说明
1、Vue 脚手架是 Vue 官方提供的标准化开发工具(开发平台)。
2、最新的版本是 5.x。
3、文档: Vue CLI
具体步骤
第一步(仅第一次执行):全局安装@vue/cli。
npm install -g @vue/cli
第二步:切换到你要创建项目的目录,然后使用命令创建项目
vue create xxxx (xxx项目名)
或者vue ui(打开创建项目ui界面)
第三步:启动项目
npm run serve
备注:
- 如出现下载缓慢请配置 npm 淘宝镜像:npm config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.org
- Vue 脚手架隐藏了所有 webpack 相关的配置,若想查看具体的 webpakc 配置,
请执行:vue inspect > output.js
脚手架文件结构:
vue_test
├── node_modules
├── public
│ ├── index.html:主页面
│ └── favicon.ico:页签图标
├── src
│ ├── assets:存放静态资源
│ │ └── logo.png
│ ├── components:存放组件
│ │ └── HelloWorld.vue
│ ├── App.vue:汇总组件
│ └── main.js:入口文件
├── .gitignore:git版本管制忽略的配置
├── babel.config.js:babel的配置文件
├── package.json:应用包配置文件
├── README.md:应用描述文件
├── package-lock.json:包版本控制文件
├── jsconfig.json
└── vue.config.js
代码视图
src下main.js代码
/*
该文件是整个项目的入口文件
*/
//引入Vue
import Vue from "vue";
//import Vue from "vue/dist/vue"; //引入完整版Vue.js
//引入App组件,他是所有组件的父组件
import App from "./App.vue";
//关闭vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
let a = 1;
/*
关于不同版本的Vue:
1、vue.js 与 vue.runtime.xxx.js 的区别:
(1)、vue.js是完整版的Vue,包含:核心功能 + 模板解析器
(2)、vue.runtime.xxx.js试运行版的Vue,只包含:核心功能;没有模板解析器。
2、因为vue.runtime.xxx.js 没有模板解析器,所以不能使用template配置项,需要使用
render函数接收到 createElement函数 去指定具体内容
完整写法:
render(createElement) {
return createElement(element, "value");
},
简写写法:
render: (createElement) => createElement(element, "value"),
*/
//创建Vue实例对象-----vm
new Vue({
el: "#app",
//下面这行代码一会解释,完成了这个功能:将App组件放入容器中
//简写:
render: (h) => h(App),
//template: `<h1>你好啊</h1>`,
// components: { App },
});
src下App.vue
<template>
<div>
<img src="./assets/logo.png" alt="" />
<School></School>
<Studen></Studen>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//引入组件
import School from "./components/School";
import Studen from "./components/Student";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
School,
Studen,
},
};
</script>
src下components里的 School.vue 和 Student.vue
// ---- School
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="school">
<h2>学校名称:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{ address }}</h2>
<button @click="showName">点我显示学校名字</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "MySchool",
data() {
return {
name: "xx",
address: "北京",
};
},
methods: {
showName() {
alert(this.name);
},
},
};
</script>
<style>
/* 组件的样式 */
.school {
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
// ---- Student
<template>
<!-- 组件的结构 -->
<div class="student">
<h2>学生名称:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄:{{ age }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "MyStuden",
data() {
return {
name: "xinze",
age: 18,
};
},
};
</script>
<style>
/* 组件的样式 */
.student {
background-color: plum;
}
</style>
public下的index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<!-- 针对IE浏览器的一个特殊配置,含义是让IE浏览器以最高的渲染级别渲染页面 -->
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<!-- 开启移动端的理想视口 -->
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0" />
<!-- 配置页签图标 -->
<link rel="icon" href="<%= BASE_URL %>favicon.ico" />
<!-- 配置网页标题 -->
<title><%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %></title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 当浏览器不支持 Js 的时候 noscript 中的元素就会被渲染-->
<noscript>
<strong
>We're sorry but <%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %> doesn't work
properly without JavaScript enabled. Please enable it to
continue.</strong
>
</noscript>
<!-- 容器 -->
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- built files will be auto injected -->
</body>
</html>
关于不同版本的 Vue
1、vue.js 与 vue.runtime.xxx.js 的区别
(1)、vue.js 是完整版的 Vue,包含:核心功能 + 模板解析器
(2)、vue.runtime.xxx.js 试运行版的 Vue,只包含:核心功能;没有模板解析器。
2、因为 vue.runtime.xxx.js 没有模板解析器,所以不能使用 template 配置项,需要使用 render
完整写法:
render(createElement) {
return createElement(element, "value");
},
简写写法:
render: (createElement) => createElement(element, "value"),vue.config.js 配置文件
使用 Vue inspect > output.js 可以查看到 Vue 脚手架的默认值。(把默认值输出到 output.js 的文件里)
使用 vue.config.js 可以对脚手架进行个性化定之,详情见:http://cli.vuejs.org/zh
在 vue.config.js 中配置 lintOnSave: false, 可以关闭关闭语法检查
const { defineConfig } = require("@vue/cli-service");
module.exports = defineConfig({
transpileDependencies: true,
//关闭语法检查
lintOnSave: false,
});
在 package.json 里的 "rules": 中配置 "no-unused-vars": "off", 可以关闭波浪线提示
"rules": {
"no-unused-vars": "off"
}ref 属性
1、被用来给元素或子组件注册引用信息(id的代替者)
2、应用在html标签上获取的是真实DOM元素,应用在组件标签上是组件实例对象(vc)
3、使用方法:
打标识:<h1 ref="xxx">...</h1> 或 <School ref="xxx"></School>
获取:this.$refs.xxx
App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1 v-text="mas" ref="title"></h1>
<button @click="showName" ref="bth">点我打印元素</button>
<!-- 组件标签的ref命名不能为 组件名标签名相同 -->
<School ref="sch" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
//引入School组件
import School from "./components/School";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { School },
data() {
return {
mas: "欢迎学习Vue",
};
},
methods: {
showName() {
console.log(this.$refs.title); //真实DOM元素
console.log(this.$refs.bth); //真实DOM元素
console.log(this.$refs.sch); //School组件的实例对象(vc)
},
},
};
</script>
配置项 props
功能:让组件接收到外部传过来的数据
(1)、传递数据:
<Demo name="xxx" :age="18">
Demo === 组件标签 name === 想传递的属性
想要传递的参数为数字获得表达式 可以添加 :单向绑定 : === v-bind:
(2)、接收数据:
第一种方式(只接受): //用的最多
props:["name","age"]
第二种方式(限制类型):
props:{
name:String,
age:Number
}
第三种方式(限制类型、限制必传性、指定默认值):
props:{
name:{
type:String, //类型
required:true //限制必传性
},
age:{
type:Number,
default:99 //没有传参时指定默认值
}
}
required:true 和 default:99没必要出现在一个属性里
备注:
props是只读的,Vue底层会监测你对props的修改,如果进行了修改,就会发出警告,
若业务需求确实需要修改,那么请复制props的内容到data中一份,然后去修改data中的数据
App.vue
<template>
<div>
<!-- 这次传参的时候 也可以用到绑定语法 -->
<Student ref="stu" name="xinze" sex="男" :age="18" />
<hr />
</div>
</template>
<script>
//引入School组件
import Student from "./components/Student";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { Student },
};
</script>
Student.vue
<template>
<div class="student">
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
<h2>名字:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>性别:{{ sex }}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{ age + 1 }}</h2>
<h2>可修改的年龄:{{ MyAge }}</h2>
<button @click="MyAge++">点我年龄+1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "MyStudent",
data() {
return {
msg: "个人信息",
MyAge: this.age,
};
},
//简单声明接收
/* props: ["name", "sex", "age"], */
//对象接收(可以控制接收类型)
/* props: {
name: String,
sex: String,
age: Number,
}, */
//对象接收:在限制传参类型的基础上 再加 是否必传 和 不传的时候现实的默认值
props: {
name: {
type: String, //类型为String
required: true, //设置这个属性就必须 传参
},
sex: {
type: String,
default: "男", //这个属性是:在没有接收到传参值的情况下 默认赋值
},
age: {
type: Number,
required: true,
},
},
};
</script>
<style>
.student {
background: pink;
}
</style>
mixin混入(合)
功能:可以把多个组件公用的配置提取成一个混入对象
使用方式:
第一步定义混合,例如:
{
data(){....},
methods:{....},
....
}
第二部使用混入,例如:
(1)、全局混入:Vue.mixin(xxx)
(2)、局部混入:mixins:['xxx']mixin.js(定义混入)
export const hunhe1 = {
methods: {
showName() {
alert(this.name);
},
},
mounted() {
console.log(this, "挂载完毕");
},
};
export const hunhe2 = {
data() {
//这里的data 谁调用了 就会参与赋值
//赋值过程中 如过调用的data中 有相同的属性 就不会参与赋值 采取使用原身的属性
return {
x: 100,
y: 200,
};
},
};
main.js(引入全局)
//引入vue
import Vue from "vue";
//引入组件App
import App from "./App.vue";
//引入 混入 全局引入
import { hunhe1, hunhe2 } from "./tools/mixin";
//使用引入的混入
Vue.mixin(hunhe1);
Vue.mixin(hunhe2);
//关闭vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
//创建vm
new Vue({
el: "#app",
render: (h) => h(App),
});
App.vue
<template>
<div>
<Student />
<School />
<hr />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import School from "./components/School";
//引入School组件
import Student from "./components/Student";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { Student, School },
};
</script>
School.vue (引入局部)
<template>
<div class="school">
<h2 @click="showName">学校名称:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>地址{{ sex }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//引入混入 局部引用
/* import { hunhe1 } from "../tools/mixin";
import { hunhe2 } from "../tools/mixin"; */
export default {
name: "MySchool",
data() {
return {
name: "清华",
sex: "北京",
};
},
/* mixins: [hunhe1, hunhe2], //调用引入的 混入 */
};
</script>
<style>
.school {
background: plum;
}
</style>
Student.vue (引入局部)
<template>
<div class="student">
<h2 @click="showName">名字:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>性别:{{ sex }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//引入混入 局部引用
/* import { hunhe1 } from "../tools/mixin";
import { hunhe2 } from "../tools/mixin"; */
export default {
name: "MyStudent",
data() {
return {
name: "xinze",
sex: "男",
x: 666,
};
},
/* mixins: [hunhe1, hunhe2], //调用引入的 混入 */
};
</script>
<style>
.student {
background: pink;
}
</style>
插件
功能:用于增强Vue
本质:包含install方法的一个对象,install的第一个参数是Vue,第二个以后的参数是插件使用者传递的数据。
定义插件:
对象.install = function (Vue, options){
//1、添加全局过滤器
Vue.filter(....)
