数据结构单向链表线性结构
Imagine you have gone to a crowded place, say to a k-pop concert with your friends and you don’t have any electronics or compass with you.
想象您去了一个拥挤的地方,与您的朋友一起参加一场韩流音乐会,而您却没有任何电子设备或指南针。
Now one of your friends wants to go a bit far away to fetch something, say light sticks. If he goes to fetch it, then he won't be able to find and reach you in the large crowd :(
现在,您的一位朋友想走很远的距离来拿东西,例如荧光棒。 如果他去拿东西,那么他将无法在大群人中找到并到达你:(
How would you solve this problem? Here is a solution for it given that you have sufficient friends with you. You have to make your friends stand in pairs with an even amount of distance between them till the target place. In the pair of your friends standing at equal distances, one of them should look at the next friend pair nearer to the target place, and the other person to look at the previous friend pair. Now your friend after reaching the target place can return to the initial place easily (and the friends who stand in pairs of course) with the help of the person in the pair who was looking over the previous pair.
您将如何解决这个问题? 考虑到您有足够的朋友,这是一个解决方案。 您必须让您的朋友成对站立,彼此之间的距离要均匀,直到到达目标位置。 在一对等距站立的朋友中,其中一个应查看目标位置附近的下一个朋友对,另一个人应查看上一个朋友对。 现在,您的朋友到达目标位置后,可以很轻松地返回初始位置(以及成对站立的朋友),这对伙伴中的人正在寻找上一个对。
If you managed to set up or understand this, then Congratulations! you have successfully implemented(understood) a doubly-linked list.
如果您成功设置或了解此内容,那么恭喜! 您已成功实现(理解)了双向链接列表。
If you didn’t understand the practical example don’t worry about it, you will understand it at the end of this article :)
如果您不了解实际示例, 请不必担心 ,在本文结尾处您将了解:)
What is a data structure and why should you care? Data structures are a core concept of Software Development. I would like to quote from Wikipedia.
什么是数据结构,为什么要关心? 数据结构是软件开发的核心概念。 我想引用维基百科。
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization, management, and storage format that enables efficient access and modification. Data structures provide a means to manage large amounts of data efficiently for uses such as large databases and internet indexing services. Usually, efficient data structures are key to designing efficient algorithms.
在计算机科学中, 数据结构是一种数据组织,管理和存储格式,可实现高效访问 和 修改。 数据结构提供了一种有效管理大量数据以供使用的方法,例如大型数据库和Internet索引服务。 通常,有效的数据结构是设计高效算法的关键。
Even though Data Structures are important but why Linked List when there are a lot of Data Structures? Here are the advantages of linked list
即使数据结构很重要,但是为什么有很多数据结构时为什么要使用链表? 这是链表的优点
Dynamic Data structure: Linked list unlike arrays is dynamic data structures. It basically means that amount of data it can store is not fixed i.e, we can increase or decrease the size of the linked list as per the needs.
动态数据结构 :与数组不同,链接列表是动态数据结构。 这基本上意味着它可以存储的数据量不是固定的,即,我们可以根据需要增加或减少链表的大小。
Insertion and deletion operations are easier.
插入和删除操作更容易。
Efficient Memory Utilization: Unlike arrays, there is no need to pre-allocate memory.
高效的内存利用率:与数组不同,无需预先分配内存。
Linear Data Structures: As it is a linear data structure, accessing the data can be done sequentially.
线性数据结构:由于它是线性数据结构,因此可以顺序访问数据。
Easy Implementation of Other Linear Data Structures: Linear Data Structures such as Stack, Queue can be easily implemented using the Linked list.
轻松实现其他线性数据结构 :可以使用链接列表轻松实现诸如栈,队列之类的线性数据结构。
With why you should learn the linked list, lets deep dive into the linked list!
为什么要学习链表,让我们深入了解链表!
Linked List is made of nodes.
链表由节点组成。
A single Node in Linked List consists of 2 parts:-
链表中的单个节点由两部分组成:
- Data: This is where the data is stored. 数据:这是存储数据的位置。
Reference to the next Node. This consists of a reference to the next node. using this reference we can access data in the next node. We generally name it as “next”
参考下一个节点。 这包括对下一个节点的引用。 使用此参考,我们可以访问下一个节点中的数据。 我们通常将其命名为“ 下一个 ”

