目录
一、领导力与变革概览
1.1 领导力定义与重要性
- 定义:领导力是影响组织或其内部群体,以实现目标的过程。(Leadership is the process of influencing an organization or group within the organization in its efforts towards achieving an aim or goal)。
- 重要性:良好的领导力被视为组织成功的关键因素。领导力不仅关乎目标的实现,还涉及激励和引导团队成员。
| 领导力是指在组织或组织内的群体中,通过影响力来实现目标的过程。有效的领导力对组织的成功至关重要,具有远见的领导者可以激励他人,并遵循伦理原则。 |
1.2 领导力角色与特质
- 愿景(Vision):领导者需要有清晰的愿景来激励他人。
- 道德伦理:是领导力的基石,影响领导者的决策和行为。
1.3 成为领导者的途径
- 战略视野(Strategic vision):领导者应具备战略视野和战略管理能力。
- 技术环境理解(Understanding the current technology environment):对当前技术环境,尤其是信息技术的深入理解。
- 公司治理(Corporate Governance:掌握公司治理的基本原则和实践。
- 道德品质(Good moral character):领导者应具备良好的道德品质和伦理观。
| 领导力的关键组成部分:
|
二、领导力深入探讨
2.1 领导与管理的区别
- 管理:提供秩序和程序,满足业务需求。
- 领导:支持变革,展示如何应对变革,激励和动员团队。
2.2 领导力理论
- 特质理论(trait of leaders):认为某些人天生适合领导职位,但也强调领导力可以通过行为学习获得。
- 行为理论(behavioural theories):从不同的领导风格理论中探讨领导力的行为模式。(根据人的行为而不是特质判断是否领导者)
- 权力-影响理论(power-influence):领导力有效性与领导者所拥有的权力类型和数量有关。
- (权变)情境理论(contingency theories):不同的领导特质、技能和行为在不同情境下有效。
- 变革型理论( transformational theories):强调团队、变革和愿景,以应对环境的快速发展。
- 整合方法:综合考虑多种领导变量。
2.3 领导力角色的具体职责
- 高层管理者:制定未来战略,调整组织结构以实现战略,体现变革。
- 中层管理者:为高层管理提供咨询,解释和调整战略,领导地方变革。
三、变革与领导力
3.1 魅力型与交易型领导
- (Transactional leadership)交易型领导:更侧重于任务完成和奖励系统。
- (Charismatic leadership)魅力型领导:通过个人魅力和影响力,激发团队的潜力和热情。
3.2 变革的类型与范围
- 变革范围:包括重新调整、转型、增量、适应、进化、“大爆炸”和重建。
- 变革性质:变革可以是渐进的或革命性的,取决于组织的需求和环境。
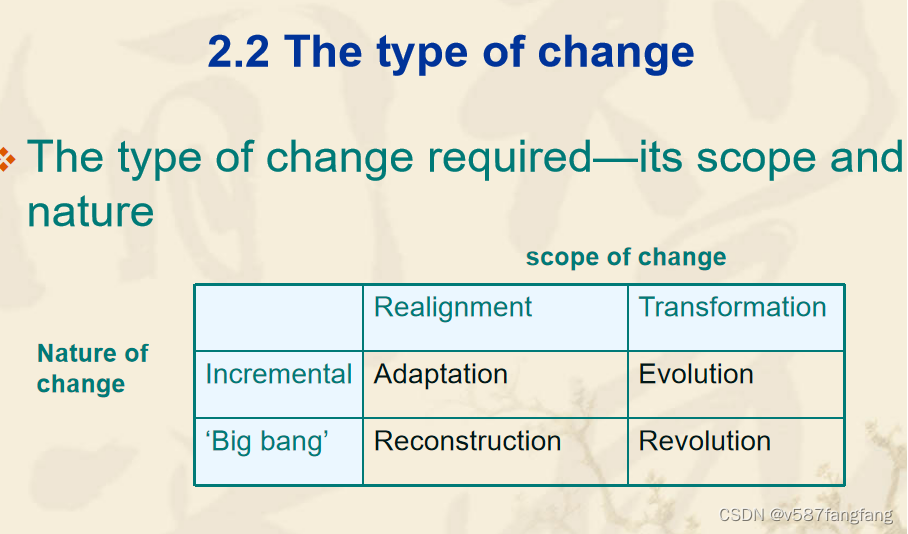
| 变革的范围(Scope of Change) Realignment(重新调整) 重新调整指的是对组织结构或流程进行较小的调整,以更好地适应当前环境或提高效率。 Transformation(转型) 转型是一种更深层次的变化,涉及到组织的核心业务模式和运营方式的根本改变,以适应市场或技术的重大变化。 变革的性质(Nature of Change) Incremental(增量) 增量变革是指逐步、小步快跑式的改进,通过连续的小改变积累起来,最终实现较大的改进效果。 ‘Big bang’(大爆炸) “大爆炸”变革是指在短时间内实施大规模、根本性的改变,这种变革往往风险较高,但如果成功,效果显著。 Adaptation(适应) 适应性变革是为了应对外部环境的变化,对组织的某些方面进行调整,以保持竞争力。 Evolution(进化) 进化变革类似于自然选择的过程,组织通过不断试错和优化,逐步发展和完善。 Reconstruction(重建) 重建变革涉及到对组织结构、流程或文化进行彻底的重构,以解决长期存在的问题或实现新的业务目标。 Revolution(革命) 革命性变革是最极端的形式,通常涉及到对组织的彻底改造,可能包括新的领导、战略方向、组织结构等。 |
3.3 变革的背景与考虑因素
- 时间:变革所需的时间。
- 文化:组织文化对变革的影响。
- 资源:变革所需的资源,包括财务、技术和管理努力。
- 员工态度:员工对变革的接受度和抵抗。
3.4 变革推动者的角色
- 战略领导者(Strategic leaders):通过不同的领导风格和方法推动变革。
- 中层管理(Middle management):在地方层面提供咨询、翻译和实施战略。
- 外部人士(Outsiders):带来新的视角和想法。
3.5 五种变革管理风格
- 教育与沟通(education and communication):通过说服来引导变革,适用于愿意接受变革的员工。
- 协作/参与(collaboration/participation):让受影响的员工参与变革过程,适用于支持性文化。
- 干预(intervention):通过变革推动者来实现变革。
- 指导(direction):使用管理权威来推动变革,可能遇到抵抗。
- 强制/命令(coercion/edict):在危机时期使用权力强加变革。
四、创业精神(Entrepreneurship)
4.1 创业精神的定义与重要性
- 创业精神:识别和利用市场机会,创造新产品或服务的过程。
- 内部创业(Intrapreneurship):在组织内应用创业原则,促进创新和增长。
案例分析:学术回收公司
- Sully Truin的领导风格:分析其在培训课程前后的领导风格变化。
- 领导风格变化的不成功原因:探讨领导风格变化失败的可能原因,如组织文化、员工接受度等。
| You work as a consultant specialising in the area of personnel and management development. You have been approached by Sully Truin who is keen for some advice about how he should be leading his organisation. Ten years ago Sully Truin formed the Academic Recycling Company (ARC) to offer a specialised waste recycling service to schools and colleges. The company has been very successful and has expanded rapidly. To cope with this expansion, Sully has implemented(实施) a tight(严格的) administrative process(行政程序) for