一. 数据源介绍
churn.csv
这个国外一个运营商的数据,有标签标记用户是否流失
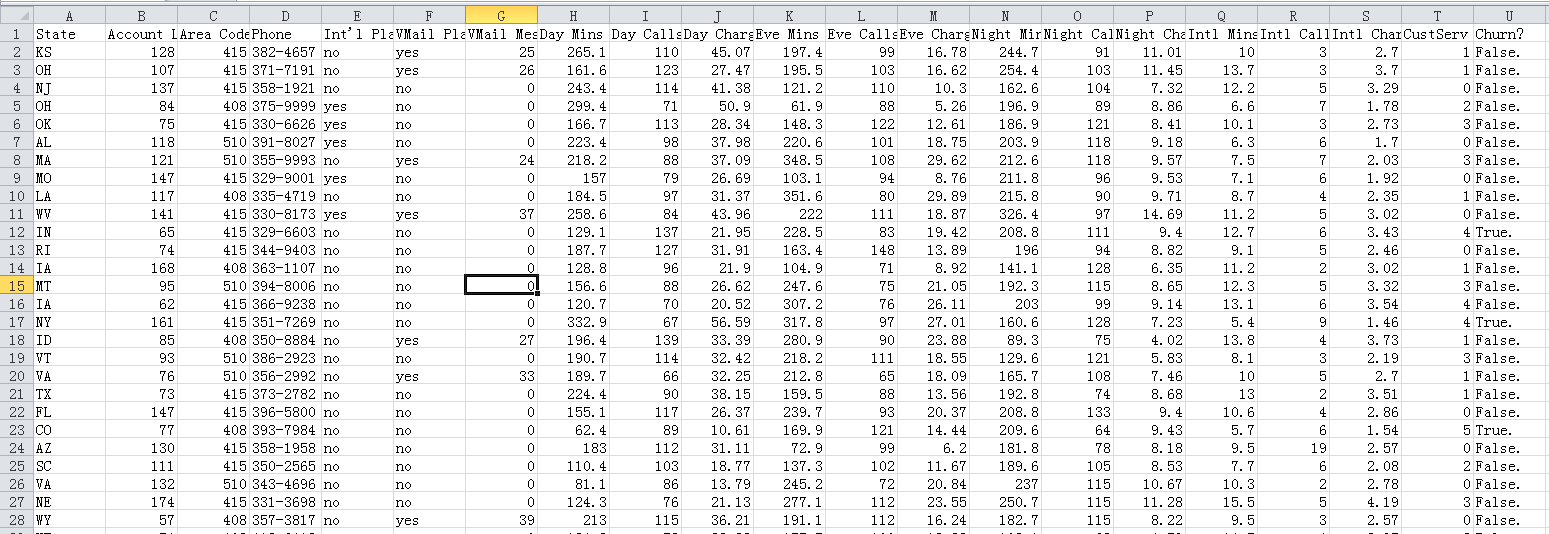
列介绍:
State: 州名/区域
Account Length: 账户长度
Area Code: 区号
Phone: 电话号码
Int'l Plan: 国际漫游需求与否
VMailPlan: 参与活动
Day Mins: 白天通话分钟数
Day Calls: 白天打电话个数
Day Charge: 白天收费情况
Eve Mins: 晚间通话分钟数
Eve Calls: 晚间打电话个数
Evr Charge: 晚间收费情况
Night Mins: 夜间通话分钟数
Night Calls: 夜间打电话个数
Night Charge: 夜间收费情况
Intl Mins: 国际通话分钟数
Intl Calls: 国际电话个数
Intl Charge: 国际收费
CusServ Calls: 客服电话数量
Churn: 是否流失
二. 数据预处理
分析数据,我们可以初步得出如下结论:
- 标签值是 True 、False,需改为 1和0.
- ‘State’,‘Area Code’,‘Phone’ 这几个特征值与是否流失关系不大
- 部分特征值为yes 、no,需改为 1和0.
- 数据需要做归一化处理
代码:
from __future__ import division
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier as RF
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier as KNN
# 读取数据源
churn_df = pd.read_csv('E:/file/churn.csv')
col_names = churn_df.columns.tolist()
# 获取标签,并将True 改为 1,False 改为 0
churn_result = churn_df['Churn?']
y = np.where(churn_result == 'True.',1,0)
# 删除不需要的列
to_drop = ['State','Area Code','Phone','Churn?']
churn_feat_space = churn_df.drop(to_drop,axis=1)
# 'yes'/'no' has to be converted to boolean values
# NumPy converts these from boolean to 1. and 0. later
yes_no_cols = ["Int'l Plan","VMail Plan"]
churn_feat_space[yes_no_cols] = churn_feat_space[yes_no_cols] == 'yes'
# 选取特征咧
features = churn_feat_space.columns
X = churn_feat_space.iloc[:,:].values.astype(np.float)
# 数据归一化
scaler = StandardScaler()
X = scaler.fit_transform(X)
print ("Feature space holds %d observations and %d features" % X.shape)
print ("Unique target labels:", np.unique(y))
print (X[0])
print (len(y[y == 0]))
测试记录:
Feature space holds 3333 observations and 17 features
Unique target labels: [0 1]
[ 0.67648946 -0.32758048 1.6170861 1.23488274 1.56676695 0.47664315
1.56703625 -0.07060962 -0.05594035 -0.07042665 0.86674322 -0.46549436
0.86602851 -0.08500823 -0.60119509 -0.0856905 -0.42793202]
2850
三. 选择算法
我们使用SVM、随机森林、KNN算法来训练模型
代码:
from __future__ import division
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier as RF
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier as KNN
# 读取数据源
churn_df = pd.read_csv('E:/file/churn.csv')
col_names = churn_df.columns.tolist()
# 获取标签,并将True 改为 1,False 改为 0
churn_result = churn_df['Churn?']
