视频讲解
1. 背景
路径规划时:用于规划出无碰撞路径;
例如:hybridAstar节点扩展时候的碰撞检测;
parking时的泊车路径;
teb里面计算和障碍物的距离;

路径跟随时:用于检测前方路径上是否会发生碰撞,用于减速或停障;
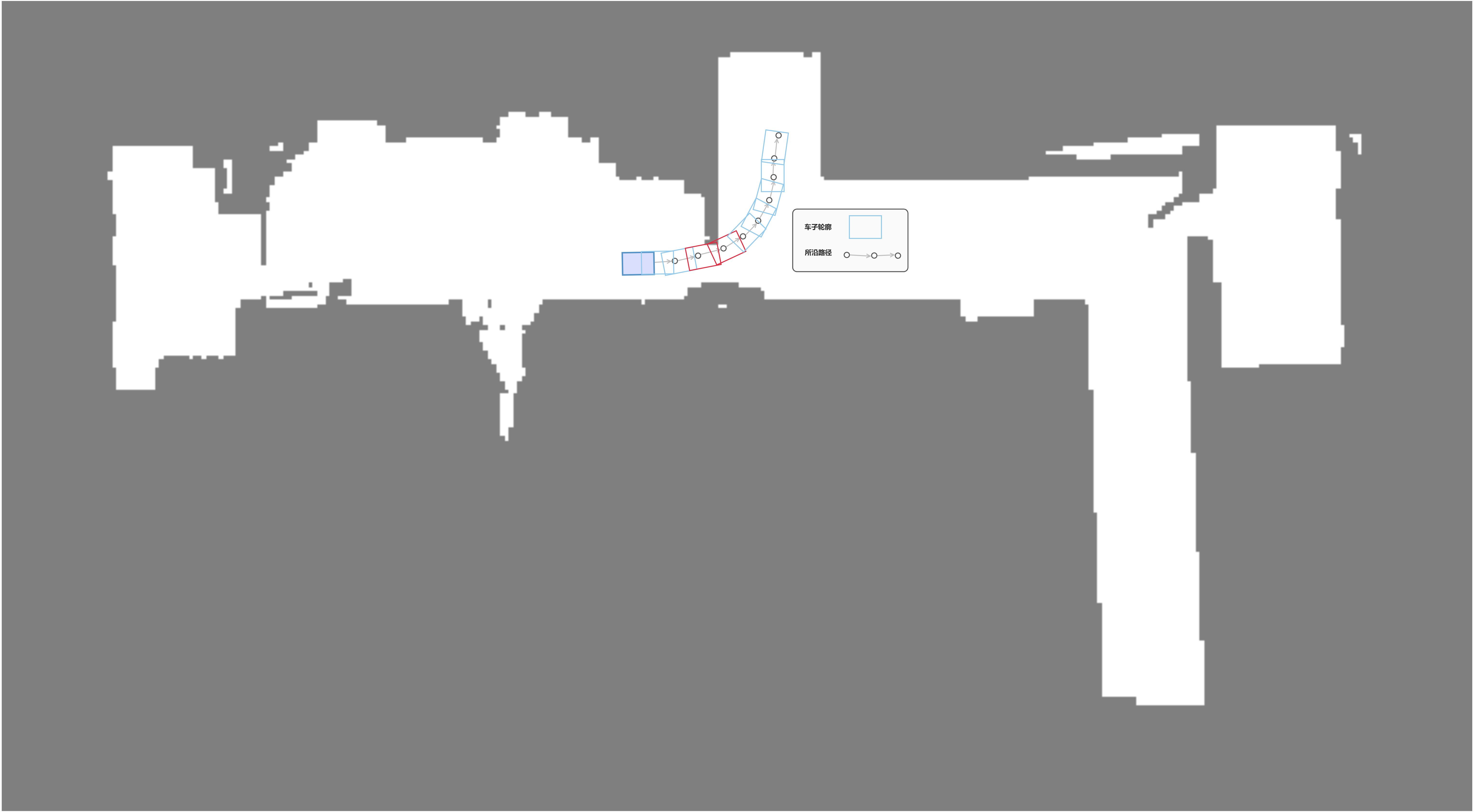
远距离减速,近距离急停;
参考:路径跟随中的障碍物检测;使用这个文档里面的插图
1.1. 示例:泊车场景


检测extend之后的bounding box是否发生碰撞;
1.2. 示例:路径规划
机器人的footprint模型;



考虑:外轮廓与障碍物距离足够或者不发生overlap认为安全;
2. 碰撞检测的方法
2.1. 使用几何方法:
2.1.1. 使用机器轮廓多边形和环境几何信息做碰撞检测;
参考: costmap converter将障碍物地图转换为几何图形;costmap_converter/src/costmap_to_polygons.cpp at e8c1d2c8c8d5e34b1980062e28e4a4dc1817bade · rst-tu-dortmund/costmap_converter
参考:teb planner;(计算到障碍物的距离时,将障碍物转换点线多边形几何图形,计算footprint到几何图形的距离)
2.1.2. 使用包围盒,AABB检测,分离轴定理检测overlap;判断障碍物点是否在机器轮廓的boundingBox里面,再将点转化到车辆坐标系下判断是否再车辆轮廓内部;
参考:计算几何视频讲解;- apollo源码参考;
apollo的math库-aabox2d.h 与 aaboxkdtree2d
2.1.3. 使用esdf结合footprint判断
例如:将footprint使用disk描述,判断disk圆心到最近障碍物点的距离是否超过阈值/或者判断disk边缘在costmap中的像素值是否为lethal;
参考:fast planner;Fast-Planner/fast_planner/bspline_opt/src/bspline_optimizer.cpp at master · HKUST-Aerial-Robotics/Fast-Planner
2.2. 使用覆盖栅格模板和查表的方法;
2.2.1. 使用机器轮廓覆盖栅格像素模板;
参考:判断点是否在机器轮廓内部的准确高效方法-使用覆盖栅格模板
包括边缘和内部;
特点:
- 全图搜索的时候,调用频繁,消耗资源;
优化方法:使用最近邻工具减少查询次数;
- 车道上做碰撞检测的时候,搜索次数少;
对密集的路径点,每个路径点使用模板检测、检测两侧的障碍物;
对直线段,选取稀疏路径点使用模板检测;
2.2.2. 覆盖栅格模板的实现
原理:计算每个采样方向下机器位于栅格原点时候轮廓所覆盖的像素坐标(描述的是相对于机器元原点的偏移量)作为这个方向上的模板;
技巧:
模板根据地图的像素尺寸计算;
计算模板时将机器原点落在原点像素四等分位置(物理原点不一定落在像素格点的正中间);
