- 🍨 本文为🔗365天深度学习训练营 中的学习记录博客
- 🍖 原作者:K同学啊
目录
一、 前期准备
1.设置GPU
import sys
sys.path.append(r'D:\Software\PyTorch') ## 指向安装 PyTorch 的目录
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
import os,PIL,pathlib,warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") #忽略警告信息
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
device2.导入数据
import os,PIL,random,pathlib
data_dir = '文件路径/'
data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir)
data_paths = list(data_dir.glob('*'))
classeNames = [str(path).split("\\")[7] for path in data_paths]
classeNames['cloudy', 'rain', 'shine', 'sunrise']
# 关于transforms.Compose的更多介绍可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38251616/article/details/124878863
train_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize([224, 224]), # 将输入图片resize成统一尺寸
# transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), # 随机水平翻转
transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL Image或numpy.ndarray转换为tensor,并归一化到[0,1]之间
transforms.Normalize( # 标准化处理-->转换为标准正太分布(高斯分布),使模型更容易收敛
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 其中 mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406]与std=[0.229,0.224,0.225] 从数据集中随机抽样计算得到的。
])
test_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize([224, 224]), # 将输入图片resize成统一尺寸
transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL Image或numpy.ndarray转换为tensor,并归一化到[0,1]之间
transforms.Normalize( # 标准化处理-->转换为标准正太分布(高斯分布),使模型更容易收敛
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 其中 mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406]与std=[0.229,0.224,0.225] 从数据集中随机抽样计算得到的。
])
total_data = datasets.ImageFolder("文件路径/",transform=train_transforms)
total_dataDataset ImageFolder
Number of datapoints: 1125
Root location: 文件路径/
StandardTransform
Transform: Compose(
Resize(size=[224, 224], interpolation=bilinear, max_size=None, antialias=True)
ToTensor()
Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
)
total_data.class_to_idx{'cloudy': 0, 'rain': 1, 'shine': 2, 'sunrise': 3}
3.划分数据集
train_size = int(0.8 * len(total_data))
test_size = len(total_data) - train_size
train_dataset, test_dataset = torch.utils.data.random_split(total_data, [train_size, test_size])
train_dataset, test_dataset
batch_size = 4
train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=1)
test_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=1)
for X, y in test_dl:
print("Shape of X [N, C, H, W]: ", X.shape)
print("Shape of y: ", y.shape, y.dtype)
break(<torch.utils.data.dataset.Subset at 0x22479dc9a90>, <torch.utils.data.dataset.Subset at 0x2247a3d8cd0>)
Shape of X [N, C, H, W]: torch.Size([4, 3, 224, 224]) Shape of y: torch.Size([4]) torch.int64
二、搭建包含C3模块的模型
1. 搭建模型
import torch.nn.functional as F
def autopad(k, p=None): # kernel, padding
# Pad to 'same'
if p is None:
p = k // 2 if isinstance(k, int) else [x // 2 for x in k] # auto-pad
return p
class Conv(nn.Module):
# Standard convolution
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=1, s=1, p=None, g=1, act=True): # ch_in, ch_out, kernel, stride, padding, groups
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, k, s, autopad(k, p), groups=g, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)
self.act = nn.SiLU() if act is True else (act if isinstance(act, nn.Module) else nn.Identity())
def forward(self, x):
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
# Standard bottleneck
def __init__(self, c1, c2, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, 3, 1, g=g)
self.add = shortcut and c1 == c2
def forward(self, x):
return x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.add else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
class C3(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck with 3 convolutions
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=True, g=1, e=0.5): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super().__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1) # act=FReLU(c2)
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(Bottleneck(c_, c_, shortcut, g, e=1.0) for _ in range(n)))
def forward(self, x):
return self.cv3(torch.cat((self.m(self.cv1(x)), self.cv2(x)), dim=1))
