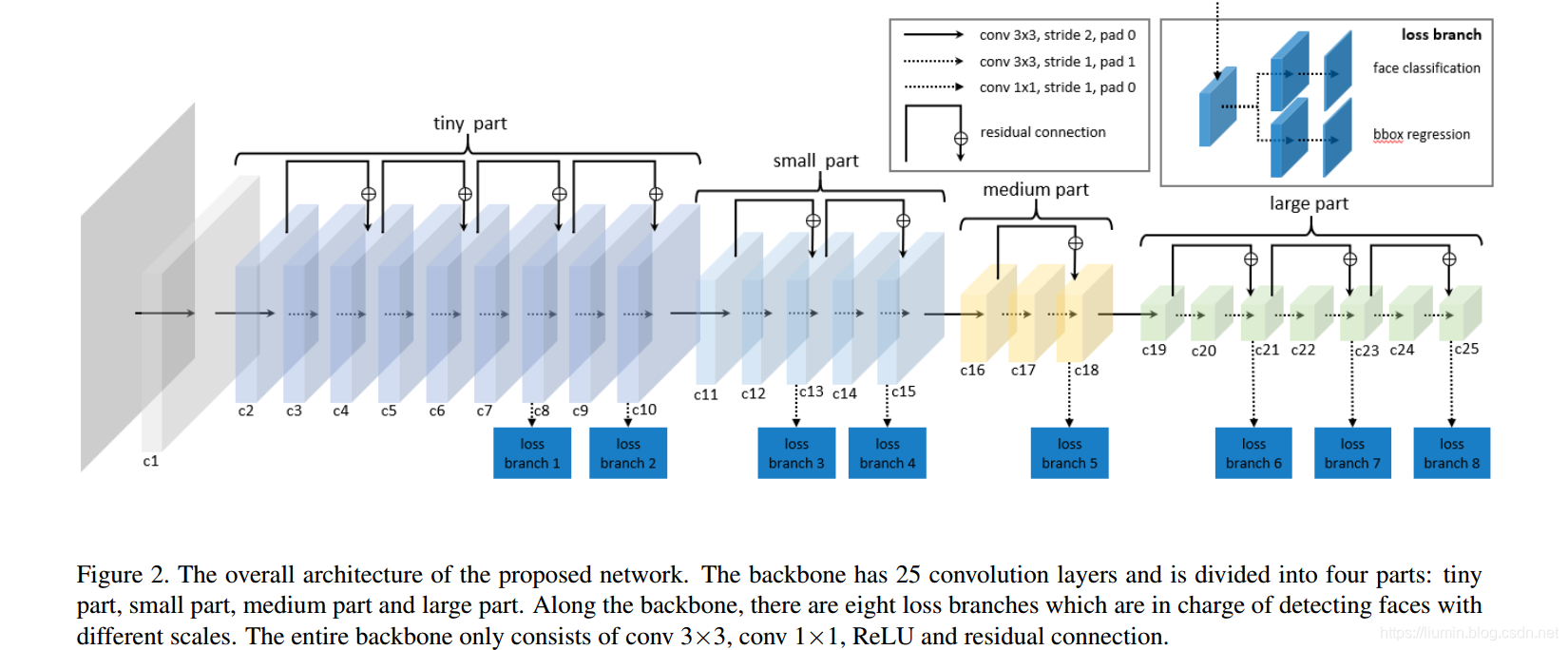
LFFD: A Light and Fast Face Detector for Edge Devices
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.10633.pdf
Pytorch代码: https://github.com/shanglianlm0525/PyTorch-Networks