//2、添加全局指令
Vue.directive(....)
//3、配置全局混入(合)
//4、添加实例方法
Vue.prototype.$myMethod = function(){....}
Vue.prototype.$myProperty = xxx
}
使用插件:
引入:
import xxx from "xxx";
开启
Vue.use()plugins.js(定义插件)
export default {
//定义 一个插件ue
install(Vue) {
console.log("@@@install");
//创建全局自定义指令 自动获取焦点
Vue.directive("fbind", {
//指令与元素成功绑定时(一上来) 调用bind()
bind(element, binding) {
element.value = binding.value;
},
//当元素插入DOM模块后 调用inserted()
inserted(element, binding) {
element.focus();
},
//指令所在的模板被重新解析时。调用update()
update(element, binding) {
element.value = binding.value;
},
});
// 设置全局过滤器 获取字符的前四位
Vue.filter("mySlice", function (value) {
return value.slice(0, 4);
});
//定义混入 给所有 vm vc实例对象添加连个属性
Vue.mixin({
data() {
//这里的data 谁调用了 就会参与赋值
//赋值过程中 如过调用的data中 有相同的属性 就不会参与赋值 采取使用原身的属性
return {
x: 100,
y: 200,
};
},
});
//给vue原型身上添加一个方法(vm和vc都能用)
Vue.prototype.hello = () => {
alert("你好!");
};
},
};
main.js(引入插件)
//引入vue
import Vue from "vue";
//引入组件App
import App from "./App.vue";
//引入插件
import insatll from "./plugins";
//关闭vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
//使用(应用)插件 要在vm实例之前使用插件
Vue.use(insatll);
//创建vm
new Vue({
el: "#app",
render: (h) => h(App),
});
使用插件
一、
<template>
<div class="school">
<h2>学校名称:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>地址{{ sex }}</h2>
<input type="text" v-fbind:value="name" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "MySchool",
data() {
return {
name: "清华",
sex: "北京",
};
},
};
</script>
<style>
.school {
background: plum;
}
</style>
二、
<template>
<div class="student">
<h2>名字:{{ name | mySlice }}</h2>
<h2>性别:{{ sex }}</h2>
<button @click="hello">欢迎</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "MyStudent",
data() {
return {
name: "xinze",
sex: "男",
};
},
methods: {
holle() {
this.hello;
},
},
};
</script>
<style>
.student {
background: pink;
}
</style>
scoped 样式
作用:让样式在局部生效,防止冲突
写法:<style scoped>
一、
<template>
<div class="demo">
<h2>学校名称:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>地址{{ sex }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "MySchool",
data() {
return {
name: "清华",
sex: "北京",
};
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
/* 默认css样式 声明了lang="xxx" 可以使用别的样式 scoped在当前组件可用 */
.demo {
background: plum;
}
</style>
二、
<template>
<div class="demo">
<h2>名字:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2 class="qwe">性别:{{ sex }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "MyStudent",
data() {
return {
name: "xinze",
sex: "男",
};
},
};
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
//默认css样式 声明了lang="xxx" 可以使用别的样式 scoped在当前组件可用
.demo {
background: pink;
.qwe {
font-size: 40px;
}
}
</style>
组件的自定义事件
绑定事件监听
<Header @addTodo="addTodo"/>
或者
<Header ref="header"/>
this.$refs.header.$on('addTodo', this.addTodo)
触发事件
this.$emit('addTodo', todo)
说明
1、一种组件间通信的方式,适用于 子组件 ===> 父组件
2、使用场景:A是父组件,B是子组件,B想给A传数据,那么就要在A中给B绑定自定义事件(时间的回调在A中)
3、绑定自定义事件:
第一种方式,在夫组件中:<Demo @xinze="test"/>或<Demo v-on:xinze="test">
第二种方式,在夫组件中:
<Demo ref = "demo">
......
mounted(){
this.$refs.xxx.$on("xinze",this.test)
}
若想让自定义事件只能触发一次,可以使用once修饰符,或$once方法。
4、触发自定义事件:this.$emit("xinze",参数)
5、解绑自定义事件:this.$off("xinze")
6、组件上也可以绑定原生DOM事件,需要使用原生事件.native修饰符。
7、注意:通过this.$refs.xxx.$on("xinze",回调函数)绑定自定义事件时,回调要么配置在methods中,要么使用箭头函数,否则this指向会出问题!
