这两天想实现yolov5的tensort加速,小白一枚,领悟甚浅,只能记录一下,防止遗忘了。
先记录一下yolov7:
yolov7的OpenCV、ONNXRuntime部署
分享一下大佬的开源作品yolov7的OpenCV、ONNXRuntime部署
大佬不但实现了yolov7的OpenCV、ONNXRuntime部署,并且无私的贡献了转换的模型,非常感谢。
ONNXRuntime部署
基于gpu运行,速度相当快,可以做到实时。
运行步骤:下载模型文件放到yolov7-opencv-onnxrun-cpp-py-main目录下
cd yolov7-opencv-onnxrun-cpp-py-main
mikdir simples #放入几张图片和视频
#运行
python onnxruntime/main.py --imgpath simples/1.jpg --modelpath models/yolov7-tiny_384x640.onnx
结果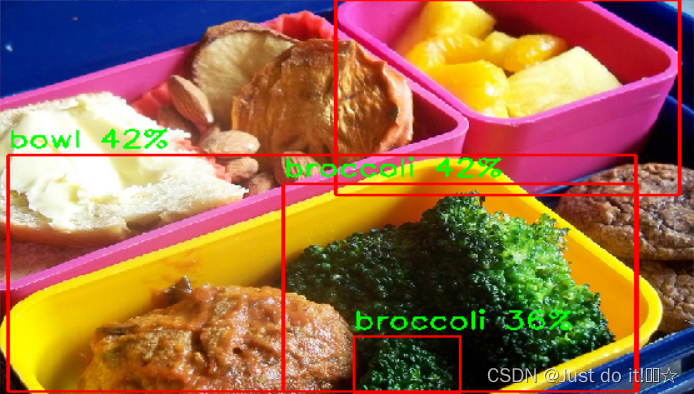
增加视频流推理
在源代码基础上加上了对视频流的推理和针对某一类的推理,代码如下:
VID_FORMATS = ['asf', 'avi', 'gif', 'm4v', 'mkv', 'mov', 'mp4', 'mpeg', 'mpg', 'wmv'] # include video suffixes
imgpath = args.imgpath
print(imgpath.split('.')[-1])
if imgpath.split('.')[-1] in VID_FORMATS:
cap =cv2.VideoCapture(imgpath)
while True:
success, srcimg = cap.read()
srcimg = imutils.resize(srcimg, width=640)
t1 = time.time()
boxes, scores, class_ids = yolov7_detector.detect(srcimg)
print(time.time() - t1)
# Draw detections
dstimg = yolov7_detector.draw_detections(srcimg, boxes, scores, class_ids)
print(time.time() - t1)
winName = 'Deep learning object detection in OpenCV'
cv2.namedWindow(winName, 0)
cv2.imshow(winName, dstimg)
cv2.waitKey(1)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
else:
srcimg = cv2.imread(args.imgpath)
# Detect Objects
t1 = time.time()
boxes, scores, class_ids = yolov7_detector.detect(srcimg)
print(time.time() - t1)
# Draw detections
dstimg = yolov7_detector.draw_detections(srcimg, boxes, scores, class_ids)
print(time.time() - t1)
winName = 'Deep learning object detection in OpenCV'
cv2.namedWindow(winName, 0)
cv2.imshow(winName, dstimg)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
修改输入源的读取方式,增加对mp4的输入支持,增加指定类的检测在代码的
def draw_detections(self, image, boxes, scores, class_ids):
for box, score, class_id in zip(boxes, scores, class_ids):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box.astype(int)
# Draw rectangle
#id对应的coconame文件的类别排序,指定识别行人
if class_id==0:
cv2.rectangle(image, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 0, 255), thickness=2)
label = self.class_names[class_id]
label = f'{label} {int(score * 100)}%'
labelSize, baseLine = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
# top = max(y1, labelSize[1])
# cv.rectangle(frame, (left, top - round(1.5 * labelSize[1])), (left + round(1.5 * labelSize[0]), top + baseLine), (255,255,255), cv.FILLED)
cv2.putText(image, label, (x1, y1 - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 0), thickness=2)
return image
结果如下
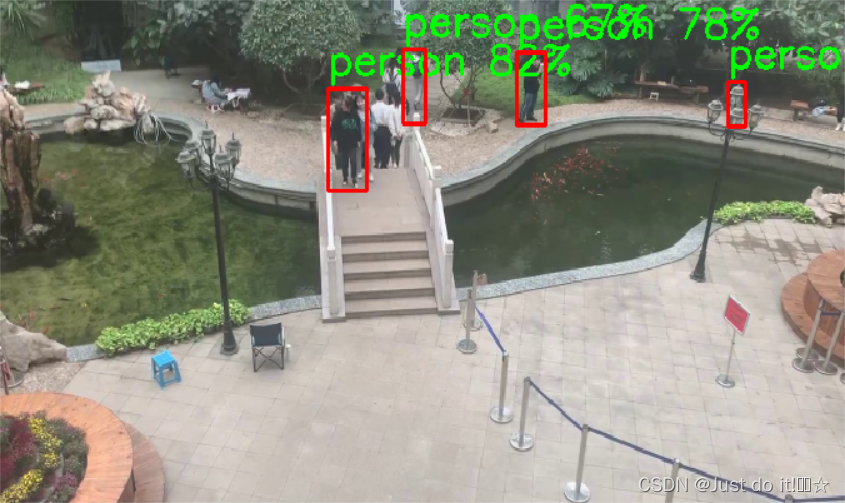

运行速度对比
均采用yolov7-tiny_384x640.onnx模型
opencv-cpu inference time:1.04 s
ONNXRuntime-gpu inference time:0.17 s























 565
565











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










