2.1.9 PDCCH monitoring set
PDCCH monitoring set是UE DL CCset的一个子集,通过定义这个子集能够减少盲解码次数、节省功耗。ZTE建议定义PDCCH monitoring子集。
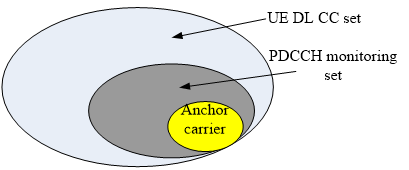
Alcatel-Lucent:建议定义PDCCH monitoring子集,能够减少盲检次数。并且提出PDCCH monitoring子集中要包含anchor CC。
Samsung在跨载波调度的情况下比较有无PDCCH monitoring set的区别。涉及到盲检、UE功率节省、UE buffering和PDCCH拥塞概率。Case 1没有定义PDCCH monitoring set,Case 2定义了PDCCH monitoring set。
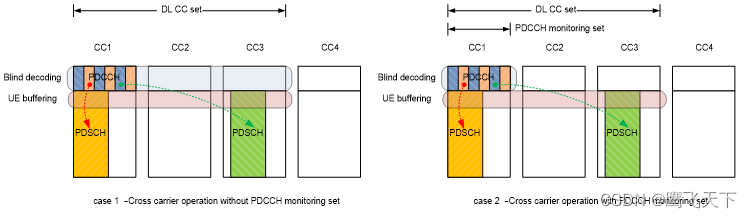
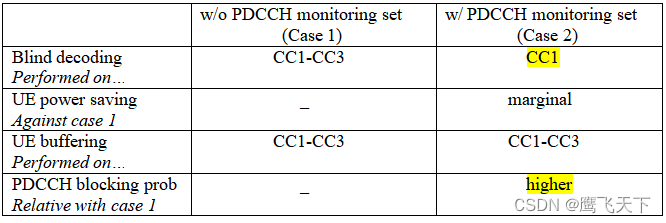
根据表格,在引入PDCCH monitoring set之后减少了盲检的次数,因为UE不需要对它所有DL CC set中的CC解码;同时也能发现,在UE节省功率和UE buffering方面的性能提升,还会带来大的拥塞概率。
RAN1结合跨载波调度讨论是否定义UE专用的“PDCCH monitoring set”。如果定义集合,UE将不会检测不发送PDCCH的CC,减少了PDCCH误检概率。RAN 1提出PDCCH monitoring set必须的两个特性:
- A set of DL CCs on which the UE is required to monitor the PDCCH
- Size is less than or equal to the size of the UE DL CC set and comprises only CCs that are in the UE DL CC set
关于是否定义PDCCH monitoring set,在RAN1#59次会议上指出,需要和RAN2一起决定。
RAN2为DL CC引入单独的激活/去激活过程,配置但处于去激活状态的CC不需要监听PDCCH,也不接受PDSCH。
2.1.10 PDSCH/PUSCH和PDCCH的联接
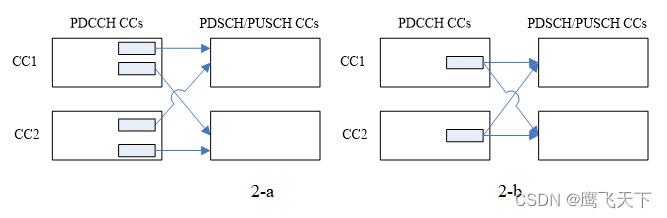
提出的PDSCH/PUSCH CC和PDCCH CC关联方案有两类。具体如下,
Option 1: Each PDSCH/PUSCH CC can be scheduled only from a single DL CC, i.e. the UE only monitors PDCCH on one DL CC for each PDSCH/PUSCH CC.
For any DL carrier with CIF where the UE monitors PDCCH, PDCCH on the DL carrier shall be able to schedule PDSCH at least on the same carrier and/or PUSCH on a linked UL carrier.