class model_K(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(model_K, self).__init__()
# 卷积模块
self.Conv = Conv(3, 32, 3, 2)
# C3模块1
self.C3_1 = C3(32, 64, 3, 2)
# 全连接网络层,用于分类
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=802816, out_features=100),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=100, out_features=4)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.Conv(x)
x = self.C3_1(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print("Using {} device".format(device))
model = model_K().to(device)
modelUsing cpu device
model_K(
(Conv): Conv(
(conv): Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act): SiLU()
)
(C3_1): C3(
(cv1): Conv(
(conv): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act): SiLU()
)
(cv2): Conv(
(conv): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act): SiLU()
)
(cv3): Conv(
(conv): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn): BatchNorm2d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act): SiLU()
)
(m): Sequential(
(0): Bottleneck(
(cv1): Conv(
(conv): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act): SiLU()
)
(cv2): Conv(
(conv): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act): SiLU()
)
)
(1): Bottleneck(
(cv1): Conv(
(conv): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act): SiLU()
)
(cv2): Conv(
(conv): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act): SiLU()
)
)
(2): Bottleneck(
(cv1): Conv(
(conv): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act): SiLU()
)
(cv2): Conv(
(conv): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(act): SiLU()
)
)
)
)
(classifier): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=802816, out_features=100, bias=True)
(1): ReLU()
(2): Linear(in_features=100, out_features=4, bias=True)
)
)
2.查看模型详情
# 统计模型参数量以及其他指标
import torchsummary as summary
summary.summary(model, (3, 224, 224))----------------------------------------------------------------
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
================================================================
Conv2d-1 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 864
BatchNorm2d-2 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 64
SiLU-3 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv-4 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv2d-5 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 1,024
BatchNorm2d-6 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 64
SiLU-7 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv-8 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv2d-9 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 1,024
BatchNorm2d-10 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 64
SiLU-11 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv-12 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv2d-13 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 9,216
BatchNorm2d-14 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 64
SiLU-15 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv-16 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Bottleneck-17 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv2d-18 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 1,024
BatchNorm2d-19 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 64
SiLU-20 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv-21 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv2d-22 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 9,216
BatchNorm2d-23 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 64
SiLU-24 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv-25 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Bottleneck-26 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv2d-27 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 1,024
BatchNorm2d-28 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 64
SiLU-29 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv-30 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv2d-31 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 9,216
BatchNorm2d-32 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 64
