Support Vector Machines
1. Cost Function
J
(
θ
)
=
C
[
∑
i
=
1
m
y
(
i
)
cost
1
(
θ
T
x
(
i
)
)
+
(
1
−
y
(
i
)
)
cost
0
(
θ
T
x
(
i
)
)
]
+
1
2
∑
j
=
1
n
θ
j
2
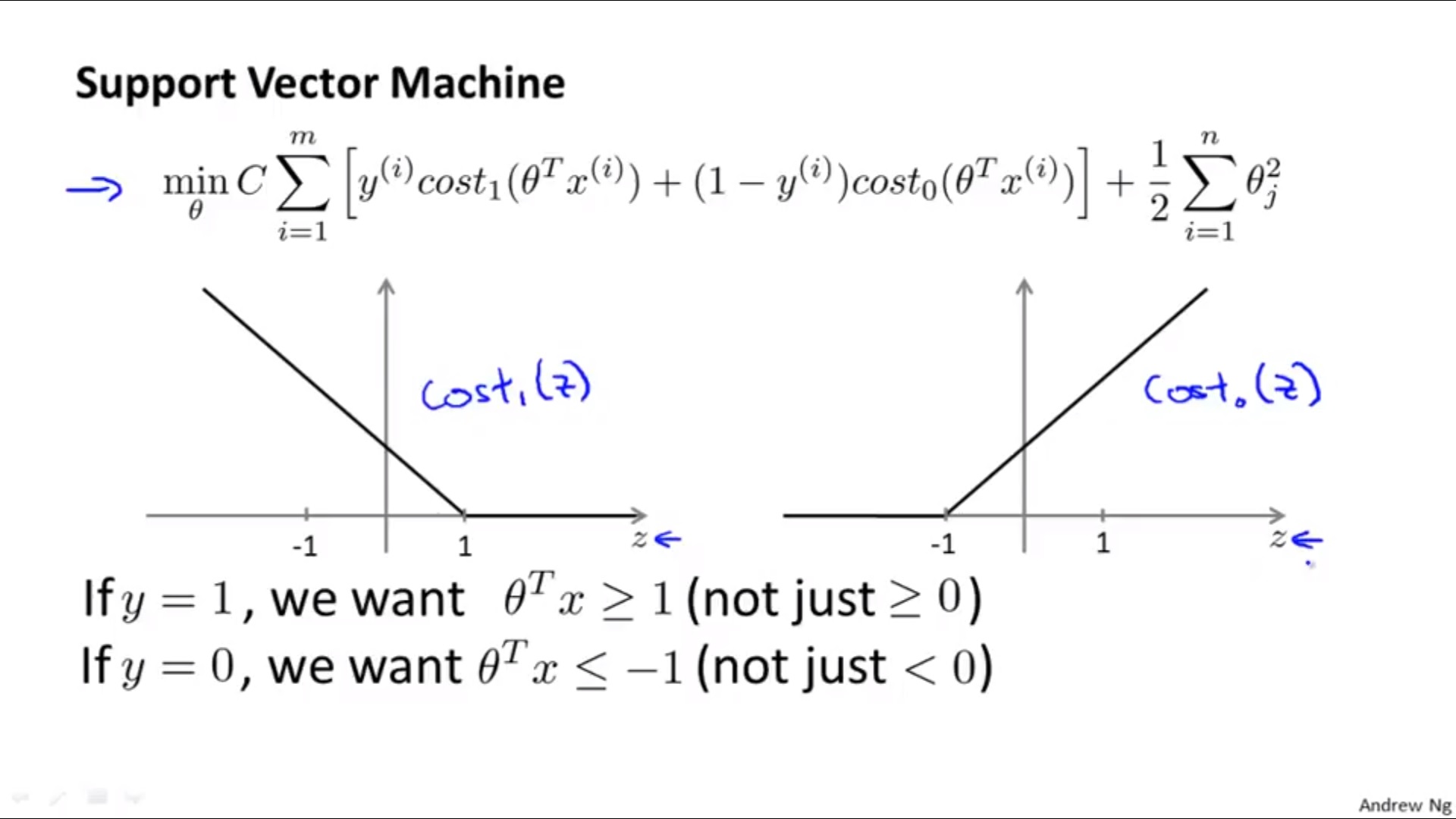
