一 、shader Cycles测试工具:
1.1 单个场景的所有shader获取
renderdoc截帧可以获取到设备反汇编出来的场景中的VS、FS shader。
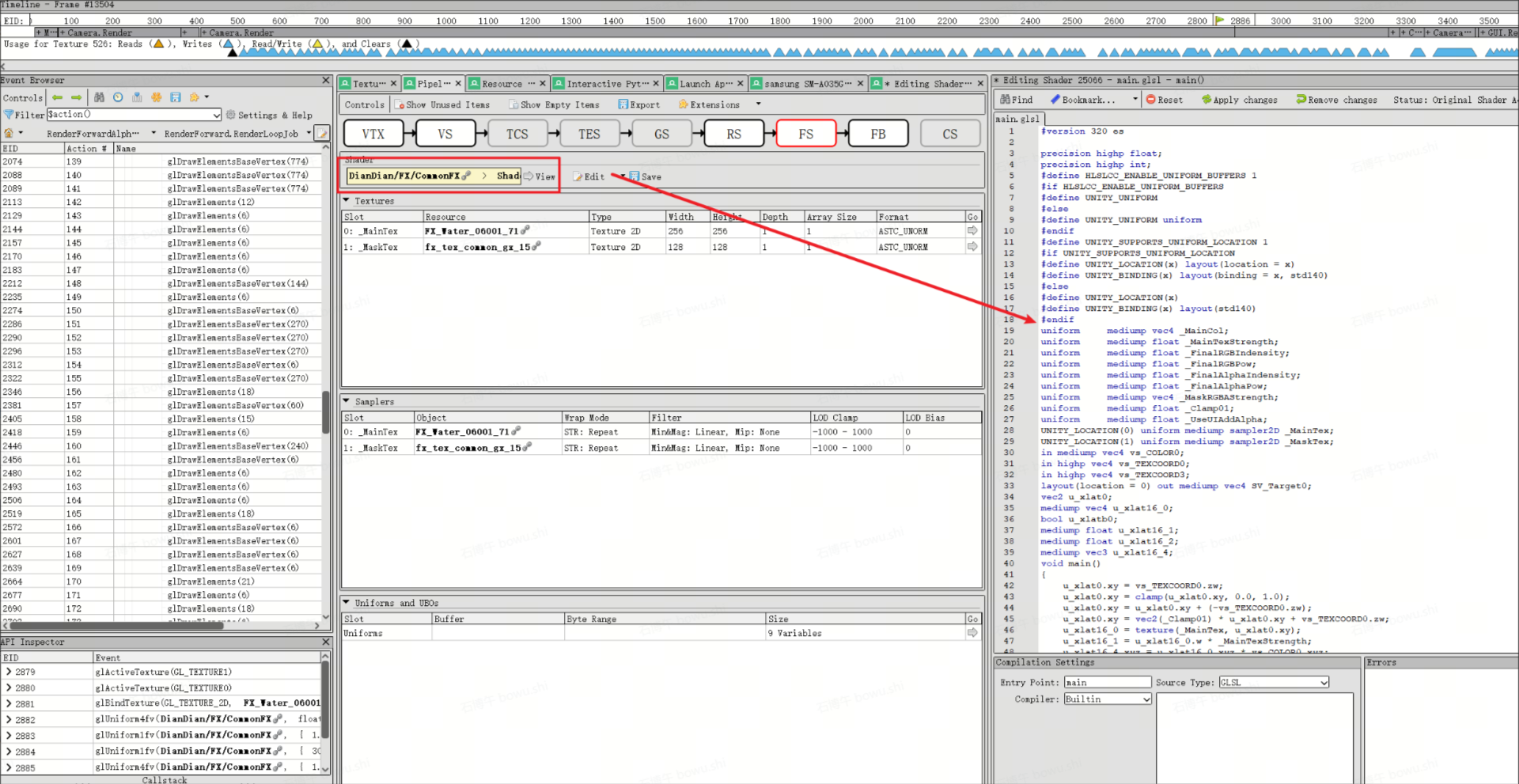
如上图在Pipeline State窗口可以查看每一个DrawCall对应的Shader代码。同时点击Save可以保存当前DC对应的FS/VS shader到本地。
但由于一个场景几百个DC,不可能一个一个点击保存shader,需要批量进行导出。
renderdoc提供了python API接口,同时在renderdoc中提供了直接运行python脚本的窗口。
https://renderdoc.org/docs/python_api/qrenderdoc/main.html#qrenderdoc.CaptureContext.CurPipelineState
为了后面工具编译数据方便,将VS Shader保存为xxx.vert,将FS Shader保存为xxx.frag
1.2 shader编译
使用Mali提供的malioc工具来编译Shader
https://developer.arm.com/Tools%20and%20Software/Mali%20Offline%20Compiler
编译指令:
malioc.exe -f "xxx.frag" -d -c Mali-G57 #Mali-G57为期望Shader编译的对应平台
1.3 编译数据
malioc.exe -f D:\my_shader_exports\高级_家园_GOFCN\ResourceId__55_Program_Hidden_Internal-GUITexture.frag -d -c Mali-G57
Mali Offline Compiler v8.7.0 (Build cbd520)
Copyright (c) 2007-2025 Arm Limited. All rights reserved.
Configuration
=============
Hardware: Mali-G57 r0p1
Architecture: Valhall
Driver: r51p0-00rel0
Shader type: OpenGL ES Fragment
Main shader
===========
Work registers: 8 (25% used at 100% occupancy)
Uniform registers: 4 (3% used)
Stack use: false
16-bit arithmetic: 33%
A FMA CVT SFU LS V T Bound
Total instruction cycles: 0.19 0.19 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.50 0.25 V
Shortest path cycles: 0.19 0.19 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.50 0.25 V
Longest path cycles: 0.19 0.19 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.50 0.25 V
A = Arithmetic, FMA = Arith FMA, CVT = Arith CVT, SFU = Arith SFU,
LS = Load/Store, V = Varying, T = Texture
Shader properties
=================
Has uniform computation: false
Has side-effects: false
Modifies coverage: false
Uses late ZS test: false
Uses late ZS update: false
Reads color buffer: false
Note: This tool shows only the shader-visible property state.
API configuration may also impact the value of some properties.
