In this tutorial, you will learn the basics and various functions of NumPy. A basic understanding of Python or any of the programming languages is recommended.
在本教程中,您将学习NumPy的基础知识和各种功能。 建议对Python或任何编程语言有基本的了解。
NumPy is a Python package. It stands for Numerical Python. It is a library consisting of multidimensional array objects and a collection of routines for processing of array. These data structures are efficient in performing large size of arrays.
NumPy是一个Python包。 它代表数值Python 。 它是一个由多维数组对象和用于数组处理的例程集合组成的库。 这些数据结构在执行大型数组时很有效。
In this tutorial, you will learn the basics and various functions of NumPy.
在本教程中,您将学习NumPy的基础知识和各种功能。
To use any library in the notebook, you can simply use import keyword. Same to import NumPy library. Here is how we import NumPy in Python:
要使用笔记本中的任何库,您只需使用import关键字即可。 与导入NumPy库相同。 这是我们如何在Python中导入NumPy的方法:
import numpy as npCreating Ndarray Object
创建Ndarray对象
First, let’s take a look at some examples of how to create arrays in NumPy. In the example below, we create an one-dimensional NumPy array A that has 3 values and regular python array B with same values.
首先,让我们看一下如何在NumPy中创建数组的一些示例。 在下面的示例中,我们创建一个具有3个值的一维NumPy数组A和具有相同值的常规python数组B。
The code block below shows the output of the code above.
下面的代码块显示了上面代码的输出。
a = [1 2 3]
b = [1, 2, 3]
A = [[1 2] [3 4]]
B = [[1, 2], [3, 4]]
Data type of A: <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
Data type of B: <class 'list'>As you see, it is similar to how we create array in python.
如您所见,它类似于我们在python中创建数组的方式。
To create a multi-dimensional array, use the same format as python array with np.array() keyword in front.
要创建多维数组,请使用与python数组相同的格式,并在其前面加上np.array()关键字。
NumPy use an N-dimensional array type called ndarray. Each element in ndarray is an object of data-type object called dtype (data-type).
NumPy使用称为ndarray的N维数组类型。 ndarray中的每个元素都是称为dtype(数据类型)的数据类型对象的对象。
NumPy supports a much greater variety of numerical types than Python does. NumPy numerical types are instances of dtype objects, each having unique characteristics. The dtypes are available as np.int, np.float, np.bool_, etc.
NumPy比Python支持更多的数字类型。 NumPy数值类型是dtype对象的实例,每个都有独特的特征。 dtypes可作为np.int,np.float,np.bool_等使用。
Converting List into NumPy Array
将列表转换为NumPy数组
To convert Python list into NumPy array, use np.assary(). The input can be lists, lists of tuples, tuples or tuples of tuples, etc.
要将Python列表转换为NumPy数组,请使用np.assary() 。 输入可以是列表,元组列表,元组或元组的元组等。
<class 'list'> : [[1, 2], [3, 4]]
<class 'numpy.ndarray'> : [[1 2] [3 4]]NumPy Data Types
NumPy数据类型
In Python, mixed data types can be used without needing to specify; as you see in example below, B gives you the output of a list that contains string, integer(int) and float values. However, in NumPy you have to declare the specific data type you want to create in the list or it’ll automatically convert all the data types in the array to be the same data type as the first value.
在Python中,无需指定即可使用混合数据类型。 如下面的示例所示, B为您提供了包含字符串,integer(int)和浮点值的列表的输出。 但是,在NumPy中,您必须在列表中声明要创建的特定数据类型,否则它将自动将数组中的所有数据类型转换为与第一个值相同的数据类型。
As you see in the example below, A gives you all string values.
如下面的示例所示, A为您提供了所有字符串值。
A = ['hello' '12' '4.0']
B = ['hello', 12, 4.0]Let’s take a look at how you can declare data type object in NumPy. Remember that the dtypes are available as np.int, np.float, np.str etc.
让我们看一下如何在NumPy中声明数据类型对象。 请记住,dtypes可作为np.int,np.float,np.str等使用。
Here is the example of how we create a data type object for integer and float.
