The str.format() method and theFormatter class share the samesyntax for format strings (although in the case ofFormatter,subclasses can define their own format string syntax). The syntax isrelated to that offormatted string literals, butthere are differences.
Format strings contain “replacement fields” surrounded by curly braces{}.Anything that is not contained in braces is considered literal text, which iscopied unchanged to the output. If you need to include a brace character in theliteral text, it can be escaped by doubling:{{ and }}.
The grammar for a replacement field is as follows:
replacement_field ::= "{" [field_name] ["!" conversion] [":" format_spec] "}"
field_name ::= arg_name ("." attribute_name | "[" element_index "]")*
arg_name ::= [identifier | digit+]
attribute_name ::= identifier
element_index ::= digit+ | index_string
index_string ::= <any source character except "]"> +
conversion ::= "r" | "s" | "a"
format_spec ::= <described in the next section>In less formal terms, the replacement field can start with afield_name that specifiesthe object whose value is to be formatted and insertedinto the output instead of the replacement field.Thefield_name is optionally followed by aconversion field, which ispreceded by an exclamation point'!', and aformat_spec, which is precededby a colon':'. These specify a non-default format for the replacement value.
See also the Format Specification Mini-Language section.
The field_name itself begins with an arg_name that is either a number or akeyword. If it’s a number, it refers to a positional argument, and if it’s a keyword,it refers to a named keyword argument. If the numerical arg_names in a format stringare 0, 1, 2, … in sequence, they can all be omitted (not just some)and the numbers 0, 1, 2, … will be automatically inserted in that order.Becausearg_name is not quote-delimited, it is not possible to specify arbitrarydictionary keys (e.g., the strings'10' or ':-]') within a format string.Thearg_name can be followed by any number of index orattribute expressions. An expression of the form'.name' selects the namedattribute usinggetattr(), while an expression of the form'[index]'does an index lookup using__getitem__().
Changed in version 3.1:The positional argument specifiers can be omitted, so'{}{}' isequivalent to'{0}{1}'.
Some simple format string examples:
"First, thou shalt count to {0}" # References first positional argument
"Bring me a {}" # Implicitly references the first positional argument
"From {} to {}" # Same as "From {0} to {1}"
"My quest is {name}" # References keyword argument 'name'
"Weight in tons {0.weight}" # 'weight' attribute of first positional arg
"Units destroyed: {players[0]}" # First element of keyword argument 'players'.The conversion field causes a type coercion before formatting. Normally, thejob of formatting a value is done by the__format__() method of the valueitself. However, in some cases it is desirable to force a type to be formattedas a string, overriding its own definition of formatting. By converting thevalue to a string before calling__format__(), the normal formatting logicis bypassed.
Three conversion flags are currently supported: '!s' which calls str()on the value,'!r' which callsrepr() and'!a' which callsascii().
Some examples:
"Harold's a clever {0!s}" # Calls str() on the argument first
"Bring out the holy {name!r}" # Calls repr() on the argument first
"More {!a}" # Calls ascii() on the argument first
总结:由上述可知:
x!r表示repr(x)
x!s表示str(x)
x!a表示ascii(x)
而更常见的则应为下面这种格式等:
return '{}({!r},{!r})'.format(class_name,*self)
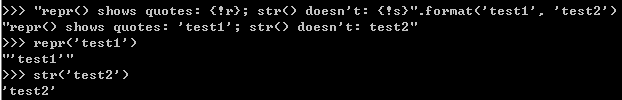
return '{!r},{!s},{!a}'.format(str1,str2,str3)如下图输出,注意repr与str的区别,前者显示引号,后者不显示:






















 3万+
3万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








