原作者博客地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/dongsheng/archive/2013/06/02/3114073.html
Description
In the Fibonacci integer sequence, F0 = 0, F1 = 1, and Fn = Fn − 1 + Fn − 2 for n ≥ 2. For example, the first ten terms of the Fibonacci sequence are:
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, …
An alternative formula for the Fibonacci sequence is
 .
.
Given an integer n, your goal is to compute the last 4 digits of Fn.
Input
The input test file will contain multiple test cases. Each test case consists of a single line containing n (where 0 ≤ n ≤ 1,000,000,000). The end-of-file is denoted by a single line containing the number −1.
Output
For each test case, print the last four digits of Fn. If the last four digits of Fn are all zeros, print ‘0’; otherwise, omit any leading zeros (i.e., print Fn mod 10000).
Sample Input
0 9 999999999 1000000000 -1
Sample Output
0 34 626 6875
Hint
As a reminder, matrix multiplication is associative, and the product of two 2 × 2 matrices is given by
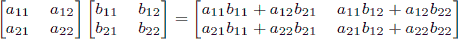 .
.
Also, note that raising any 2 × 2 matrix to the 0th power gives the identity matrix:
 .
.
Source
分析:通过这道题,不仅学会了矩阵的快速幂的做法,同时也提供了求Fibonacci的高效算法#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MOD = 10000;
struct matrix
{
int m[2][2];
}ans, base;
matrix multi(matrix a, matrix b)
{
matrix tmp;
for(int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 2; ++j)
{
tmp.m[i][j] = 0;
for(int k = 0; k < 2; ++k)
tmp.m[i][j] = (tmp.m[i][j] + a.m[i][k] * b.m[k][j]) % MOD;
}
}
return tmp;
}
int fast_mod(int n) // 求矩阵 base 的 n 次幂
{
base.m[0][0] = base.m[0][1] = base.m[1][0] = 1;
base.m[1][1] = 0;
ans.m[0][0] = ans.m[1][1] = 1; // ans 初始化为单位矩阵
ans.m[0][1] = ans.m[1][0] = 0;
while(n)
{
if(n & 1) //实现 ans *= t; 其中要先把 ans赋值给 tmp,然后用 ans = tmp * t
{
ans = multi(ans, base);
}
base = multi(base, base);
n >>= 1;
}
return ans.m[0][1];
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d", &n) && n != -1)
{
printf("%d\n", fast_mod(n));
}
return 0;
}






















 3985
3985

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