这是我们如何为整数和浮点数创建数据类型对象的示例。
int64
float64
A = [12 5 9]
B = [12. 5. 9.]Dtype allows you to define a structured data type that is applied to ndarray object. If you want to know more about structured dtypes visit the tutorial website here: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/numpy/numpy_data_types.htm .
Dtype允许您定义应用于ndarray对象的结构化数据类型。 如果您想了解有关结构化dtypes的更多信息,请访问以下教程网站: https ://www.tutorialspoint.com/numpy/numpy_data_types.htm。
Ndarray Attributes
Ndarray属性
We have learned about dtypes. Now, let’s look at the various array attributes of NumPy.
我们已经了解了dtype。 现在,让我们看一下NumPy的各种数组属性。
ndarray.shape returns a tuple consisting of array dimensions. As we see in the example below, A.shape returns (2, 3), meaning that the array A has 2 rows and 3 columns.
ndarray.shape返回一个由数组维组成的元组。 正如我们在下面的示例中看到的, A.shape返回(2,3) ,这意味着数组A具有2行3列 。
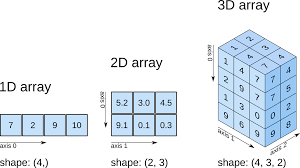
Another cool feature of ndarray.shape is that it can be used to resize the array. In the example, we changed the dimensions of A from (2, 3) to (3, 2). When you print A now you’ll see that A has 3 rows and 2 columns with the same values.
ndarray.shape的另一个很酷的功能是它可以用来调整数组的大小。 在示例中,我们将A的尺寸从(2,3)更改为(3,2) 。 现在打印A时,您会看到A有3行和2列具有相同的值 。
A = [[1 2 3] [4 5 6]]
The dimension of A is (2, 3)
After reshaping, the shape of A is (3, 2)
A = [[1 2] [3 4] [5 6]]
After reshaping into 6x1, the shape of A is (6, 1)
A = [[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]]We can also use ndarray.reshape() to resize the dimension of the array. When reshaping the array, we need to be careful of converting dimensions. For example, we can reshape the array of 3x2 into 6x1 or 2x3 but not 4x2 or other dimensions. The reason is that in 3x2 array, there are total of 6 elements and when we convert to either 6x1 or 2x3 the number of elements remain the same. (3 * 2 = 6, 6 * 1 = 6, and 2 * 3 = 6) In summary, we only can reshape ndarrays into the dimensions that give the same number of elements.
我们还可以使用ndarray.reshape()来调整数组的大小。 重塑数组时,我们需要注意转换尺寸。 例如,我们可以将3x2的数组重塑为6x1或2x3,而不是4x2或其他尺寸。 原因是在3x2数组中, 总共有6个元素 ,当我们转换为6x1或2x3时 ,元素的数量保持不变。 (3 * 2 = 6、6 * 1 = 6和2 * 3 = 6)总而言之,我们只能将ndarray整形为给出相同数量元素的维。
See some examples below.
请参阅下面的一些示例。
Before reshaping, the shape of B is (4, 3)
After reshaping into 12x1, the shape of B is (12, 1)
After reshaping into 3x4, the shape of B is (3, 4)
After reshaping into 6x2, the shape of B is (6, 2)Creating an Empty Ndarray
创建一个空的Ndarray
Unlike regular array, we cannot use append() to add to the Ndarray. One way we can do it to create an empty array. An empty array is an uninitialized array of specified shape and dtype. The following code shows how to create an empty array.
与常规数组不同,我们不能使用append()添加到Ndarray。 一种创建空数组的方法。 空数组是指定形状和dtype的未初始化数组。 以下代码显示了如何创建一个空数组。
[[ 27663120 140561394696192]
[ 0 0]
[ 0 0]]Note that when you print the empty array, the element in the array show random values since they are not initialized. There is another way we can initialize an array is by using np.zeros which creates a new array of specified size filled with zeros or ones. See the next section for details.
请注意,在打印空数组时,数组中的元素会显示随机值,因为它们尚未初始化。 我们还有另一种初始化数组的方法,即使用np.zeros创建一个指定大小的新数组,该数组填充有零或一。 有关详细信息,请参见下一部分。
Ndarray of All Zeros and Ones
Ndarray全零和一
Next, we will learn how to create a new array of specified size, filled with zeros and ones. np.zeros() and np.ones() returns arrays with all zeros and all ones.
