1. 准备数据集
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# prepare dataset
batch_size = 64
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))])
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST('data/MNIST/', train=True, transform=transform, download=True)
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_dataset = datasets.MNIST('data/MNIST/', train=False, transform=transform, download=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(dataset=test_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
2. 教师模型
class TeacherModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=10):
super(TeacherModel, self).__init__()
# 特征提取部分
'''
N = (W - F + 2P) / S + 1
'''
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=5, padding=2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=5) # padding默认0
# 分类部分
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, num_classes)
# 现代改进:添加Dropout防止过拟合
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5)
def forward(self, x):
# 使用ReLU激活函数和最大池化
x = F.relu(self.conv1(x)) # [batch, 6, 28, 28]
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2) # [batch, 6, 14, 14]
x = F.relu(self.conv2(x)) # [batch, 16, 10, 10]
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2) # [batch, 16, 5, 5]
# 展平
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # [batch, 16*5*5]
# 全连接层
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.dropout(x)
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
3. 学生模型
class StudentModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=10):
super(StudentModel, self).__init__()
# 仅保留一层卷积
# 使用更小的卷积核和更少的通道
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 2, kernel_size=3, padding=1) # 仅2个通道 28-3+2+1=28
self.fc = nn.Linear(2 * 14 * 14, num_classes) # 直接连接到输出
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.conv1(x)) # 28
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2) # [batch, 2, 14, 14]
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc(x)
训练和测试函数
'''
通用train
'''
def train(model, train_loader, epochs, learning_rate, device):
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
model.train()
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 一个epoch打印一次
running_loss = 0.0
for inputs, labels in train_loader:
# inputs: A collection of batch_size images
# labels: A vector of dimensionality batch_size with integers denoting class of each image
# inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(inputs)
# outputs: Output of the network for the collection of images. A tensor of dimensionality batch_size x num_classes
# labels: The actual labels of the images. Vector of dimensionality batch_size
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}, Loss: {running_loss / len(train_loader)}")
def test(model, test_loader, device):
# model.to(device)
model.eval()
correct = 0
total = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for inputs, labels in test_loader:
# inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device)
outputs = model(inputs)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
accuracy = 100 * correct / total
print(f"Test Accuracy: {accuracy:.2f}%")
return accuracy
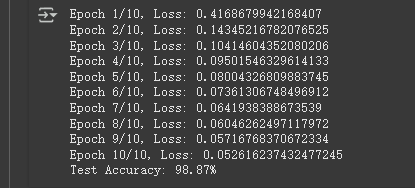
训练教师模型
torch.manual_seed(42)
net_teacher = TeacherModel(num_classes=10).to(device)
train(net_teacher, train_loader, epochs=10, learning_rate=0.001, device=device)
test_accuracy_teacher = test(net_teacher, test_loader, device
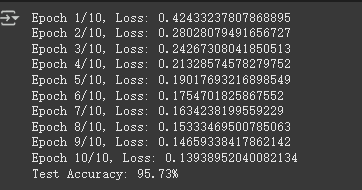
训练学生模型
torch.manual_seed(42)
net_student = StudentModel(num_classes=10).to(device)
torch.manual_seed(42)
net_student_1 = StudentModel(num_classes=10).to(device)
train(net_student, train_loader, epochs=10, learning_rate=0.001, device=device)
test_accuracy_student = test(net_student, test_loader, device)
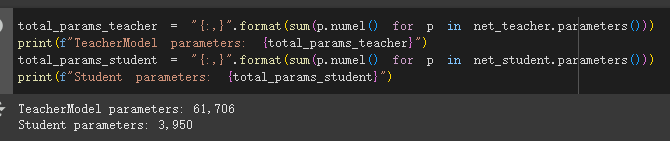
3. 原始损失函数
- The first objective function is the cross
entropy with the soft targets and this cross entropy is computed using the same high temperature in the softmax of the distilled model as was used for generating the soft targets from the cumbersome model - The second objective function is the cross entropy with the correct labels. This is computed
using exactly the same logits in softmax of the distilled model but at a temperature of 1
交叉熵:p是实际labels,q是预测logits
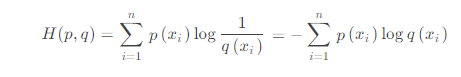
# Hinton原始损失函数
''' The first objective function is the cross
entropy with the soft targets and this cross entropy is computed using the same high temperature in
the softmax of the distilled model as was used for generating the soft targets from the cumbersome
model.
The second objective function is the cross entropy with the correct labels. This is computed
using exactly the same logits in softmax of the distilled model but at a temperature of 1.'''
def kd_loss(student_logits, teacher_logits, kd_temperature, kd_alpha, labels):
ce_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# soft loss, 教师和学生以同样的T
soft_teacher = F.softmax(teacher_logits / kd_temperature, dim=1) # 列维度消失
soft_student = F.log_softmax(student_logits / kd_temperature, dim=1)
distill_loss = -(soft_teacher * soft_student).sum(dim=1).mean() * (kd_temperature * kd_temperature)
# hard loss, T=1, cross entropy
student_loss = ce_loss(student_logits, labels)
# 组合损失
return kd_alpha * distill_loss + (1 - kd_alpha) * student_loss
def train_knowledge_distillation(teacher, student, train_loader, epochs, learning_rate, T, alpha):
ce_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(student.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
teacher.eval() # Teacher set to evaluation mode
student.train() # Student to train mode
for epoch in range(epochs):
running_loss = 0.0
for inputs, labels in train_loader:
# inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
# Forward pass with the teacher model - do not save gradients here as we do not change the teacher's weights
# 获取teacher logits
with torch.no_grad():
teacher_logits = teacher(inputs)
# Forward pass with the student model
# 获取student logits
student_logits = student(inputs)
# 计算蒸馏损失
loss = kd_loss(student_logits, teacher_logits, T, alpha, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}, Loss: {running_loss / len(train_loader)}")
# Apply ``train_knowledge_distillation`` with a temperature of 2. Arbitrarily set the weights to 0.75 for CE and 0.25 for distillation loss.
train_knowledge_distillation(teacher=net_teacher, student=net_student_1, train_loader=train_loader, epochs=10, learning_rate=0.001, T=3, alpha=0.75)
test_accuracy_kd = test(net_student_1, test_loader, device)




















 6712
6712

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