App.vue
<template>
<div class="app">
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
<h2>学生姓名:{{ stuName }}</h2>
<!-- 通过父组件给自子组件传递函数的props实现:子给夫传递数据 -->
<School :getSchoolNmae="getSchoolNmae" />
<!-- 通过父组件给子组件绑定一个自定义事件实现:子给夫传递数据 (第一种写法,使用@或v-on)-->
<!-- <Student @xinze.once="getStudentName" /> -->
<!--
绑定一个自定义事件 @事件名="函数名"
绑定原生DOM事件 @click.native 不能直接传原生DOM事件 不然vue会认定为他是自定义事件 原生DOM事件需要加上 .navite
-->
<Student @xinze="getStudentName" @demo="m1" @click.native="show" />
<!-- 通过父组件给子组件绑定一个自定义事件实现:子给夫传递数据 (第二种写法,使用ref)-->
<!-- <Student ref="student" /> -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
import School from "./components/School";
//引入School组件
import Student from "./components/Student";
export default {
name: "App",
components: { Student, School },
data() {
return {
msg: "你好~",
stuName: "",
};
},
methods: {
getSchoolNmae(schooleName) {
console.log("app接收到了学校名:", schooleName);
},
getStudentName(stundentName, ...params) {
//...params 会把其余的参数封装成一个数组
console.log("app接收到了学生名:", stundentName, "其余参数:", params);
this.stuName = stundentName;
},
m1() {
console.log("demo事件被执行");
},
show() {
alert(11);
},
},
mounted() {
/* 绑定自定义事件 */
//this.$refs.student.$on("xinze", this.getStudentName);
/* 绑定自定义事件 直接写函数 记住不能写 普通函数是有自身的this 而箭头函数是往外找的this */
/* this.$refs.student.$on("xinze", (stundentName) => {
console.log(this);
this.stuName = stundentName;
}); */
//this.$refs.student.$once("xinze", this.getStudentName); //绑定自定义事件 (一次性)
},
};
</script>
<style>
.app {
background-color: pink;
padding: 5px;
}
</style>
Stundent.vue
<template>
<div class="student">
<h2>名字:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>性别:{{ sex }}</h2>
<h2>当前num值:{{ num }}</h2>
<button @click="add()">点我num++</button>
<button @click="tranStudentName">把学生名传入app中</button>
<button @click="unbind">解绑xinze事件</button>
<button @click="del">点我删除当前vc实例</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "MyStudent",
data() {
return {
name: "xinze",
sex: "男",
num: 1,
};
},
methods: {
tranStudentName() {
//使用自定义事件 this。$emit(事件名,(传参))
//this.$emit("xinze", { name: this.name, a: 444, b: 333, c: 111 });
this.$emit("xinze", this.name, 444, 333, 111);
this.$emit("demo");
},
unbind() {
this.$off("xinze"); //解绑一个自定义事件
//this.$off("xinze", "demo"); //解绑多个自定义事件
//this.$off(); //解绑所有的自定义事件
},
add() {
console.log("add()被回了");
this.num++;
},
del() {
this.$destroy(); //销毁了当前Student的组件实例,销毁后所有Student实例的自定义事件全都不奏效。
},
},
};
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
//默认css样式 声明了lang="xxx" 可以使用别的样式 scoped在当前组件可用
.student {
background: plum;
padding: 5px;
margin-top: 30px;
}
</style>
School.vue
<template>
<div class="school">
<h2>学校名称:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>地址{{ sex }}</h2>
<button @click="tranSchoolName">把学校名传入app中</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "MySchool",
props: ["getSchoolNmae"],
data() {
return {
name: "清华",
sex: "北京",
};
},
methods: {
tranSchoolName() {
this.getSchoolNmae(this.name);
},
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
/* 默认css样式 声明了lang="xxx" 可以使用别的样式 scoped在当前组件可用 */
.school {
background: palevioletred;
padding: 5px;
}
</style>
全局事件总线
Vue 原型对象上包含事件处理的方法
$on(eventName, listener): 绑定自定义事件监听
$emit(eventName, data): 分发自定义事件
$off(eventName): 解绑自定义事件监听
$once(eventName, listener): 绑定事件监听, 但只能处理一次
所有组件实例对象的原型对象的原型对象就是 Vue 的原型对像
VueComponent.prototyp.__proto__ === Vue.prototype
所有组件对象(vc)都能看到 Vue (vm)原型对象上的属性和方法
Vue.prototype.$bus = new Vue(), 所有的组件对象都能看到$bus 这个属性对象
什么是全局事件总线
包含事件处理相关方法的对象(只有一个)
一种组件间通信的方式,适用于任意组件间通信。
安装全局事件总线
new Vue({
.....
beforeCreate(){
Vue.prototype.$bus = this //安装全局事件总线,$bus就是当前应用的vm
},
.....
})使用事件总线
接收数据:A组件想接受数据,则在A组件中给$bus绑定自定义事件,时间的回调留在A组件自身
mounted() {
//挂载前 给全局事件总线上绑定一个getName事件
this.$bus.$on("getName", (val) =>
console.log("我是Shool组件,我收到了:", val)
);
},
或者
methods(){
demo(val){
console.log("我是Shool组件,我收到了:", val)
}
}
......