D:\[opencv_source_navigation]\hybrid-a-star-annotation-master\include\lookup.h
#ifndef COLLISIONLOOKUP
#define COLLISIONLOOKUP
#include "dubins.h"
#include "constants.h"
namespace HybridAStar {
namespace Lookup {
//###################################################
// DUBINS LOOKUP
//###################################################
inline void dubinsLookup(float* lookup) {
bool DEBUG = false;
std::cout << "I am building the Dubin's lookup table...";
DubinsPath path;
int width = Constants::dubinsWidth / Constants::cellSize;//这里是相对长度
// // increase the width by one to make it square
// if (width % 2 != 0) {
// width++;
// }
const int headings = Constants::headings;//这里是将heading(朝向)进行分段的数量
// start and goal vector
double start[3];//分别表示 (x, y, theta)
double goal[] = {0, 0, 0};
// iterate over the X index of a grid cell
for (int X = 0; X < width; ++X) {
start[0] = X;//索引值:X-方向
// iterate over the Y index of a grid cell
for (int Y = 0; Y < width; ++Y) {
start[1] = Y;//索引值:Y-方向
// iterate over the start headings
for (int h0 = 0; h0 < headings; ++h0) {
start[2] = Constants::deltaHeadingRad * h0;//分辨率乘以相对值为真实的角度
//这里是角度, start=(X, Y, Theta), X和Y是索引值,Theta是角度(degree)
// iterate over the goal headings
for (int h1 = 0; h1 < headings; ++h1) {
//同上,不过这里是goal的角度: (0, 0, Theta)
goal[2] = Constants::deltaHeadingRad * h1;
// calculate the actual cost
//依据最小转弯半径生成一条从start到goal的path??
