len(vectors))]
##这些节点在后续的操作中会被分配到合适的值
assignment_value = tf.placeholder("int32")
cluster_assigns = []
for assignment in assignments:
cluster_assigns.append(tf.assign(assignment,assignment_value))
##下面创建用于计算平均值的操作节点
# 输入的placeholder
mean_input = tf.placeholder("float", [None, dim])
# 节点/OP接受输入,并且计算0维度的平均值,譬如输入的向量列表
mean_op = tf.reduce_mean(mean_input, 0)
##用于计算欧几里得距离的节点
v1 = tf.placeholder("float", [dim])
v2 = tf.placeholder("float", [dim])
euclid_dist = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow(tf.subtract(v1, v2), 2)))
##这个OP会决定应该将向量归属到哪个节点
##基于向量到中心点的欧几里得距离
# Placeholder for input
centroid_distances = tf.placeholder("float", [noofclusters])
cluster_assignment = tf.argmin(centroid_distances, 0)
##初始化所有的状态值
##这会帮助初始化图中定义的所有Variables。Variable-initializer应该定
##义在所有的Variables被构造之后,这样所有的Variables才会被纳入初始化
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 初始化所有的变量
sess.run(init_op)
#集群遍历
#接下来在K-Means聚类迭代中使用最大期望算法。为了简单起见,只让它执行固定的次数,而不设置一个终止条件
noofiterations = 20
for iteration_n in range(noofiterations):
#期望步骤
#基于上次迭代后算出的中心点的未知
#the _expected_ centroid assignments.
#首先遍历所有的向量
for vector_n in range(len(vectors)):
vect = vectors[vector_n]
# 计算给定向量与分配的中心节点之间的欧几里得距离
distances = [sess.run(euclid_dist, feed_dict={v1: vect, v2: sess.run(centroid)})for centroid in centroids]
# 下面可以使用集群分配操作,将上述的距离当做输入
assignment = sess.run(cluster_assignment, feed_dict={centroid_distances: distances})
# 接下来为每个向量分配合适的值
sess.run(cluster_assigns[vector_n], feed_dict={assignment_value: assignment})
##最大化的步骤
# 基于上述的期望步骤,计算每个新的中心点的距离从而使集群内的平方和最小
for cluster_n in range(noofclusters):
# 收集所有分配给该集群的向量
assigned_vects = [vectors[i] for i in range(len(vectors))if sess.run(assignments[i]) == cluster_n]
# 计算新的集群中心点
new_location = sess.run(mean_op, feed_dict={mean_input: array(assigned_vects)})
# 为每个向量分配合适的中心点
sess.run(cent_assigns[cluster_n], feed_dict={centroid_value: new_location})
# 返回中心节点和分组
centroids = sess.run(centroids)
assignments = sess.run(assignments)
return centroids, assignments
############生成测试数据###############
sampleNo = 300 # 数据数量
# 二维正态分布
mu = np.array([[1, 5]])
Sigma = np.array([[1, 0.5], [1.5, 3]])
R = cholesky(Sigma)
srcdata = np.dot(np.random.randn(sampleNo, 2), R) + mu
plt.plot(srcdata[:, 0], srcdata[:, 1], 'bo')
############kmeans算法计算###############
k = 3
center, result = KMeansCluster(srcdata, k)
print(center)
############利用seaborn画图###############
res = {"x": [], "y": [], "kmeans_res": []}
for i in range(len(result)):
res["x"].append(srcdata[i][0])
res["y"].append(srcdata[i][1])
res["kmeans_res"].append(result[i])
pd_res = pd.DataFrame(res)
sns.lmplot("x", "y", data=pd_res, fit_reg=False, size=5, hue="kmeans_res")
plt.show()
3 result
reference:
链接: Tensorflow快速入门1–实现K-Means聚类算法.





















 7530
7530











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