mounted() {
this.$bus.$on("getName", this.demo(val));
}, 提供数据 :this.$bus.$emit("xxx",数据)
最好在beforeDestroy钩子中用$off去解绑当前组件所用到的事件
beforeDestroy() {
//销毁前 解绑自身给全局事件总线身上绑定的事件
this.$bus.off("getName");
},main.js
//引入vue
import Vue from "vue";
//引入组件App
import App from "./App.vue";
//关闭vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
//创建vm
new Vue({
el: "#app",
render: (h) => h(App),
beforeCreate() {
//Vue实力创建前
Vue.prototype.$bus = this; //安装全局事件总线
},
});
School.vue
<template>
<div class="school">
<h2>学校名称:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>地址{{ sex }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "MySchool",
data() {
return {
name: "清华",
sex: "北京",
};
},
mounted() {
//挂载前 给全局事件总线上绑定一个getName事件
this.$bus.$on("getName", (val) =>
console.log("我是Shool组件,我收到了:", val)
);
},
beforeDestroy() {
//销毁前 解绑自身给全局事件总线身上绑定的事件
this.$bus.off("getName");
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
/* 默认css样式 声明了lang="xxx" 可以使用别的样式 scoped在当前组件可用 */
.school {
background: palevioletred;
padding: 5px;
}
</style>
Student.vue
<template>
<div class="student">
<h2>名字:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>性别:{{ sex }}</h2>
<button @click="tranName">点我给School发送学生名</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "MyStudent",
data() {
return {
name: "xinze",
sex: "男",
};
},
methods: {
tranName() {
this.$bus.$emit("getName", this.name);
},
},
};
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
//默认css样式 声明了lang="xxx" 可以使用别的样式 scoped在当前组件可用
.student {
background: plum;
padding: 5px;
margin-top: 30px;
}
</style>
消息订阅与发布
使用说明
1、一种组件间通信的方式,适用于任意组件间通信。
2、使用步骤:
安装 pubsub.js:npm i pubsub-js
引入包:import pubsub from 'pubsub-js'
3、接收数据:A组件想接受数据,则在A组件中订阅消息,订阅消息的回调留在A组件自身。
mounted() {
this.pubId = pubsub.subscribe("hello", (msgName, data) => {
//订阅一个名为 hello的消息 他的回调函数有两个参数 第一个时 消息名,第二个开始才是你传入的数据
console.log("有人发布了hello消息,hello消息的回调执行了", msgName, data);
});
},
或者
methods(){
demo( msgName, data){
console.log("有人发布了hello消息,hello消息的回调执行了", msgName, data);
}
}
......
mounted() {
this.pubId = pubsub.subscribe("hello",demo
}, 4、提供数据:pubsub.publish('xxxx',数据)
methods: {
tranName() {
/* this.$bus.$emit("getName", this.name); */
pubsub.publish("hello", 666); //发布一个消息 消息名时helo ,额外参数 666
},
},5、最好在beforDestory钩子中,用pubsub.unsubscribe(pid)去取消订阅
pubsub.unsubscribe(this.pubId); //pubId时创建订阅的时候接收到的School.vue
<template>
<div class="school">
<h2>学校名称:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>地址{{ sex }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//引入 pubsub库(消息订阅与发布)
import pubsub from "pubsub-js";
export default {
name: "MySchool",
data() {
return {
name: "清华",
sex: "北京",
};
},
mounted() {
//挂载前 给全局事件总线上绑定一个getName事件
/* this.$bus.$on("getName", (val) =>
console.log("我是Shool组件,我收到了:", val)
); */
this.pubId = pubsub.subscribe("hello", (msgName, data) => {
//订阅一个名为 hello的消息 他的回调函数有两个参数 第一个时 消息名,第二个开始才是你传入的数据
console.log("有人发布了hello消息,hello消息的回调执行了", msgName, data);
});
},
beforeDestroy() {
//销毁前 解绑自身给全局事件总线身上绑定的事件
/* this.$bus.off("getName"); */
pubsub.unsubscribe(this.pubId);
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
/* 默认css样式 声明了lang="xxx" 可以使用别的样式 scoped在当前组件可用 */
.school {
background: palevioletred;
padding: 5px;
}
</style>
Student.vue
<template>
<div class="student">
<h2>名字:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>性别:{{ sex }}</h2>
<button @click="tranName">点我给School发送学生名</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//引入 pubsub库(消息订阅与发布)
import pubsub from "pubsub-js";
export default {
name: "MyStudent",
data() {
return {
name: "xinze",
sex: "男",
};
},
methods: {
tranName() {
/* this.$bus.$emit("getName", this.name); */
pubsub.publish("hello", 666); //发布一个消息 消息名时helo ,额外参数 666
},
},
};
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
//默认css样式 声明了lang="xxx" 可以使用别的样式 scoped在当前组件可用
.student {
background: plum;
padding: 5px;
margin-top: 30px;
}
</style>
nextTick()
1、语法:this.$nextTick(回调函数)
2、作用:在下一次DOM 更新结束后执行其指定的回调。
3、什么时候用:当改变数据后,要基于更新后的新DOM进行某些操作时,要在nextTick()所指定的会点函数中进行。
说明:因为vue 你只要改了数据 就会从新解析 DOM 如果你刚改数据就执行某些操作,那么等下次解析DOM 的时候就会失去功能 而设置了nextTice里的回调函数里的操作 会在 下一次解析完DOM 才执行