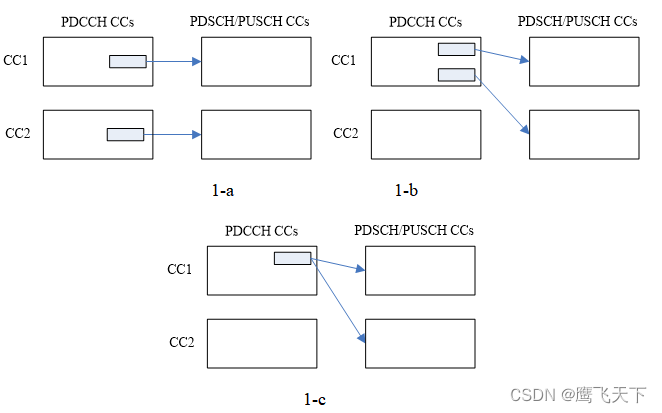
Option 2: Support scheduling a PDSCH/PUSCH CC from more than one DL CC
- For a given UE, each PDSCH/PUSCH CC can be scheduled only from a single DL CC in a given subframe in carrier aggregation scenario
- For any DL carrier with CIF where the UE monitors PDCCH, PDCCH on the DL carrier shall be able to schedule PDSCH at least on the same carrier and/or PUSCH on a linked UL carrier
- This shall not increase the number of PDCCH blind decodes and or the PDCCH CRC false detection rate compared to a system not having CIF
2.1.11 LTE-A 的DCI格式和盲检
2.1.11.1 DCI格式与搜索空间
之前的会议讨论确定3比特的CIF跨载波调度操作,但是并没有定义哪一些DCI格式必须包含CIF,或者是否全部的DCI格式都包含CIF。下面讨论具体何种DCI格式需要包含DCI。
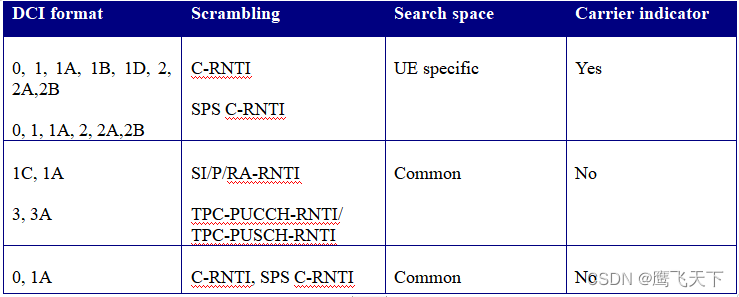
2.1.11.1.1 公共搜索空间DCI格式
公共搜索空间的DCI格式是否要包含CIF,对于用不同RNTI加扰的DCI格式分别讨论。一般来说,用P/SI/RA/TPC-RNTI加扰的DCI格式都应该能被R8和R10的UE共享,因此不能包含CIF。否则,eNB必须发送两种类型的公共DCI格式,其中一种包含CIF,一种不包含CIF。这样做的结果是使得eNB的执行变的复杂,同时增加了盲解码的次数和公共搜索空间PDCCH拥塞概率。
SI-RNTI加扰的DCI
系统信息在PDSCH上发送,为了保持和R8的兼容性,不建议包含CIF。
因为当R10 UE开机时,在进入载波聚合模式之前的初始工作和R8 UE是一样的。当UE配置在其他CC或者增加CC上发送接受,RAN2中采用专用信令发送CC的“urgent system information”,因此不需要CIF。
此外,如果包含CIF,由于公共搜索空间容量限制带来PDCCH拥塞概率和盲解码次数的增加。
P-RNTI加扰的DCI
对于R10的UE,如果在空闲模式下,仅仅需要在驻留的CC上监听寻呼信息,如果在连接状态下,需要基于每一个CC监听寻呼信息。也不需要CIF。
RA-RNTI加扰的DCI
对于随机接入过程,R10和R8的机制是一样的,在初始接入时两者的行为一样,因此不需要CIF。
C/SPS-RNTI加扰的DCI 0/1A
