OpenCV中最小外接矩形
-
说明
brief Finds a rotated rectangle of the minimum area enclosing the input 2D point set.
查找包含输入二维点集的最小区域的旋转矩形。该函数计算并返回指定点集的最小区域边界矩形(可能已旋转)。开发人员应记住,当数据接近包含Mat元素的边界时,返回的RotatedRect可以包含负索引。

-
声明
RotatedRect minAreaRect( InputArray points ); -
参数
points: 输入的存储在std::vector<>或Mat中的二维向量点。返回值: RotatedRect类矩形对象,外接旋转矩形主要成员有:center、size、angle、points
应用
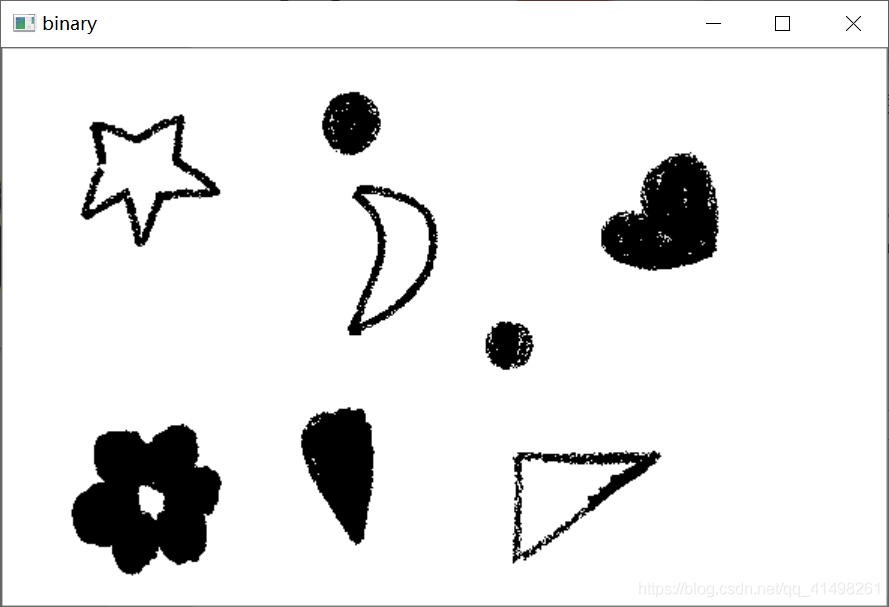
- 应用1——画出最小外接矩形
void minBinaryImgAreaRect(Mat &src) {
//1.查找轮廓
//1.1转化成灰度图像
Mat dst, gray, binary;
imshow("src", src);
cvtColor(src, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
imshow("gray", gray);
//1.2转化成二值图像
threshold(gray, binary, 100, 255, THRESH_BINARY | THRESH_OTSU);
imshow("binary", binary);
//1.3 查找所有轮廓
vector<vector<Point>> contours;
findContours(binary, contours, RETR_LIST, CHAIN_APPROX_NONE);
//2.确定最小外接矩形
//2.1 定义RotatedRect类型的vector容器rotatedRects存放最小外接矩形,初始化大小为轮廓的个数。
vector<RotatedRect> rotatedRects(contours.size());
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
int w = 0;
int h = 0;
//2.2遍历每一个轮廓
for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++)
{
//2.3 由轮廓(点集)确定出最小外接矩形
rotatedRects[i] = minAreaRect(contours[i]);
//2.31 旋转矩形类RotatedRect中有Point()方法,参数Point2f* pts,将旋转矩形的四个端点存储进pts.
Point2f pts[4] = { Point(0,0) };
rotatedRects[i].points(pts);
//2.4 画出最小外接矩形
RNG rng(time(0));
Scalar color = Scalar(rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255));
//rectangle(src, pts[0],pts[2], color, 2);
line(src, pts[0], pts[1], color, 2, 8);
line(src, pts[1], pts[2], color, 2, 8);
line(src, pts[2], pts[3], color, 2, 8);
line(src, pts[3], pts[0], color, 2, 8);
}
imshow("dst", src);
}
int main() {
Mat src = imread("D:/test/huahua.png");
minBinaryImgAreaRect(src);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}