dubins_init(start, goal, Constants::r, &path);
//存储到查找表中
lookup[X * headings * headings * width + Y * headings * headings + h0 * headings + h1] = dubins_path_length(&path);
if (DEBUG && lookup[X * headings * headings * width + Y * headings * headings + h0 * headings + h1] < sqrt(X * X + Y * Y) * 1.000001) {
std::cout << X << " | " << Y << " | "
<< Constants::deltaHeadingDeg* h0 << " | "
<< Constants::deltaHeadingDeg* h1 << " length: "
<< lookup[X * headings * headings * width + Y * headings * headings + h0 * headings + h1] << "\n";
}
}
}
}
}
std::cout << " done!" << std::endl;
}
//###################################################
// COLLISION LOOKUP
//###################################################
// _____________
// SIGN FUNCTION:符号函数
inline int sign(double x) {
if (x >= 0) { return 1; }
else { return -1; }
}
// _________________________
// COLLISION LOOKUP CREATION
// 在原点,取多个朝向,生成覆盖栅格模板,组成一个表
// 判断前方路径点上机器是否会碰撞到融合地图里面的障碍物,用来提前避障
// 更加准确,原点细分,朝向角度细分
inline void collisionLookup(Constants::config* lookup) {
bool DEBUG = false;
std::cout << "I am building the collision lookup table...";
// cell size
const float cSize = Constants::cellSize;//为1
// bounding box size length/width
const int size = Constants::bbSize;// 为 (车的面积+4)/cellsize
struct point {//定义点的数据结构
double x;
double y;
};
// ______________________
// VARIABLES FOR ROTATION
//center of the rectangle
point c;//表示方形中心
point temp;//临时值
// points of the rectangle
point p[4];//四个点的坐标
point nP[4];
// turning angle
double theta;//转向角
// ____________________________
// VARIABLES FOR GRID TRAVERSAL
// vector for grid traversal //网格遍历的变量
point t;//
point start;//起点
point end;//终点
// cell index
int X;//用于网格索引, X-方向
int Y;//用于网格索引, Y-方向
// t value for crossing vertical and horizontal boundary
double tMaxX;// X-方向的t值
double tMaxY;// Y-方向的t值
// t value for width/heigth of cell
double tDeltaX; //单元格宽度方向的t值
double tDeltaY; //单元格高度方向的t值
// positive or negative step direction
int stepX;//步进方向,可为正亦可为负
int stepY;
// grid
bool cSpace[size * size]; //size为网格数量(车的面积),
bool inside = false; //在里面
int hcross1 = 0;
int hcross2 = 0;
// _____________________________
// VARIABLES FOR LOOKUP CREATION 创建查找表的变量
int count = 0;
const int positionResolution = Constants::positionResolution;//每个位置的cell的分辨率,表示该cell下有多少个划分的小网格
const int positions = Constants::positions;//实际就是 positionResolution * positionResolution,表示数量
point points[positions];//转化为点表示
// generate all discrete positions within one cell
for (int i = 0; i < positionResolution; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < positionResolution; ++j) {
points[positionResolution * i + j].x = 1.f / positionResolution * j;
points[positionResolution * i + j].y = 1.f / positionResolution * i;
}//从左上方开始,给每个点的x、y赋值,实际上是计算出每个点的位置(偏移量)
}
for (int q = 0; q < positions; ++q) {
// set the starting angle to zero;
theta = 0;
// set points of rectangle(cell中心为(size/2, size/2),加上偏移量是在分辨率下的小网格的位置)
c.x = (double)size / 2 + points[q].x;
c.y = (double)size / 2 + points[q].y;
p[0].x = c.x - Constants::length / 2 / cSize; //车的左上角位置
p[0].y = c.y - Constants::width / 2 / cSize;
p[1].x = c.x - Constants::length / 2 / cSize;//车的左下角位置
p[1].y = c.y + Constants::width / 2 / cSize;
p[2].x = c.x + Constants::length / 2 / cSize;//车的右下角位置
p[2].y = c.y + Constants::width / 2 / cSize;
p[3].x = c.x + Constants::length / 2 / cSize;//车的右上角位置
p[3].y = c.y - Constants::width / 2 / cSize;
for (int o = 0; o < Constants::headings; ++o) {//将朝向划分为72份(离散化)
if (DEBUG) { std::cout << "\ndegrees: " << theta * 180.f / M_PI << std::endl; }
// initialize cSpace
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < size; ++j) {
cSpace[i * size + j] = false;//初化为值为false,表示?