二、shader Cycles影响因素测试
2.1 同一个shader在不同架构的GPU上的表现研究
|
设备 |
三星Galaxy A03 |
红米12 C |
|
GPU |
Mali-G57 MP1 |
Mali-G52 MC2 |
|
GPU 架构 |
Valhall |
Bifrost |
|
Shader interPolator Cycles |
2.06百万Cycles |
2.72百万Cycles |
|
Shader Arithmetic Cycles |
3.16百万Cycles |
5.79百万Cycles |
|
Shader LoadStore Cycles |
0.01百万cycles |
0.04百万Cycles |
|
Shader Texture Cycles |
0.32百万Cycles |
0.65百万Cycles |
|
Work registers |
31 (96% used at 100% occupancy) |
31 (96% used at 100% occupancy) |
|
Uniform registers |
20 (15% used) |
26 (20% used) |
|
Total instruction cycles A |
2.53 |
2.92 |
|
Total instruction cycles FMA |
2.53 |
———— |
|
Total instruction cycles CVT |
0.16 |
———— |
|
Total instruction cycles SFU |
1.88 |
———— |
|
Total instruction cycles LS |
0.00 |
0.00 |
|
Total instruction cycles V |
1.50 |
1.50 |
|
Total instruction cycles T |
0.00 |
0.00 |
上表中同一个shader在不同GPU上的主要差异:
Uniform registers使用数量不同:
这里简单了解下什么是Work Registers寄存器与Uniform Registers寄存器。
寄存器是GPU内部用来存放变量的存储单元,Work Registers为线程独享用来存放临时变量和中间结果的寄存器。Uniform为用来存放所有线程共享,shader外部传入的常量的寄存器。
Work Registers寄存器与计算复杂度有关但总体是GPU自行调度,想要优化的GPU Shader Cycles整体关系不大,暂时忽略。Uniform registers数量不同,同样为架构特性。
Mali-G52与Mali-G57算数单元同一个shader,算数单元Cycles差别比较大:
Mali-G52为Bifrost架构,Mali-G57为Valhall架构。下图官方文档中两种架构的架构图。可以发现在Valhall架构上,算数单元被细分同时可以并行执行。减少了算数指令在单一算数单元中排队等待的情况。
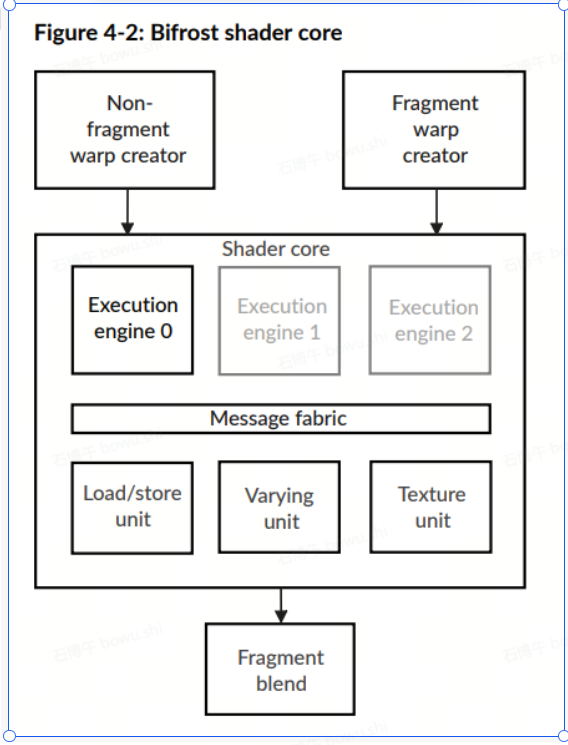
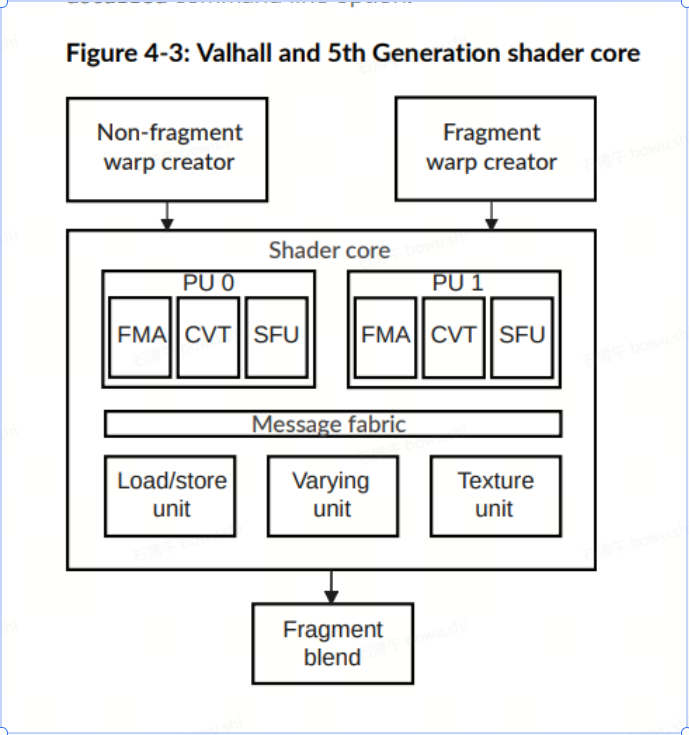
本测试得到的结论:
更复杂的数学运算对于Mali bifrost架构的设备对GPU占用的影响远比Valhall高的多,shader 不同硬件上做LOD是必要的,不同硬件做LOD时LOD值的指定应该考虑不同GPU架构的情况。
2.2 变量精度对shader Cycles的影响:highp、mediump(float、half)
测试用例:unity中找一个shader改成两份变量精度分别为Float,Half的shader。真机测试查看其Shader Cycles情况。
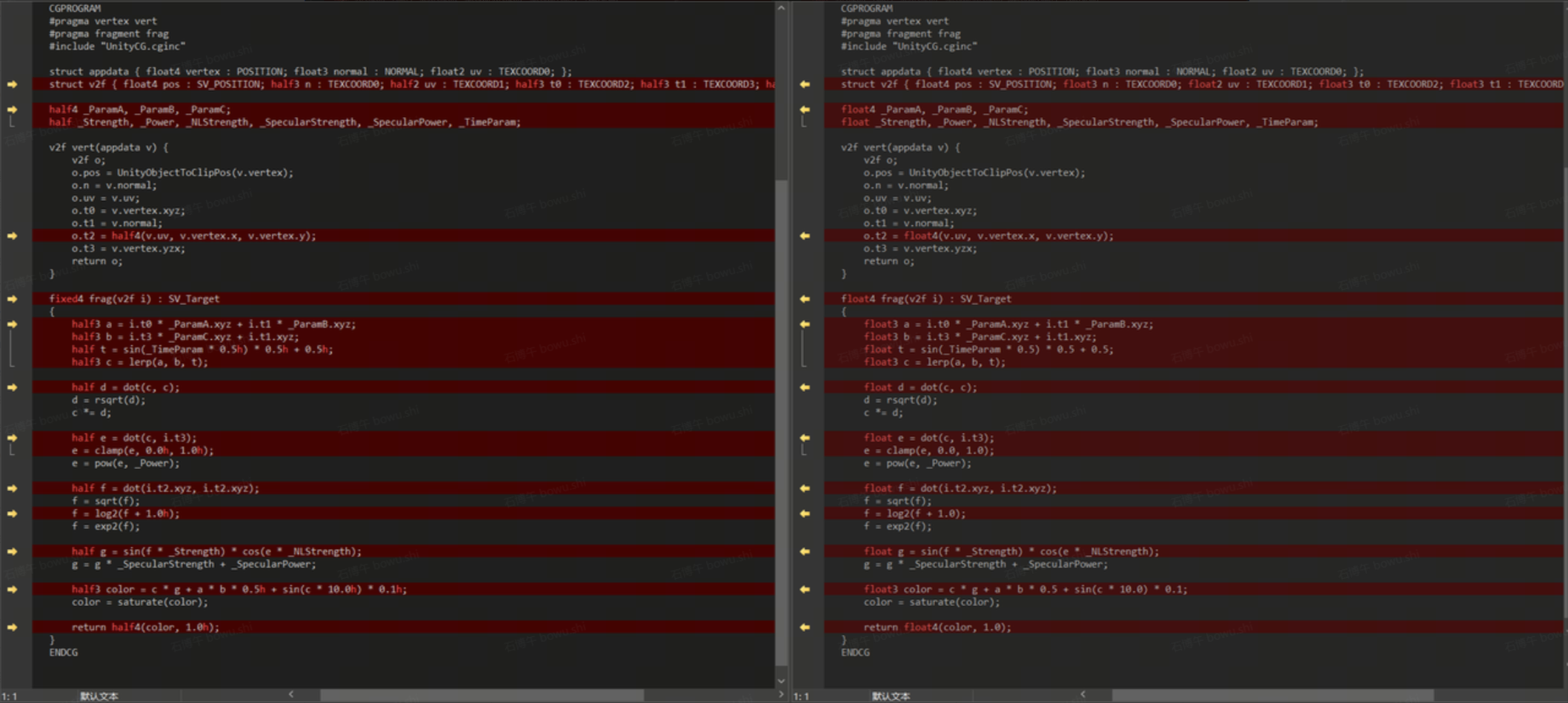
|
设备_精度 |
三星Galaxy A03_mediump |
三星Galaxy A03_highp |
红米12 C_mediump |
红米12 C_highp |
|
GPU |
Mali-G57 MP1 |
Mali-G57 MP1 |
Mali-G52 MC2 |
Mali-G52 MC2 |
|
GPU 架构 |
Valhall |
Valhall |
Bifrost |
Bifrost |
|
Shader interPolator Cycles |
1.2百万Cycles |
2.06百万Cycles |
1.53百万Cycles |
2.72百万Cycles |
|
Shader Arithmetic Cycles |
2.9百万Cycles |
3.16百万Cycles |
5.19百万Cycles |
5.79百万Cycles |
|
Shader LoadStore Cycles |
0.01百万Cycles |
0.01百万cycles |
0.04百万Cycles |
0.04百万Cycles |
|
Shader Texture Cycles |
0.32百万Cycles |
0.32百万Cycles |
0.64百万Cycles |
0.65百万Cycles |
|
片段着色器数据: | ||||
|
Work registers |
32 (100% used at 100% occupancy) |
31 (96% used at 100% occupancy) |
30 (93% used at 100% occupancy) |
31 (96% used at 100% occupancy) |
|
Uniform registers |
14 (10% used) |
20 (15% used) |
20 (15% used) |
26 (20% used) |
