LFM(Latent Factor Model)
参考了[Key_Ky博客](%28http://www.cnblogs.com/Key-Ky/p/3579363.html%29)的潜在矩阵分解的代码,实践了一下。[图及公式取自Harry Huang博客](http://blog.csdn.net/harryhuang1990/article/details/9924377)
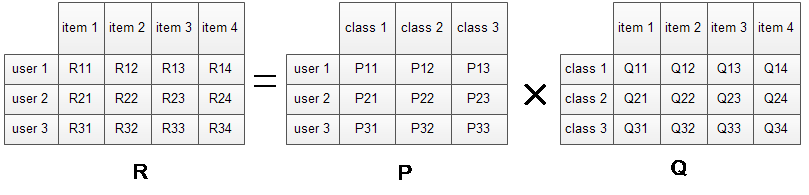
矩阵分解图
目标函数(最小平方误差):
随机梯度求解目标函数中的参数
梯度:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
import math
class LFM:
'''
LFM 使用随机梯度下降法,求解LFM参数
'''
data_address = ''
datasets = []
np_training_datasets =np.zeros(1)
decompose_u = np.zeros(1)
decompose_v = np.zeros(1)
factor = 0
size_training_datasets_x = 0
size_training_datasets_y = 0
alpha = 0.1
iter_num = 20
Lambda = 0.1
epsilon = 0.01
delta_error = []
def __init__(self,data_address,factor,iter_num = 20,alpha = 0.1,Lambda = 0.1,epsilon = 0.01):
'''
@summary: 初始化参数
'''
self.data_address = data_address
self.factor = factor
self.alpha = alpha
self.iter_num = iter_num
self.Lambda = Lambda
self.epsilon = epsilon
def loadData(self):
'''
@summary: 加载原始数据
'''
input_file = open(self.data_address,'r')
for line in input_file:
tmp = line[:-1].split()
self.datasets.append([int(i) for i in tmp])
input_file.close()
self.np_training_datasets = np.array(self.datasets)
def initModel(self):
'''
@summary: 初始化U,V的潜在因子矩阵
'''
[x,y] = self.np_training_datasets.shape
self.size_training_datasets_x = x
self.size_training_datasets_y = y
self.decompose_u = np.ones([x,self.factor])
self.decompose_v = np.ones([self.factor,y])
def fNormcalc(self,matrix):
'''
@summary: 计算矩阵的F范数,即所有元素的平方和再开方
'''
[x,y] = matrix.shape
f_norm = 0
for i in range(x):
for j in range(y):
f_norm += pow(matrix[i][j],2)
f_norm = math.sqrt(f_norm)
return f_norm
#构建目标函数
def c_error_cacl(self):
'''
@summary: 构建目标函数,即误差平方和,以及加上正则化项,防止过拟合
'''
error_sum = 0
for i in range(self.size_training_datasets_x):
for j in range(self.size_training_datasets_y):
if self.np_training_datasets[i][j] != 0 :
#即如果用户i对商品j有评分
eui=0
for m in range(self.factor):
# eui += eui + self.decompose_u[i][m] * self.decompose_v[m][j] #预测的评分!!!!!!!!!!
eui += self.decompose_u[i][m] * self.decompose_v[m][j]
error_sum += pow(self.np_training_datasets[i][j] - eui,2) + self.Lambda * pow(self.fNormcalc(self.decompose_u),2) + self.Lambda * pow(self.fNormcalc(self.decompose_v),2)
return error_sum