}
}
// shape rotation
for (int j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
// translate point to origin
temp.x = p[j].x - c.x;//以车的中心为坐标原点
temp.y = p[j].y - c.y;
// rotate and shift back:将车旋转theta角度
nP[j].x = temp.x * cos(theta) - temp.y * sin(theta) + c.x;
nP[j].y = temp.x * sin(theta) + temp.y * cos(theta) + c.y;
}//nP存储的是车旋转theta角度的坐标
// create the next angle 下个角度(360度分成72份,步长是: deltaHeadingRad=2*pi/72)
theta += Constants::deltaHeadingRad;
// cell traversal clockwise
// 在cspace里面先把边界涂成白色;bresenham
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
// create the vectors clockwise
if (k < 3) {
start = nP[k];
end = nP[k + 1];
} else {
start = nP[k];
end = nP[0];
}//找到始点、终点
//set indexes
X = (int)start.x;
Y = (int)start.y;
// std::cout << "StartCell: " << X << "," << Y << std::endl;
cSpace[Y * size + X] = true;
t.x = end.x - start.x;
t.y = end.y - start.y;//t为从始点到终点的向量
stepX = sign(t.x);//方向
stepY = sign(t.y);
// width and height normalized by t
if (t.x != 0) {
tDeltaX = 1.f / std::abs(t.x);
} else {
tDeltaX = 1000;
}
if (t.y != 0) {
tDeltaY = 1.f / std::abs(t.y);
} else {
tDeltaY = 1000;
}
// set maximum traversal values 设置行走值,即离一个cell偏离了多少(取值)
if (stepX > 0) {
tMaxX = tDeltaX * (1 - (start.x - (long)start.x));
} else {
tMaxX = tDeltaX * (start.x - (long)start.x);
}
if (stepY > 0) {
tMaxY = tDeltaY * (1 - (start.y - (long)start.y));
} else {
tMaxY = tDeltaY * (start.y - (long)start.y);
}
while ((int)end.x != X || (int)end.y != Y) {
// only increment x if the t length is smaller and the result will be closer to the goal
if (tMaxX < tMaxY && std::abs(X + stepX - (int)end.x) < std::abs(X - (int)end.x)) {
tMaxX = tMaxX + tDeltaX;//更新
X = X + stepX;
cSpace[Y * size + X] = true;//标记已走
// only increment y if the t length is smaller and the result will be closer to the goal
} else if (tMaxY < tMaxX && std::abs(Y + stepY - (int)end.y) < std::abs(Y - (int)end.y)) {
tMaxY = tMaxY + tDeltaY;
Y = Y + stepY;
cSpace[Y * size + X] = true;
} else if (2 >= std::abs(X - (int)end.x) + std::abs(Y - (int)end.y)) {
if (std::abs(X - (int)end.x) > std::abs(Y - (int)end.y)) {
X = X + stepX;
cSpace[Y * size + X] = true;
} else {
Y = Y + stepY;
cSpace[Y * size + X] = true;
}
} else {
// this SHOULD NOT happen
std::cout << "\n--->tie occured, please check for error in script\n";
break;
}
}
}
// FILL THE SHAPE,把边界里面涂成白色;水平扫描,找到最左和最右的白色点
// 原理:在栅格地图里面绘制轮廓多边形,计算多边形覆盖的像素坐标(扫描线);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
// set inside to false
inside = false;
for (int j = 0; j < size; ++j) {
// determine horizontal crossings
for (int k = 0; k < size; ++k) {
if (cSpace[i * size + k] && !inside) {
hcross1 = k;
inside = true;
}
if (cSpace[i * size + k] && inside) {
hcross2 = k;
}
}
// if inside fill
if (j > hcross1 && j < hcross2 && inside) {
cSpace[i * size + j] = true;
}
}
}
// GENERATE THE ACTUAL LOOKUP
count = 0;//生成查找表
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < size; ++j) {