|
16-bit arithmetic: |
32% |
0% |
29% |
0% |
|
Total instruction cycles A |
2.40 |
2.53 |
2.67 |
2.92 |
|
Total instruction cycles FMA |
2.40 |
2.53 |
———— |
———— |
|
Total instruction cycles CVT |
0.16 |
0.16 |
———— |
———— |
|
Total instruction cycles SFU |
1.88 |
1.88 |
———— |
———— |
|
Total instruction cycles LS |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
|
Total instruction cycles V |
1.00 |
1.50 |
1.00 |
1.50 |
|
Total instruction cycles T |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
|
顶点着色器数据: | ||||
|
--Position variant | ||||
|
Work registers |
16 (50% used at 100% occupancy) |
16 (50% used at 100% occupancy) |
32 (100% used at 100% occupancy) |
32 (100% used at 100% occupancy) |
|
Uniform registers |
40 (31% used) |
40 (31% used) |
48 (37% used) |
48 (37% used) |
|
16-bit arithmetic: |
0% |
0% |
0% |
0% |
|
Total instruction cycles A |
1.40 |
1.40 |
1.21 |
1.21 |
|
Total instruction cycles FMA |
1.40 |
1.40 |
———— |
———— |
|
Total instruction cycles CVT |
0.19 |
0.19 |
———— |
———— |
|
Total instruction cycles SFU |
0.12 |
0.12 |
———— |
———— |
|
Total instruction cycles LS |
3.00 |
3.00 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
|
Total instruction cycles T |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
|
--Varying variant | ||||
|
Work registers |
13 (40% used at 100% occupancy) |
20 (62% used at 100% occupancy) |
23 (71% used at 100% occupancy) |
24 (75% used at 100% occupancy) |
|
Uniform registers |
8 (6% used) |
8 (6% used) |
40 (31% used) |
40 (31% used) |
|
16-bit arithmetic: |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Total instruction cycles A |
0.28 |
0.28 |
0.08 |
0.08 |
|
Total instruction cycles FMA |
0.00 |
0.00 |
———— |
———— |
|
Total instruction cycles CVT |
0.28 |
0.28 |
———— |
———— |
|
Total instruction cycles SFU |
0.00 |
0.00 |
———— |
———— |
|
Total instruction cycles LS |
7.00 |
9.00 |
15.00 |
15.00 |
|
Total instruction cycles T |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
测试结论:
shader变量全局使用float对比half会导致:插值操作相关的shader Cycles大量增加,主要消耗发生在片元阶段对像素的插值操作。在对精度要求不是那么高在手机游戏上,尽可能的使用half精度的变量可以较大的减少Shader interPolator Cycles。
2.3 插值变量数量对Shader Cycles的影响
|
设备_精度 |
三星Galaxy A03_插值变量一个 |
三星Galaxy A03_插值变量5个 |
|
GPU |
Mali-G57 MP1 |
Mali-G57 MP1 |
|
GPU 架构 |
Valhall |
Valhall |
|
Shader interPolator Cycles |
0.8百万Cycles |
2.06百万Cycles |
|
Shader Arithmetic Cycles |
0.3百万Cycles |
0.63百万Cycles |
|
Shader LoadStore Cycles |
0.01百万Cycles |
0.01百万Cycles |
