1、预测sin函数
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
from keras.layers import LSTM
from keras import optimizers
from keras.utils import np_utils
TIMESTEP = 10
HIDDEN_UNITS = 100
BATCH_SIZE = 10
EPOCH = 10
model_store = 'model\lstm_sin_model.h5'
# 数据可视化
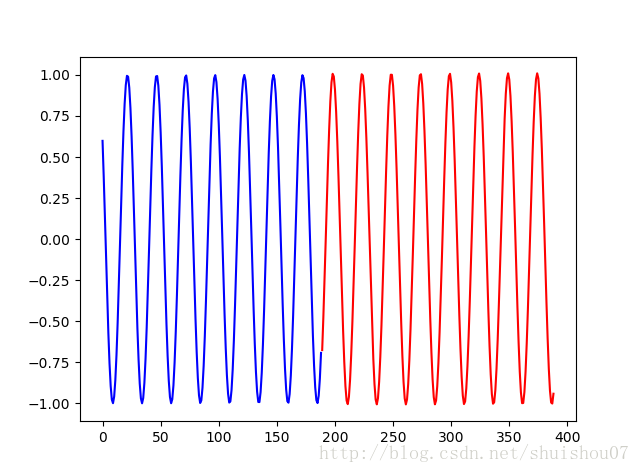
def draw(data1, data2):
ax = plt.subplot(111)
ax.plot(list(range(len(data1))), data1, 'b-', list(range(len(data1), len(data1) + len(data2))), data2, 'r-')
plt.show()
# 获取数据
def get_data():
x = np.linspace(start=0, stop=50, num=200, endpoint=False)
y = np.sin(x)
X = []
Y = []
for i in range(y.shape[0] - TIMESTEP - 1):
X.append(y[i:i + TIMESTEP])
Y.append(y[i + TIMESTEP])
X = np.array(X).reshape(-1, TIMESTEP, 1)
Y = np.array(Y).reshape(-1, 1)
return X, Y
x, y = get_data()
# 模型
def lstm_model():
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(HIDDEN_UNITS, input_shape=(TIMESTEP, 1)))
model.add(Dense(1))
return model
# 训练模型
def train_model():
model = lstm_model()
# model.compile(loss='mean_squared_error',optimizer='adam')
model.compile(loss='mean_squared_error',
optimizer=optimizers.Adamax(lr=0.002, beta_1=0.9, beta_2=0.999, epsilon=1e-08))
model.fit(x, y, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, nb_epoch=EPOCH, verbose=1)
#模型保存
model.save_weights(model_store)
# 预测模型
def predict_model():
model = lstm_model()
# 模型加载
model.load_weights(model_store)
result = list()
tmp = x[-1]
print('tmp', tmp)
for i in range(200):
p = model.predict(tmp.reshape(1, TIMESTEP, 1))
result.append(p[0])
tmp[:TIMESTEP - 1, :] = tmp[1:TIMESTEP, :]
tmp[TIMESTEP - 1, :] = p[0]
result = np.array(result)
print('prediction:', result)
draw(y, result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
train_model()
predict_model()
2、预测字母,如输入‘abc’输出‘d’
import string
import numpy as np
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
from keras.layers import LSTM
from keras import optimizers
from keras.utils import np_utils
TIMESTEP = 3
HIDDEN_UNITS = 100
BATCH_SIZE = 10
EPOCH = 10
alphabet = string.ascii_letters
# create mapping of characters to integers (0-25) and the reverse
char_to_int = dict((c, i) for i, c in enumerate(alphabet))
int_to_char = dict((i, c) for i, c in enumerate(alphabet))
# prepare the dataset of input to output pairs encoded as integers
model_store = 'model\lstm_char_model.h5'
LEN_CHARS = len(alphabet)
alphabet_one_hot = np_utils.to_categorical(range(LEN_CHARS))
def get_data():
dataX = []
dataY = []
for i in range(0, len(alphabet) - TIMESTEP, 1):
seq_in = alphabet_one_hot[i:i + TIMESTEP]
seq_out = alphabet_one_hot[i + TIMESTEP]
dataX.append(seq_in)
dataY.append(seq_out)
return np.array(dataX), np.array(dataY)
x, y = get_data()
# 模型
def lstm_model():
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(HIDDEN_UNITS, input_shape=(TIMESTEP, LEN_CHARS)))
model.add(Dense(LEN_CHARS))
return model
# 训练模型
def train_model():
model = lstm_model()
# model.compile(loss='mean_squared_error',optimizer='adam')
model.compile(loss='mean_squared_error',
optimizer=optimizers.Adamax(lr=0.002, beta_1=0.9, beta_2=0.999, epsilon=1e-08))
model.fit(x, y, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, nb_epoch=EPOCH, verbose=1)
# 模型保存
model.save_weights(model_store)
# 预测模型
def predict_model():
model = lstm_model()
# 模型加载
model.load_weights(model_store)
for i in range(LEN_CHARS - 3):
str_in = alphabet[i:i + TIMESTEP]
str_to_int = [char_to_int[item] for item in str_in]
str_to_one_hot = np.array([alphabet_one_hot[item] for item in str_to_int])
p = model.predict(str_to_one_hot.reshape(-1, TIMESTEP, LEN_CHARS))
p = ''.join([int_to_char[item] for item in np.argmax(p, axis=1)])
print('input:{}->prediction:{}'.format(str_in, p))
if __name__ == '__main__':
train_model()
# predict_model()
#输出结果
#input:abc->prediction:d
#input:bcd->prediction:e
#input:cde->prediction:f
#input:def->prediction:g
#input:efg->prediction:h
#input:fgh->prediction:i
#input:ghi->prediction:j
#input:hij->prediction:k
#input:ijk->prediction:l
#input:jkl->prediction:m





















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