// $nextTick() 会在模板解析下一次执行里面的函数
this.$nextTick(() => this.$refs.inputFocus.focus());Vue封装的过渡与动画
1、作用:再插入、更新或移除DOM元素时,再合适的时候给元素添加样式类名。
2、图示:
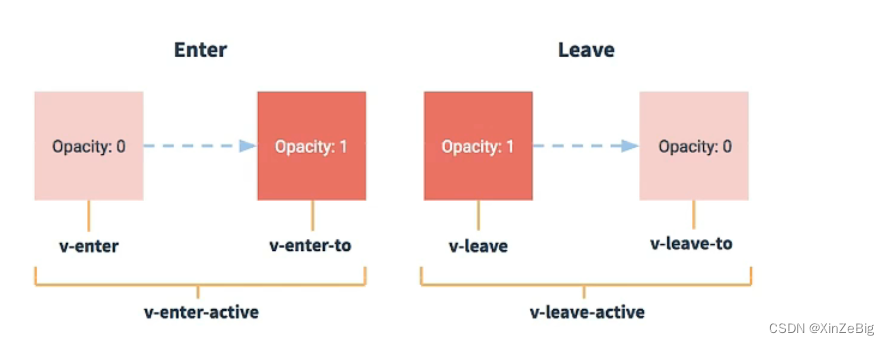
3、写法:
-
准备好样式:
-
元素进入时的样式:
-
v-enter:进入的起点
-
v-enter-active:进入过程中
-
v-enter-to:进入的终点
-
-
元素离开的样式:
-
v-leave:离开的起点
-
v-leave-active:离开过程中
-
v-leave-to:离开的终点
-
-
-
使用
<transition>包裹要过度的元素,并配置name属性:
name 可以替换掉 动画类名开头 的 v
<transition name="h1" appear>
<!-- appear 初始执行 -->
<h1 v-show="isShow">你好~</h1>
</transition>-
备注:若有多个元素需要过度,则需要使用:
<transition-group>,且每个元素都要指定key值
动画
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow = !isShow">点我显示隐藏</button>
<!-- transition 标签是动画标签 不会被解析 仅供vue实现动过效果用的 -->
<!-- 标签下仅支持写一个根元素
开始动画的时候会自动调用 .v-enter-active
结束动画时会自动调用 .v-leave-active
如果标签内写了 name属性 那么name里的值就可以替换掉上面的 v
-->
<transition name="h1" appear>
<!-- appear 初始执行 -->
<h1 v-show="isShow">你好~</h1>
</transition>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Test-1",
data() {
return {
isShow: true,
};
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
h1 {
background-color: pink;
}
.h1-enter-active {
animation: goto 0.5s linear;
}
.h1-leave-active {
animation: goto 0.5s linear reverse;
}
@keyframes goto {
from {
transform: translateX(-100%);
}
to {
transform: translateX(0%);
}
}
</style>
过渡
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow = !isShow">点我显示隐藏</button>
<!--
如果有多个根元素 需要变化标签为 transition-group
不过需要把每个根元素加一个 key 来识别
-->
<transition-group name="h1" appear>
<!-- appear 初始执行 -->
<h1 v-show="isShow" key="1">你好~</h1>
<h1 v-show="!isShow" key="2">你好~</h1>
</transition-group>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Test-2",
data() {
return {
isShow: true,
};
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
h1 {
/* 第一种 谁用 给谁属性里添加 */
/* 设置过度 0.5s linear 匀速 */
/* transition: 0.5s linear; */
background-color: pink;
}
/* 第二种动画 执行 */
.h1-enter-active,
.h1-leave-active {
transition: 0.5s linear;
}
/* 进入的起点 和离开的终点*/
.h1-enter,
.h1-leave-to {
transform: translateX(-100%);
}
/* 进入的终点 和离开的起点*/
.h1-enter-to,
.h1-leave {
transform: translateX(0);
}
</style>
第三方动画库

<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow = !isShow">点我显示隐藏</button>
<!--
第三发库
引入
将官方说的类名加入到name中
appear 初始执行
enter-active-class 开始执行 后面可加 库里面的类名
leave-active-class 结束执行 后面可加 库里面的类名
-->
<transition-group
name="animate__animated animate__bounce"
appear
enter-active-class="animate__swing"
leave-active-class="animate__backOutUp"
>
<!-- appear 初始执行 -->
<h1 v-show="isShow" key="1">你好~</h1>
<h1 v-show="isShow" key="2">你好~</h1>
</transition-group>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//引入
import "animate.css";
export default {
name: "Test-3",
data() {
return {
isShow: true,
};
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
h1 {
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
Vue脚手架配置代理
方法一
在vue.config.js中添加如下配置:
devServer: {
proxy: "http://localhost:5000",
},说明:
1、优点:配置简单,请求资源时直接发给前端(8080)即可。
2、缺点:不能配置多个代理,不能灵活的控制请求是否走代理
3、工作方式:若按照上述配置代理,当请求了前端不存在的资源时,那么该请求会转发给服务器(优先匹配前端资源(8080))
方法二
编写vue.config.js配置具体代理规则:
//开启代理服务器(方式二)可以配置多个代理
devServer: {
proxy: {
"/xinze": { //匹配所有以 "/xinze"开头的请求路径
target: "http://localhost:5000", //代理目标的基础路径
pathRewrite: { "^/xinze": "" }, //将开头为 "/xinze" 转为 ""
//ws: true, //用于支持websocket 默认为true
//changeOrigin: true, //默认为true 用于控制请求头中的host值
//写了true 隐藏自身端口号 访问那个 就是那个的端口号 false 表明自身的端口号
},
"/demo": {
target: "http://localhost:5001",
pathRewrite: { "^/demo": "" },
//ws: true, //用于支持websocket
//changeOrigin: true, // 用于控制请求头中的host值
},
},
},
/*
changeOrigin设置为true时,服务器收到的请求头中的host为: localhost :5000
change0rigin设置为false时,服务器收到的请求头中的host为: localhost:8080
change0rigin默认值为true
*/
说明:
1、优点:可以配置多个代理,且可以灵活的控制请求是否走代理。
2、缺点:配置略微繁琐,请求资源时必须加前缀。
App.vue
<template>
<div>
<button @click="getStudents">获取学生信息</button>
<button @click="getCars">获取汽车信息</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//引入 axios
import axios from "axios";
export default {
name: "App",
methods: {
getStudents() {
axios.get("http://localhost:8080/xinze/students").then(
(response) => {
