决策树
关于CART与ID3,C4.5的区别和联系
知识点
代码
# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
class DTreeID3(object):
def __init__(self, epsilon=0.0001):
self.tree = Node()
self.epsilon = epsilon
def fit(self, X_train, Y_train):
A_recorder = np.arange(X_train.shape[1])
self._train(X_train, Y_train, self.tree, A_recorder)
def predict(self, X):
n = X.shape[0]
Y = np.zeros(n)
for i in range(n):
Y[i] = self.tree.predict_classification(X[i, :])
return Y
def visualization(self):
return self._visualization_dfs(self.tree)
def _train(self, A, D, node, AR):
# 1. 结束条件:若 D 中所有实例属于同一类,决策树成单节点树,直接返回
if np.any(np.bincount(D) == len(D)):
node.y = D[0]
return
# 2. 结束条件:若 A 为空,则返回单结点树 T,标记类别为样本默认输出最多的类别
if A.size == 0:
node.y = np.argmax(np.bincount(D))
return
# 3. 计算特征集 A 中各特征对 D 的信息增益,选择信息增益最大的特征 A_g
max_info_gain, g = self._feature_choose_standard(A, D)
# 4. 结束条件:如果 A_g 的信息增益小于阈值 epsilon,决策树成单节点树,直接返回
if max_info_gain <= self.epsilon:
node.y = np.argmax(np.bincount(D))
return
# 5. 对于 A_g 的每一可能值 a_i,依据 A_g = a_i 将 D 分割为若干非空子集 D_i,将当前结点的标记设为样本数最大的 D_i 对应
# 的类别,即对第 i 个子节点,以 D_i 为训练集,以 A - {A_g} 为特征集,递归调用以上步骤,得到子树 T_i,返回 T_i
node.label = AR[g]
a_cls = np.bincount(A[:, g])
new_A, AR = np.hstack((A[:, 0:g], A[:, g+1:])), np.hstack((AR[0:g], AR[g+1:]))
for k in range(len(a_cls)):
a_row_idxs = np.argwhere(A[:, g] == k).T[0].T
child = Node(k)
node.append(child)
A_child, D_child = new_A[a_row_idxs, :], D[a_row_idxs]
self._train(A_child, D_child, child, AR)
def _feature_choose_standard(self, A, D):
row, col = A.shape
prob = self._cal_prob(D)
prob = np.array([a if 0 < a <= 1 else 1 for a in prob])
entropy = -np.sum(prob * np.log2(prob))
max_info_gain_ratio = None
g = None
for j in range(col):
a_cls = np.bincount(A[:, j])
condition_entropy = 0
for k in range(len(a_cls)):
a_row_idxs = np.argwhere(A[:, j] == k)
# H(D)
prob = self._cal_prob(D[a_row_idxs].T[0])
prob = np.array([a if 0 < a <= 1 else 1 for a in prob])
H_D = -np.sum(prob * np.log2(prob))
# H(D|A)=SUM(p_i * H(D|A=a_i))
condition_entropy += a_cls[k] / np.sum(a_cls) * H_D
feature_choose_std = entropy - condition_entropy
if max_info_gain_ratio is None or max_info_gain_ratio < feature_choose_std:
max_info_gain_ratio = feature_choose_std
g = j
return max_info_gain_ratio, g
def _cal_prob(self, D):
statistic = np.bincount(D)
prob = statistic / np.sum(statistic)
return prob