if (cSpace[i * size + j]) {
// compute the relative position of the car cells
lookup[q * Constants::headings + o].pos[count].x = j - (int)c.x;
lookup[q * Constants::headings + o].pos[count].y = i - (int)c.y;
// add one for the length of the current list
count++;
}
}
}
lookup[q * Constants::headings + o].length = count;
if (DEBUG) {
//DEBUG
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
std::cout << "\n";
for (int j = 0; j < size; ++j) {
if (cSpace[i * size + j]) {
std::cout << "#";
} else {
std::cout << ".";
}
}
}
//TESTING
std::cout << "\n\nthe center of " << q* Constants::headings + o << " is at " << c.x << " | " << c.y << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < lookup[q * Constants::headings + o].length; ++i) {
std::cout << "[" << i << "]\t" << lookup[q * Constants::headings + o].pos[i].x << " | " << lookup[q * Constants::headings + o].pos[i].y << std::endl;
}
}
}
}
std::cout << " done!" << std::endl;
}
}
}
#endif // LOOKUP2.2.3. 使用机器轮廓边缘像素模板查表;
仅仅使用机器边缘轮廓对应的像素;
特点:
对于小的障碍物,如果检测的路径点太稀疏会漏检测;
2.2.4. 覆盖栅格模板怎么使用
2.2.4.1. 使用障碍物地图和查找表判断一个位姿下是否发生碰撞;
D:\[opencv_source_navigation]\hybrid-a-star-annotation-master\src\collisiondetection.cpp
// 使用覆盖栅格模板做碰撞检测
bool CollisionDetection::configurationTest(float x, float y, float t) {
int X = (int)x;
int Y = (int)y;
int iX = (int)((x - (long)x) * Constants::positionResolution);//得出X方向在cell中的偏移量
iX = iX > 0 ? iX : 0;
int iY = (int)((y - (long)y) * Constants::positionResolution);//Y方向在cell中的偏移量
iY = iY > 0 ? iY : 0;
int iT = (int)(t / Constants::deltaHeadingRad);
int idx = iY * Constants::positionResolution * Constants::headings + iX * Constants::headings + iT;
int cX;
int cY;
for (int i = 0; i < collisionLookup[idx].length; ++i) {
cX = (X + collisionLookup[idx].pos[i].x);
cY = (Y + collisionLookup[idx].pos[i].y);
// make sure the configuration coordinates are actually on the grid
if (cX >= 0 && (unsigned int)cX < grid->info.width && cY >= 0 && (unsigned int)cY < grid->info.height) {
if (grid->data[cY * grid->info.width + cX]) {
return false;
}//若grid的某个小网格存在值,说明有障碍,则返回false表示不在自由网格
}
}
return true;//所有检测都没有检测到被占用,说明没有障碍,可以通行
}2.2.4.2. 判断一段路径上是否发生碰撞

示例1
bool SpiralFollower::CheckIsObstacleFrontWithLidar(Pose2D &collision_pose, uint32_t &collision_pose_index_on_curve)
{
if (GetCurrentTickMs() - mLastTickMsUseLidar < kUseLidarCheckIntervalThresh) {
return false;
}
mLastTickMsUseLidar = GetCurrentTickMs();
Pose2D curPose = POSEPROVIDER->GetEstimatedPose();
std::vector<Pose2D> &path_points = GetPaths();
uint32_t cur_path_pose_index = GetCurrentIndex();
Pose2D cur_path_pose = path_points[cur_path_pose_index];
// 计算前方路径上要检测碰撞的路径点
std::vector<Pose2D> check_poses; // 前方直线路径上做碰撞检测的路径点位姿
check_poses = GetCheckPoses(k_lidar_check_obs_dis_thresh, curPose, path_points, cur_path_pose_index, cur_path_pose);
// 路径点稀疏化,减少检测耗时
do {
// 路径点太少,不做稀疏化
if (check_poses.size() <= 2) {
break;
}
std::vector<Pose2D> sparse_poses; // 稀疏后的路径点
sparse_poses.push_back(check_poses.front()); // 第一个一定加入