SiLU-33 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv-34 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Bottleneck-35 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv2d-36 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 1,024
BatchNorm2d-37 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 64
SiLU-38 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv-39 [-1, 32, 112, 112] 0
Conv2d-40 [-1, 64, 112, 112] 4,096
BatchNorm2d-41 [-1, 64, 112, 112] 128
SiLU-42 [-1, 64, 112, 112] 0
Conv-43 [-1, 64, 112, 112] 0
C3-44 [-1, 64, 112, 112] 0
Linear-45 [-1, 100] 80,281,700
ReLU-46 [-1, 100] 0
Linear-47 [-1, 4] 404
================================================================
Total params: 80,320,536
Trainable params: 80,320,536
Non-trainable params: 0
----------------------------------------------------------------
Input size (MB): 0.57
Forward/backward pass size (MB): 150.06
Params size (MB): 306.40
Estimated Total Size (MB): 457.04
----------------------------------------------------------------
三、 训练模型
1. 编写训练函数
# 训练循环
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 训练集的大小
num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目, (size/batch_size,向上取整)
train_loss, train_acc = 0, 0 # 初始化训练损失和正确率
for X, y in dataloader: # 获取图片及其标签
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
# 计算预测误差
pred = model(X) # 网络输出
loss = loss_fn(pred, y) # 计算网络输出和真实值之间的差距,targets为真实值,计算二者差值即为损失
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad() # grad属性归零
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 每一步自动更新
# 记录acc与loss
train_acc += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
train_loss += loss.item()
train_acc /= size
train_loss /= num_batches
return train_acc, train_loss2. 编写测试函数
测试函数和训练函数大致相同,但是由于不进行梯度下降对网络权重进行更新,所以不需要传入优化器
def test (dataloader, model, loss_fn):
size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 测试集的大小
num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目, (size/batch_size,向上取整)
test_loss, test_acc = 0, 0
# 当不进行训练时,停止梯度更新,节省计算内存消耗
with torch.no_grad():
for imgs, target in dataloader:
imgs, target = imgs.to(device), target.to(device)
# 计算loss
target_pred = model(imgs)
loss = loss_fn(target_pred, target)
test_loss += loss.item()
test_acc += (target_pred.argmax(1) == target).type(torch.float).sum().item()
test_acc /= size
test_loss /= num_batches
return test_acc, test_loss3. 正式训练
import copy
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr= 1e-4)
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 创建损失函数
epochs = 20
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_loss = []
test_acc = []
best_acc = 0 # 设置一个最佳准确率,作为最佳模型的判别指标
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss = train(train_dl, model, loss_fn, optimizer)
model.eval()
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, model, loss_fn)
# 保存最佳模型到 best_model
if epoch_test_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = epoch_test_acc
best_model = copy.deepcopy(model)
train_acc.append(epoch_train_acc)
train_loss.append(epoch_train_loss)
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
# 获取当前的学习率
lr = optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr']
template = ('Epoch:{:2d}, Train_acc:{:.1f}%, Train_loss:{:.3f}, Test_acc:{:.1f}%, Test_loss:{:.3f}, Lr:{:.2E}')
print(template.format(epoch+1, epoch_train_acc*100, epoch_train_loss,
epoch_test_acc*100, epoch_test_loss, lr))
# 保存最佳模型到文件中
PATH = './best_model.pth' # 保存的参数文件名
torch.save(best_model.state_dict(), PATH)
print('Done')Epoch: 1, Train_acc:71.6%, Train_loss:0.977, Test_acc:80.9%, Test_loss:0.678, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 2, Train_acc:86.9%, Train_loss:0.419, Test_acc:88.9%, Test_loss:0.355, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 3, Train_acc:91.7%, Train_loss:0.223, Test_acc:84.9%, Test_loss:0.434, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 4, Train_acc:95.4%, Train_loss:0.149, Test_acc:84.4%, Test_loss:0.457, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 5, Train_acc:98.3%, Train_loss:0.053, Test_acc:78.2%, Test_loss:0.766, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 6, Train_acc:97.4%, Train_loss:0.116, Test_acc:84.4%, Test_loss:0.572, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 