|
Shader Texture Cycles |
0.43百万Cycles |
0.32百万Cycles |
|
片段着色器数据: | ||
|
Work registers |
6 (18% used at 100% occupancy) |
17 (53% used at 100% occupancy) |
|
Uniform registers |
0 (0% used) |
0 (0% used) |
|
16-bit arithmetic: |
N/A |
0% |
|
Total instruction cycles A |
0.09 |
0.44 |
|
Total instruction cycles FMA |
0.00 |
0.44 |
|
Total instruction cycles CVT |
0.09 |
0.03 |
|
Total instruction cycles SFU |
0.00 |
0.12 |
|
Total instruction cycles LS |
0.00 |
0.00 |
|
Total instruction cycles V |
0.25 |
1.25 |
|
Total instruction cycles T |
0.00 |
0.00 |
测试结论:
插值变量数量主要对Shader interPolator Cycles的影响较大
2.4 计算复杂度对shader Cycles的影响
测试方法:每个shader只使用单独的计算函数且尽量只用一行计算。
| FileName | Shader Arithmetic Cycles | Total instruction cycles _A | Total instruction cycles _FMA | Total instruction cycles _CVT | Total instruction cycles _SFU | Total instruction cycles _LS | Total instruction cycles _V | Total instruction cycles _T |
| cos) | 0.33百万Cycles | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0 | 0.12 | 0 |
| sin() | 0.33百万Cycles | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0 | 0.12 | 0 |
| sqrt() | 0.25百万Cycles | 0.25 | 0 | 0.09 | 0.25 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| exp() | 0.25百万Cycles | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| LerpClamp() | 0.25百万Cycles | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| log() | 0.21百万Cycles | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| log2() | 0.21百万Cycles | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| exp2() | 0.21百万Cycles | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| 加减乘除 | 0.22百万Cycles | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| max() | 0.22百万Cycles | 0.12 | 0 | 0.12 | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| rsqrt() | 0.18百万Cycles | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| dot() | 0.14百万Cycles | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| Pow() | 0.14百万Cycles | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0 | 0 | 0.12 | 0 |
| FileName | Shader Arithmetic Cycles | Total instruction cycles _A | Total instruction cycles _LS | Total instruction cycles _V | Total instruction cycles _T |
| cos() | 1.03 | 0.46 | 0 | 0.12 | 0 |
| sin() | 1.03 | 0.46 | 0 | 0.12 | 0 |
