约束满足问题(Constraint Satisfaction Problem, CSP)的Java实现(一)原理部分
问题的定义
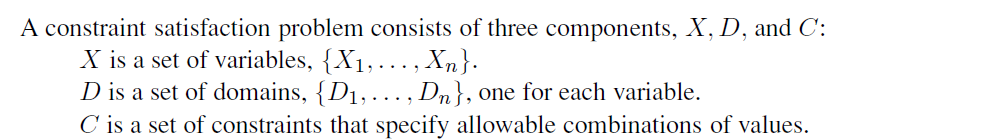
一个约束满足问题由三个部分组成,即 变量, 可行域, 约束。按照本人理解,变量为需要求解的量,可行域为变量中每个变量对应的可选择的值域,一般考虑为离散的问题。约束一般分为unary constraint, binary constraint,和多约束,但多约束也可以转换为binary constraint。
unary constraint:
T
1
≠
d
1
T_1 \neq d_1
T1=d1
binary constraint:
T
1
+
d
1
≤
T
2
T_1 + d_1 \leq T_2
T1+d1≤T2
多约束:
T
1
+
T
2
≤
T
3
T_1 + T_2 \leq T_3
T1+T2≤T3
约束的预处理:Inference
Node consistency 节点相容
A single variable (corresponding to a node in the CSP network) is node-consistent if all the values in the variable’s domain satisfy the variable’s unary constraints. For example, in the variant of the Australia map-coloring problem (Figure 6.1) where South Australians dislike green, the variable SA starts with domain {red , green, blue}, and we can make it node consistent by eliminating green, leaving SA with the reduced domain {red , blue}.
即通过将变量可行域中,不满足单约束的值提前去掉。
Arc consistency 弧相容
A variable in a CSP is arc-consistent if every value in its domain satisfies the variable’s binary constraints. 对于
X
i
X_i
Xi来说,如果其域中的每一个值
D
i
D_i
Di,在
X
j
X_j
Xj的域中都有一个值
D
j
D_j
Dj能够满足其条件,则说明
X
i
X_i
Xi对
X
j
X_j
Xj是弧相容的。在预处理中,我们需要让所有点都弧相容,因此我们会检测每一段弧,并将不符合要求的domain剔除。如果最后有domain的大小为0,则说明问题无解。一般采用AC-3算法实现。

回溯搜索与变量排序
回溯搜索一般采用DFS配和剪枝进行。
MRV排序
Minimum-remaining-values (MRV) heuristic. It also has been called the “most constrained variable” or REMAINING-VALUES “fail-first” heuristic, the latter because it picks a variable that is most likely to cause a failure soon, thereby pruning the search tree. If some variable X has no legal values left, the MRV heuristic will select X and failure will be detected immediately—avoiding pointless searches through other variables. The MRV heuristic usually performs better than a random or static ordering, sometimes by a factor of 1,000 or more, although the results vary widely depending on the problem.
MRV选择具有最少可行值得变量进行排序,先用最少得,可以保证能够“快速失败”
Degree Heuristic排序
根据节点的度进行排序。选择度最多的节点,以使得其他更深节点的选择性变小。
conflict-directed backjumping
之后再详细展开讲
Local search
同样也之后展开讲。








 本文介绍了约束满足问题(CSP)的Java实现原理,包括变量、可行域和不同类型的约束。重点讲解了预处理中的节点一致性与弧一致性,以及回溯搜索中的MRV排序和Degree Heuristic。后续还会涉及局部搜索、冲突直接回溯跳跃等高级技术。
本文介绍了约束满足问题(CSP)的Java实现原理,包括变量、可行域和不同类型的约束。重点讲解了预处理中的节点一致性与弧一致性,以及回溯搜索中的MRV排序和Degree Heuristic。后续还会涉及局部搜索、冲突直接回溯跳跃等高级技术。
















 1977
1977

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