接下来,我们将学习如何创建一个指定大小的新数组,并用零和一填充。 np.zeros()和np.ones()返回具有全零和全1的数组。
See the example below how we can create an array of five zeros and ones.
请参见下面的示例,我们如何创建一个由五个零和一组成的数组。
a1 = [0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
a2 = [0 0 0 0 0]
a3 = [1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]The arrays a1, a2 and a3 you see in example above are called rank-one arrays; it has one dimension.
您在上面的示例中看到的数组a1 , a2和a3被称为等级1数组 ; 它有一个维度。
See examples below the difference between np.zeros(3) vs np.zeros(3,) vs np.zeros(3,1).
请参阅下面的示例np.zeros(3)与np.zeros(3,)与np.zeros(3,1)之间的区别。
a1 = [0. 0. 0.]
shape of a1 is (3,)a2 = [0. 0. 0.]
shape of a2 is (3,)b1 = [[0. 0. 0.]]
shape of b1 is (1, 3)b2 = [[0.]
[0.]
[0.]]
shape of B is (3, 1)a1 and a2 will give you the same one-dimension array of 3 zeros. As you see the shape of a1 and a2 is (3,), meaning it has 3 elements and it only has one dimension.
a1和a2将为您提供由3个零组成的相同一维数组。 如您所见, a1和a2的形状为(3,) ,这意味着它具有3个元素,并且只有一个尺寸。
b1 and b2 meanwhile return the shape of (1, 3) and (3,1).
b1和b2同时返回(1,3)和(3,1)的形状。
So, what is the difference between a1 and b1?
那么, a1和b1有什么区别?
To answer this, let’s take a look at some definitions of matrices. A matrix with only one row is called a row vector, and a matrix with one column is called a column vector, but there is no distinction between rows and columns in a one-dimensional array of ndarray.
为了回答这个问题,让我们看一下矩阵的一些定义。 只有一行的矩阵称为行向量,只有一列的矩阵称为列向量,但是在ndarray的一维数组中行和列之间没有区别。
Only a two-dimensional array is used to clearly indicate that rows or columns are present. Since array b1 and b2 are two-dimensional(2D) arrays, we can say that b1 is a row vector and b2 is a column vector, but not a1 and a2.
仅使用二维数组来清楚地指示存在行或列。 由于数组b1和b2是二维(2D)数组,因此可以说b1是行向量, b2是列向量,但a1和a2不是 。
If it is confusing for you, don’t worry about it. Just remember these two: ndarray.zeros((n,1)) (n is any number) for row vector and ndarray.zeros((1,n)) for column vector and you can forget about rank-one arrays.
如果您感到困惑,请不要担心。 只需记住这两个:ndarray.zeros((n,1))(n是任意数字)表示行向量,ndarray.zeros((1,n))表示列向量,您可能会忘记排名第一的数组。
A = [[0. 0.]
[0. 0.]
[0. 0.]]B = [[1. 1.]
[1. 1.]]The example above shows how to create a multi-dimensional array of zeros and ones.
上面的示例显示了如何创建零和一的多维数组。
Indexing and Slicing
索引和切片
Ndarray object can be accessed and modified by indexing or slicing, just like Python’s built-in container objects. See the examples below to see how we can slice the one-dimensional and multi-dimensional ndarrays.
可以通过索引或切片来访问和修改Ndarray对象,就像Python的内置容器对象一样。 请参阅下面的示例,以了解如何分割一维和多维ndarray。
Note that similar to Python’s array, we can use negative index to select from the last element in the array.
请注意,类似于Python的数组,我们可以使用负索引从数组的最后一个元素中进行选择。
A = [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
A[0] = 0 , A[1] = 1last element in A: 9
last 3 elements in A: [7 8 9]A[2:] = [2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
A[2:5] = [2 3 4]See the examples below for slicing 2D array in row-wise.