J(\theta)= C \left[\sum_{i=1}^m y^{(i)} \text{cost}_1(\theta^T x^{(i)})+(1-y^{(i)}) \text{cost}_0(\theta^T x^{(i)})\right] + \frac{1}{2}\sum_{j=1}^n\theta^2_j
J(θ)=C[i=1∑my(i)cost1(θTx(i))+(1−y(i))cost0(θTx(i))]+21j=1∑nθj2
2. Hypothesis
f ( x ) = { 1 if θ T x>=0 0 otherwise f(x)= \begin{cases} 1& \text{if $\theta^T$x>=0}\\ 0& \text{otherwise} \end{cases} f(x)={10if θTx>=0otherwise
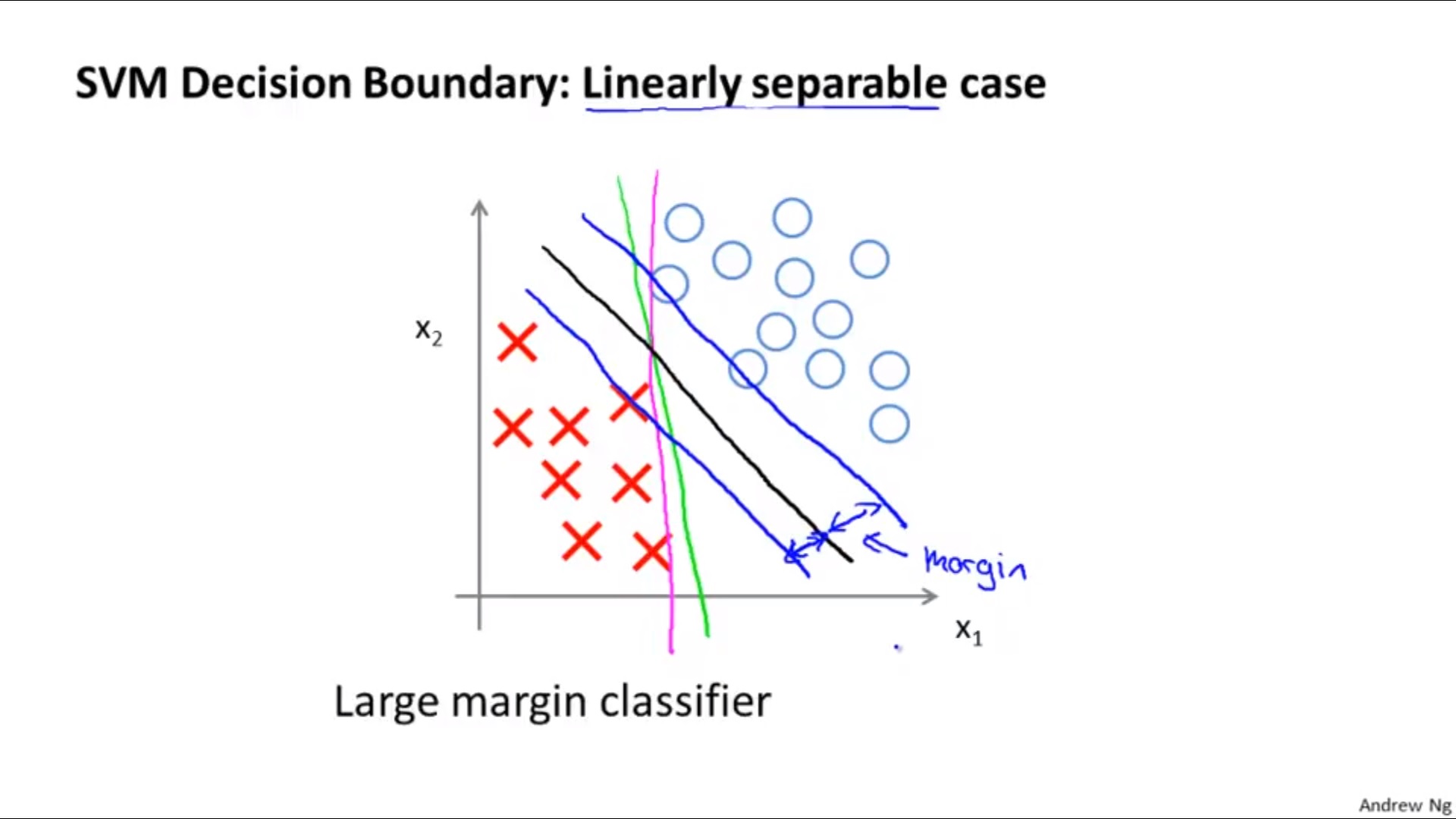
3. Margin of SVM