console.log("请求成功了", response.data);
},
(error) => {
console.log("请求失败了", error.message);
}
);
},
getCars() {
axios.get("http://localhost:8080/demo/cars").then(
(response) => {
console.log("请求成功了", response.data);
},
(error) => {
console.log("请求失败了", error.message);
}
);
},
},
};
</script>
vue.config.js
const { defineConfig } = require("@vue/cli-service");
module.exports = defineConfig({
transpileDependencies: true,
//关闭语法检查
lintOnSave: false,
//开启代理服务器(方式一)
/* devServer: {
proxy: "http://localhost:5000",
}, */
//开启代理服务器(方式二)可以配置多个代理
devServer: {
proxy: {
"/xinze": {
target: "http://localhost:5000",
pathRewrite: { "^/xinze": "" },
//ws: true, //用于支持websocket 默认为true
//写了true 隐藏自身端口号 访问那个 就是那个的端口号 false 表明自身的端口号
//changeOrigin: true, //默认为true 用于控制请求头中的host值
},
"/demo": {
target: "http://localhost:5001",
pathRewrite: { "^/demo": "" },
//ws: true, //用于支持websocket
//changeOrigin: true, // 用于控制请求头中的host值
},
},
},
});
vue 项目中常用的 2 个 Ajax 库
axios
通用的 Ajax 请求库, 官方推荐,使用广泛
安装:npm i axios
引用:import axios from "axios";
vue-resource插件
Vue里的发送ajax请求 插件
安装:npm i vue-resource
使用:
//引入vue-rusource
import vueResource from "vue-resource";
//使用插件
Vue.use(vueResource);vue 插件库, vue1.x 使用广泛,官方已不维护。(不推荐)
插槽
说明
1、作用:让父组件可以向子组件指定位置插入 html结构,也是一种组件间通信的方式,适用于
父组件 ===> 子组件
2、分类:默认插槽、具名插槽、作用域插槽
3、使用方式:
-
默认插槽
父组件中: <category> <div>html结构</div> </category> 子组件中: <template> <div> <!-- 定义一个插槽(挖个坑,等组件的使用者进行填充) 如果没传入值 就会显示标签体内的内容--> <slot>插槽默认值</slot> </div> </template> -
具名插槽
父组件中: <category> //slot="xxx" 对应插槽的 name <div slot="center">html结构</div> </category> <!-- 这里可以写v-slot:footer来指定插槽 但是这种写法仅支持 template标签 --> <template v-slot:footer> //v-slot:xxx 对应插槽的 name </template> 子组件中: <template> <div> <!-- 定义一个插槽(挖个坑,等组件的使用者进行填充) 如果没传入值 就会显示标签体内的内容--> <!-- 这里的name属性是根据 传入结构的时候如果需要命名该 name值 才能指定的插入当前插槽 --> <slot name="center">插槽默认值</slot> <slot name="footer">插槽默认值</slot> </div> </template> -
作用域插槽
-
理解:数据在组件自身,但根据数据生成的结构需要组件的使用者来决定。(game数据在Category组件中,但使用数据所遍历出来的结构有App组件做决定)
-
具体编码
父组件---》 <!-- 接收作用域插槽里的绑定的参数方法: 1、scope="{games}" {} 是吧该插槽绑定的数据转外参数使用 这种使用的前提必须实在template中接受 2、slot-scope="{ games }" 这个可以在普通元素标签中接受 3、v-slot="{ games }" 也可以在普通元素标签中接受 备注:作用域插槽 也可以具名(name) 写法: v-slot:插槽名=“games” --> <category title="游戏"> 方法一 <template scope="{games}"> <ul> <li v-for="(item, index) in games" :key="index">{{ item }}</li> </ul> </template> </category> <category title="游戏"> 方法二 <template slot-scope="{ games }"> <ol> <li v-for="(item, index) in games" :key="index">{{ item }}</li> </ol> </template> </category> <category title="游戏"> 方法三 <template v-slot="{ games }"> <h4 v-for="(item, index) in games" :key="index">{{ item }}</h4> </template> </category> ---》子组件 <!-- 作用域插槽: 给插槽绑定一个参数 , 使用者需要接收该插槽里的参数(接受方法有三种) 但是接收名必须跟这边的插槽对应上才能拿到该插槽 备注:作用域插槽 也可以具名(name) --> <template> <div> <slot :games="games">插槽默认值</slot> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Category-list", data() { 数据在子组件中 return { games: ["红色警戒", "穿越火线", "劲舞团", "超级玛丽"], }; }, }; </script>
-
默认插槽
App.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<category title="美食" :ListData="foods">
<img src="https://s3.ax1x.com/2021/01/16/srJlq0.jpg" alt="" />
</category>
<category title="游戏" :ListData="games">
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in games" :key="index">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
</category>
<category title="电影" :ListData="films">
<video
controls
src="http://clips.vorwaerts-gmbh.de/big_buck_bunny.mp4"
></video>
</category>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Category from "./components/Category.vue";
export default {
components: { Category },
name: "App",
data() {
return {
foods: ["火锅", "烧烤", "小龙虾", "牛排"],
games: ["红色警戒", "穿越火线", "劲舞团", "超级玛丽"],
films: ["《教父》", "《拆弹专家》", "《你好,李焕英》", "《功夫》"],
};
},
};
</script>
<style lang="css">
.container {
/* 设置弹性布局 默认想右水平方向排序 */
display: flex;
/*定义项目在主轴上的对齐方式 设置属性剧中*/
justify-content: space-around;
}
</style>
components/Category.vue
<template>
<div class="category">
<h3>{{ title }}分类</h3>
<!-- 定义一个插槽(挖个坑,等组件的使用者进行填充) 如果没传入值 就会显示标签体内的内容-->