请参阅下面的示例,以按行切片二维数组。
A =
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]
[7 8 9]]A[1:] =
[[4 5 6]
[7 8 9]]A[1:,:] =
[[4 5 6]
[7 8 9]]A[:2] =
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]A[:2,:] =
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]A[1:2] = [[4 5 6]]A[1:2,:] = [[4 5 6]]Now, see the follwoing examples on how to slice 2D array in column-wise.
现在,请参阅下面的示例,了解如何按列分割2D数组。
A =
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]
[7 8 9]]A[:,0] = [1 4 7]A[:,1:] =
[[2 3]
[5 6]
[8 9]]a_corner =
[[1 2]
[4 5]]Creating an Array Copy
创建阵列副本
The idea of using copy() is to clone Numpy array. In Numpy using assignment such that a = b will not work. We’ll see why it won’t work in the following example.
使用copy()的想法是克隆Numpy数组。 在Numpy中使用赋值使a = b不起作用。 在下面的示例中,我们将了解为什么它不起作用。
It seems alright when we print C. It has the same elements as in A. If you know C++, you know how reference variable works, and same thing happened here when we assign C = A.
当我们打印C时似乎还好。 它具有与A中相同的元素。 如果您了解C ++,就会知道引用变量的工作原理,并且当我们分配C = A时,也会发生同样的事情。
Now, let’s change some values in C to zeros.
现在,让我们将C中的某些值更改为零。
A = [[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]C = [[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]After making changes to C
C = [[0 2 3]
[4 5 0]]A = [[0 2 3]
[4 5 0]]As we see in the example above, the values of A have changed!
如上例所示, A的值已更改!
This is because that C is acting as a reference pointer to A and it doesn’t have its own array values on the memory. Instead, it is pointing to where A is so that when we change the values of C, the values of A also changed.
这是因为C充当指向A的引用指针,并且在内存中没有自己的数组值。 相反,它指向A在哪里,因此当我们更改C的值时, A的值也会更改。
To solve this, we can use copy(). This actually create an array C on memory and copy the whole array A into C.
为了解决这个问题,我们可以使用copy() 。 这实际上在内存上创建了一个数组C ,并将整个数组A复制到C中 。
In the example below, we see that changing the values of B doesn’t change the values of A.
在下面的示例中,我们看到更改B的值不会更改A的值。
A = [[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]B = [[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]After making changes to B
B = [[0 2 3]
[4 5 0]]A = [[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]Iterating Over Array
遍历数组
Unlike Python array, NumPy has an iterator object numpy.nditer that is an efficient multidimensional iterator object to iterate over an array.
与Python数组不同,NumPy具有一个迭代器对象numpy.nditer ,它是在数组上进行迭代的高效多维迭代器对象。
# for Python array and using for loop
A = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
shape of A is ( 2 , 3 )
1
2
3
4
5
6
Time taken to loop all the elements: 0.759124755859375 ms# for NumPy array and using nditer
A = [[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
1
2
3
4
5
6
Time taken to loop all the elements: 0.2589225769042969 msAs we see in the examples above, when we iterate using for loop in Python array, it takes more time to run the same number of elements in the array than using NumPy iterator object. The time difference may be only about 1 ms now but when we are dealing with very large array size, the time difference become large.
从上面的示例中可以看到,当我们在Python数组中使用for循环进行迭代时,与使用NumPy迭代器对象相比,在数组中运行相同数量的元素需要花费更多的时间。 现在时差可能只有1毫秒左右,但是当我们处理非常大的阵列大小时,时差会变大。
We will see more examples of how we can avoid using for loop and use vectorization (in NumPy) to speed up our code.
我们将看到更多示例,这些示例说明了如何避免使用for循环和使用矢量化(在NumPy中)来加快代码速度。
Ndarray Operations and Vectorization
Ndarray运算和向量化
Here we will see how vectorization works. This is the most exciting part of the tutorial since it shows you why we prefer using NumPy arrays over Python arrays.
在这里,我们将看到矢量化的工作原理。 这是本教程中最令人兴奋的部分,因为它向您展示了为什么我们更喜欢使用NumPy数组而不是Python数组。
In NumPy, arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication on arrays are usually done on corresponding elements. Take a look at the following example. Usually, you will need to loop through the number of element in arrays and perform multiplication one element by one. However, NumPy arrays can speed up this by using vectorization. This helps the arrays perform the operations on corresponding elements simultaneously.