for (size_t i = 1; i < check_poses.size() - 1; i++) {
// 只有距离上一个点距离或者航向差值达到thresh才加入sparse_poses
const float phi_diff_thresh = 0.1f;
const float dis_thresh = 0.3f;
if (check_poses[i].GetDistance(sparse_poses.back()) > dis_thresh ||
fabs(check_poses[i].Phi() - sparse_poses.back().Phi()) > phi_diff_thresh) {
sparse_poses.push_back(check_poses[i]);
}
}
sparse_poses.push_back(check_poses.back());
// check_poses 置换为稀疏的路径点
check_poses = sparse_poses;
} while (0);
// 检测是否发生碰撞
{
// todo 检测位姿是否超过地图范围
TMapData zmap; // todo 搞成一个成员变量或者动态分配
bool ret = LOCAL_ZMAP_EX->GetZmapPreciseCopy(zmap); // 现在都是lidar数据投影到局部planMap,高分辨率
if (ret == false) {
// LOGD("------can not get local zmap to check obstacle in path.");
return false; // 地图没法用,认为没有障碍物,直接撞就好了
}
// debug 判断机器是否在地图之外了
if (0) {
Pose2D zmap_center;
zmap_center.X = zmap.mapParam.xMin + zmap.mapParam.width * 0.5 * zmap.mapParam.resolution;
zmap_center.Y = zmap.mapParam.yMin + zmap.mapParam.height * 0.5 * zmap.mapParam.resolution;
// curPose = POSEPROVIDER->GetEstimatedPose();
auto dis = zmap_center.GetDistance(POSEPROVIDER->GetEstimatedPose());
// 打印稀疏一点
if (dis > 1.f && LOG_INTERVAL_CHECK(100)) {
LOGD("[sparse log] curpose far from zmaplidar center,dis[%f],curpose[%f,%f],map center[%f,%f]", dis, curPose.X, curPose.Y, zmap_center.X, zmap_center.Y);
}
}
// 去除footprint内的黑点
{
// CollisionCheck::RemoveBlackPixelInCarPoseFootprint(&zmap, cur_path_pose); // 最近的一个位姿轮廓里面的黑点去掉的话近距离可能会导致碰撞
bool remove_self_footprint = CollisionCheck::RemoveBlackPixelInCarPoseFootprint(&zmap, curPose);
// 打印是否车身位姿超出地图范围
if (remove_self_footprint == false && LOG_INTERVAL_CHECK(2000)) {
LOGW("--carpose beyond localzmap range");
}
}
uint32_t index_add = 0;
for (auto point : check_poses) {
int obsPointNum = 0;
std::vector<Pose2D> vec_obs_pose_in_zmap; // 障碍物点的物理坐标
auto ret = CollisionCheck::CheckFootPrintCollisionInZmap(TARGETNAVI_EX->GetCollisionLookup(), zmap, point, obsPointNum, vec_obs_pose_in_zmap); // 超出zmap范围的点不考虑
const int k_obs_point_num_thresh = 4;
if (ret == true && obsPointNum >= k_obs_point_num_thresh) {
collision_pose = point; // 前方直线段上会发生碰撞的位姿
collision_pose_index_on_curve = cur_path_pose_index + index_add; // 计算collision_pose的序号
if (LOG_INTERVAL_CHECK(200)) {
LOGD("----lidar check obs at pathPose[%f,%f,%f]", collision_pose.X, collision_pose.Y, collision_pose.Phi());
}
return true; // 存在障碍物
}
index_add++;
}
return false;
}
}示例2
// 判断当前路径上是否有碰撞,使用lidar地图
// return:obsDistance为障碍物到当前点的距离, collision_pose_in_global_path检测到碰撞的路径点的位姿, collision_index_in_globdal_path检测到碰撞的路径点的序号
// return: true 表示路径足迹上有障碍物
bool CTargetNavigatorEx::CheckFootPrintCollisionInPath_ZmapLidar(float &obsDistance, Pose2D &collision_pose_in_global_path, uint32_t &collision_index_in_global_path)
{
//TODO: pathfollower的每一个循环周期都会拷贝一次地图,资源消耗太大了 / not care
//done 路径点太密集,调用频繁,耗时太大;done 检测稀疏一点
TMapData zmap; // todo 搞成一个成员变量或者动态分配
bool ret = LOCAL_ZMAP_EX->GetZmapPreciseCopy(zmap); // 现在都是lidar数据投影到局部planMap,高分辨率