#随机梯度下降法,迭代
def iterator(self):
for step in range(self.iter_num):
old_error = 0.5 * self.c_error_cacl() #目标函数1/2可以再梯度下不用乘以2,方便计算
print 'old_error ',old_error
for i in range(self.size_training_datasets_x):
for j in range(self.size_training_datasets_y):
if self.np_training_datasets[i][j] != 0 :
for f in range(self.factor):
eui = 0
for m in range(self.factor):
eui = eui + self.decompose_u[i][m] * self.decompose_v[m][j]
self.decompose_u[i][f] += self.alpha * ((self.np_training_datasets[i][j] - eui) * self.decompose_v[f][j] - self.Lambda * self.decompose_u[i][f])
self.decompose_v[f][j] += self.alpha * ((self.np_training_datasets[i][j] - eui) * self.decompose_u[i][f] - self.Lambda * self.decompose_v[f][j])
new_error = 0.5 * self.c_error_cacl()
print 'new_error ',new_error
if abs(new_error - old_error) < self.epsilon:
break
self.delta_error.append(abs(new_error - old_error)) #保存每一次迭代的误差
if __name__=='__main__':
# randomdata('F://rating.txt')
lfm=LFM(r'F:\rating1.txt',3,100)
lfm.loadData()
lfm.initModel()
lfm.iterator()
print lfm.decompose_u
print lfm.decompose_v
ex = range(len(lfm.delta_error))
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(ex,lfm.delta_error)
plt.show()简单的测试数据集:
0 1 2 0 0 4 0
0 0 0 5 0 6 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 9 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
10 0 9 8 0 0 0
分解的P矩阵:
[[ 0.36717743 1.07801356 0.83258288]
[ 1.22030144 1.19854111 1.16571532]
[ 1. 1. 1. ]
[ 2.05226677 1.46459895 1.31047188]
[ 1. 1. 1. ]
[ 2.75487483 1.50212454 1.32204588]]
分解的Q矩阵:
[[ 2.04842494 0.47546457 2.41670178 1.63844667 2.33548542 1.71443626 1. ]
[ 1.61164606 0.42750604 0.79754534 1.23739612 1.5793569 1.76219035 1. ]
[ 1.38761605 0.50476132 0.77759064 1.15922173 1.36918913 1.47754311 1. ]]
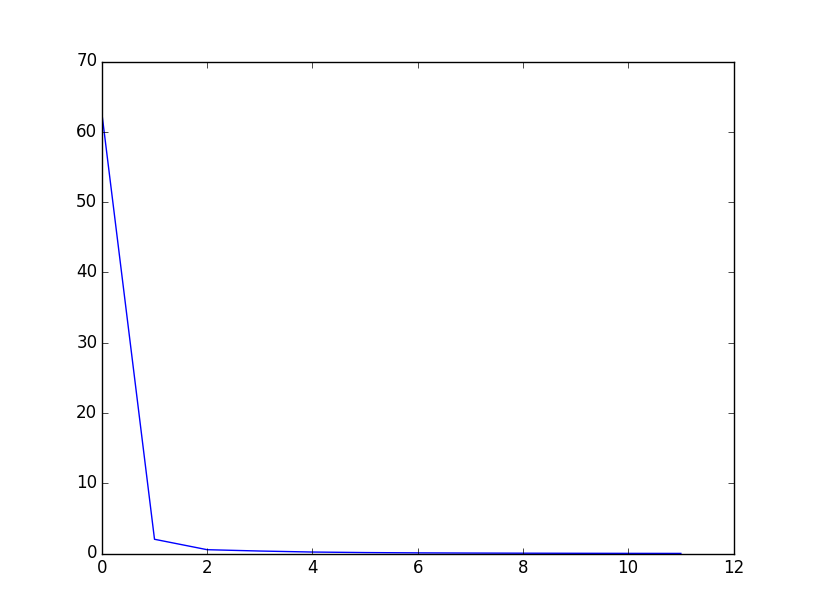
误差函数曲线:
参考文献:
Key_Ky博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/Key-Ky/p/3579363.html
Harry Huang:http://blog.csdn.net/harryhuang1990/article/details/9924377








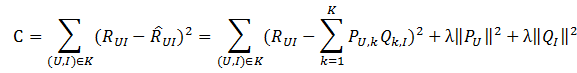
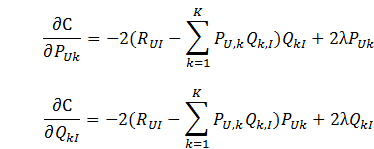
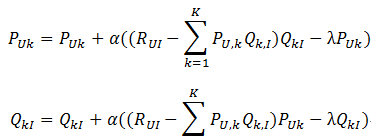














 4766
4766

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