| log() | 0.88 | 0.38 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| log2() | 0.8 | 0.38 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| exp2() | 0.88 | 0.33 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| sqrt() | 0.8 | 0.33 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| dot() | 0.65 | 0.29 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| exp() | 0.88 | 0.29 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| 加减乘除 | 0.88 | 0.29 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| Pow() | 0.65 | 0.29 | 0 | 0.12 | 0 |
| rsqrt() | 0.73 | 0.29 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| LerpClamp() | 0.73 | 0.25 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
| max() | 0.58 | 0.25 | 0 | 0.25 | 0 |
测试结论:
更复杂的数学函数计算直接影响Shader Arithmetic Cycles,三角函数计算是所有数学计算中复杂程度最高的。
valhall架构由于可以并行计算对比bifrost架构优化比较明显。
2.5 贴图对shaderCycles的影响
Mali-G57:
| 测试用例 | Shader Texture Cycles | Total instruction cycles_A | Total instruction cycles_FMA | Total instruction cycles_CVT | Total instruction cycles_SFU | Total instruction cycles_LS | Total instruction cycles_V | Total instruction cycles_T |
| 1张512*512贴图 采样1次 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| 1张512*512贴图 采样2次 | 0.9 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| 1张512*512贴图 采样3次 | 1.18 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.75 |
| 采样1张贴图 每张1次 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| 采样2张贴图 每张1次 | 0.9 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| 采样3张贴图 每张1次 | 1.18 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.75 |
| 1张256*256贴图 采样3次 | 1.18 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.75 |
| 1张512*512贴图 采样3次 | 1.18 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.75 |
| 1张1024*1024贴图 采样3次 | 1.18 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.75 |
Mali-G52
| FileName | Total instruction cycles_A | Total instruction cycles_LS | Total instruction cycles_V | Total instruction cycles_T |
| 1张512*512贴图 采样1次 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| 1张512*512贴图 采样2次 | 0.21 | 0 | 0.25 | 1 |
| 1张512*512贴图 采样3次 | 0.38 | 0 | 0.25 | 1.5 |
| 采样1张贴图 每张1次 | 0.38 | 0 | 0.25 | 1.5 |
| 采样2张贴图 每张1次 | 0.38 | 0 | 0.25 | 1.5 |
| 采样3张贴图 每张1次 | 0.38 | 0 | 0.25 | 1.5 |
| 1张256*256贴图 采样3次 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| 1张512*512贴图 采样3次 | 0.17 | 0 | 0.25 | 1 |
| 1张1024*1024贴图 采样3次 | 0.21 | 0 | 0.25 | 1.5 |
测试结论:
Shader Texture Cycles主要受实际shader中采样次数的影响,采三张贴图在shader中每张采样一次和采样一张贴图在shader中每张采样三次总的Shader Texture Cycles相同。同时Shader Texture Cycles不受实际贴图的分辨率影响。
2.6 Overdraw对场景Shader Cycles的影响
测试方法:
1.不采样贴图的半透面片叠加
2.采样贴图的半透面片叠加
