文章目录
- 前期知识
- 股票问题
- 相关题目练习
- 买卖股票的最佳时机 https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/
- 买卖股票的最佳时机 III https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iii/
- 买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费 https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-with-transaction-fee/
- 最大子序列交替和 https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-alternating-subsequence-sum/
前期知识
先来看一下 股票题目家族。
一类 不限制交易次数;一类 交易 k 次。

股票问题
买卖股票的最佳时机 II
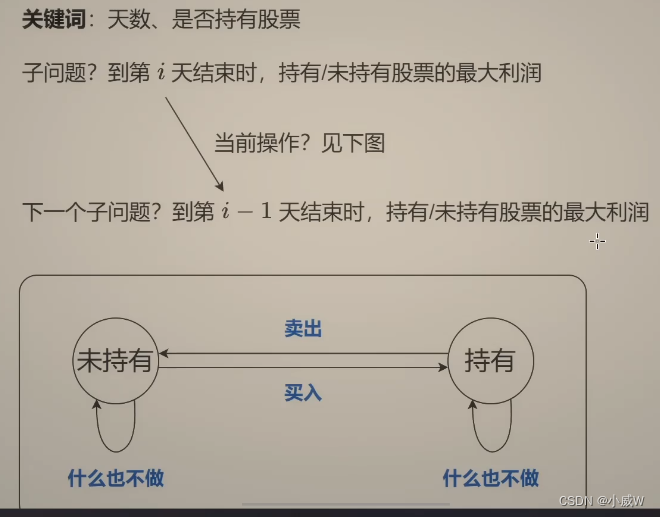
上图中的转换过程就是状态机。
状态转移方程如下:

定义成两个 dp 数组 buy 和 sell 会更清晰一些。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
int[] sell = new int[n], buy = new int[n];
buy[0] = -prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
sell[i] = Math.max(sell[i - 1], buy[i - 1] + prices[i]);
buy[i] = Math.max(buy[i - 1], sell[i - 1] - prices[i]);
}
return sell[n - 1];
}
}
由于 无后效性 ,因此两个数组可以空间优化成两个变量。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
int sell = 0, buy = -prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int newSell = Math.max(sell, buy + prices[i]);
buy = Math.max(buy, sell - prices[i]);
sell = newSell;
}
return sell;
}
}
最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期
这是 买卖股票的最佳时机 II 的一道变形题,唯一的区别在于,卖出股票之后的第二天不能购买股票。
直接把上一题的代码抄过来进行修改。
由于冷冻期的限制,buy[i] 的状态需要从 sell[i - 2] 转移过来,除此之外没有任何区别了。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
if (n == 1) return 0;
int[] sell = new int[n], buy = new int[n];
buy[0] = -prices[0];
buy[1] = Math.max(buy[0], -prices[1]);
sell[1] = Math.max(sell[0], buy[0] + prices[1]);
for (int i = 2; i < n; ++i) {
sell[i] = Math.max(sell[i - 1], buy[i - 1] + prices[i]);
buy[i] = Math.max(buy[i - 1], sell[i - 2] - prices[i]);
}
return sell[n - 1];
}
}
由于循环中的 下标 开始位置变成了 2,因此前面的初始化过程要写到 buy[1] 和 sell[1] 。
买卖股票的最佳时机 IV
买卖股票的最佳时机 IV
一个直接的方法就是将 dp 数组再扩展一维:dp[i][j]表示在第 i 天第 j 次交易时买入/卖出的最大收益。
对于每天之间的转移是不变的;每次交易之间的转移,buy 只能从上次交易的 sell 转移而来,sell 从这次交易的 buy 转移而来。(因为一个 buy + sell 是一次完整的交易)
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int k, int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
// dp[i][j]表示在第i天第j次交易时买入/卖出的最大收益
int[][] buy = new int[n][k], sell = new int[n][k];
Arrays.fill(buy[0], -prices[0]); // dp数组初始化
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
// 处理在第i天第0次交易的情况
buy[i][0] = Math.max(-prices[i], buy[i - 1][0]);
sell[i][0] = Math.max(sell[i - 1][0], buy[i - 1][0] + prices[i]);
for (int j = 1; j < k; ++j) {
buy[i][j] = Math.max(buy[i - 1][j], sell[i - 1][j - 1] - prices[i]);
sell[i][j] = Math.max(sell[i - 1][j], buy[i - 1][j] + prices[i]);
}
}
return sell[n - 1][k - 1];
}
}
解读一下
buy[i][j] = Math.max(buy[i - 1][j], sell[i - 1][j - 1] - prices[i]);
sell[i][j] = Math.max(sell[i - 1][j], buy[i - 1][j] + prices[i]);
和 买卖股票的最佳时机 II 这道题的代码
sell[i] = Math.max(sell[i - 1], buy[i - 1] + prices[i]);
buy[i] = Math.max(buy[i - 1], sell[i - 1] - prices[i]);
相比,状态转移的第一维下标是相同的。
而 每次交易之间的转移,buy 只能从上次交易的 sell 转移而来,sell 从这次交易的 buy 转移而来。(因为一个 buy + sell 是一次完整的交易),这决定了第二维下标的选择。
一维 dp 版本(实际上是去掉了二维 dp 的第一维)
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int k, int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
int[] buy = new int[k], sell = new int[k];
Arrays.fill(buy, -prices[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
buy[0] = Math.max(buy[0], -prices[i]);
sell[0] = Math.max(sell[0], buy[0] + prices[i]);
for (int j = 1; j < k; ++j) {
buy[j] = Math.max(buy[j], sell[j - 1] - prices[i]);
sell[j] = Math.max(sell[j], buy[j] + prices[i]);
}
}
return sell[k - 1];
}
}
补充:恰好k次 / 至少k次 怎么做?