def _visualization_dfs(self, node, layer=0):
prefix = '\n' if layer else ''
output_str = [prefix + ' ' * 4 * layer, '%r+%r ' % (node.y, node.label)]
if not node.child:
return ''.join(output_str)
for child in node.child:
output_str.append(self._visualization_dfs(child, layer=layer + 1))
return ''.join(output_str)
class DTreeC45(DTreeID3):
def _feature_choose_standard(self, A, D):
row, col = A.shape
prob = self._cal_prob(D)
prob = np.array([a if 0 < a <= 1 else 1 for a in prob])
entropy = -np.sum(prob * np.log2(prob))
max_info_gain_ratio = None
g = None
for j in range(col):
a_cls = np.bincount(A[:, j])
condition_entropy = 0
for k in range(len(a_cls)):
a_row_idxs = np.argwhere(A[:, j] == k)
# H(D) = -SUM(p_i * log(p_i))
prob = self._cal_prob(D[a_row_idxs].T[0])
prob = np.array([a if 0 < a <= 1 else 1 for a in prob])
H_D = -np.sum(prob * np.log2(prob))
# H(D|A)=SUM(p_i * H(D|A=a_i))
condition_entropy += a_cls[k] / np.sum(a_cls) * H_D
feature_choose_std = entropy / (condition_entropy + 0.0001)
if max_info_gain_ratio is None or max_info_gain_ratio < feature_choose_std:
max_info_gain_ratio = feature_choose_std
g = j
return max_info_gain_ratio, g
class DTreeCART(DTreeID3):
def _train(self, A, D, node, AR):
self.visited_set = set()
self._train_helper(A, D, node, AR)
def _train_helper(self, A, D, node, AR):
# 1. 结束条件:若 D 中所有实例属于同一类,决策树成单节点树,直接返回
if np.any(np.bincount(D) == len(D)):
node.y = D[0]
return
# 2. 与 ID3, C4.5 不一样, 不会直接去掉 A
if A.size == 0:
node.y = np.argmax(np.bincount(D))
return
# 3. 与 ID3, C4.5 不一样, 不仅要确定最优切分特征,还要确定最优切分值
max_info_gain, g, v, a_idx, other_idx = self._feature_choose_standard(A, D)
if (g, v) in self.visited_set:
node.y = np.argmax(np.bincount(D))
return
self.visited_set.add((g, v))
# 4. 结束条件:如果 A_g 的信息增益小于阈值 epsilon,决策树成单节点树,直接返回
if max_info_gain <= self.epsilon:
node.y = np.argmax(np.bincount(D))
return
# 5. 与 ID3, C4.5 不一样, 不是 len(a_cls) 叉树,而是二叉树
node.label = AR[g]
idx_list = a_idx, other_idx
for k, row_idx in enumerate(idx_list):
row_idx = row_idx.T[0].T
child = Node(k)
node.append(child)
A_child, D_child = A[row_idx, :], D[row_idx]
self._train_helper(A_child, D_child, child, AR)
def _feature_choose_standard(self, A, D):
row, col = A.shape
min_gini, g, v, a_idx, other_idx = None, None, None, None, None
for j in range(col):
a_cls = np.bincount(A[:, j])
# 与 ID3, C4.5 不一样,不仅要确定最优切分特征,还要确定最优切分值
for k in range(len(a_cls)):