y = np.where(churn_result == 'True.',1,0)
# 删除不需要的列
to_drop = ['State','Area Code','Phone','Churn?']
churn_feat_space = churn_df.drop(to_drop,axis=1)
# 'yes'/'no' has to be converted to boolean values
# NumPy converts these from boolean to 1. and 0. later
yes_no_cols = ["Int'l Plan","VMail Plan"]
churn_feat_space[yes_no_cols] = churn_feat_space[yes_no_cols] == 'yes'
# 选取特征咧
features = churn_feat_space.columns
X = churn_feat_space.iloc[:,:].values.astype(np.float)
# 数据归一化
scaler = StandardScaler()
X = scaler.fit_transform(X)
# 交叉验证
def run_cv(X,y,clf_class,**kwargs):
# Construct a kfolds object
kf = KFold(n_splits=5, random_state=None, shuffle=True)
y_pred = y.copy()
# Iterate through folds
for train_index, test_index in kf.split(X):
X_train, X_test = X[train_index], X[test_index]
y_train = y[train_index]
# Initialize a classifier with key word arguments
clf = clf_class(**kwargs)
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
y_pred[test_index] = clf.predict(X_test)
return y_pred
def accuracy(y_true,y_pred):
# NumPy interprets True and False as 1. and 0.
return np.mean(y_true == y_pred)
# 训练模型
print ("Support vector machines:")
print ("%.3f" % accuracy(y, run_cv(X,y,SVC)))
print ("Random forest:")
print ("%.3f" % accuracy(y, run_cv(X,y,RF)))
print ("K-nearest-neighbors:")
print ("%.3f" % accuracy(y, run_cv(X,y,KNN)))
测试记录:
Support vector machines:
0.917
Random forest:
0.955
K-nearest-neighbors:
0.890
四. 模型选择
模型选择我们不能只看准确率,需要考虑召回率等指标,也可以根据实际情况选择最适合的模型
代码:
from __future__ import division
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier as RF
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier as KNN
import warnings
# 忽略警告
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# 读取数据源
churn_df = pd.read_csv('E:/file/churn.csv')
col_names = churn_df.columns.tolist()
# 获取标签,并将True 改为 1,False 改为 0
churn_result = churn_df['Churn?']
y = np.where(churn_result == 'True.',1,0)
# 删除不需要的列
to_drop = ['State','Area Code','Phone','Churn?']
churn_feat_space = churn_df.drop(to_drop,axis=1)
# 'yes'/'no' has to be converted to boolean values
# NumPy converts these from boolean to 1. and 0. later
yes_no_cols = ["Int'l Plan","VMail Plan"]
churn_feat_space[yes_no_cols] = churn_feat_space[yes_no_cols] == 'yes'
# 选取特征咧
features = churn_feat_space.columns
X = churn_feat_space.iloc[:,:].values.astype(np.float)
# 数据归一化
scaler = StandardScaler()
X = scaler.fit_transform(X)
# 交叉验证
def run_prob_cv(X, y, clf_class, **kwargs):
kf = KFold(n_splits=5, random_state=None, shuffle=True)
y_prob = np.zeros((len(y),2))
for train_index, test_index in kf.split(X):
X_train, X_test = X[train_index], X[test_index]
y_train = y[train_index]
clf = clf_class(**kwargs)
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
# Predict probabilities, not classes
y_prob[test_index] = clf.predict_proba(X_test)
return y_prob
# Use 10 estimators so predictions are all multiples of 0.1
pred_prob = run_prob_cv(X, y, RF, n_estimators=10)
#print pred_prob[0]
pred_churn = pred_prob[:,1]
is_churn = y == 1
# Number of times a predicted probability is assigned to an observation
counts = pd.value_counts(pred_churn)
#print counts
# calculate true probabilities
true_prob = {}
for prob in counts.index:
true_prob[prob] = np.mean(is_churn[pred_churn == prob])
true_prob = pd.Series(true_prob)
# pandas-fu
counts = pd.concat([counts,true_prob], axis=1).reset_index()
counts.columns = ['pred_prob', 'count', 'true_prob']
print(counts)
测试记录:
pred_prob 代表用户流失的概率 (调用sklearn 的 predict_proba API即可)
true_prob 是该类概率下的用户真是流失的比例
pred_prob count true_prob
0 0.0 1753 0.029093
1 0.1 742 0.022911
2 0.2 240 0.041667
3 0.3 113 0.123894
4 0.8 96 0.947917
5 0.9 89 0.966292
6 0.4 69 0.362319
7 0.7 63 0.888889
8 1.0 63 0.984127
9 0.6 54 0.759259
10 0.5 51 0.588235
参考:
- https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1003590004#/courseDetail?tab=1


























 4595
4595











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