相关题目练习
买卖股票的最佳时机 https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/
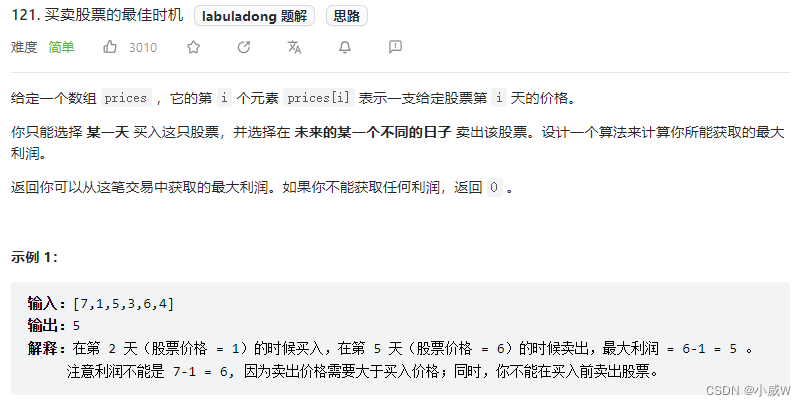
解法1——状态机DP
我们还是按照上面题目的做法来做,这道题目相当于只能买 1 次股票。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
int[] sell = new int[n], buy = new int[n];
buy[0] = -prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
buy[i] = Math.max(buy[i - 1], -prices[i]);
sell[i] = Math.max(sell[i - 1], buy[i - 1] + prices[i]);
}
return sell[n - 1];
}
}
代码整体几乎和 122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II 一样,唯一不同的点在于:buy[i] 不能从 sell[i - 1] 转移来了,因为最多只能买一次股票。
对应代码中把 buy[i] = Math.max(buy[i - 1], sell[i - 1] - prices[i]); 改成了 buy[i] = Math.max(buy[i - 1], -prices[i]);。
解法2——贪心

