一、概述
Layout 本身其实不是参与到布局里面,主要是给GridLayout、RowLayout或ColumnLayout上的项提供附加属性。一个Layout类型的对象被附加到布局的子元素上,以提供关于 Item 的特定于布局的信息。附加对象的属性会影响布局如何安排 Item 。同时每一个不同的布局器支持的 Layout 的属性也不一样的,并不是所有的 像 GridLayout、RowLayout或ColumnLayout都支持所有的布局属性的,有些是有区别的。
例如,如果默认值不理想,可以指定minimumWidth、preferredWidth 和 maximumWidth。
当布局被调整大小时,元素可能会变大或缩小。因此,物品有minimum size, preferred size 和 maximum size。
如果没有显式指定项的最小尺寸,则尺寸设置为0。如果没有显式指定项的最大长度,则设置为Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY。
对于布局,隐含的最小和最大尺寸取决于布局的内容。
fillWidth 和 fillHeight 属性可以是 true 或 false。如果为false,则 Item 的尺寸将固定为其首选尺寸。否则,它将随着布局的调整而在其最小和最大尺寸之间增大或缩小。
注意:不要在布局中绑定 Item 的x、y、width或height属性,因为这将与布局的目标冲突,还可能导致绑定循环。布局引擎使用width和height属性来存储根据最小/首选/最大附加属性计算出的 Item 的当前大小,并且在每次布局 Item 时都会被重写。使用布局。preferredWidth和布局。preferredHeight或implicitWidth和implicitHeight指定元素的首选尺寸。
二、简单使用
Layout 本身不参与,主要是他的这些属性可以被布局里面的元素使用。
一般就是 layout.Layout的属性: 值
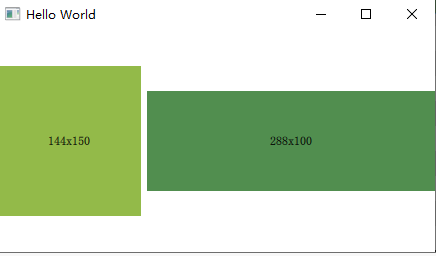
就像这个 第一个 Rectangle 里面的 Layout.fillWidth: true;Layout.minimumWidth: 50 都是依赖属性。
import QtQuick 2.14
import QtQuick.Window 2.3
import QtQuick.Layouts 1.3
RowLayout {
id: layout
anchors.fill: parent
spacing: 6
Rectangle {
color: "#93ba49"
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.minimumWidth: 50
Layout.preferredWidth: 100
Layout.maximumWidth: 300
Layout.minimumHeight: 150
Text {
anchors.centerIn: parent
text: parent.width + 'x' + parent.height
}
}
Rectangle {
color: "#518e4f"
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.minimumWidth: 100
Layout.preferredWidth: 200
Layout.preferredHeight: 100
Text {
anchors.centerIn: parent
text: parent.width + 'x' + parent.height
}
}
}
三、常见的依赖属性
1.alignment
这个属性允许你指定一个元素在它占据的单元格中的对齐方式。
默认值为0,这意味着它将是Qt.AlignVCenter | Qt.AlignLeft。如果只指定了水平或垂直标志,这些默认值也适用:如果只指定了水平标志,默认的垂直标志是Qt.AlignVCenter,如果只指定了垂直标志,默认的水平标志是Qt.AlignLeft。
- Qt::AlignLeft
- Qt::AlignHCenter
- Qt::AlignRight
- Qt::AlignTop
- Qt::AlignVCenter
- Qt::AlignBottom
- Qt::AlignBaseline
2. margins
设置项外部的边距为相同的值。项目本身不评估自己的利润率。父母有责任决定是否要设置外边距。
具体来说,外边距仅由ColumnLayout、RowLayout、GridLayout和其他类似布局的容器(如SplitView)计算,其中项目的有效单元格大小将随着外边距的增加而增加。
因此,如果带边距的项是另一项的子项,那么它的位置、大小和隐式大小将保持不变。
将边距和对齐方式结合起来会对齐item,包括它的边距。例如,垂直居中的元素上边界为1,下边界为9,会导致元素在单元格内的有效对齐距离为中心上方4像素。默认值为0。
四、要点
控制Layout中元素的尺寸大小,并不是直接控制子元素的height、width等属性,而是使用Layout的附加属性,如下:
我想实现让布局器中的元素高度跟随布局变化,使用heigt属性会失效
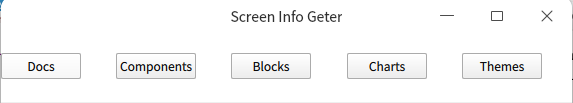
Rectangle {
id: header
Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignLeft
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.preferredHeight: 60
RowLayout {
anchors.fill: parent
Button {
text: "Docs"
height: header.Layout.preferredHeight
}
Button {
text: "Components"
height: 60
}
Button { text: "Blocks" }
Button { text: "Charts" }
Button { text: "Themes" }
}
}
而使用 Layout 的附加属性正常
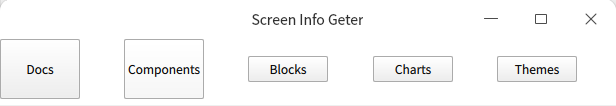
Rectangle {
id: header
Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignLeft
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.preferredHeight: 60
RowLayout {
anchors.fill: parent
Button {
text: "Docs"
Layout.preferredHeight: header.Layout.preferredHeight
}
Button {
text: "Components"
Layout.preferredHeight: 60
}
Button { text: "Blocks" }
Button { text: "Charts" }
Button { text: "Themes" }
}
}





 文章介绍了QtQuick中的Layout系统,用于给GridLayout、RowLayout或ColumnLayout的子项添加附加属性,影响布局的排列。Layout包含如alignment和margins等属性,用于控制元素的对齐方式和内外边距。Layout的fillWidth和fillHeight属性决定元素是否随布局调整大小。此外,文章提供了简单的代码示例展示如何使用这些属性。
文章介绍了QtQuick中的Layout系统,用于给GridLayout、RowLayout或ColumnLayout的子项添加附加属性,影响布局的排列。Layout包含如alignment和margins等属性,用于控制元素的对齐方式和内外边距。Layout的fillWidth和fillHeight属性决定元素是否随布局调整大小。此外,文章提供了简单的代码示例展示如何使用这些属性。

















 1685
1685

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