| 测试用例 | 总shader Cycles | Shader InterPolator Cycles | shader Arithmetic Cycles | Shader LoadStore Cycles | shader Texture Cycles |
| 不采样贴图,叠加1个半透面片 | 2.38 | 1.25 | 0.79 | 0.02 | 0.32 |
| 不采样贴图,叠加100个半透面片 | 4.6 | 1.31 | 2.87 | 0.06 | 0.36 |
| 采样1张雾效贴图,叠加1个半透面片 | 2.64 | 1.36 | 0.82 | 0.02 | 0.44 |
| 采样1张雾效贴图,叠加一百个半透面片 | 16.69 | 7.4 | 2.42 | 0.42 | 6.44 |
测试结论:
Overdraw会线性放大Shader的所有消耗,对于采样了贴图的半透明特效贴图采样和插值消耗增加尤其明显。
2.7 向量归一化计算:dot+inversesqrt 与直接使用normalize计算之间的区别

官方文档中有这样一段话:避免编写自己的运算。
dot+inversesqrt是做归一化向量计算的
normalize也是做归一化向量计算的
猜想:直接使用normalize指令更少性能更好
验证发现:
在移动端真机上normalize会被转化成dot+inversesqrt再做计算 性能没有差异
同样的pow会被转换成log2+exp2的形式计算
2.8 总结
Shader Interpolator Cycles
-
含义:主要统计由顶点着色器到片段着色器插的插值操作
-
影响因素:插值变量的数量、插值变量的精度(float/half)
Shader Arithmetic Cycles
-
含义:统计所有算术运算的消耗,包括加减乘除、三角函数、对数等等
-
影响因素:单个shader中计算量的多少及数学运算函数的复杂度
Shader Texture Cycles
-
含义:统计纹理采样的消耗
-
影响因素:纹理采样次数
三、shader Cycles到底是怎么统计出来的以及shader各种指标的探究
3.1 shaderCyclesde的计算方法
从上面简单的测试,得到了shaderCycles的的一部分影响因素。
官方的测试工具Streamline中并不直接统计GPU Shader Cycles,只有UWA这样统计,官方统计的是统计的core unit Utilization。

不过从core unit Utilization的计算方式可以反推出GPU Shader Cycles的计算方式:
Arithmetic unit utilization: max(min(($MaliALUInstructionsExecutedInstructions / $MaliShaderCoreCyclesExecutionCoreActive) * 100, 100), 0)
Varying unit utilization: max(min((($MaliVaryingUnitIssues32BitInterpolationIssues + $MaliVaryingUnitIssues16BitInterpolationIssues) / $MaliShaderCoreCyclesExecutionCoreActive) * 100, 100), 0)
Texture unit utilization: max(min(($MaliTextureUnitCyclesTextureFilteringActive / $MaliShaderCoreCyclesExecutionCoreActive) * 100, 100), 0)
Load/store unit utilization: max(min((($MaliLoadStoreUnitCyclesFullRead + $MaliLoadStoreUnitCyclesPartialRead + $MaliLoadStoreUnitCyclesFullWrite + $MaliLoadStoreUnitCyclesPartialWrite + $MaliLoadStoreUnitCyclesAtomicAccess) / $MaliShaderCoreCyclesExecutionCoreActive) * 100, 100), 0)
上方所有除号前面的值就是每个unit的Cycles。
从上面的计算方法可以得到,计算单元、插值单元、贴图采样单元、LS单元工作的总Cycles加来等于MaliShaderCoreCyclesExecutionCoreActive的Cycles,也就是所有着色器核心活跃的周期数。那么一个GPU的着色器核心总Cycles上限应该是多少?
https://developer.arm.com/documentation/102642/0107/Shader-core-data-path?lang=en
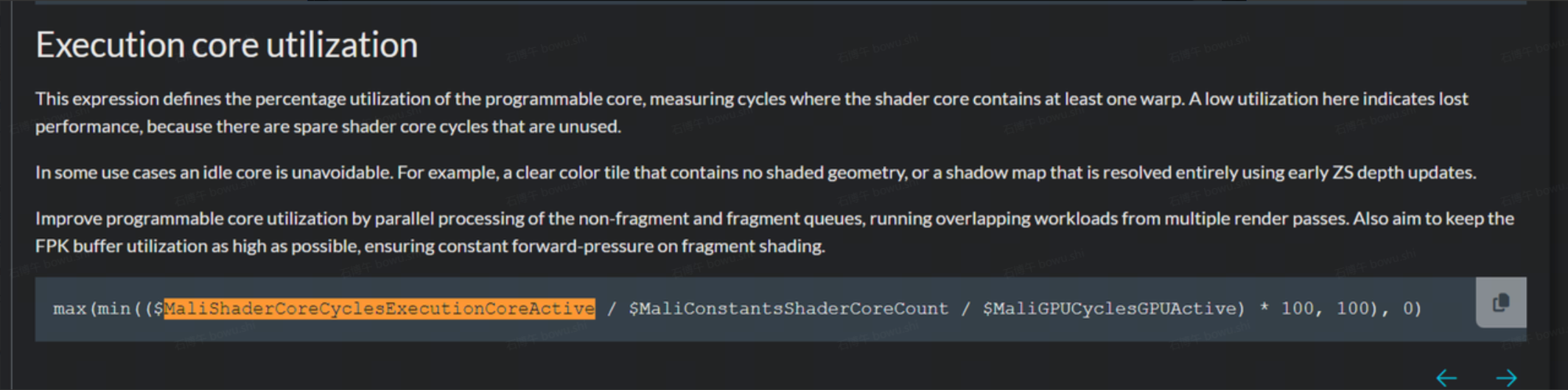
在官网中找到了这样一段关于着色器核心利用率计算的描述:
着色器核心利用率=(着色器核心活跃周期数/着色器核心个数/GPU活跃周期数)*100%
那么其实就可以得到某个GPU着色器核心活跃周期数的上限:
MaliShaderCoreCyclesExecutionCoreActive的最大值=着色器核心个数*GPU理论上最大的活跃周期数
以Mali-G57 MP1为例:
GPU Clocks:GPU 频率:

384MHz~650MHz之间切换
GPU 时钟周期数: 384,000,000 cycles~650,000,000 cycles
时钟周期为时钟频率取倒数即GPU 时钟周期耗时为 1/384,000,000~1/650,000,000=2.604ns~1.538ns