class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length, ans = 0, mn = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int price: prices) {
mn = Math.min(mn, price);
ans = Math.max(ans, price - mn);
}
return ans;
}
}
买卖股票的最佳时机 III https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iii/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-iii/
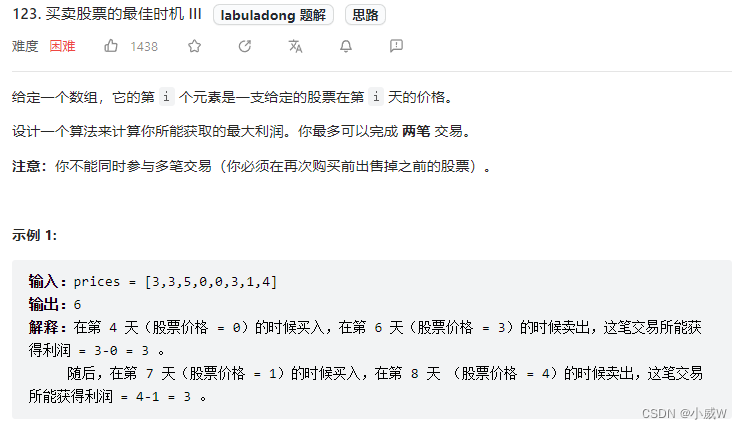
这道题目很熟悉对吧,其实就是 最多 k 次交易那道题目。(k = 2 时的特例)
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
int[][] buy = new int[n][2], sell = new int[n][2];
buy[0][0] = buy[0][1] = -prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
buy[i][0] = Math.max(buy[i - 1][0], -prices[i]);
sell[i][0] = Math.max(sell[i - 1][0], buy[i - 1][0] + prices[i]);
buy[i][1] = Math.max(buy[i - 1][1], sell[i - 1][0] - prices[i]);
sell[i][1] = Math.max(sell[i - 1][1], buy[i - 1][1] + prices[i]);
}
return sell[n - 1][1];
}
}
买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费 https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-with-transaction-fee/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-with-transaction-fee/
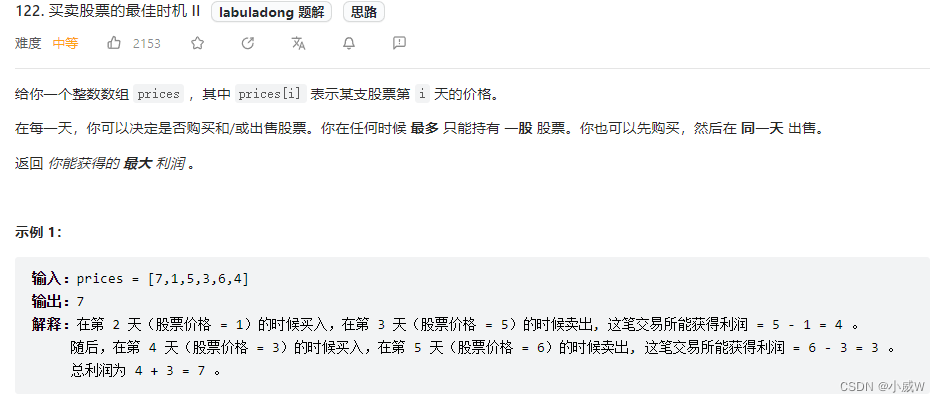
122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II 的变形题,只需要修改状态转移部分,在每次购买或卖出股票时加上一个手续费即可。
买入时加上手续费:
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices, int fee) {
int n = prices.length;
int sell = 0, buy = -prices[0] - fee;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int newSell = Math.max(sell, buy + prices[i]);
buy = Math.max(buy, sell - prices[i] - fee);
sell = newSell;
}
return sell;
}
}
卖出时加上手续费:
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices, int fee) {
int n = prices.length;
int sell = 0, buy = -prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int newSell = Math.max(sell, buy + prices[i] - fee);
buy = Math.max(buy, sell - prices[i]);
sell = newSell;
}
return sell;
}
}
最大子序列交替和 https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-alternating-subsequence-sum/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-alternating-subsequence-sum/
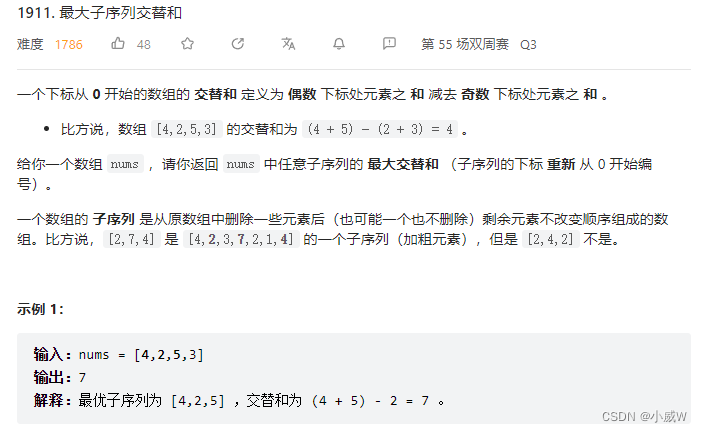
理解方式1:一个可以先卖出一个股票,再买入的 122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II 。
理解方式2:按 122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II 来计算怎么能亏得最多,最后的结果取负号。
理解1写法
class Solution {
public long maxAlternatingSum(int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
long sell = prices[0], buy = 0; // 只需要修改初始状态
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
long newSell = Math.max(sell, buy + prices[i]);
buy = Math.max(buy, sell - prices[i]);
sell = newSell;
}
return sell;
}
}
理解2写法
class Solution {
public long maxAlternatingSum(int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
long sell = 0, buy = -prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
// 从求max变成求min
long newSell = Math.min(sell, buy + prices[i]);
buy = Math.min(buy, sell - prices[i]);
sell = newSell;
}
return -buy; // 亏损最大值取负号
}
}
注意这道题目的必须使用 long 数据类型。(毕竟人家返回值都是 long 了)























 390
390











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