在NumPy中 ,算术运算(例如加法,减法,数组乘法)通常是在相应元素上完成的。 看下面的例子。 通常,您将需要遍历数组中元素的数量,然后将一个元素与一个元素相乘。 但是, NumPy数组可以通过使用vectorization加快此过程。 这有助于数组同时对相应元素执行操作。
a = [1 2 3 4]
b = [10 20 30 40]
c = [ 10 40 90 160]Note that NumPy arrays allows you to perform the operations on arrays in one line of code without needing to use for loop. But, some of you may argue that why we need to use NumPy and why not use for loop instead.
请注意, NumPy数组允许您在一行代码中对数组执行操作, 而无需使用for循环 。 但是,有些人可能会争辩说,为什么我们需要使用NumPy ,为什么不使用for循环 。
We saw that the difference in computation time between using for loop and NumPy’s iterator object. Same reason applies here; when we perform operations on each element in for loop it is much slower. Vectorization allows you to perform the operations on all the corresponding elements at the same time hence it saves a lot of time.
我们看到了使用for循环和NumPy的迭代器对象之间的计算时间差异。 同样的原因在这里适用; 当我们在for循环中的每个元素上执行操作时,它要慢得多。 向量化可让您同时对所有相应元素执行操作,因此可以节省大量时间。
Say we want to compute addition of arrays a and b and save the result in c. Let’s take a look at how we normally do the operation using for loop vs. how we can speed up the code with vectorization.
假设我们要计算数组a和b的加法并将结果保存在c中 。 让我们看一下通常如何使用for循环进行操作以及如何通过向量化来加速代码 。
We can declare an array with random values in NumPy with one line of code by using np.randn(). And, let’s create 2 arrays (a and b) of size 1000000 initialized with some random values, and an array c of same size with all zeros.
我们可以使用np.randn()在NumPy中用一行代码声明一个具有随机值的数组。 并且,让我们创建2个大小为1000000的数组( a和b ),它们使用一些随机值初始化,而数组c的大小全部为零。
Time taken with for loop: 539.0114784240723 ms
Time taken with vectorization: 3.8535594940185547 msAs we see the time taken with for loop is more than 100 times slower than with vectorization. And, as we see that NumPy simplifies the code so that it requires only one line of code. But, of course the dimensions have to match to do any math operations.
正如我们看到的,for循环所花的时间比矢量化要慢100倍以上。 而且,如我们所见, NumPy简化了代码,因此只需要一行代码。 但是,当然,尺寸必须匹配才能进行任何数学运算。
We can use NumPy’s Math functions such as np.multiply(), np.dot(), np.sin(), etc.
我们可以使用NumPy的Math函数,例如np.multiply() , np.dot() , np.sin()等。
sin(a) = [0.04988483 0.80621872 0.56432645 0.0483301 0.67950184 0.60500273
0.2333741 0.8102268 0.12549575 0.41646099] ...Instead of using for loop to apply sin() function on each element in the array, applying vectorization allows us to apply sin() function on the whole array thus it speeds up the operation.
代替使用for循环在数组中的每个元素上应用sin()函数,应用矢量化允许我们在整个数组上应用sin()函数,从而加快了运算速度。
Broadcasting
广播
Broadcasting is an interesting technique in NumPy. The term broadcasting refers to the ability of NumPy to treat arrays of different shapes during arithmetic operations. You saw how vectorization works in previous examples. If we have two arrays that are of the same shape, then we can perform operations without needing for loop.
在NumPy中, 广播是一种有趣的技术。 术语广播是指NumPy 在算术运算期间处理不同形状的数组 的能力 。 您在前面的示例中看到了矢量化的工作原理。 如果我们有两个形状相同的数组,那么我们可以执行操作而无需循环。
But, if the dimensions of two arrays are different, element-to-element operations are not possible. This is how broadcasting comes in handy. Operations on arrays of different shapes are still possible in NumPy, because of the broadcasting capability.