if (ret == false) {
LOGDPC("------can not get local zmap to check obstacle in path.");
return false; // 地图没法用,认为没有障碍物,直接撞就好了
}
// 调试, 发送地图
{
// debug 发送local zmap
// if (LOG_INTERVAL_CHECK(5000)) {
// LOGDPC("----- SendTmap zmapPrecise");
// VisualizationUtil::Instance()->SendTmap(1, zmap);
// }
// debug 发送原始slam地图
if (LOG_INTERVAL_CHECK(8000)) {
static TMapData planMap; //搞成静态存储
int res = LOCAL_ZMAP_EX->GetPlanMapData(planMap);
if (res == 0) {
LOGDPC("----- SendTmap planMap");
// VisualizationUtil::Instance()->SendTmap(0, planMap);
} else {
LOGDPC("----- GetPlanMapData failed");
}
}
}
// 去除footprint内的黑点
{
CollisionCheck::RemoveBlackPixelInCarPoseFootprint(&zmap, mCurrentPose);
}
// mCollisionLookup 查表,检测footprint碰撞
TMapData checkPathMapShow = zmap; // debug 检测的足迹绘制到图片上,用于调试
checkPathMapShow.map.assign(checkPathMapShow.map.size(), 0); // debug 用于显示检测的区域
// 获取路径和当前跟踪的路径点序号
if (mCurveFollower == nullptr || mCurveFollower->GetPaths().size() < 2) {
return false;
}
std::vector<Pose2D> path = mCurveFollower->GetPaths();
unsigned int index = mCurveFollower->GetCurrentIndex();
{
static unsigned int lastIndex = index;
if (index != lastIndex ) {
LOGDPC("----check curve collision, path index:%d / path size:%d", index, path.size());
}
lastIndex = index;
}
unsigned int startIndex = index; // 第一个判断的路径点序号,用于判断后面的路径点和第一个判断点角度偏差,用于提前结束判断
float disAccumulate = 0.0f; // 沿路径检测的距离
float angleDiff = 0.0f; // 沿路径检测时偏转的角度,角度太大就直接结束了
// done: 这里应该还有转角要求,路径转角太大就不应该判断这么远的距离
while (disAccumulate < k_COLLISION_CHECK_MAX_DIS_MAX && index < path.size()) {
Pose2D currentPose = path[index];
//TODO 越界检查,localZMap可能更新不及时
int obsNum = 0; // 足迹上的障碍物格点统计
// 判断footprint 碰撞 start
float x = (currentPose.X - zmap.mapParam.xMin)/zmap.mapParam.resolution;
float y = (currentPose.Y - zmap.mapParam.yMin)/zmap.mapParam.resolution;
float t = currentPose.Phi();
if (t < 0.f) {
t += M_2PI; // fix 角度转换到0~2pi; 参考:E:\[opencv_source_navigation]\hybrid-a-star-annotation-master\src\collisiondetection.cpp
}
int X = (int)x; // 机器在 zmap 中的坐标
int Y = (int)y; // 机器在 zmap 中的坐标
int iX = (int)((x - (long)x) * LookupConstants::positionResolution); // X方向在cell中的偏移量
iX = iX > 0 ? iX : 0;
int iY = (int)((y - (long)y) * LookupConstants::positionResolution); // Y方向在cell中的偏移量
iY = iY > 0 ? iY : 0;
int iT = (int)(t / LookupConstants::deltaHeadingRad);
int idx = iY * LookupConstants::positionResolution * LookupConstants::headings + iX * LookupConstants::headings + iT;
int cX;
int cY;
for (int i = 0; i < mCollisionLookup[idx].length; ++i) {
cX = (X + mCollisionLookup[idx].pos[i].x); // 在 zmap 中需要查询的坐标
cY = (Y + mCollisionLookup[idx].pos[i].y); // 在 zmap 中需要查询的坐标
// make sure the configuration coordinates are actually on the grid
if (cX >= 0 && cX < zmap.mapParam.width && cY >= 0 && cY < zmap.mapParam.height) {
// if (grid->data[cY * grid->info.width + cX]) {
// return false;
// }//若grid的某个小网格存在值,说明有障碍,返回false表示不在自由网格
// zmap.map[cY * zmap.mapParam.width + cX] == 0;