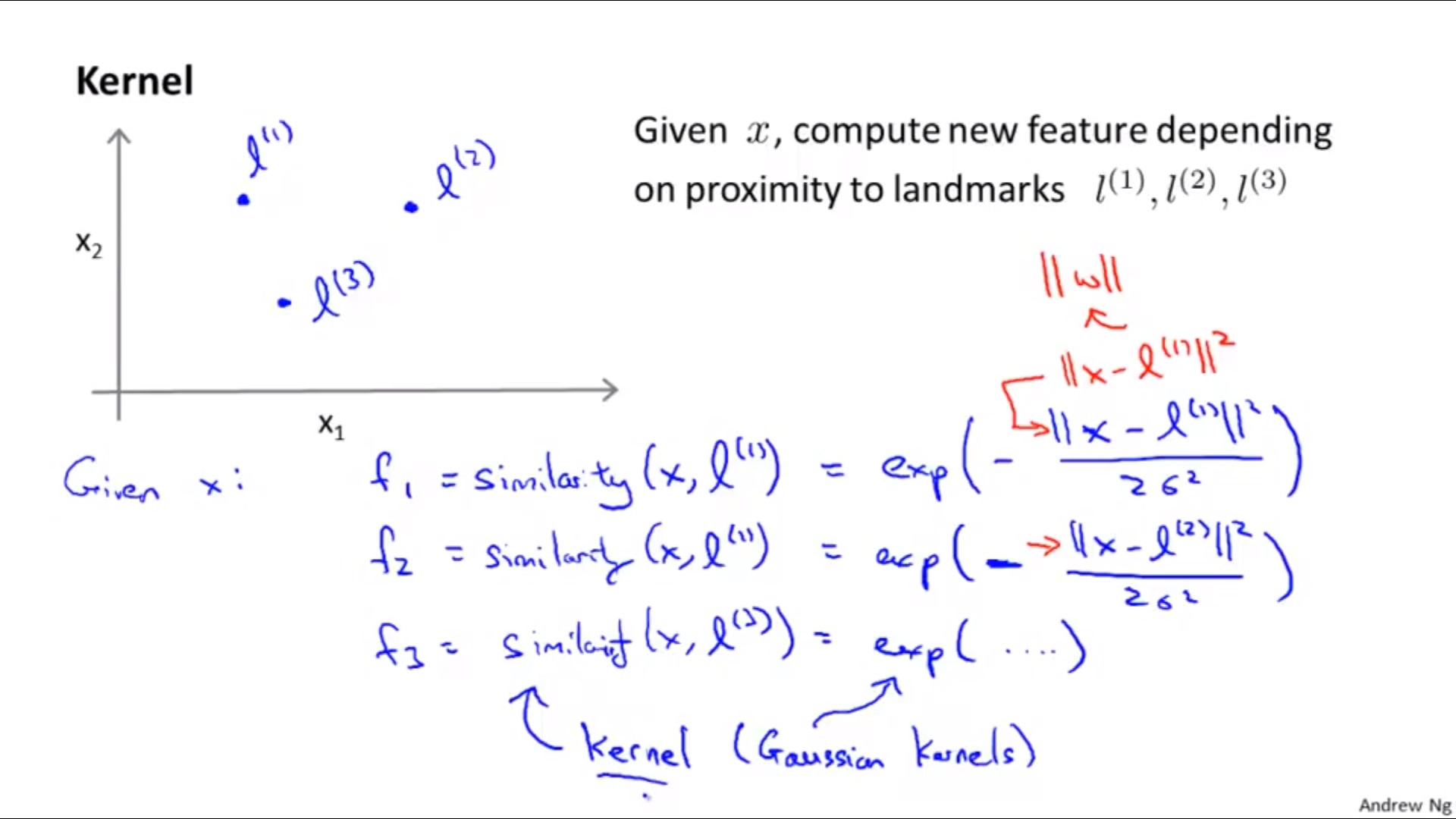
4. Kernels
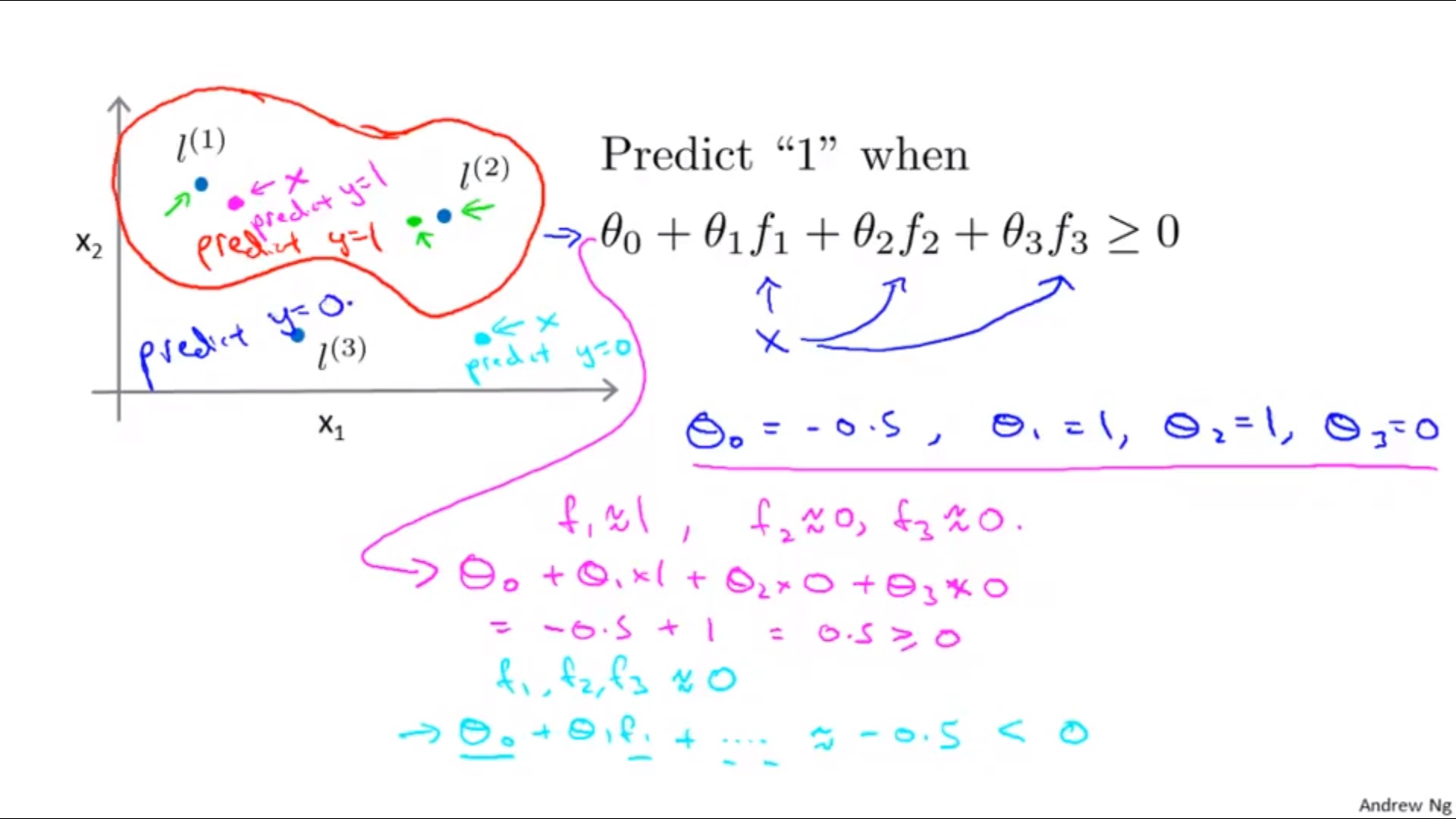
Define landmarks
l
l
l
Using
f
f
f and
θ
\theta
θ when making predictions…
5. How to Get Landmarks
One way is to use the first m training examples.
