# 转换 Transforms
class Rescale(object): # 缩放图片
"""Rescale the image in a sample to a given size.
Args:
output_size (tuple or int): Desired output size. If tuple, output is
matched to output_size. If int, smaller of image edges is matched
to output_size keeping aspect ratio the same.
"""
def __init__(self, output_size): # assert语句是一种插入调试断点到程序的一种便捷的方式。
assert isinstance(output_size, (int, tuple)) # 判断一个变量是否是某个类型可以用isinstance()判断:
self.output_size = output_size
def __call__(self, sample):
image, landmarks = sample['image'], sample['landmarks']
h, w = image.shape[:2] # 通道的高和宽
if isinstance(self.output_size, int):
if h > w:
new_h, new_w = self.output_size * h / w, self.output_size
else:
new_h, new_w = self.output_size, self.output_size * w / h
else:
new_h, new_w = self.output_size
new_h, new_w = int(new_h), int(new_w)
img = transform.resize(image, (new_h, new_w))
# h and w are swapped for landmarks because for images,
# x and y axes are axis 1 and 0 respectively
landmarks = landmarks * [new_w / w, new_h / h]
return {'image': img, 'landmarks': landmarks}
class RandomCrop(object): # 对图片进行随机裁剪。这是一种数据增强操作
"""Crop randomly the image in a sample.
Args:
output_size (tuple or int): Desired output size. If int, square crop
is made.
"""
def __init__(self, output_size):
assert isinstance(output_size, (int, tuple))
if isinstance(output_size, int):
self.output_size = (output_size, output_size)
else:
assert len(output_size) == 2
self.output_size = output_size
def __call__(self, sample):
image, landmarks = sample['image'], sample['landmarks']
h, w = image.shape[:2]
new_h, new_w = self.output_size
top = np.random.randint(0, h - new_h)
left = np.random.randint(0, w - new_w)
image = image[top: top + new_h,
left: left + new_w]
landmarks = landmarks - [left, top]
return {'image': image, 'landmarks': landmarks}
class ToTensor(object): # 把 numpy 格式图片转为 torch 格式图片 (我们需要交换坐标轴).
"""Convert ndarrays in sample to Tensors."""
def __call__(self, sample):
image, landmarks = sample['image'], sample['landmarks']
# swap color axis because
# numpy image: H x W x C
# torch image: C X H X W
image = image.transpose((2, 0, 1))
return {'image': torch.from_numpy(image),
'landmarks': torch.from_numpy(landmarks)}
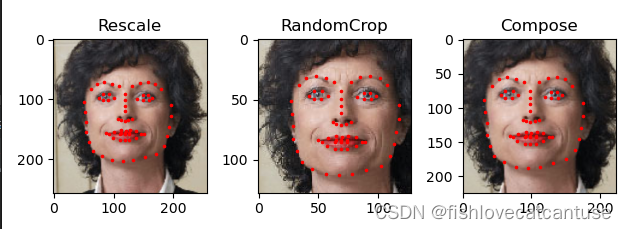
scale = Rescale(256)
crop = RandomCrop(128)
composed = transforms.Compose([Rescale(256), # 将transforms组合在一起
RandomCrop(224)])
# Apply each of the above transforms on sample.
fig = plt.figure()
sample = face_dataset[65]
for i, tsfrm in enumerate([scale, crop, composed]): #枚举
transformed_sample = tsfrm(sample)
ax = plt.subplot(1, 3, i + 1)
plt.tight_layout() # 自动调整绘图区的大小及间距,使所有的绘图区及其标题、坐标轴标签等都可以不重叠的完整显示在画布上。
ax.set_title(type(tsfrm).__name__) # 返回类型,并设为标题
show_landmarks(**transformed_sample)
plt.show()
# 整合起来以创建一个带组合转换的数据集
transformed_dataset = FaceLandmarksDataset(csv_file='../data/faces/face_landmarks.csv',
root_dir='../data/faces/',
transform=transforms.Compose([
Rescale(256),
RandomCrop(224),
ToTensor()
]))
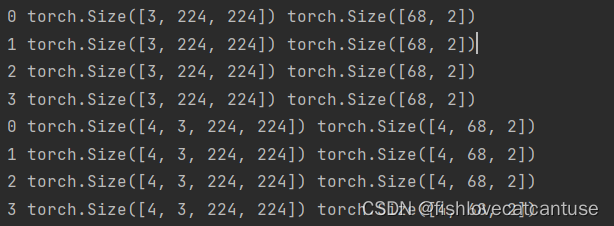
for i in range(len(transformed_dataset)):
sample = transformed_dataset[i]
print(i, sample['image'].size(), sample['landmarks'].size())
if i == 3:
break
dataloader = DataLoader(transformed_dataset, batch_size=4,
shuffle=True, num_workers=0)
# Helper function to show a batch
def show_landmarks_batch(sample_batched):
"""Show image with landmarks for a batch of samples."""
images_batch, landmarks_batch = sample_batched['image'], sample_batched['landmarks']
batch_size = len(images_batch)
im_size = images_batch.size(2) # 第二个数字224
grid = utils.make_grid(images_batch) # 将一个batch的图片在一张图中显示 make_grid的作用是将若干幅图像拼成一幅图像
#print(grid.numpy().shape) # (3, 228, 906) 正常的展示应该是(h,w,c) 所以需要transpose
plt.imshow(grid.numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))) # transpose()函数的作用就是调换x,y,z的位置,也就是数组的索引值。
# 正常的数组索引值为(0,1,2),等于(x,y,z)
for i in range(batch_size):
plt.scatter(landmarks_batch[i, :, 0].numpy() + i * im_size,
landmarks_batch[i, :, 1].numpy(),
s=10, marker='.', c='r')
plt.title('Batch from dataloader')
for i_batch, sample_batched in enumerate(dataloader):
print(i_batch, sample_batched['image'].size(),
sample_batched['landmarks'].size())
# observe 4th batch and stop.
if i_batch == 3:
plt.figure()
show_landmarks_batch(sample_batched)
plt.axis('off') # 关闭坐标轴
plt.ioff() # 关闭交互,此刻代码在图片展示完后才可以运行
plt.show()
break
运行结果:























 4322
4322











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