# 根据切分值划为两类
a_row_idxs, other_row_idxs = np.argwhere(A[:, j] == k), np.argwhere(A[:, j] != k)
# H(D) = -SUM(p_i * log(p_i))
a_prob, other_prob = self._cal_prob(D[a_row_idxs].T[0]), self._cal_prob(D[other_row_idxs].T[0])
a_gini_D, other_gini = 1 - np.sum(a_prob * a_prob), 1 - np.sum(other_prob * other_prob)
# H(D|A)=SUM(p_i * H(D|A=a_i))
gini_DA = a_cls[k] / np.sum(a_cls) * a_gini_D + (1 - a_cls[k] / np.sum(a_cls)) * other_gini
if min_gini is None or min_gini > gini_DA:
min_gini, g, v, a_idx, other_idx = gini_DA, j, k, a_row_idxs, other_row_idxs
return min_gini, g, v, a_idx, other_idx
class DTreeRegressionCART(object):
def __init__(self, max_depth=1):
self.tree = Node()
self.max_depth = max_depth
def fit(self, X_train, Y_train):
A_recorder = np.arange(X_train.shape[1])
self._train(X_train, Y_train, self.tree, A_recorder)
def predict(self, X):
n = X.shape[0]
Y = np.zeros(n)
for i in range(n):
Y[i] = self.tree.predict_regression(X[i, :])
return Y
def _train(self, A, D, node, AR, depth=0):
# 1. 结束条件:到最后一层 | A 或 D 一样
if depth == self.max_depth or np.all(D == D[0]) or np.all(A == A[0]):
node.y = np.mean(D)
return
# 2. 选择第j个变量A_j(切分变量splitting variable)和 切分点s(splitting point)
min_f, min_j, min_s, min_idx1, min_idx2 = None, None, None, None, None
row, col = A.shape
for j in range(col):
a_col = A[:, j]
# 这里实现比较简化,s 就直接取最值的平均数
s = (np.max(a_col) + np.min(a_col)) * 0.5
R1_idx, R2_idx = np.argwhere(a_col <= s).T[0], np.argwhere(a_col > s).T[0]
if R1_idx.size == 0 or R2_idx.size == 0:
continue
c1, c2 = np.mean(D[R1_idx]), np.mean(D[R2_idx])
f1, f2 = np.sum(np.square(D[R1_idx] - c1)), np.sum(np.square(D[R2_idx] - c2))
if min_f is None or min_f > f1 + f2:
min_f, min_j, min_s, min_idx1, min_idx2 = f1 + f2, j, s, R1_idx, R2_idx
if min_f is None:
node.y = np.mean(D)
return
# 3. 向下一层展开
node.label, node.s = AR[min_j], min_s
for i, idx_list in enumerate((min_idx1, min_idx2)):
child = Node(i)
node.append(child)
self._train(A[idx_list, :], D[idx_list], child, AR, depth+1)
def visualization(self):
return self._visualization_dfs(self.tree)
def _visualization_dfs(self, node, layer=0):
prefix = '\n' if layer else ''
output_str = [prefix + ' ' * 4 * layer, '%r+%r+%r' % (node.y, node.label, node.s)]
if not node.child:
return ''.join(output_str)
for child in node.child:
output_str.append(self._visualization_dfs(child, layer=layer + 1))