<slot>我是一些默认值,当使用者没有传递具体结构时,我会出现</slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ["title", "ListData"],
name: "Category-list",
};
</script>
<style>
.category {
background-color: pink;
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
}
h3 {
text-align: center;
background-color: palevioletred;
}
img,
video {
width: 100%;
}
</style>
具名插槽
App.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<category title="美食" :ListData="foods">
<img
slot="center"
src="https://s3.ax1x.com/2021/01/16/srJlq0.jpg"
alt=""
/>
<div class="foot" slot="footer">
<a href="#">更多美食</a>
</div>
</category>
<category title="游戏" :ListData="games">
<ul slot="center">
<li v-for="(item, index) in games" :key="index">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
<div class="foot" slot="footer">
<a href="#">单机游戏</a>
<a href="#">网络游戏</a>
</div>
</category>
<category title="电影" :ListData="films">
<video
slot="center"
controls
src="http://clips.vorwaerts-gmbh.de/big_buck_bunny.mp4"
></video>
<!-- 这里可以写v-slot:footer来指定插槽 但是这种写法仅支持 template标签 -->
<template v-slot:footer>
<div class="foot">
<a href="#">经典</a>
<a href="#">热门</a>
<a href="#">推荐</a>
</div>
<h4>欢迎前来观影</h4>
</template>
</category>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Category from "./components/Category.vue";
export default {
components: { Category },
name: "App",
data() {
return {
foods: ["火锅", "烧烤", "小龙虾", "牛排"],
games: ["红色警戒", "穿越火线", "劲舞团", "超级玛丽"],
films: ["《教父》", "《拆弹专家》", "《你好,李焕英》", "《功夫》"],
};
},
};
</script>
<style lang="css">
.container,
.foot {
/* 设置弹性布局 默认想右水平方向排序 */
display: flex;
/*定义项目在主轴上的对齐方式 设置属性剧中*/
justify-content: space-around;
}
img,
video {
width: 100%;
}
h4 {
text-align: center;
}
</style>
components/Category.vue
<template>
<div class="category">
<h3>{{ title }}分类</h3>
<!-- 定义一个插槽(挖个坑,等组件的使用者进行填充) 如果没传入值 就会显示标签体内的内容-->
<!-- 这里的name属性是根据 传入结构的时候如果需要命名该 name值 才能指定的插入当前插槽 -->
<slot name="center">
我是一些默认值,当使用者没有传递具体结构时,我会出现1
</slot>
<slot name="footer">
我是一些默认值,当使用者没有传递具体结构时,我会出现2
</slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ["title", "ListData"],
name: "Category-list",
};
</script>
<style>
.category {
background-color: pink;
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
}
h3 {
text-align: center;
background-color: palevioletred;
}
</style>
具名插槽
App.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<!-- 接收插槽里的绑定的参数方法:
1、scope="{games}" {} 是吧该插槽绑定的数据转外参数使用
这种使用的前提必须实在template中接受
2、slot-scope="{ games }" 这个可以在普通元素标签中接受
3、v-slot="{ games }" 也可以在普通元素标签中接受
-->
<category title="游戏">
<template scope="games">
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in games.games" :key="index">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
</template>
</category>
<category title="游戏">
<template slot-scope="{ games }">
<ol>
<li v-for="(item, index) in games" :key="index">{{ item }}</li>
</ol>
</template>
</category>
<category title="游戏">
<template v-slot="{ games }">
<h4 v-for="(item, index) in games" :key="index">{{ item }}</h4>
</template>
</category>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Category from "./components/Category.vue";
export default {
components: { Category },
name: "App",
data() {
return {};
},
};
</script>
<style lang="css">
.container,
.foot {
/* 设置弹性布局 默认想右水平方向排序 */
display: flex;
/*定义项目在主轴上的对齐方式 设置属性剧中*/
justify-content: space-around;
}
img,
video {
width: 100%;
}
h4 {
text-align: center;
}
</style>
components/Category.vue
<template>
<div class="category">
<h3>{{ title }}分类</h3>
<!-- 定义一个插槽(挖个坑,等组件的使用者进行填充) 如果没传入值 就会显示标签体内的内容-->
<!--
作用域插槽: 给插槽绑定一个参数 ,
使用者需要接收该插槽里的参数(接受方法有三种)但是接收名必须跟这边的插槽对应上才能拿到该插槽-->
<slot :games="games"> 我是一些默认值 </slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ["title", "ListData"],
name: "Category-list",
data() {
return {
games: ["红色警戒", "穿越火线", "劲舞团", "超级玛丽"],
};
},
};
</script>
<style>
.category {
background-color: pink;
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
}
h3 {
text-align: center;
background-color: palevioletred;
}
img,
video {
width: 100%;
}
</style>























 3万+
3万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