但是,如果两个数组的维数不同,则不可能进行元素到元素的操作。 这就是广播派上用场的方式。 由于具有广播功能,因此在NumPy中仍可以对不同形状的数组进行操作。
a = [1 2 3 4]
b = [10]
c = [10 20 30 40]As we see in the example above, a and b have different shapes but b, which has smaller dimension than a, is broadcast into the same shape as a, so that the operation can continue as usual.
正如我们在上面的例子中看到的,a和b具有不同的形状,但B,其具有比更小的尺寸,被广播到相同的形状为a,使得操作可以照常继续。
Let’s look at another example with multi-dimensional arrays.
让我们看一下多维数组的另一个例子。
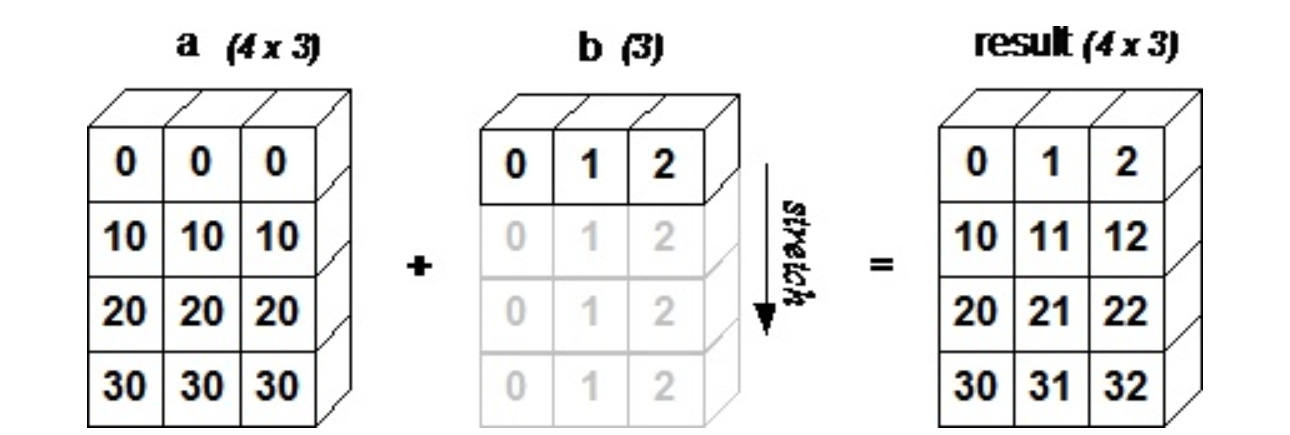
A = [[ 0 0 0]
[10 10 10]
[20 20 20]
[30 30 30]]
B = [0 1 2]
C = [[ 0 1 2]
[10 11 12]
[20 21 22]
[30 31 32]]The smaller array is broadcast to the size of the larger array so that they have compatible shapes. The diagram below explains how broadcasting works.
将较小的阵列广播到较大的阵列,使其具有兼容的形状。 下图说明了广播的工作方式。
Feel free to make a copy of the notebook provided below and try out your own code to practice. Notice that the code in the notebook is slightly different since the notebook is intended for use of NumPy in Computer Vision tutorials.
请随意制作下面提供的笔记本的副本,并尝试自己的代码进行练习。 请注意,笔记本中的代码略有不同,因为笔记本旨在用于Computer Vision教程中的NumPy。
If you want to learn more about NumPy, this is the official website: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/numpy/index.htm .
如果您想了解有关NumPy的更多信息,请访问以下官方网站: https : //www.tutorialspoint.com/numpy/index.htm 。
Thank you for reading and I hope you get some knowledge on NumPy from this tutorial.
感谢您的阅读,希望本教程对NumPy有一定的了解。
If you see any mistakes or you have any questions, feel free to comment below and I’ll try to answer as soon as possible.
如果您发现任何错误或有任何疑问,请在下面发表评论,我将尽快答复。
翻译自: https://medium.com/@mo000007/numpy-for-beginners-19d64e164df6





















 8万+
8万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








