abstract
the resting membrane potential results from the separation of charge across the cell membrane
the resting membrane potential is determined by nongated and gated ion channels
open channels in glial cells are permeable to potassium only
open channels in resting nerve cells are permeable to several ion species
the electrochemical gradients of sodium, potassium, and calcium are established by active transport of the ions
chloride ions are also actively transported
the balance of ion fluxes that maintains the resting membrane potential is abolished during the action potential
the contribution of different ions to the resting membrane potential can be quantified by the Goldman equation
the functional properties of the neuron can be represented as an electrical equivalent circuit
the passive electrical properties of the neuron affect electrical signaling
membrane capacitance slows the time course of electrical signals
membrane and axoplasmic resistance affect the efficiency of signal conduction
large axons are more easily excited than small axons
passive membrane properties and axon diameter affect the velocity of action potential propagation
an overall view
content
the resting membrane potential results from the separation of charge across the cell membrane
127
a reduction or reversal membrane potential, is called depolarization. an increase in charge separation, leading to a more negative membrane potential, is called hyperpolarization
the resting membrane potential is determined by nongated and gated ion channels
open channels in glial cells are permeable to potassium only
open channels in resting nerve cells are permeable to several ion species
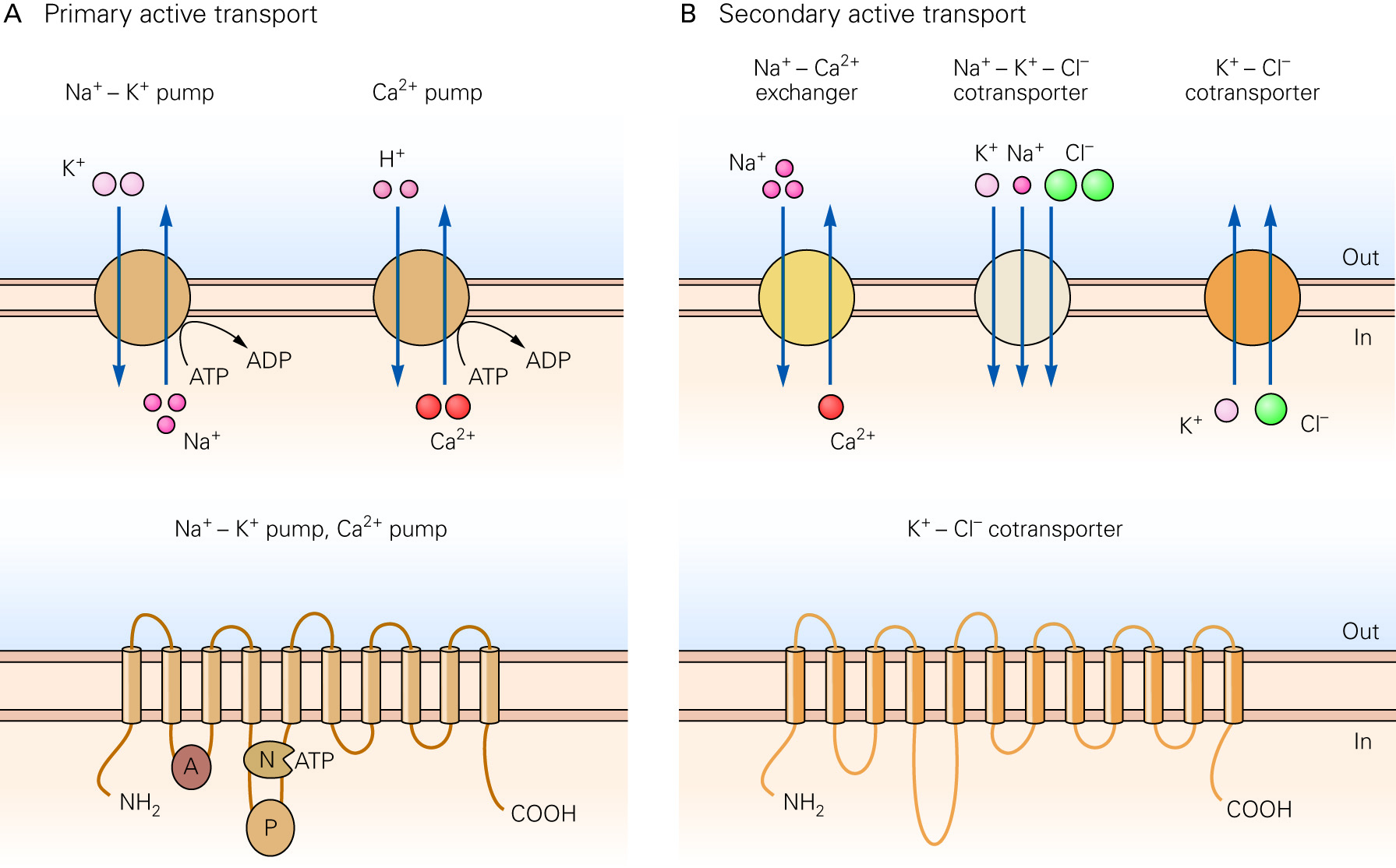
the electrochemical gradients of sodium, potassium, and calcium are established by active transport of the ions
pumps and transporters regulate the chemical concentration gradients of Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Cl- ions
chloride ions are also actively transported
the balance of ion fluxes that maintain the resting membrane potential is abolished during the action potential
the contributions of different ions to the resting membrane potential can be quantified by the Goldman equation
the functional properties of the neuron can be represented as an electrical equivalent circuit
the passive electrical properties of the neuron affect electrical signaling
138
neurons have three passive electrical properties that are important for electrical signaling. we have already considered the resting membrane conductance or resistance and the membrane capacitance. a third important property that determines signal propagation along dendrites or axons is their intracellular axial resistance
membrane capacitance slows the time course of electrical signals
membrane and axoplasmic resistance affect the efficiency of signal conduction
large axons are more easily excited than small axons
passive membrane properties and axon diameter affect the velocity of action potential propagation
145
to prevent the action potential from dying out, the myelin sheath is interrupted every 1 to 2 mm by bare patches of axon membrane approximately 1 um in length, the nodes of Ranvier. although the area of membrane at each node is quite small, the nodal membrane is rich in voltage-gated Na+ channels and thus can generate an intense depolarizing inward Na+ current in response to the passive spread of depolarization down the axon. these regularly distributed nodes thus boost the amplitude of the action potential periodically, preventing it from decaying with distance






















 264
264

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








