- created by gloomyfish
图像处理之霍夫变换圆检测算法
之前写过一篇文章讲述霍夫变换原理与利用霍夫变换检测直线, 结果发现访问量还是蛮
多,有点超出我的意料,很多人都留言说代码写得不好,没有注释,结构也不是很清晰,所以
我萌发了再写一篇,介绍霍夫变换圆检测算法,同时也尽量的加上详细的注释,介绍代码
结构.让更多的人能够读懂与理解.
一:霍夫变换检测圆的数学原理
根据极坐标,圆上任意一点的坐标可以表示为如上形式, 所以对于任意一个圆, 假设
中心像素点p(x0, y0)像素点已知, 圆半径已知,则旋转360由极坐标方程可以得到每
个点上得坐标同样,如果只是知道图像上像素点, 圆半径,旋转360°则中心点处的坐
标值必定最强.这正是霍夫变换检测圆的数学原理.
二:算法流程
该算法大致可以分为以下几个步骤
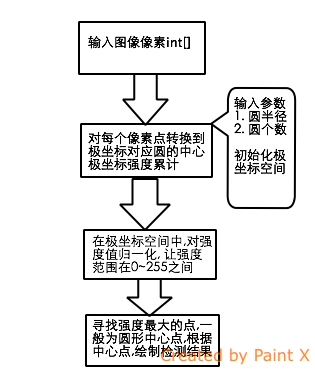
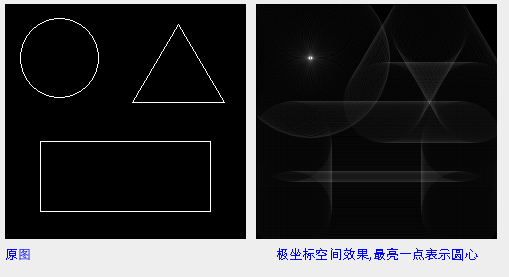
三:运行效果
图像从空间坐标变换到极坐标效果, 最亮一点为圆心.
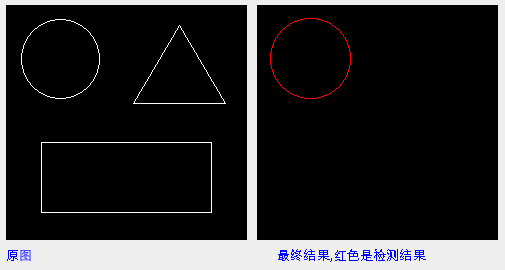
图像从极坐标变换回到空间坐标,检测结果显示:
四:关键代码解析
个人觉得这次注释已经是非常的详细啦,而且我写的还是中文注释
/**
* 霍夫变换处理 - 检测半径大小符合的圆的个数
* 1. 将图像像素从2D空间坐标转换到极坐标空间
* 2. 在极坐标空间中归一化各个点强度,使之在0〜255之间
* 3. 根据极坐标的R值与输入参数(圆的半径)相等,寻找2D空间的像素点
* 4. 对找出的空间像素点赋予结果颜色(红色)
* 5. 返回结果2D空间像素集合
* @return int []
*/
public int[] process() {
// 对于圆的极坐标变换来说,我们需要360度的空间梯度叠加值
acc = new int[width * height];
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
acc[y * width + x] = 0;
}
}
int x0, y0;
double t;
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
if ((input[y * width + x] & 0xff) == 255) {
for (int theta = 0; theta < 360; theta++) {
t = (theta * 3.14159265) / 180; // 角度值0 ~ 2*PI
x0 = (int) Math.round(x - r * Math.cos(t));
y0 = (int) Math.round(y - r * Math.sin(t));
if (x0 < width && x0 > 0 && y0 < height && y0 > 0) {
acc[x0 + (y0 * width)] += 1;
}
}
}
}
}
// now normalise to 255 and put in format for a pixel array
int max = 0;
// Find max acc value
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
if (acc[x + (y * width)] > max) {
max = acc[x + (y * width)];
}
}
}
// 根据最大值,实现极坐标空间的灰度值归一化处理
int value;
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
value = (int) (((double) acc[x + (y * width)] / (double) max) * 255.0);
acc[x + (y * width)] = 0xff000000 | (value << 16 | value << 8 | value);
}
}
// 绘制发现的圆
findMaxima();
System.out.println("done");
return output;
} package com.gloomyfish.image.transform.hough;
/***
*
* 传入的图像为二值图像,背景为黑色,目标前景颜色为为白色
* @author gloomyfish
*
*/
public class CircleHough {
private int[] input;
private int[] output;
private int width;
private int height;
private int[] acc;
private int accSize = 1;
private int[] results;
private int r; // 圆周的半径大小
public CircleHough() {
System.out.println("Hough Circle Detection...");
}
public void init(int[] inputIn, int widthIn, int heightIn, int radius) {
r = radius;
width = widthIn;
height = heightIn;
input = new int[width * height];
output = new int[width * height];
input = inputIn;
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
output[x + (width * y)] = 0xff000000; //默认图像背景颜色为黑色
}
}
}
public void setCircles(int circles) {
accSize = circles; // 检测的个数
}
/**
* 霍夫变换处理 - 检测半径大小符合的圆的个数
* 1. 将图像像素从2D空间坐标转换到极坐标空间
* 2. 在极坐标空间中归一化各个点强度,使之在0〜255之间
* 3. 根据极坐标的R值与输入参数(圆的半径)相等,寻找2D空间的像素点
* 4. 对找出的空间像素点赋予结果颜色(红色)
* 5. 返回结果2D空间像素集合
* @return int []
*/
public int[] process() {
// 对于圆的极坐标变换来说,我们需要360度的空间梯度叠加值
acc = new int[width * height];
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
acc[y * width + x] = 0;
}
}
int x0, y0;
double t;
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
if ((input[y * width + x] & 0xff) == 255) {
for (int theta = 0; theta < 360; theta++) {