GPU名称中的MP1为此GPU的最大核心数量。
也就是说Valhall架构的最大核心数为1的Mali-G57 MP1,其理论上着色器核心活跃周期数的上限等于GPU活跃时钟周期数的上限,也就是每秒650,000,000Cycles。
用一个Mali-G76 MP10的设备,使用unity构建一个使用了无比复杂的shader的场景的demo真机测试采集数据:
Mali-G76 MP10的shader核心数量为10个,理论上复杂场景的GPU Total cycles应该远大于GPU 时钟周期数,见下图数据,GPU ToTal Cycles的总数为GPU 活跃时钟周期数的9.22倍,符合理论。
从这里再次回看3.1的对比测试,在之前的理解里,Mali-G52 MC2设备上,总的shader Cycles更高,GPU性能消耗更大,GPU耗时会更高。但现在看来似乎并非如此。找到之前的某一份测试数据对数据做补充整理数据如下表:
|
设备 |
三星Galaxy A03 |
红米12 C |
|
GPU |
Mali-G57 MP1 |
Mali-G52 MC2 |
|
GPU 架构 |
Valhall |
Bifrost |
|
Shader Core Count |
1 |
2 |
|
Total Sahder Cycles |
1.27百万Cycles/帧 |
2.36百万Cycles/帧 |
|
GPU Clocks |
133.24万Clocks/帧 |
87.06万cycles/帧 |
|
GPU Time |
6.20ms |
5.70ms |
|
Fragment shaded |
236.85万个/帧 |
244.05万个/帧 |
|
GPU shader instructions |
0.32 百万个/帧 |
1.02百万个/帧 |
|
GPU Cycles/Pixel |
0.57 Cycles/帧 |
0.36 cycles/帧 |
可以发现,虽然Mali-G52 MC2上的shader Cycles更高,但整体GPU耗时其实更低。不能说明shader在Mali-G52 MC2运行表现的性能更差。
3.2 Mali官方各指标的计算方法解析
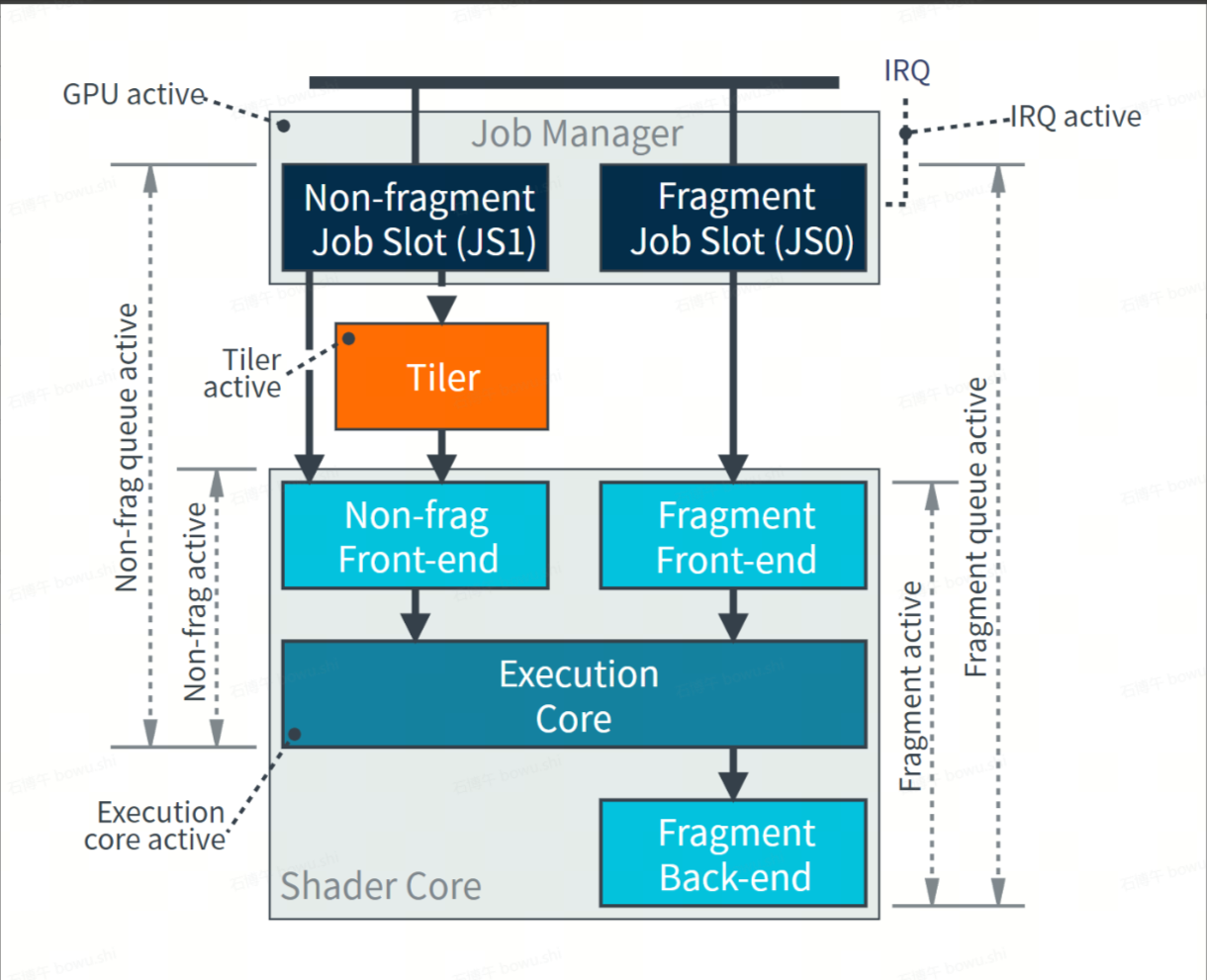
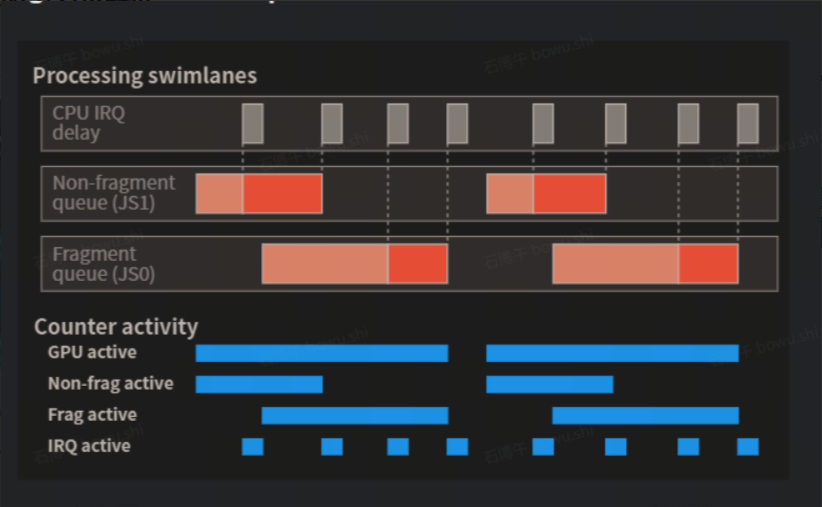
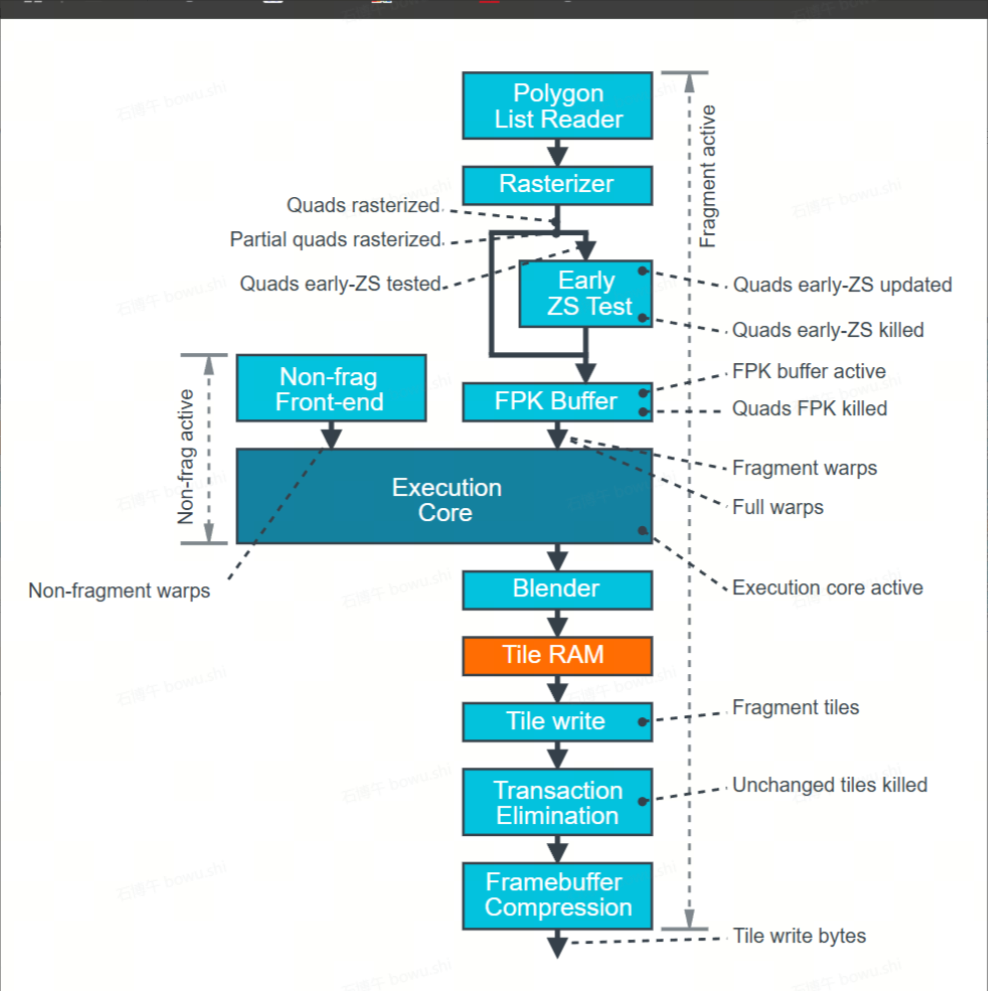
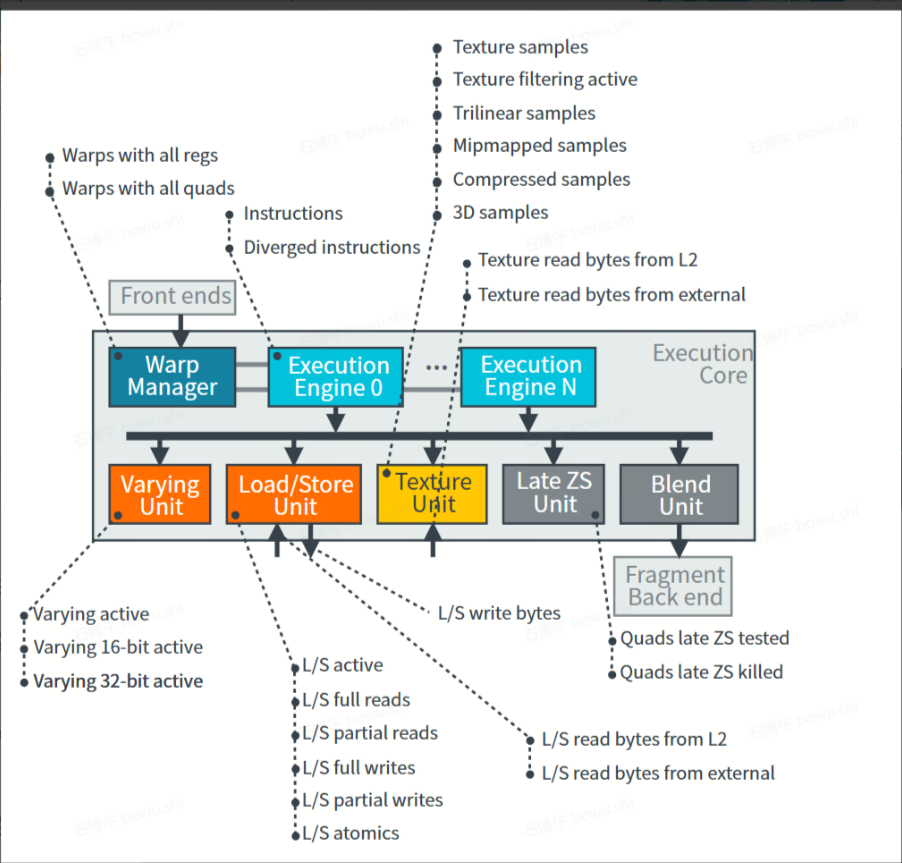
3.2.1 GPU 性能的汇总指标:Mali GPU Usage、Mali GPU Utilization GPU
对应GPU top level图。
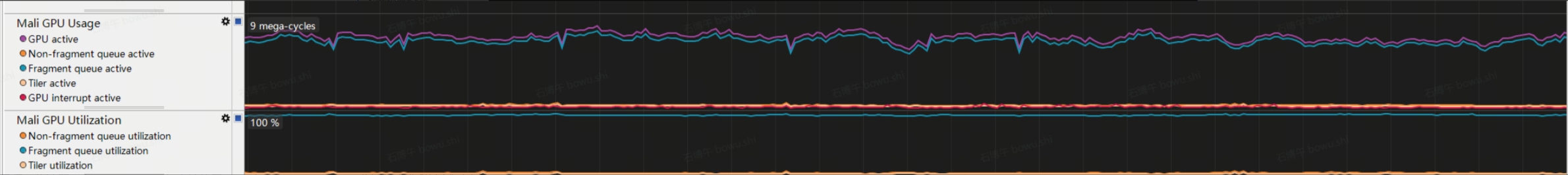
GPU active cycles:
GPU 活跃周期,只要GPU中任意队列工作,此指标都会递增。
Non-Fragment QueQue active:
非片元队列活跃周期。
Fragment QueQue active:
片元队列活跃周期
3.2.2 shader Core的汇总指标:Mali Core Utilization、Mali shader Core Cycles


指标统计重点关注一下Utilization的计算方法:
Non-fragment utilization:
max(min(($MaliShaderCoreCyclesNonFragmentActive / $MaliConstantsShaderCoreCount / $MaliGPUCyclesGPUActive) * 100, 100), 0)
Fragment utilization:
max(min(($MaliShaderCoreCyclesFragmentActive / $MaliConstantsShaderCoreCount / $MaliGPUCyclesGPUActive) * 100, 100), 0)
Fragment FPK buffer utilization:
max(min(($MaliShaderCoreCyclesFragmentFPKBufferActive / $MaliShaderCoreCyclesFragmentActive) * 100, 100), 0)
Execution core utilization:
max(min(($MaliShaderCoreCyclesExecutionCoreActive / $MaliConstantsShaderCoreCount / $MaliGPUCyclesGPUActive) * 100, 100), 0)
可以发现计算都是各指标除以shader core数量再除以Mali GPU cycles
3.2.3 shader core unit相关指标
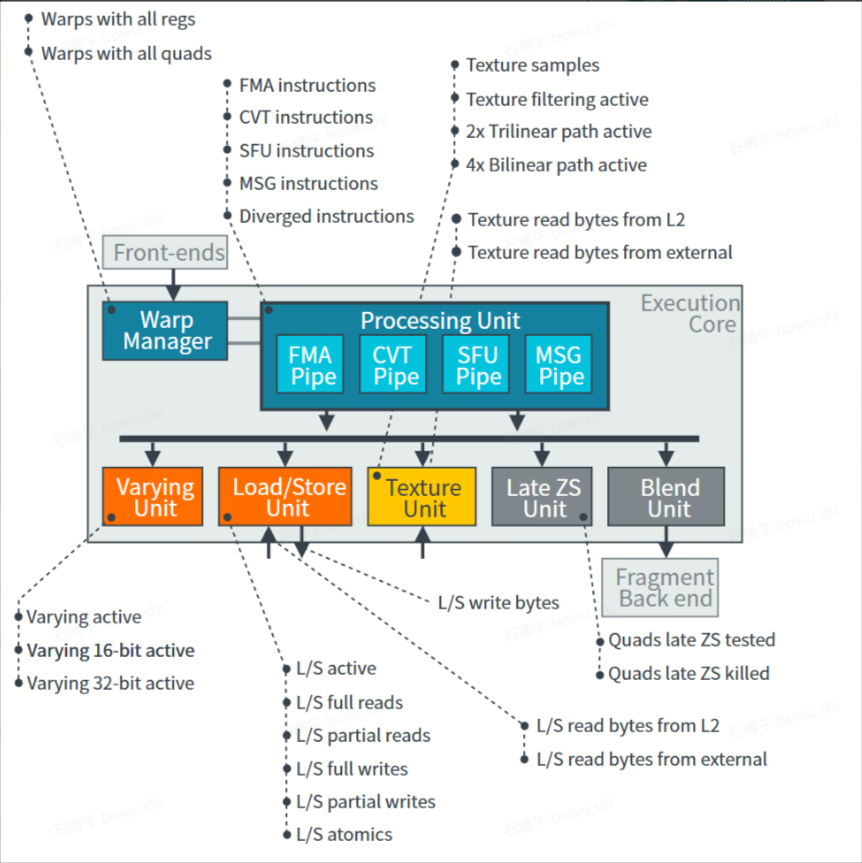
3.2.3.1 Mali ALU Instructions
Valhall架构
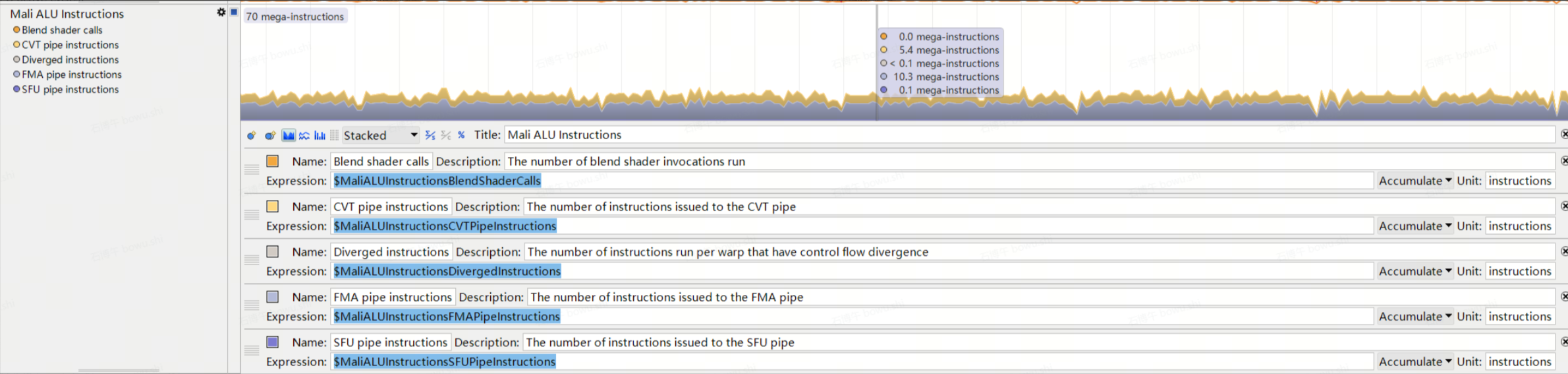
$MaliALUInstructionsBlendShaderCalls: 混合着色器调用次数
$MaliALUInstructionsCVTPipeInstructions:类型转换管线执行指令数
$MaliALUInstructionsDivergedInstructions:分支指令执行数
$MaliALUInstructionsFMAPipeInstructions:乘加融合计算指令执行执行数
$MaliALUInstructionsSFUPipeInstructions:特殊函数计算指令执行数