// TODO:优化,这里重复搜索了
auto index_check = cY * zmap.mapParam.width + cX;
checkPathMapShow.map[index_check] = 127;
if (zmap.map[index_check] <= 127) {
obsNum ++;
checkPathMapShow.map[index_check] = 200; // 碰撞的点涂白一点
}
}
}
// 判断footprint 碰撞 end 上面的这部分判断可以直接使用函数CheckFootPrintInZmap用记录的序号涂抹checkPathMap,这里也可以重新写一遍,避免函数调用开销,或者直接写成inline ;
// 判断obsNum是否足够
if (obsNum > k_COLLISION_CHECK_OBS_NUM_THRESH) {
obsDistance = disAccumulate;
collision_pose_in_global_path = path[index];
collision_index_in_global_path = index;
// if (LOG_INTERVAL_CHECK(2000)) {
// VisualizationUtil::Instance()->SendTmap(2, checkPathMapShow); // 检测到障碍物时,也发送当前搜索的足迹路线
// }
return true;
}
// hybrid路径点太密集,不能每一个路径点都做碰撞检测
if (mCurveFollower->IsUsingHybridPath() == true) {
if (index + 4 < path.size()) {
if (fabs(path[index + 4].Phi() - currentPose.Phi()) < DEG2RAD(5)) {
index += 4;
} else {
index += 2;
}
} else {
if (index + 2 < path.size()) {
index += 2;
} else {
index += 1;
}
}
} else {
index += 1;
}
if(index >= path.size()) {
break; // 遍历到终点了还没有碰撞,直接结束
}
disAccumulate += currentPose.GetDistance(path[index]);
// 角度相差太大也直接结束,不检测了,因为雷达可能打不到
angleDiff = fabs(currentPose.Phi() - path[startIndex].Phi());
//TODO 转角的大小测试调整
// const float k_collision_angle_valid_thresh = DEG2RAD(45); // 遍历的路径转角超过了45度,直接结束 todo:45度有待调整,正确的应该是根据雷达来判断,雷达打不到的路径点就不需要判断了
if (angleDiff >= k_collision_angle_valid_thresh) {
break; // 遍历的路径转角超过了45度,直接结束 todo:45度有待调整,正确的应该是根据雷达来判断,雷达打不到的路径点就不需要判断了
}
}
// 发送检测路径上的足迹
// if (LOG_INTERVAL_CHECK(3000)) {
// VisualizationUtil::Instance()->SendTmap(2, checkPathMapShow);
// }
return false;
}3. 使用静态地图做碰撞检测时的技巧
将静态的障碍物建立一个空间索引;做最近邻搜索;
例如:
对一米范围内的障碍物做最近邻查询,再使用几何方法判断是否发生碰撞;
因为障碍物不会变;用空间换时间;
3.1. 适用场景:路径搜索中的碰撞检测;
3.2. 可以使用最近邻工具优化;
使用覆盖栅格模板结合最近邻搜索;
参考
D:\[OPENSOURCE_CODE]\teb\include\robot_footprint_model
4. 在动态环境使用实时局部融合地图做碰撞检测时的技巧
4.1. 为什么使用高分辨率局部地图?
问题:
障碍物地图分辨率太低可能导致机器距离障碍无太近时规划卡死或者不必要的停障或动作;
大地图刷新速度慢,精度低,窄通道问题;
传感器感受范围有限,不需要考虑资源消耗,保留数据精度;
需要融合多种感知信息,丢失精度;
4.2. 多个局部障碍物地图如何叠加和尺寸对齐?
全局格点对齐;
分别检测,不叠加;
有些离散的检测信息不投影到障碍物地图,不记录历史信息,直接使用几何方法判断碰撞;
4.3. 感知信息的生命周期管理,如何利用感知信息的时空上下文
4.3.1. 目标跟踪和数据关联;
example:
动态障碍物检测;
rgb检测结果bounding box与depth数据关联;GMM,用于深度图中检测人的距离
2d lidar数据下的人腿检测与跟踪;
多目标检测匹配与data association;2d雷达特征点检测和匹配,回环检测
ai检测目标的跟踪;
3d lidar 动态cluster的检测和跟踪;hdl graph slam / tracking;
4.3.2. 沿墙数据的生命周期管理;
沿墙数据:
线激光数据;投影到局部地图;
lidar局部地图;去除近距离数据;
超声波单帧实时数据,注意数据丢失防错;
沿墙数据的更新:
4.3.3. 局部清图策略
历史数据序列中时间空间间隔范围外的数据清除;
优先级不高的数据优先清除;
4.4. 不同感知信息的优先级
优先使用高频实时的数据;
优先检测近处感知数据;
4.5. 急停和碰撞应激反应的处理
5. vision sensor等离散型感知结果用于地图标记、碰撞检测、减速、停障;
5.1. 不规则物体的描述和空间索引
boundingBox记录;使用多边形记录;
使用octree记录,投影到二维平面;
在障碍物地图中标记,膨胀处理;







 该博客围绕自动驾驶中的碰撞检测展开。介绍了碰撞检测在路径规划和避障中的应用,如泊车和路径规划场景。详细阐述了几何方法、覆盖栅格模板和查表法等碰撞检测方法,还分享了在静态地图和动态环境中做碰撞检测的技巧,以及离散型感知结果的应用。
该博客围绕自动驾驶中的碰撞检测展开。介绍了碰撞检测在路径规划和避障中的应用,如泊车和路径规划场景。详细阐述了几何方法、覆盖栅格模板和查表法等碰撞检测方法,还分享了在静态地图和动态环境中做碰撞检测的技巧,以及离散型感知结果的应用。


















 1518
1518

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