t = (theta * 3.14159265) / 180; // 角度值0 ~ 2*PI
x0 = (int) Math.round(x - r * Math.cos(t));
y0 = (int) Math.round(y - r * Math.sin(t));
if (x0 < width && x0 > 0 && y0 < height && y0 > 0) {
acc[x0 + (y0 * width)] += 1;
}
}
}
}
}
// now normalise to 255 and put in format for a pixel array
int max = 0;
// Find max acc value
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
if (acc[x + (y * width)] > max) {
max = acc[x + (y * width)];
}
}
}
// 根据最大值,实现极坐标空间的灰度值归一化处理
int value;
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
value = (int) (((double) acc[x + (y * width)] / (double) max) * 255.0);
acc[x + (y * width)] = 0xff000000 | (value << 16 | value << 8 | value);
}
}
// 绘制发现的圆
findMaxima();
System.out.println("done");
return output;
}
private int[] findMaxima() {
results = new int[accSize * 3];
int[] output = new int[width * height];
// 获取最大的前accSize个值
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
int value = (acc[x + (y * width)] & 0xff);
// if its higher than lowest value add it and then sort
if (value > results[(accSize - 1) * 3]) {
// add to bottom of array
results[(accSize - 1) * 3] = value; //像素值
results[(accSize - 1) * 3 + 1] = x; // 坐标X
results[(accSize - 1) * 3 + 2] = y; // 坐标Y
// shift up until its in right place
int i = (accSize - 2) * 3;
while ((i >= 0) && (results[i + 3] > results[i])) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
int temp = results[i + j];
results[i + j] = results[i + 3 + j];
results[i + 3 + j] = temp;
}
i = i - 3;
if (i < 0)
break;
}
}
}
}
// 根据找到的半径R,中心点像素坐标p(x, y),绘制圆在原图像上
System.out.println("top " + accSize + " matches:");
for (int i = accSize - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
drawCircle(results[i * 3], results[i * 3 + 1], results[i * 3 + 2]);
}
return output;
}
private void setPixel(int value, int xPos, int yPos) {
/// output[(yPos * width) + xPos] = 0xff000000 | (value << 16 | value << 8 | value);
output[(yPos * width) + xPos] = 0xffff0000;
}
// draw circle at x y
private void drawCircle(int pix, int xCenter, int yCenter) {
pix = 250; // 颜色值,默认为白色
int x, y, r2;
int radius = r;
r2 = r * r;
// 绘制圆的上下左右四个点
setPixel(pix, xCenter, yCenter + radius);
setPixel(pix, xCenter, yCenter - radius);
setPixel(pix, xCenter + radius, yCenter);
setPixel(pix, xCenter - radius, yCenter);
y = radius;
x = 1;
y = (int) (Math.sqrt(r2 - 1) + 0.5);
// 边缘填充算法, 其实可以直接对循环所有像素,计算到做中心点距离来做
// 这个方法是别人写的,发现超赞,超好!
while (x < y) {
setPixel(pix, xCenter + x, yCenter + y);
setPixel(pix, xCenter + x, yCenter - y);
setPixel(pix, xCenter - x, yCenter + y);
setPixel(pix, xCenter - x, yCenter - y);
setPixel(pix, xCenter + y, yCenter + x);
setPixel(pix, xCenter + y, yCenter - x);
setPixel(pix, xCenter - y, yCenter + x);
setPixel(pix, xCenter - y, yCenter - x);
x += 1;
y = (int) (Math.sqrt(r2 - x * x) + 0.5);
}
if (x == y) {
setPixel(pix, xCenter + x, yCenter + y);
setPixel(pix, xCenter + x, yCenter - y);
setPixel(pix, xCenter - x, yCenter + y);
setPixel(pix, xCenter - x, yCenter - y);
}
}
public int[] getAcc() {
return acc;
}
} 









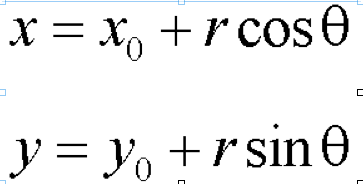














 3448
3448

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