operating and monitoring contracts. This administrative procedure is undertaken by the Contracts Office, which tracks(跟踪) that collections have been made by the field recycling teams. Sully has sole responsibility for obtaining and establishing recycling contracts, but he leaves the day-to-day responsibility for administering and monitoring the contracts to the Contracts Office. He has closely defined what needs to be done for each contract and how this should be monitored. I needed to do this,' he said, 'because workers in this country are naturally lazy and, lack initiative. I have found that if you don't tell them exactly what to do and how to do it, then it won't get done properly. Most of the employees working in the Contracts Office like and respect Sully for his business success and ability to take instant decisions when they refer a problem to him. Some of ARC's employees have complained about his autocratic style of leadership, but most of these have now left the company to work for other organisations. A few months ago, conscious that he was a self-taught manager, Sully enrolled himself on a week's course with Gapminding, a training consultancy which actively advocates and promotes a democratic style of management. The course caused Sully to question his previous approach to leadership. It was also the first time, for three years, that Sully had been out of the office during working hours for a prolonged period of time. However, each night, while he was attending the course, he had to deal with emails from the Contracts Office listing problems with contracts and asking him what action they should take. He became exasperated by his employees' inability to take actions to resolve these issues. He discussed this problem with his course tutors. They suggested that his employees would be more effective and motivated if their jobs were enriched and that they were empowered to make decisions themselves. On his return from the course, Sully called a staff meeting with the Contracts Office where he announced that, from now on, employees would have responsibility for taking control actions themselves, rather than referring the problem to him. Sully, in turn, was to focus on gaining more contracts and setting them up. However, problems with the new arrangements arose very quickly. Fearful of making mistakes and unsure about what they were doing led to employees discussing issues amongst themselves at length before coming to a tentative decision. The operational (field) recycling teams were particularly critical of the new approach. One commented that 'before, we got a clear decision very quickly. Now decisions can fake several days and appear to lack authority.' The new approach also caused tensions and stress within the Contracts Office and absenteeism increased. At the next staff meeting, employees in the Contracts Office asked Sully to return to his old management style and job responsibilities. 'We prefer the old Sully Truin,1 they said, 'the training course has spoilt you.’ Reluctantly, Sully agreed to their requests and so all problems are again referred up to him. However, he is unhappy with this return to the previous way of working. He is working long hours and is concerned about his health. Also, he realises that he has little time for obtaining and planning contracts and this is severely restricting the capacity of the company to expand. Required: Analyse Sully Truin's leadership style before and immediately after the training course and explain why the change of leadership style at ARC was unsuccessful. (12 marks) Professional skills marks are available for demonstrating analysis skills as part of your diagnosis of the leadership styles on display here. (2 marks) |
| You work as a consultant specialising in the area of personnel and management development. 你是一名专注于人事和管理发展的顾问。 You have been approached by Sully Truin who is keen for some advice about how he should be leading his organisation. Sully Truin 找到了你,希望能得到关于如何领导他的组织的一些建议。 Ten years ago Sully Truin formed the Academic Recycling Company (ARC) to offer a specialised waste recycling service to schools and colleges. 十年前,Sully Truin 成立了学术回收公司(ARC),为学校和学院提供专业的废物回收服务。 The company has been very successful and has expanded rapidly. 公司取得了很大的成功,并迅速扩展。 To cope with this expansion, Sully has implemented a tight administrative process for operating and monitoring contracts. 为了应对这种扩展,Sully 实施了一套严格的行政程序来操作和监控合同。 This administrative procedure is undertaken by the Contracts Office, which tracks that collections have been made by the field recycling teams. 这个行政程序由合同办公室执行,合同办公室跟踪现场回收团队的收集情况。 Sully has sole responsibility for obtaining and establishing recycling contracts, but he leaves the day-to-day responsibility for administering and monitoring the contracts to the Contracts Office. Sully 独自负责获取和建立回收合同,但他将合同的日常管理和监控责任交给合同办公室。 He has closely defined what needs to be done for each contract and how this should be monitored. 他详细规定了每个合同需要完成的工作以及如何监控。 'I needed to do this,' he said, 'because workers in this country are naturally lazy and, lack initiative. “我必须这么做,”他说,“因为这个国家的工人天生懒惰,缺乏主动性。 I have found that if you don't tell them exactly what to do and how to do it, then it won't get done properly. 我发现,如果你不明确告诉他们该做什么和怎么做,事情就不会正确完成。 Most of the employees working in the Contracts Office like and respect Sully for his business success and ability to take instant decisions when they refer a problem to him. 合同办公室的大多数员工喜欢和尊敬 Sully,因为他的商业成功和在他们向他报告问题时能够迅速做出决定的能力。 Some of ARC's employees have complained about his autocratic style of leadership, but most of these have now left the company to work for other organisations. 一些 ARC 的员工抱怨他的专制领导风格,但大多数员工现在已经离开公司到其他组织工作。 A few months ago, conscious that he was a self-taught manager, Sully enrolled himself on a week's course with Gapminding, a training consultancy which actively advocates and promotes a democratic style of management. 几个月前,意识到自己是自学成才的管理者,Sully 报名参加了 Gapminding 培训咨询公司的一周课程,该公司积极倡导和推广民主的管理风格。 The course caused Sully to question his previous approach to leadership. 这门课程使 Sully 开始质疑他以前的领导方式。 It was also the first time, for three years, that Sully had been out of the office during working hours for a prolonged period of time. 