Pytorch代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
def Conv1x1ReLU(in_channels,out_channels):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
)
def Conv3x3ReLU(in_channels,out_channels,stride,padding):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=padding),
nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
)
class LossBranch(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_channels, mid_channels=64):
super(LossBranch, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = Conv1x1ReLU(in_channels, mid_channels)
self.conv2_score = Conv1x1ReLU(mid_channels, mid_channels)
self.classify = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=mid_channels, out_channels=2, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
self.conv2_bbox = Conv1x1ReLU(mid_channels, mid_channels)
self.regress = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=mid_channels, out_channels=4, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
cls = self.classify(self.conv2_score(x))
reg = self.regress(self.conv2_bbox(x))
return cls,reg
class LFFDBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride):
super(LFFDBlock, self).__init__()
mid_channels = out_channels
self.downsampling = True if stride == 2 else False
if self.downsampling:
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=mid_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=0)
self.branch1_relu1 = nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
self.branch1_conv1 = Conv3x3ReLU(in_channels=mid_channels, out_channels=mid_channels, stride=1, padding=1)
self.branch1_conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=mid_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.relu = nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
if self.downsampling:
x = self.conv(x)
out = self.branch1_conv2(self.branch1_conv1(self.branch1_relu1(x)))
return self.relu(out+x)
class LFFD(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, classes_num = 2):
super(LFFD, self).__init__()
self.tiny_part1 = nn.Sequential(
Conv3x3ReLU(in_channels=3, out_channels=64, stride=2, padding = 0),
LFFDBlock(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, stride=2),
LFFDBlock(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, stride=1),
LFFDBlock(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, stride=1),
)
self.tiny_part2 = LFFDBlock(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, stride=1)
self.small_part1 = LFFDBlock(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, stride=2)
self.small_part2 = LFFDBlock(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, stride=1)
self.medium_part = nn.Sequential(
LFFDBlock(in_channels=64, out_channels=128, stride=2),
LFFDBlock(in_channels=128, out_channels=128, stride=1),
)
self.large_part1 = LFFDBlock(in_channels=128, out_channels=128, stride=2)
self.large_part2 = LFFDBlock(in_channels=128, out_channels=128, stride=1)
self.large_part3 = LFFDBlock(in_channels=128, out_channels=128, stride=1)
self.loss_branch1 = LossBranch(in_channels=64)
self.loss_branch2 = LossBranch(in_channels=64)
self.loss_branch3 = LossBranch(in_channels=64)
self.loss_branch4 = LossBranch(in_channels=64)
self.loss_branch5 = LossBranch(in_channels=128)
self.loss_branch6 = LossBranch(in_channels=128)
self.loss_branch7 = LossBranch(in_channels=128)
self.loss_branch8 = LossBranch(in_channels=128)
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.tiny_part1(x)
branch2 = self.tiny_part2(branch1)
branch3 = self.small_part1(branch2)
branch4 = self.small_part2(branch3)
branch5 = self.medium_part(branch4)
branch6 = self.large_part1(branch5)
branch7 = self.large_part2(branch6)
branch8 = self.large_part3(branch7)
cls1,loc1 = self.loss_branch1(branch1)
cls2,loc2 = self.loss_branch2(branch2)
cls3,loc3 = self.loss_branch3(branch3)
cls4,loc4 = self.loss_branch4(branch4)
cls5,loc5 = self.loss_branch5(branch5)
cls6,loc6 = self.loss_branch6(branch6)
cls7,loc7 = self.loss_branch7(branch7)
cls8,loc8 = self.loss_branch8(branch8)
cls = torch.cat([cls1.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(loc1.size(0), -1),
cls2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(loc1.size(0), -1),
cls3.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(loc1.size(0), -1),
cls4.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(loc1.size(0), -1),
cls5.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(loc1.size(0), -1),
cls6.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(loc1.size(0), -1),
cls7.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(loc1.size(0), -1),
cls8.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(loc1.size(0), -1)], dim=1)
loc = torch.cat([loc1.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(loc1.size(0), -1),
loc2.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(loc1.size(0), -1),
loc3.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(loc1.size(0), -1),
loc4.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(loc1.size(0), -1),
loc5.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(loc1.size(0), -1),
loc6.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(loc1.size(0), -1),
loc7.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(loc1.size(0), -1),
loc8.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(loc1.size(0), -1)], dim=1)
out = (cls,loc)
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
net = LFFD()
print(net)
input = torch.randn(1,3,480,640)
output = net(input)
print(output[0].shape)
print(output[1].shape)
























 1601
1601











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