7, Train_acc:98.1%, Train_loss:0.060, Test_acc:87.1%, Test_loss:0.538, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 8, Train_acc:98.4%, Train_loss:0.074, Test_acc:90.7%, Test_loss:0.375, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 9, Train_acc:99.0%, Train_loss:0.035, Test_acc:90.2%, Test_loss:0.537, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:10, Train_acc:98.2%, Train_loss:0.071, Test_acc:86.7%, Test_loss:0.577, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:11, Train_acc:99.6%, Train_loss:0.018, Test_acc:87.6%, Test_loss:0.487, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:12, Train_acc:99.8%, Train_loss:0.008, Test_acc:90.2%, Test_loss:0.396, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:13, Train_acc:99.9%, Train_loss:0.005, Test_acc:91.6%, Test_loss:0.458, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:14, Train_acc:98.7%, Train_loss:0.046, Test_acc:90.2%, Test_loss:0.546, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:15, Train_acc:97.9%, Train_loss:0.101, Test_acc:87.1%, Test_loss:0.593, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:16, Train_acc:98.2%, Train_loss:0.049, Test_acc:88.0%, Test_loss:0.710, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:17, Train_acc:98.9%, Train_loss:0.038, Test_acc:86.7%, Test_loss:0.676, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:18, Train_acc:99.4%, Train_loss:0.018, Test_acc:82.7%, Test_loss:0.788, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:19, Train_acc:98.9%, Train_loss:0.042, Test_acc:88.4%, Test_loss:0.740, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:20, Train_acc:98.8%, Train_loss:0.045, Test_acc:84.4%, Test_loss:0.825, Lr:1.00E-04 Done
四、 结果可视化
1. Loss与Accuracy图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#隐藏警告
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") #忽略警告信息
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 100 #分辨率
from datetime import datetime
current_time = datetime.now() # 获取当前时间
epochs_range = range(epochs)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 3))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(epochs_range, train_acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(epochs_range, test_acc, label='Test Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
plt.xlabel(current_time) # 打卡请带上时间戳,否则代码截图无效
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(epochs_range, train_loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(epochs_range, test_loss, label='Test Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.show()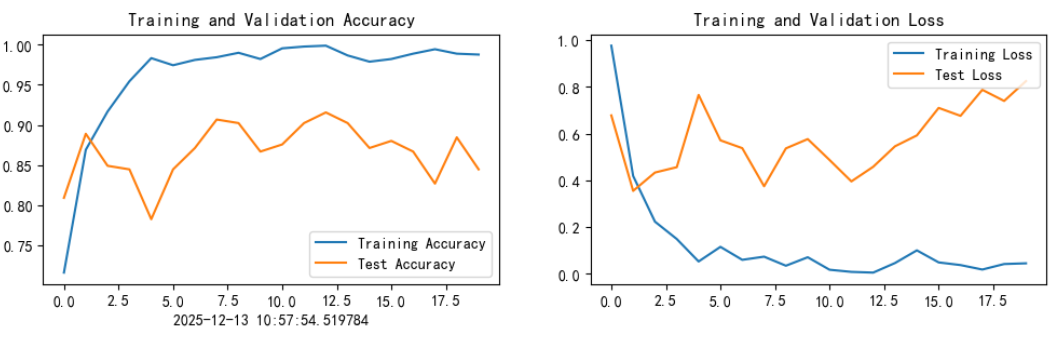
2. 模型评估
best_model.eval()
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, best_model, loss_fn)
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss
# 查看是否与我们记录的最高准确率一致
epoch_test_acc0.9155555555555556
五、YOLOv5-C3模块
YOLO(You Only Look Once)系列模型自 2015 年由 Joseph Redmon 提出 YOLOv1 开始,便以其单阶段(one-stage)实时目标检测架构闻名,将检测任务转化为回归问题,通过一次前向传播同时预测边界框和类别概率。这种设计不同于双阶段模型(如 Faster R-CNN),强调速度和简洁性,但早期版本(如 YOLOv1 到 YOLOv3)在处理小物体或拥挤场景时存在局限,主要依赖 Darknet 框架和残差连接来深化网络。
转折点出现在 2020 年,随着 YOLOv4 的发布(由 Alexey Bochkovskiy 等开发),引入了 CSPNet(Cross Stage Partial Network)架构。这是一种创新的网络设计,旨在解决深层网络中的梯度流动问题和计算冗余。CSPNet 通过将特征图分成两部分——一部分直接传递,另一部分经过密集处理后合并——实现了更好的梯度传播和参数效率。YOLOv4 的主干网络 CSPDarknet-53 正是基于此,显著提升了模型在准确性和速度上的平衡。
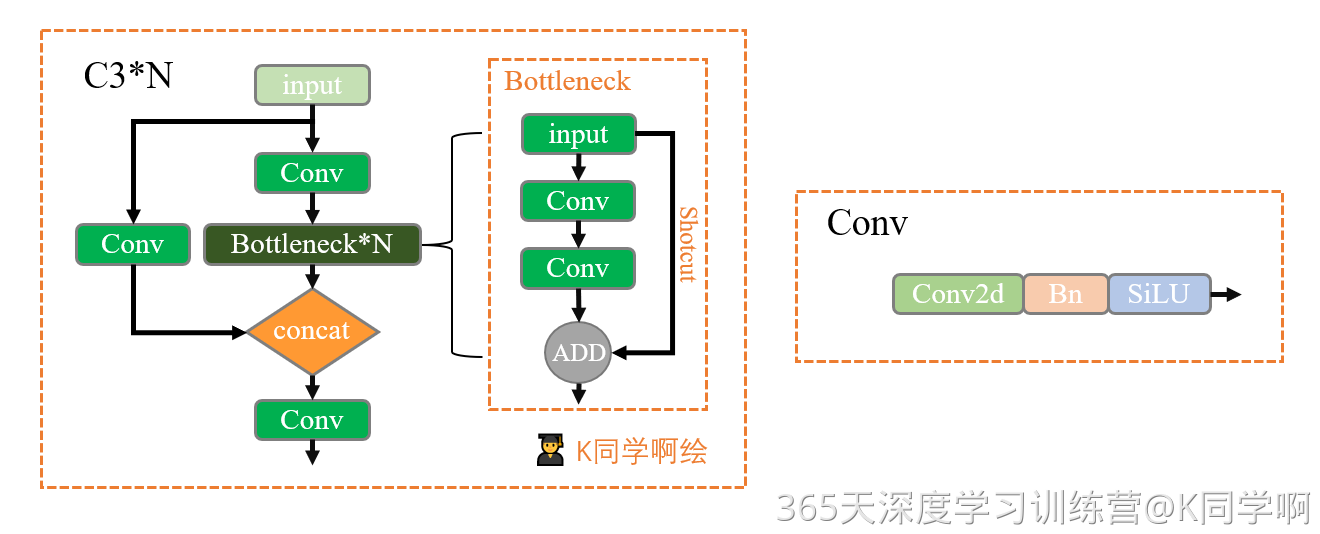
同年,Ultralytics 团队发布了 YOLOv5,这是 YOLO 系列的重大里程碑。它首次完全转向 PyTorch 框架(而非之前的 Darknet),提高了模型的模块化和可移植性,便于训练和部署。YOLOv5 继承了 YOLOv4 的 CSP 思想,但进行了优化:在主干和颈部(neck)引入了 C3 模块(全称 Cross Stage Partial Bottleneck with 3 convolutions)。C3 的构建灵感直接来源于 CSPNet,但专为 YOLOv5 的高效实时检测需求量身定制。它于 2020 年随 YOLOv5 首次亮相,并成为模型的核心构建块,帮助 YOLOv5 在 COCO 数据集上实现更高的 mAP(mean Average Precision)和更低的计算开销。YOLOv5 还推出了多个变体(如 YOLOv5s、m、l、x),通过复合缩放(compound scaling,借鉴 EfficientDet)调整深度和宽度,以适应不同硬件。
C3 模块的开发目的是在保持轻量级的同时,提升特征提取效率。它由三个卷积层组成:输入特征图被分成两支,一支直接通过一个 1x1 卷积进行维度调整,另一支经过瓶颈结构(Bottleneck,通常包括两个 3x3 卷积和残差连接),然后两支合并。这种“跨阶段部分”设计减少了参数量,同时改善了梯度流动,避免深层网络中的信息丢失。 在 YOLOv5 的主干中,C3 与 CBS(Conv + BatchNorm + SiLU)模块堆叠,形成高效的特征提取管道;颈部则结合 SPPF(Spatial Pyramid Pooling Fast)模块,进一步处理多尺度特征。





















 2103
2103

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