这种DCI在公共搜索空间是否包含CIF需要在调度灵活性和盲解码次数之间权衡。如果包含CIF,那就是每个CC增加了6次的盲解码,相反限制了调度的灵活性。
考虑到公共搜索空间的容量,不建议包含CIF。
TPC-RNTI加扰的DCI 3/3A
该格式用于PUCCH/PUSCH的功率控制。多个UE的功率控制信息在一个DCI格式3/3A上发送,为了提供和R8的兼容性,建议DCI 3/3A不要包含CIF,如果有UE专用的TPC,通过RRC配置。如果UE的多个CC的TPC不在一个DCI 3/3A上发送就需要包含CIF。NSN认为需要包含CIF,主要是考虑到不对称的配置中潜在的跨载波调度上行功控,这样牺牲兼容性为代价。
2.1.11.1.2 专用搜索空间DCI格式
LTE在UE专用搜索空间中支持的DCI格式有0,1,1A,1B,1D,2,2A和2B。由于CIF是UE专用的,因此跨载波调度的CIF应该包含在 UE专用搜索空间中所有的DCI格式里。考虑到盲解码的复杂度和跨载波资源分配的限制,为了简单方便,总是显示的表示CIF。
2.1.11.1.3 搜索空间设计
对于same-CC调度,一个CC上的搜索空间应该和R8保持一致。存在跨载波调度时,在一个CC上调度的PDSCH/PUSCH CC的DCI 能影响搜索空间结构。
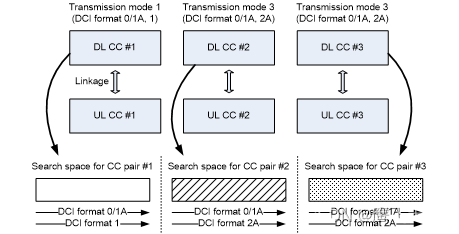
- 多个PDSCH/PUSCH CC共享搜索空间
这种结构下,在一个CC上为一个UE配置一个搜索空间。根据R8中聚合等级为4和8的盲解码次数为2,共享搜索空间不能支持超过2个聚合等级(4 or 8)的CC。如果支持共享搜索空间,首先要排除在一个 CC上聚合3个或者以上聚合等级为4/8的情况。
在没有跨载波调度的情况下,搜索空间设计和R8一样,一个DL CC上的PDCCH搜索空间只对应本下行CC和联接的上行CC。
- 多个PDSCH/PUSCH CC拥有独立的搜索空间
每个PDSCH/PUSCH CC都有各自的搜索空间,拥塞概率没有增加。
有跨载波调度的情况下,整个搜索时空间由多个搜索空间构成,这些搜索空间的起始点可以是独立的也可以是相同的。从图能看出,在有相同的DCI大小时,能够共享搜索空间,也就是说这些相同大小的DCI能够在共享搜索空间的任何候选PDCCH上发送。这样的好处是,这些DCI的调度更加灵活,同时也没有增加盲解码的次数。
对于那些大小不一样的DCI,LG建议采用bit padding使它们的大小一样。

2.1.11.1.4 搜索空间重叠问题
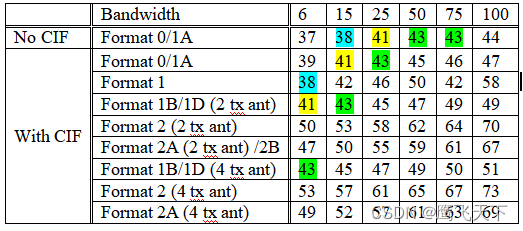
DCI 0/1A在公共搜索空间不包含CIF,如果一个配置包含有CIF的DCI格式和这个DCI 0/1A有相同的大小,会导致在公共搜索空间和UE专用搜索空间重叠区域有潜在的冲突。UE不能在重叠区域辨识出是公共搜索空间还是UE专用搜索空间的DCI,表格 由于相同DCI payload size潜在的冲突的格式看出可能存在的冲突。






















 2万+
2万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