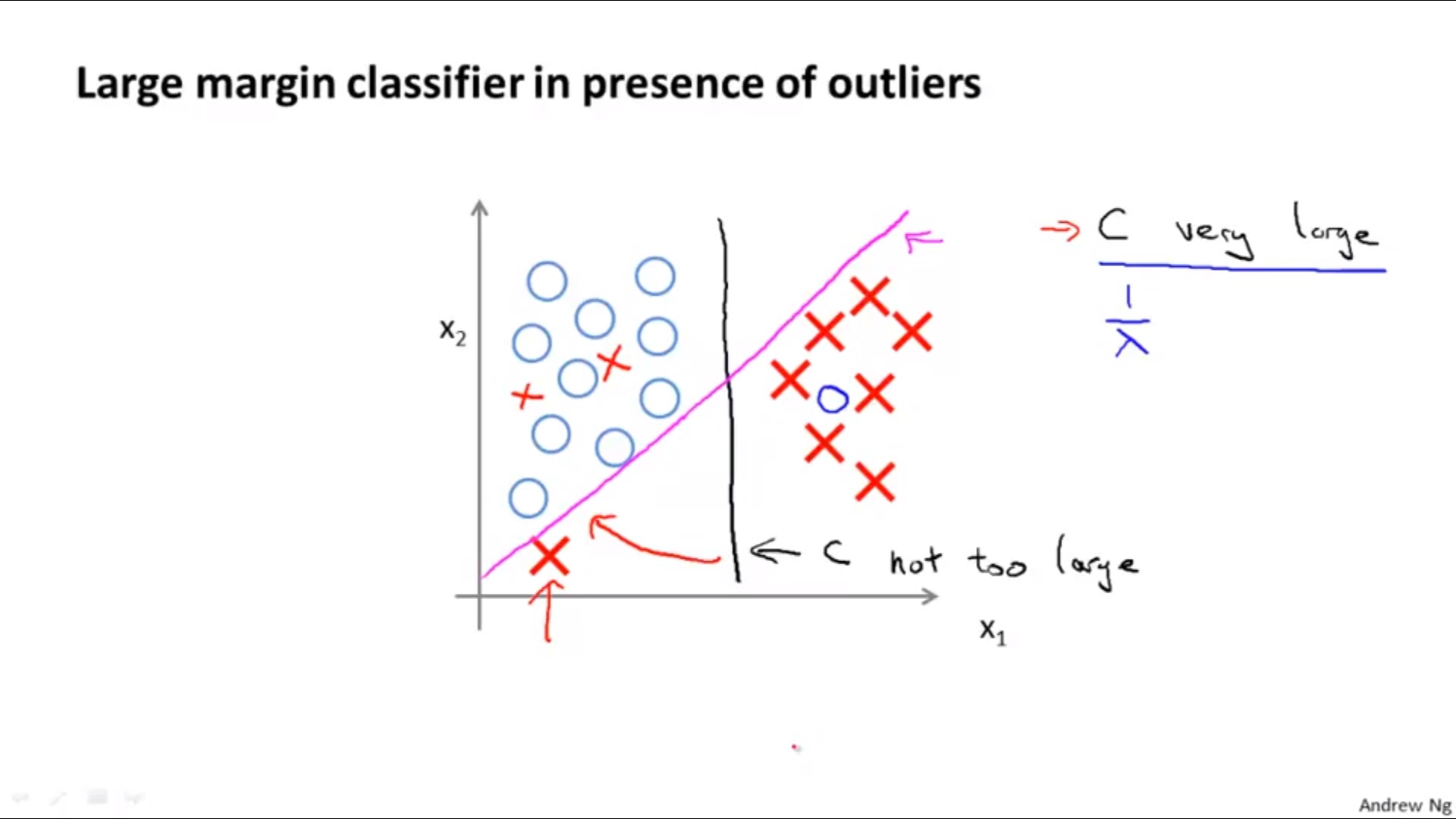
6. The Effects of Parameters in SVM
1) For
C
C
C
Large C : λ small, low bias, high variance
Small C : λ big, high bias, low variance
2) For
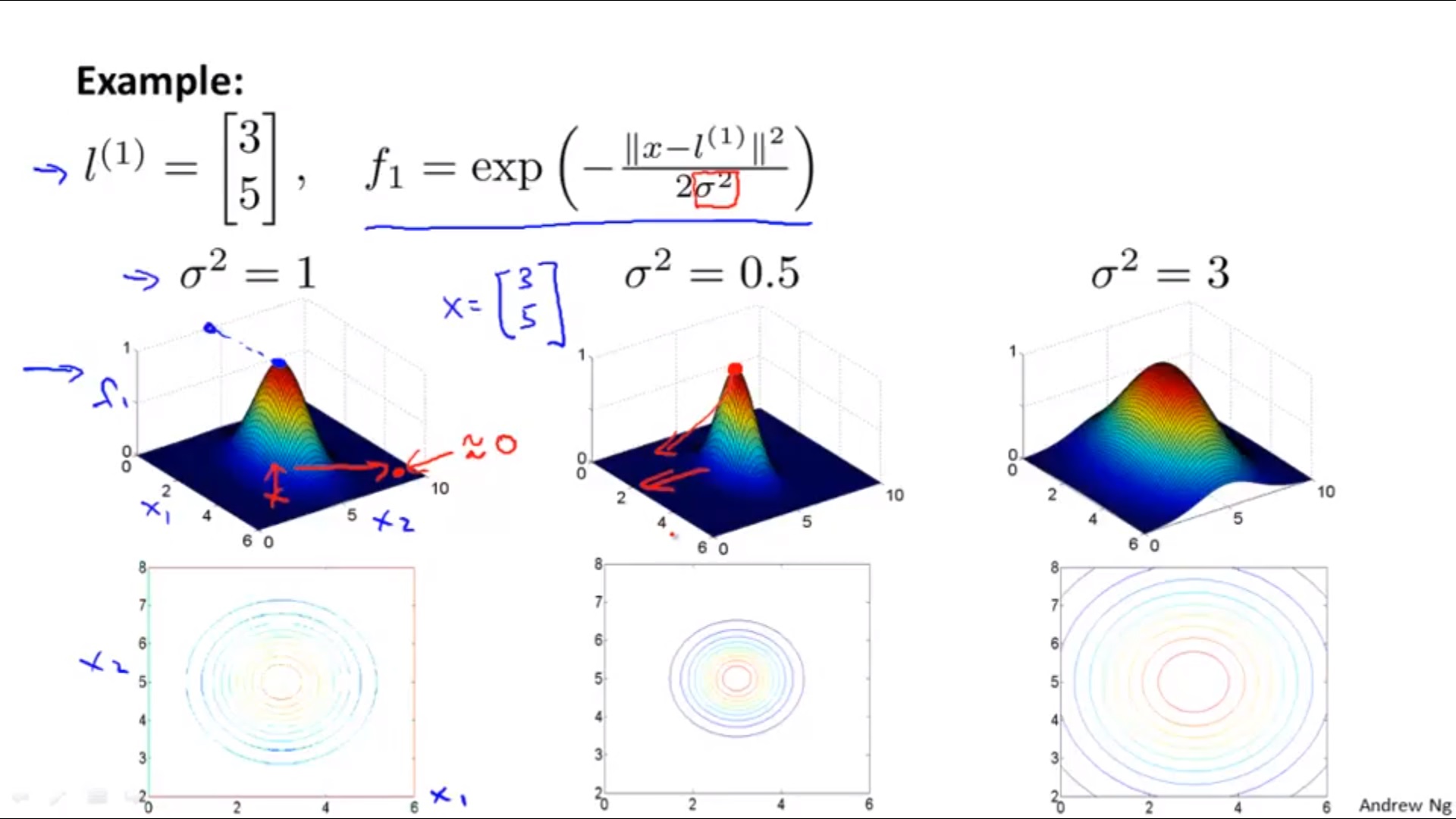
σ
2
\sigma^2
σ2
Large
σ
2
\sigma^2
σ2 : high bias, low variance
Small
σ
2
\sigma^2
σ2 : low bias, high variance
7. Choice of Kernal
Need to satisfy Mercer’s Theorem.
- No kernal (Linear Kernal)
when n is large/ n is small && m is large - Gaussian Kernal
when n is small, m is intermediate
Need to use feature scaling before using! - Other Alternative Choices:
Polynomial Kernal, String Kernal, Chi-Square Kernal, Intersection Kernal…






















 3万+
3万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