return ''.join(output_str)
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, x=None):
self.label = None
self.x = x
self.s = None # Number
self.child = []
self.y = None
self.data = None
def append(self, child):
self.child.append(child)
def predict_classification(self, features):
if self.y is not None:
return self.y
for child in self.child:
if child.x == features[self.label]:
return child.predict_classification(features)
return self.child[1].predict_classification(features)
def predict_regression(self, features):
if self.y is not None:
return self.y
child_idx = 0 if features[self.label] <= self.s else 1
return self.child[child_idx].predict_regression(features)
datalabel = np.array(['年龄(特征1)', '有工作(特征2)', '有自己的房子(特征3)', '信贷情况(特征4)', '类别(标签)'])
train_sets = np.array([
['青年', '否', '否', '一般', '否'],
['青年', '否', '否', '好', '否'],
['青年', '是', '否', '好', '是'],
['青年', '是', '是', '一般', '是'],
['青年', '否', '否', '一般', '否'],
['中年', '否', '否', '一般', '否'],
['中年', '否', '否', '好', '否'],
['中年', '是', '是', '好', '是'],
['中年', '否', '是', '非常好', '是'],
['中年', '否', '是', '非常好', '是'],
['老年', '否', '是', '非常好', '是'],
['老年', '否', '是', '好', '是'],
['老年', '是', '否', '好', '是'],
['老年', '是', '否', '非常好', '是'],
['老年', '否', '否', '一般', '否'],
['青年', '否', '否', '一般', '是']])
map_table = {'青年': 0, '中年': 1, '老年': 2,
'否': 0, '是': 1,
'一般': 0, '好': 1, '非常好': 2}
if __name__ == '__main__':
row_, col_ = train_sets.shape
train_sets_encode = np.array([[map_table[train_sets[i, j]] for j in range(col_)] for i in range(row_)])
X_t, Y_t = train_sets_encode[:, :-1], train_sets_encode[:, -1]
for model in (DTreeID3(), DTreeC45(), DTreeCART()):
model.fit(X_t, Y_t)
print('=' * 20 + model.__class__.__name__ + '=' * 20)
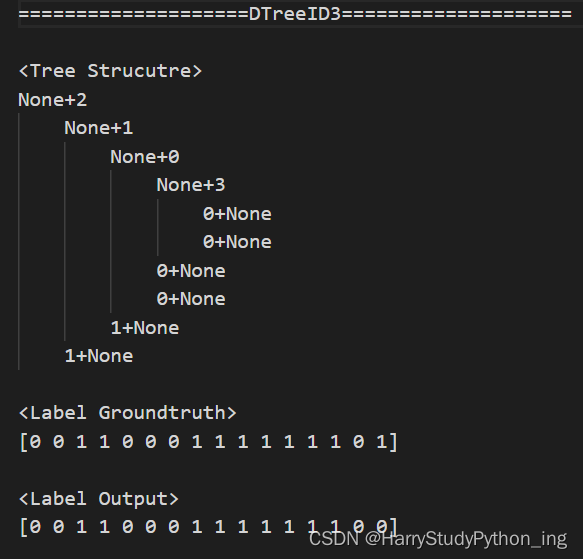
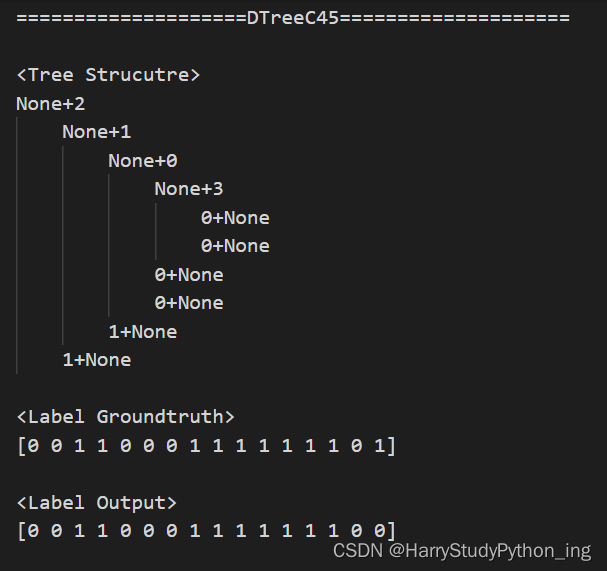
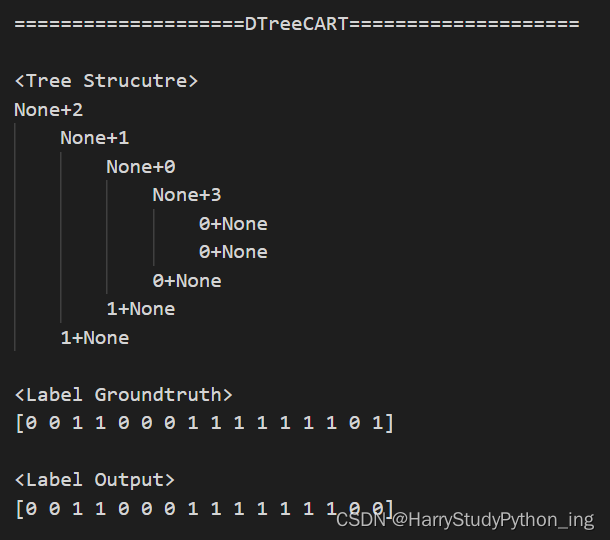
print('\n<Tree Strucutre>')
print(model.visualization())
print('\n<Label Groundtruth>')
print(Y_t)
print('\n<Label Output>')
print(model.predict(X_t).astype(int))
print()
model = DTreeRegressionCART(max_depth=2)
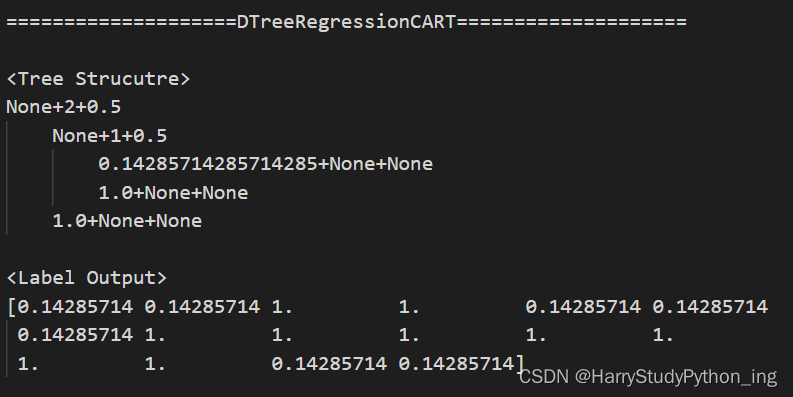
print('=' * 20 + model.__class__.__name__ + '=' * 20)
model.fit(X_t, Y_t)
print('\n<Tree Strucutre>')
print(model.visualization())
print('\n<Label Output>')
print(model.predict(X_t))
输出






















 3007
3007











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








