归并排序算法完全遵循分治模式。直观上其操作如下:
- 分解:分解待排序的n个元素的序列成各具n/2个元素的两个子序列。
- 解决:使用归并排序递归地排序两个子序列。
- 合并:合并两个已排序的子序列以产生已排序的答案。
我们直接来看例子理解算法的过程,下面是要排序的数组,总共8个元素,我们划分为左右两个数组L和R(L和R都已经是有序的),L是原数组左边4个元素,R是原数组右边4个元素,为了让排序终止,两个数组的末尾加了一个无穷,用k指针指向原数组第一个元素2,i指针指向L数组第一个元素2,j指针指向R数组第一个元素1:
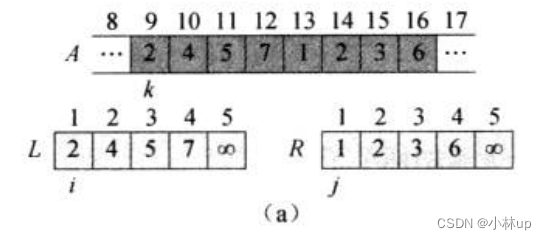
比较i指针所指2和j指针所指1:j指针所指1更小,k指针对应第一个元素赋值为1,j和k指针右移。
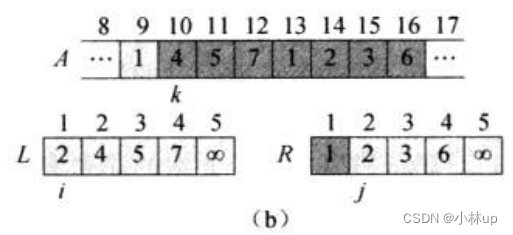
比较i指针所指2和j指针所指2:一样大,k指针对应第2个元素赋值为2,i和k指针右移。
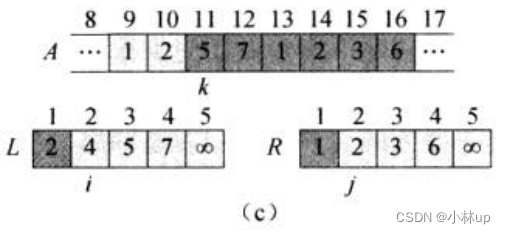
比较i指针所指4和j指针所指2:j指针所指2更小,k指针对应第3个元素赋值为2,j和k指针右移。
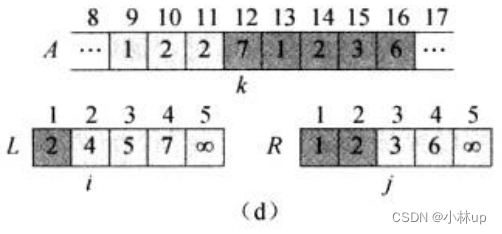
如此做下去,直到i和j指针都遍历到最后:
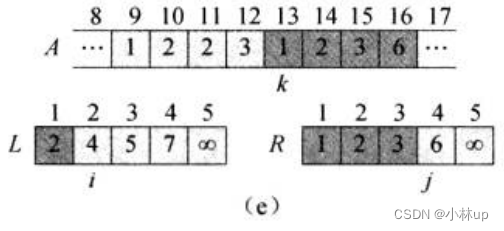
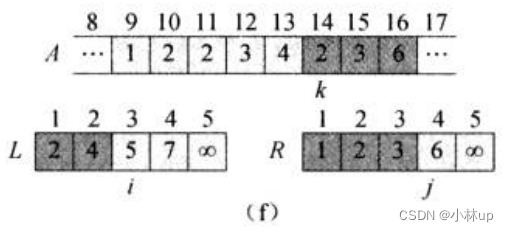
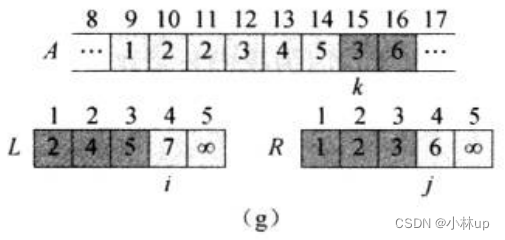
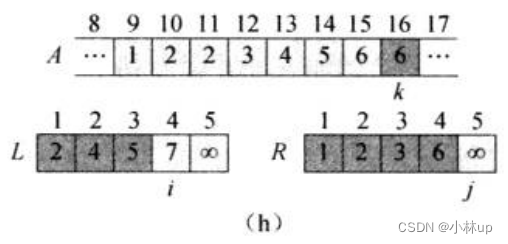
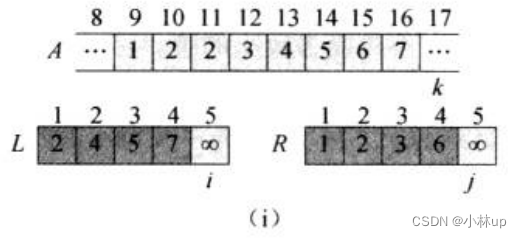
对于上面的逻辑我们可以写作一个函数叫merge,它的目的是合并两个有序数组为一个新的有序数组,它的伪代码是:
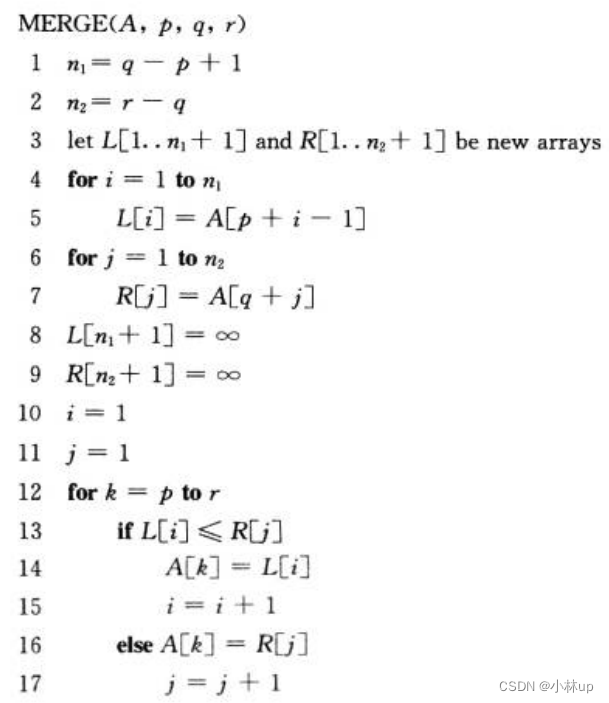
其中A是一个数组,p、q和r是数组下标,满足p≤q<r。该过程假设子数组A[p.q]和A[q+1,r]都已排好序。它合并这两个子数组形成单一的已排好序的子数组并代替当前的子数组A[p.r]。
用C++实现一下:
void merge(std::vector<int>& A, int p, int q, int r)
{
int n1 = q - p + 1;
int n2 = r - q;
std::vector<int> L(n1, 0);//[p,q]
std::vector<int> R(n2, 0);//[q+1,r]
for (int i = 0; i < n1; ++i)
L[i] = A[p + i];
for (int i = 0; i < n2; ++i)
R[i] = A[q + i - 1];
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (int k = p; k <= r; ++k)
{
if (i == n1)
{
A[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
else if (j == n2)
{
A[k] = L[i];
i++;
}
else if (L[i] <= R[j])
{
A[k] = L[i];
i++;
}
else
{
A[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
}
}
这样我们可以得到自底向上的排序:

算法的伪代码是:

void mergeSort(std::vector<int> &A, int p, int r)
{
if (p < r)
{
int q = (p + r) / 2;
mergeSort(A, p, q);
mergeSort(A, q + 1, r);
merge(A, p, q, r);
}
}
测试代码:
int main()
{
std::vector<int> A({1, 3, 2, 4, 5, 6, 2, 3});