这也是三年来 Sully 第一次在工作时间长时间离开办公室。 However, each night, while he was attending the course, he had to deal with emails from the Contracts Office listing problems with contracts and asking him what action they should take. 然而,在他上课的每个晚上,他都不得不处理来自合同办公室的电子邮件,这些邮件列出了合同的问题,并询问他应该采取什么行动。 He became exasperated by his employees' inability to take actions to resolve these issues. 他对员工无法采取行动解决这些问题感到恼火。 He discussed this problem with his course tutors. 他与课程导师讨论了这个问题。 They suggested that his employees would be more effective and motivated if their jobs were enriched and that they were empowered to make decisions themselves. 他们建议,如果员工的工作得到丰富,并且有权自行做决定,他们会更有效率和积极性。 On his return from the course, Sully called a staff meeting with the Contracts Office where he announced that, from now on, employees would have responsibility for taking control actions themselves, rather than referring the problem to him. 从课程归来后,Sully 召集了合同办公室的员工会议,并宣布从现在开始,员工将负责自行采取控制行动,而不是将问题提交给他。 Sully, in turn, was to focus on gaining more contracts and setting them up. Sully 反过来要专注于获得更多的合同并建立它们。 However, problems with the new arrangements arose very quickly. 然而,新安排的问题很快就出现了。 Fearful of making mistakes and unsure about what they were doing led to employees discussing issues amongst themselves at length before coming to a tentative decision. 害怕犯错和不确定自己在做什么导致员工在做出暂定决定前,长时间讨论问题。 The operational (field) recycling teams were particularly critical of the new approach. 现场回收团队特别批评这种新方法。 One commented that 'before, we got a clear decision very quickly. Now decisions can take several days and appear to lack authority.' 一位员工评论说:“以前,我们很快就能得到明确的决定。现在,决定可能需要几天,而且似乎缺乏权威。” The new approach also caused tensions and stress within the Contracts Office and absenteeism increased. 这种新方法还导致合同办公室内的紧张和压力增加,缺勤率上升。 At the next staff meeting, employees in the Contracts Office asked Sully to return to his old management style and job responsibilities. 在下一次员工会议上,合同办公室的员工要求 Sully 回到以前的管理风格和工作职责。 'We prefer the old Sully Truin,' they said, 'the training course has spoilt you.' “我们更喜欢以前的 Sully Truin,”他们说,“培训课程把你毁了。” Reluctantly, Sully agreed to their requests and so all problems are again referred up to him. Sully 不情愿地同意了他们的要求,因此所有问题再次提交给他。 However, he is unhappy with this return to the previous way of working. 然而,他对回到以前的工作方式感到不满。 He is working long hours and is concerned about his health. 他工作时间很长,对自己的健康感到担忧。 Also, he realises that he has little time for obtaining and planning contracts and this is severely restricting the capacity of the company to expand. 此外,他意识到自己没有多少时间来获取和规划合同,这严重限制了公司的扩展能力。 Required: Analyse Sully Truin's leadership style before and immediately after the training course and explain why the change of leadership style at ARC was unsuccessful. (12 marks) 要求:分析 Sully Truin 在培训课程之前和之后的领导风格,并解释为什么 ARC 的领导风格变革不成功。(12 分) Professional skills marks are available for demonstrating analysis skills as part of your diagnosis of the leadership styles on display here. (2 marks) 展示分析技能的专业技能分数将作为对这里展示的领导风格诊断的一部分。(2 分) |
|






















 4916
4916

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








