现实世界中的数据科学 (Data Science in the Real World)
This article aims to present two ways of calculating non linear correlation between any number of discrete variables. The objective for a data analysis project is twofold : on the one hand, to know the amount of information the variables share with each other, and therefore, to identify whether the data available contain the information one is looking for ; and on the other hand, to identify which minimum set of variables contains the most important amount of useful information.
本文旨在介绍两种计算任意数量的离散变量之间的非线性相关性的方法。 数据分析项目的目标是双重的:一方面,了解变量之间共享的信息量,从而确定可用数据是否包含人们正在寻找的信息; 另一方面,确定哪些最小变量集包含最重要的有用信息量。
变量之间的不同类型的关系 (The different types of relationships between variables)
线性度 (Linearity)
The best-known relationship between several variables is the linear one. This is the type of relationships that is measured by the classical correlation coefficient: the closer it is, in absolute value, to 1, the more the variables are linked by an exact linear relationship.
几个变量之间最著名的关系是线性关系。 这是用经典相关系数衡量的关系类型:绝对值越接近1,变量之间通过精确的线性关系链接的越多。
However, there are plenty of other potential relationships between variables, which cannot be captured by the measurement of conventional linear correlation.
但是,变量之间还有许多其他潜在的关系,无法通过常规线性相关性的测量来捕获。
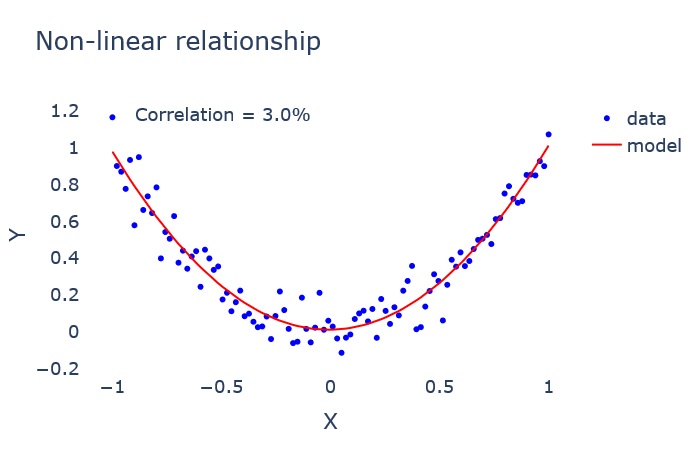
To find such non-linear relationships between variables, other correlation measures should be used. The price to pay is to work only with discrete, or discretized, variables.
为了找到变量之间的这种非线性关系,应该使用其他相关度量。 要付出的代价是仅对离散变量或离散变量起作用。
In addition to that, having a method for calculating multivariate correlations makes it possible to take into account the two main types of interaction that variables may present: relationships of information redundancy or complementarity.
除此之外,拥有一种用于计算多元相关性的方法,可以考虑变量可能呈现的两种主要交互类型:信息冗余或互补性的关系。
冗余 (Redundancy)
When two variables (hereafter, X and Y) share information in a redundant manner, the amount of information provided by both variables X and Y to predict Z will be inferior to the sum of the amounts of information provided by X to predict Z, and by Y to predict Z.
当两个变量(以下,X和Y)以冗余的方式共享信息,由两个变量X和Y中提供的信息来预测的Z量将不如由X所提供的预测的Z信息的量的总和,和由Y预测Z。
In the extreme case, X = Y. Then, if the values taken by Z can be correctly predicted 50% of the times by X (and Y), the values taken by Z cannot be predicted perfectly (i.e. 100% of the times) by the variables X and Y together.
在极端情况下, X = Y。 然后,如果可以通过X (和Y )正确地预测Z所取的值的50%,则变量X和Y不能一起完美地预测Z所取的值(即100%的时间)。
╔═══╦═══╦═══╗
║ X ║ Y ║ Z ║
╠═══╬═══╬═══╣
║ 0 ║ 0 ║ 0 ║
║ 0 ║ 0 ║ 0 ║
║ 1 ║ 1 ║ 0 ║
║ 1 ║ 1 ║ 1 ║
╚═══╩═══╩═══╝互补性 (Complementarity)
The complementarity relationship is the exact opposite situation. In the extreme case, X provides no information about Z, neither does Y, but the variables X and Y together allow to predict perfectly the values taken by Z. In such a case, the correlation between X and Z is zero, as is th








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 949
949











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