for (auto &a : A)
{
std::cout << a << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
int len = A.size();
mergeSort(A, 0, len - 1);
for (auto &a : A)
{
std::cout << a << " ";
}
return 0;
}
第一行是未排序,第二行是排序以后的结果。

完整代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
void merge(std::vector<int> &A, int p, int q, int r)
{
int n1 = q - p + 1;
int n2 = r - q;
std::vector<int> L(n1, 0); //[p,q]
std::vector<int> R(n2, 0); //[q+1,r]
for (int i = 0; i < n1; ++i)
L[i] = A[p + i];
for (int i = 0; i < n2; ++i)
R[i] = A[q + i + 1];
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (int k = p; k <= r; ++k)
{
if (i == n1)
{
A[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
else if (j == n2)
{
A[k] = L[i];
i++;
}
else if (L[i] <= R[j])
{
A[k] = L[i];
i++;
}
else
{
A[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
}
}
void mergeSort(std::vector<int> &A, int p, int r)
{
if (p < r)
{
int q = (p + r) / 2;
mergeSort(A, p, q);
mergeSort(A, q + 1, r);
merge(A, p, q, r);
}
}
int main()
{
std::vector<int> A({1, 3, 2, 4, 5, 6, 2, 3});
for (auto &a : A)
{
std::cout << a << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
int len = A.size();
mergeSort(A, 0, len - 1);
for (auto &a : A)
{
std::cout << a << " ";
}
return 0;
}
力扣相关题目
21.合并两个有序链表
学完了归并排序可以顺带把力扣的21.合并两个有序链表也做一下,等同于上面的merge函数
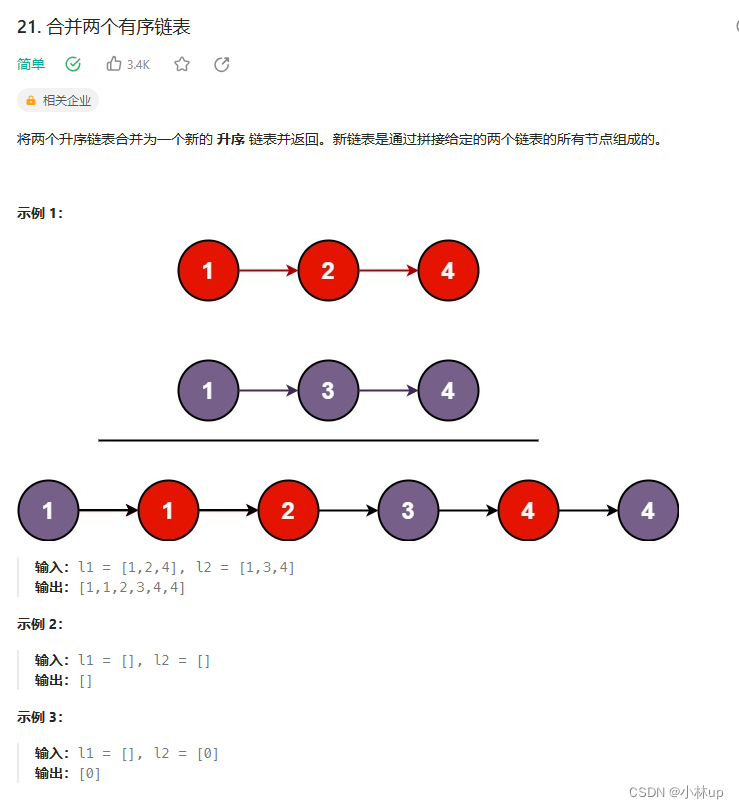
模拟的写法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* node = dummy;
while (list1 != NULL && list2 != NULL)
{
if (list1->val < list2->val)
{
node->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
}
else
{
node->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
node = node->next;
}
node->next = list1 == NULL ? list2 : list1;
return dummy->next;
}
};
另一种递归的写法:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