那么对于此架构的GPU 总的着色器指令数就是
Mali ALU Instructions = MaliALUInstructionsCVTPipeInstructions + MaliALUInstructionsFMAPipeInstructions + MaliALUInstructionsSFUPipeInstructions
Bifrost架构

对于Bifrost架构,计算单元中没有再被细分,因此这里统计:$MaliALUInstructionsExecutedInstructions 就是总的shader指令数
3.2.3.2 Mali Core Unit Utilization
Valhall架构
Arithmetic unit utilization:
计算单元在可编程核心中的利用百分比。计算公式如下:
max(min((max($MaliALUInstructionsFMAPipeInstructions, max($MaliALUInstructionsCVTPipeInstructions, $MaliALUInstructionsSFUPipeInstructions * 4)) / $MaliShaderCoreCyclesExecutionCoreActive) * 100, 100), 0)
从这个公式可以发现,由于Valhall架构计算单元中FMA、CVT、SFU并行,最终的占用百分比是取三个计算管线中最大的一个来除以shader Core的活跃周期。
在优化计算单元时应该结合各个计算管线的指令先优化指令数最高的管线。
Varying unit utilization:
变量单元的利用率。计算公式如下:
max(min((($MaliVaryingUnitIssues32BitInterpolationIssues + $MaliVaryingUnitIssues16BitInterpolationIssues) / $MaliShaderCoreCyclesExecutionCoreActive) * 100, 100), 0)
从公式看优化的方式主要就是减少变量的数量。
Texture unit utilization:
纹理单元的利用率。
max(min(($MaliTextureUnitCyclesTextureFilteringActive / $MaliShaderCoreCyclesExecutionCoreActive) * 100, 100), 0)
对于纹理单元,官方的计算方法是纹理过滤操作活跃的周期数。每次采样纹理都会触发一次过滤操作,同时不同的采样方式差别较大,优化方式主要是应该减少采样次数同时使用性能更好的过滤方式。
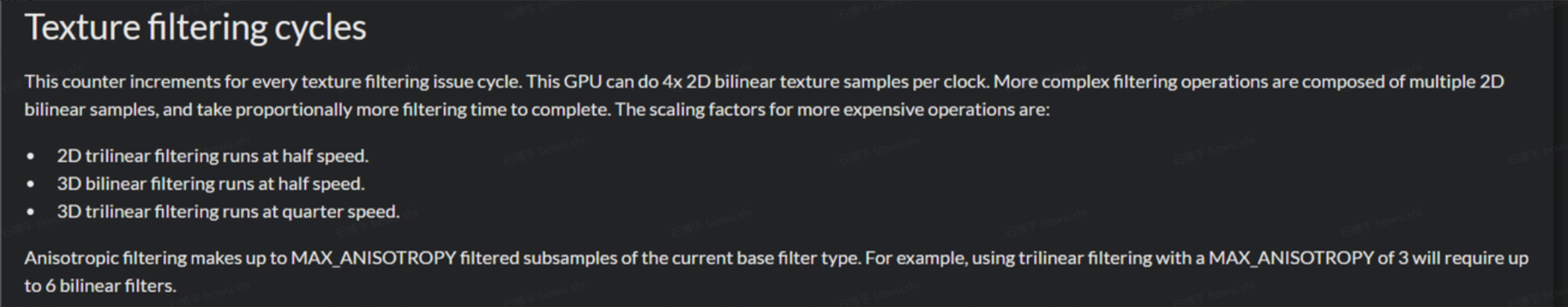
Bifrost架构
Arithmetic unit utilization:
max(min(($MaliALUInstructionsExecutedInstructions / $MaliShaderCoreCyclesExecutionCoreActive) * 100, 100), 0)
Varying unit utilization:
max(min((($MaliVaryingUnitIssues32BitInterpolationIssues + $MaliVaryingUnitIssues16BitInterpolationIssues) / $MaliShaderCoreCyclesExecutionCoreActive) * 100, 100), 0)
Texture unit utilization:
max(min(($MaliTextureUnitCyclesTextureFilteringActive / $MaliShaderCoreCyclesExecutionCoreActive) * 100, 100), 0)
Load/store unit utilization:
max(min((($MaliLoadStoreUnitCyclesFullRead + $MaliLoadStoreUnitCyclesPartialRead + $MaliLoadStoreUnitCyclesFullWrite + $MaliLoadStoreUnitCyclesPartialWrite + $MaliLoadStoreUnitCyclesAtomicAccess) / $MaliShaderCoreCyclesExecutionCoreActive) * 100, 100), 0)
四、shader Cycles在GPU分析中的的作用
同样的需要从GPU架构的角度去思考:
先判断问题出在FS还是VS阶段:
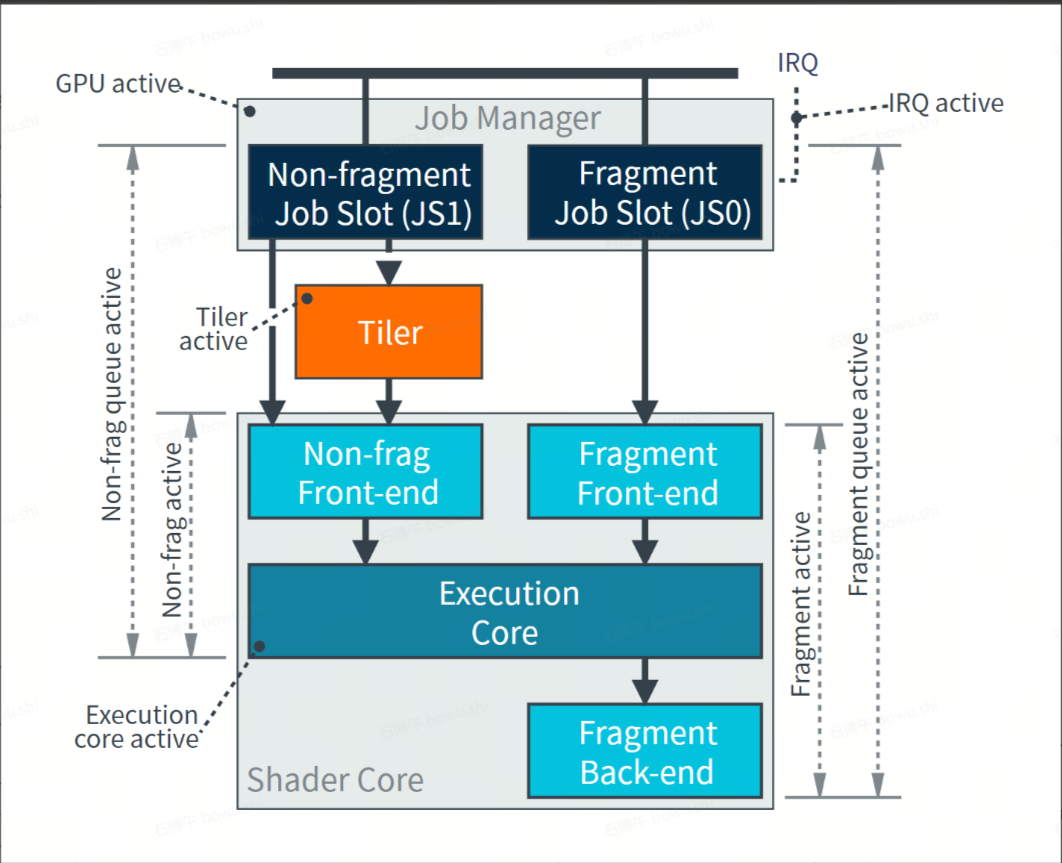
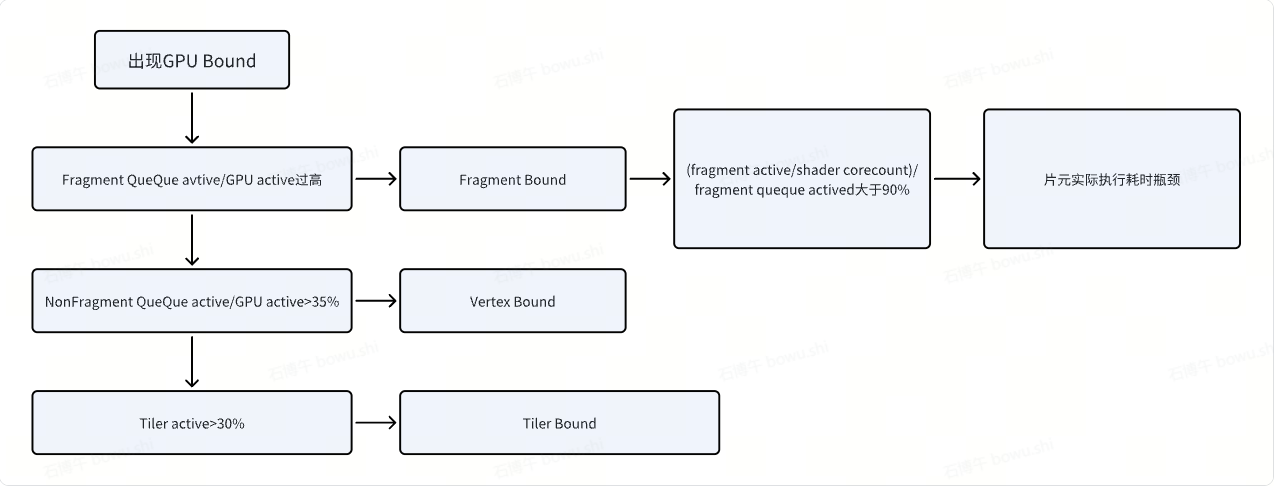
再判断Execution core以外的消耗
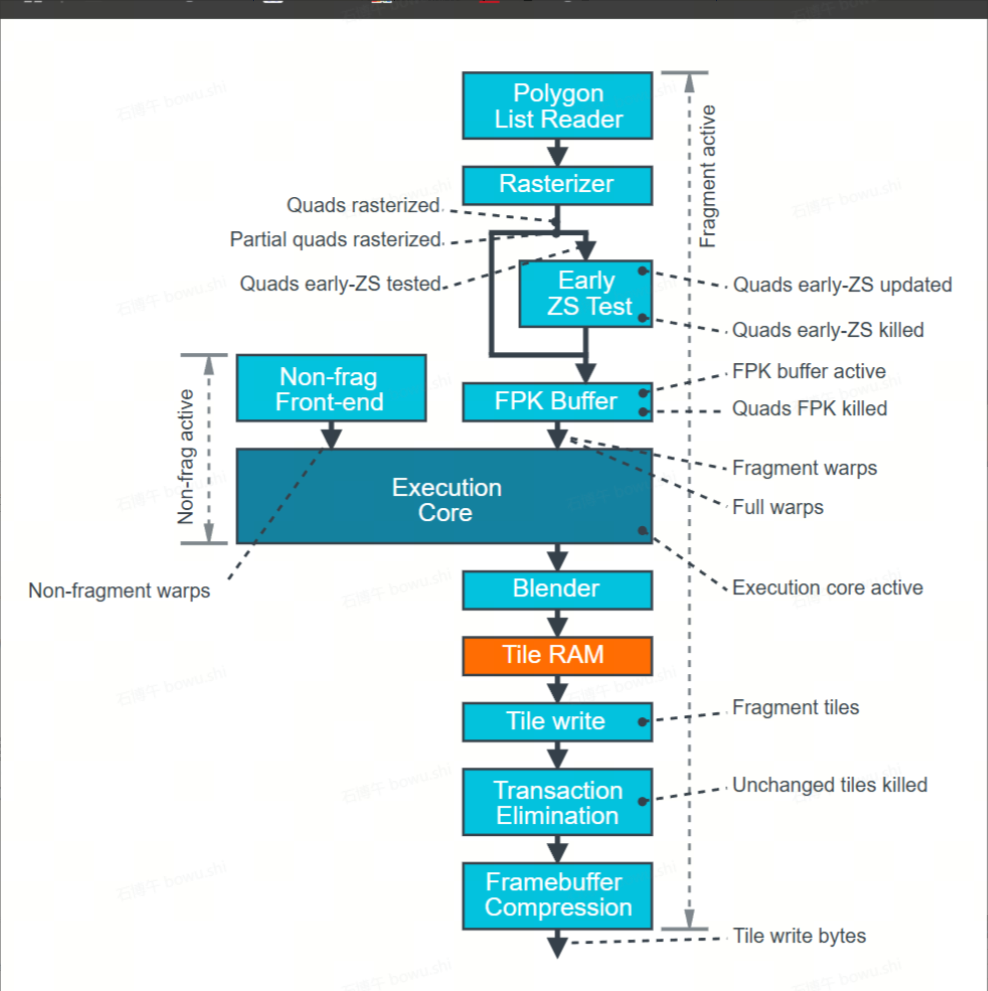

这里一般主要关注Fragment warps数量是不是增加
UWA 中的FS Shaded应该就是这里的 Fragment warps * 此GPU架构每个Warps的thread数量
最后判断Execution core中到底是哪个单元消耗较大
如果 Fragment warps没有变大 则再去分析Execution core是不是增加的的比较多,里面最高的unit是什么。




















 1242
1242

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








