State Threads(ST)学习笔记
一、ST简介
ST是一个C语言微线程开源库:http://sourceforge.net/projects/state-threads/
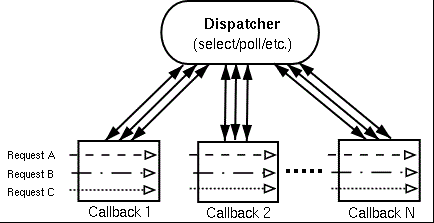
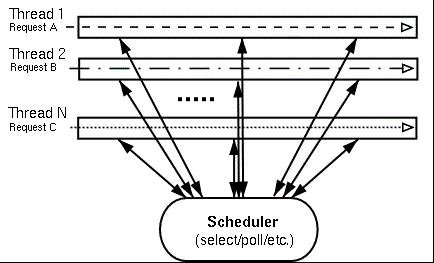
微线程最大的好处就是将传统的EDSM(Event Drive State Machine)异步化多路复用编程(epoll/select等)串行化。通过在一个进程内模拟多个微线程并发,使得异步编程像同步一样简单。但是ST的本质仍然是基于EDSM模型,ST将请求抽象为thread概念,ST的调度器(scheduler)对于用户来说是透明的,不像dispatcher那种将执行状态(execute state)暴露给回调方式。
传统EDSM调度模型
ST调度模型
ST通过setjmp和longjmp来实现微线程调用栈上下文(仅包括寄存器状态)的保存与恢复。而调用栈是通过额外分配堆内存来保存的,并没有与物理进程共享调用栈。
二、ST的栈结构介绍
1. // 栈结构
2. typedef struct _st_stack {
3. _st_clist_t links;
4. char *vaddr; /* Base of stack's allocated memory */
5. int vaddr_size; /* Size of stack's allocated memory */
6. int stk_size; /* Size of usable portion of the stack */
7. char *stk_bottom; /* Lowest address of stack's usable portion */
8. char *stk_top; /* Highest address of stack's usable portion */
9. void *sp; /* Stack pointer from C's point of view */
10. } _st_stack_t;
11. //线程结构
12. typedef struct _st_thread {
13. int state; /* Thread's state */
14. int flags; /* Thread's flags */
15. void *(*start)(void *arg); /* The start function of the thread */
16. void *arg; /* Argument of the start function */
17. void *retval; /* Return value of the start function */
18. _st_stack_t *stack; /* Info about thread's stack */
19. _st_clist_t links; /* For putting on run/sleep/zombie queue */
20. _st_clist_t wait_links; /* For putting on mutex/condvar wait queue */
21. st_utime_t due; /* Wakeup time when thread is sleeping */
22. _st_thread_t *left; /* For putting in timeout heap */
23. _st_thread_t *right; /* -- see docs/timeout_heap.txt for details */
24. int heap_index;
25. void **private_data; /* Per thread private data */
26. _st_cond_t *term; /* Termination condition variable for join */
27. jmp_buf context; /* Thread's context */
28. } st_thread_t;
微线程栈结构图
上图是栈分配后的结果,两边是REDZONE使用mprotect保护不被访问(仅debug模式开启),extra是用于开启随机栈地址空间使用的,随机栈地址开启后会调整bottom和top,就是随机的向右边移动一点。应该是用于防止栈溢出攻击。总之,最后使用的,对外提供的接口就是[bottom, top]这个内存区域,[bottom, top]区域又进一步分为:
ptds:微线程的私有数据(private_data),是12个指针(ST_KEYS_MAX指定),参考st_key_create()。
trd:st_thread_t结构本身也是在这个stack中分配的。
pad+align:在trd之后是对齐和pad(_ST_STACK_PAD_SIZE指定)。
sp:微线程实际的栈指针。
st_thread_create函数创建微线程时会初始化sp。微线程栈的分配详情参考_st_stack_new函数。
三、重要函数注释
1)st_thread_create
1. /*
2. * 创建微线程
3. * @start微线程start函数
4. * @arg入口函数参数列表
5. * @joinablejoinable标记
6. * @stk_size微线程栈大小
7. */
8. _st_thread_t *st_thread_create(void *(*start)(void *arg), void *arg, int joinable, int stk_size)
9. {
10. _st_thread_t *thread;
11. _st_stack_t *stack;
12. void **ptds;
13. char *sp;
14.
15. /* 调整线程栈大小 */
16. if (stk_size == 0)
17. /* 如果stk_size为0,设置为默认大小 */
18. stk_size = ST_DEFAULT_STACK_SIZE;
19. /* 否则调整栈大小为内存页的整数倍 */
20. stk_size = ((stk_size + _ST_PAGE_SIZE - 1) / _ST_PAGE_SIZE) * _ST_PAGE_SIZE;
21. /* 申请占空间并对栈空间结构初始化,参见微线程栈结构图 */
22. stack = _st_stack_new(stk_size);
23. if (!stack)








 本文深入介绍了State Threads (ST) 模块,这是一个C语言实现的微线程库。文章详细讲解了ST如何通过setjmp和longjmp实现微线程调用栈的保存与恢复,以及ST线程的栈结构和线程结构。此外,还阐述了重要的函数如st_thread_create、st_thread_exit和调度过程。ST通过将异步编程串行化,简化了事件驱动的状态机模型。最后,文中提供了ST线程生命周期的概述及示例代码,帮助读者理解ST的使用。
本文深入介绍了State Threads (ST) 模块,这是一个C语言实现的微线程库。文章详细讲解了ST如何通过setjmp和longjmp实现微线程调用栈的保存与恢复,以及ST线程的栈结构和线程结构。此外,还阐述了重要的函数如st_thread_create、st_thread_exit和调度过程。ST通过将异步编程串行化,简化了事件驱动的状态机模型。最后,文中提供了ST线程生命周期的概述及示例代码,帮助读者理解ST的使用。

 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 480
480

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