if (list1 == NULL)
return list2;
else if (list2 == NULL)
return list1;
else if (list1->val < list2->val)
{
list1->next = mergeTwoLists(list1->next, list2);
return list1;
}
else
{
list2->next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2->next);
return list2;
}
}
};
148. 排序链表
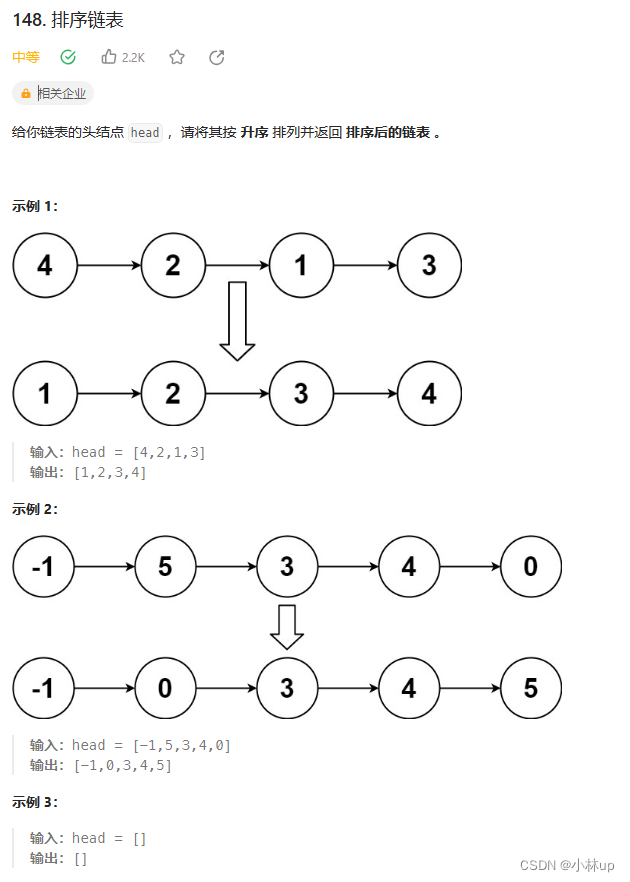
自顶向下的排序。使用的是左闭右开的思路,传入的两个指针一个是头指针,一个可以是空指针(开区间)。然后使用快慢指针找中点确定mid的位置。这样就可以递归地合并链表mergeTwoLists(sortList(head, mid), sortList(mid, tail))。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
return sortList(head, NULL);
}
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head, ListNode* tail)
{
if (head == NULL)
return head;
if (head->next == tail)//左闭右开
{
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while (fast != tail)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
if (fast != tail)
fast = fast->next;
}
ListNode* mid = slow;
return mergeTwoLists(sortList(head, mid), sortList(mid, tail));
}
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* head1, ListNode* head2)
{
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* cur = dummy;
ListNode* cur1 = head1;
ListNode* cur2 = head2;
while (cur1 != NULL && cur2 != NULL)
{
if (cur1->val < cur2->val)
{
cur->next = cur1;
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
else
{
cur->next = cur2;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = (cur1 == NULL ? cur2 : cur1);
return dummy->next;
}
};
还有一种自底向上的排序,使用的就是前面讲的方法。自底向上的排序,先排序1个长度的链表,然后2个,4个,以此类推,这里每两个链表也是使用最重要的是找到两个链表的头指针:
查找最后一个不为空的链表指针:
while (node->next != NULL)//node不为空
{
node = node->next;
}
从node开始第subLength个指针(node不为空)
for (int i = 1; node->next != NULL && i < subLength; i++)//node确定不为空
{
node = node->next;//到subLength的尾部
}
从node开始第subLength个指针,如果node可能为空:
for (int i = 1; node != NULL && node->next != NULL && i < subLength; i++)//node确定不为空
{
node = node->next;//到subLength的尾部
}
每次找到subLength个指针的位置,把它后面的位置记录下来,然后它后面的位置设为空指针。方便后面的链表的合并。用mergeTwoLists合并两个链表,赋值头结点给pre的next指针,然后next指针移动到这个链表的尾部,后面还要继续相同的操作。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == NULL)
return head;
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode* temp = dummy;
int length = 0;
while (temp->next != NULL)
{
temp = temp->next;
length++;
}
for (int subLength = 1; subLength < length; subLength <<= 1)
{
ListNode* pre = dummy;
ListNode* cur = dummy->next;
while (cur != NULL)
{
ListNode* head1 = cur;
for (int i = 1; cur->next != NULL && i < subLength; i++)
{
cur = cur->next;//到subLength的尾部
}
ListNode* head2 = cur->next;
cur->next = NULL;
cur = head2;
for (int i = 1; cur != NULL && cur->next != NULL && i < subLength; i++)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
ListNode* next = NULL;
if (cur != NULL)
{
next = cur->next;
cur->next = NULL;
}
pre->next = mergeTwoLists(head1, head2);
while (pre->next != NULL)
{
pre = pre->next;
}
cur = next;
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* head1, ListNode* head2)
{
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* cur = dummy;
ListNode* cur1 = head1;
ListNode* cur2 = head2;
while (cur1 != NULL && cur2 != NULL)
{
if (cur1->val < cur2->val)
{
cur->next = cur1;
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
else
{
cur->next = cur2;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = (cur1 == NULL ? cur2 : cur1);
return dummy->next;
}
};








 本文详细介绍了归并排序算法的工作原理,包括其遵循的分治策略,如何通过递归分解、合并有序子序列以及C++中的具体实现,包括链表和数组的合并示例。
本文详细介绍了归并排序算法的工作原理,包括其遵循的分治策略,如何通过递归分解、合并有序子序列以及C++中的具体实现,包括链表和数组的合并示例。














 222
222











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