-
应用2——倾斜物体矫正提取
知识点:
-
使用Canny算法在输入图像中找到边缘,并在输出地图边缘中对其进行标记。
OpenCV–035: Canny边缘检测器
void minBinaryImgAreaRect(Mat &src) {
//1.查找轮廓
//1.1转化成灰度图像
Mat dst,binary;
dst = src.clone();
imshow("src", src);
cvtColor(src, src, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
Canny(src, src, 100, 200);
Mat kernel = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(5, 5), Point(-1, -1));
dilate(src, src, kernel, Point(-1, -1));
erode(src, src, kernel, Point(-1, -1));
imshow("预处理", src);
//threshold(gray, binary, 0, 255, THRESH_BINARY | THRESH_OTSU);
//imshow("binary", binary);
//1. 查找所有轮廓
vector<vector<Point>> contours;
findContours(src, contours, RETR_EXTERNAL, CHAIN_APPROX_NONE);
//2.确定最小外接矩形
//2.1.1 定义Rect类型的vector容器boundRect存放正外接矩形,初始化大小为contours.size()即轮廓个数
vector<Rect> boundRect(contours.size());
//2.1.2 定义RotatedRect类型的vector容器rotatedRects存放最小外接矩形,初始化大小为轮廓的个数。
vector<RotatedRect> rotatedRects(contours.size());
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
int w = 0;
int h = 0;
//2.2遍历每一个轮廓
for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++)
{
//2.3 由轮廓(点集)确定出正外接矩形并绘制
boundRect[i] = boundingRect(Mat(contours[i]));
//2.3.1 获得正外接矩形的左上角坐标及宽高
w = boundRect[i].width;
h = boundRect[i].height;
x = boundRect[i].x;
y = boundRect[i].y;
//2.3.2 通过正外接矩形的宽高,进行一次筛选,小的直接滤过
if (w < 100 || h < 100)
continue;
//2.3.3 画出正外接矩形
rectangle(dst, Rect(x, y, w, h), Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2, 8);
//2.4 由轮廓(点集)确定出最小外接矩形
rotatedRects[i] = minAreaRect(contours[i]);
//2.4.1 旋转矩形类RotatedRect中有Point()方法,参数Point2f* pts,将旋转矩形的四个端点存储进pts.
Point2f pts[4] = { Point(0,0) };
rotatedRects[i].points(pts);
//2.5 画出最小外接矩形
RNG rng(time(0));
Scalar color = Scalar(rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255));
//rectangle(src, pts[0],pts[2], color, 2);
line(dst, pts[0], pts[1], color, 2, 8);
line(dst, pts[1], pts[2], color, 2, 8);
line(dst, pts[2], pts[3], color, 2, 8);
line(dst, pts[3], pts[0], color, 2, 8);
//3. 通过仿射变换变换图像
//3.1 求出最小外接矩形的中心点并画出中心点
Point center=rotatedRects[i].center;
circle(src, center, 5, color, -1);
//3.2 求出图形的旋转角度
double angle = rotatedRects[i].angle;
//3.3 通过仿射变换旋转图像
//3.31 对角度进行处理
if (0 < abs(angle) && abs(angle) <= 45) {//逆时针
angle = angle;
}
else if(45<abs(angle) && abs(angle)<90){//顺时针
angle = 90 - abs(angle);
}
Mat m = getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, 1);
warpAffine(dst, dst, m, src.size());
//3.4
double w = rotatedRects[i].size.width;
double h = rotatedRects[i].size.height;
Mat roi = dst(Rect(center.x - w / 2, center.y - h / 2, w, h));
String name="";
name += i;
cout << "name=" << name << endl;
imshow(name, roi);
}
imshow("dst", dst);
}

canny:
预处理:













 本文介绍如何使用OpenCV的minAreaRect函数来查找包含输入二维点集的最小旋转矩形,提供了两个实际应用案例,一是画出图像中的最小外接矩形,二是进行倾斜物体的矫正提取。
本文介绍如何使用OpenCV的minAreaRect函数来查找包含输入二维点集的最小旋转矩形,提供了两个实际应用案例,一是画出图像中的最小外接矩形,二是进行倾斜物体的矫正提取。
















 2461
2461

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