If you are using low-level language like C then you will be using pointers to create a reference to the next node. pointers are nothing but variables that hold the address of another variable. So we will be storing the address of the next node in the reference part of the node.
如果使用的是C之类的低级语言,则将使用指针创建对下一个节点的引用。 指针不过是保存另一个变量地址的变量。 因此,我们将下一个节点的地址存储在该节点的参考部分中。
In case you are using other languages then you create a reference just by assigning another variable to it.
如果您使用其他语言,则只需给它分配另一个变量即可创建引用。
What I mean by “A references B” is that the variable “A” and the variable “B”, share the same memory block. So changing A changes the value stored and hence changes the value accessed by B. In other words, A and B reference the same memory block.
我所说的“ A引用B”是指变量“ A”和变量“ B”共享同一存储块 。 因此,更改A会更改存储的值,因此也会更改B所访问的值。换句话说,A和B 引用同一存储块。
class Node:
def __init__(self,data):
self.data = data
self.next = Noneclass Node {
int data;
Node* next;
Node(int data){
this->data = data;
this->next = nullptr;
}
Node(){
this->data = 0;
this->next = nullptr;
}
}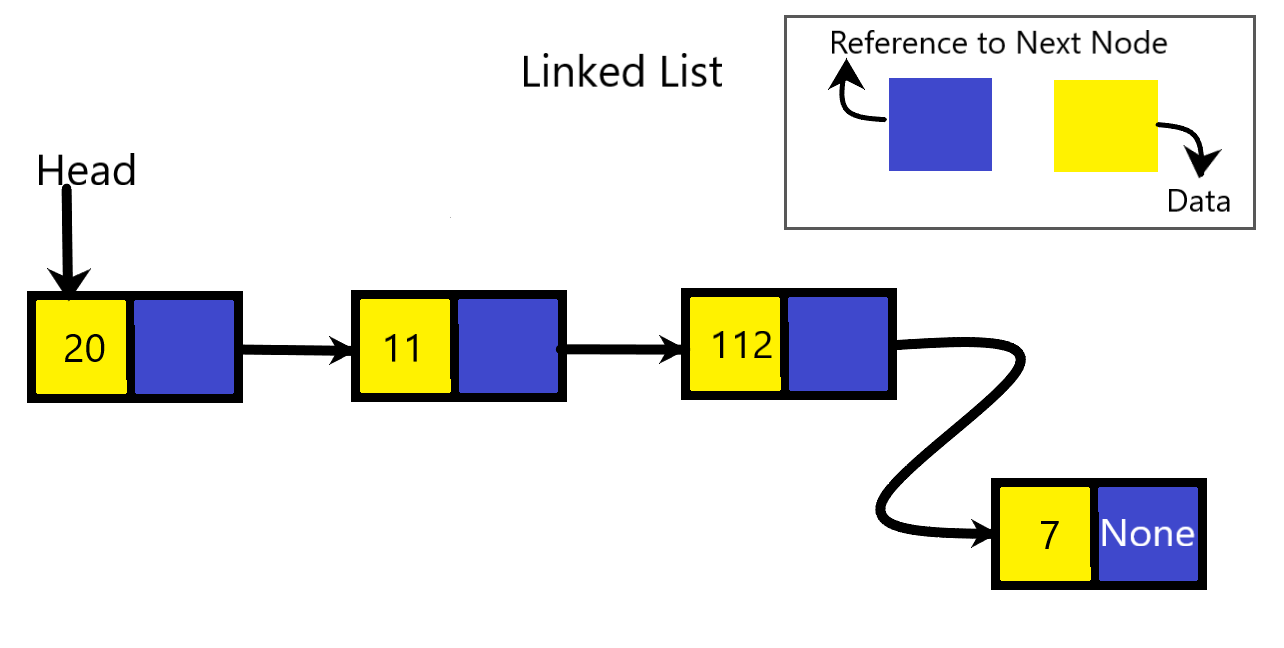
This is what a typical Linked List Looks like 👆.
这就是典型的链接列表的外观。
Here are some key things to note:-
以下是一些重要注意事项:
- we have each node’s reference part referencing its next node. 我们有每个节点的参考部分引用其下一个节点。
- We have a variable named “head” that references the first node. 我们有一个名为“ head”的变量,它引用第一个节点。
- The last Node in the linked list has no node after it, so it’s reference part stores NULL/null / None(this is a special value in programming languages) 链表中的最后一个节点之后没有节点,因此它的参考部分存储NULL / null / None(这是编程语言中的特殊值)
Let's start to build our linked list!
让我们开始构建链接列表!
Adding Nodes to a Linked List
将节点添加到链接列表
We will start with the head variable referencing nothing or in other words, we initialize it with null/NULL/None.
我们将从没有引用任何内容的head变量开始,换句话说,我们使用null / NULL / None对其进行初始化。

Now let's add our first Node. Let's create a new instance of the Node class and assign it to the“ head”. As there is no Node after the first Node, its reference part will reference nothing.
现在,让我们添加第一个节点。 让我们创建Node类的新实例,并将其分配给“ head”。 由于第一个节点之后没有节点,因此其参考部分将不参考任何内容。

Now let's add another Node!
现在让我们添加另一个节点!
We can add a new Node to a linked list in three ways:-
我们可以通过三种方式将新节点添加到链表中:
- In the beginning. This is the fastest way of adding a Node to the linked list. It only takes constant time every time! 在一开始的时候。 这是将节点添加到链表的最快方法。 每次只需要恒定的时间!
- In the last. You can do it in two ways. One takes constant time and the other takes linear time. If you maintain a variable holding reference to the last Node, then it will take constant time. In the other case, you would have to transverse the whole list to reach the end of the linked list, So it takes a linear amount of time. 在最后。 您可以通过两种方式来实现。 一个花费恒定的时间,另一个花费线性的时间。 如果您维护一个变量来保存对最后一个节点的引用,那么它将花费固定的时间。 在另一种情况下,您将必须横穿整个列表才能到达链接列表的末尾,因此需要花费线性时间。
- In between the beginning and last. The time taken varies between the above cases. 在开始和最后之间。 在上述情况之间花费的时间有所不同。
Psuedo code to add the new Node to the beginning of Linked List:-
将新节点添加到链接列表开头的伪代码:-

if head is null
then, assign new Node to head, i.e head references the new Node
else
assign head, to the next of new Node.
assign newNode to the headPsuedo Code to add the new Node to the last of the list if you don’t maintain a variable to hold a reference to the last Node. This is a slow implementation as it takes a linear amount of time, So its best to maintain a tail variable holding reference to the last Node, then it will take constant time.
如果您不维护变量来保存对最后一个节点的引用,则使用Psuedo代码将新节点添加到列表的最后一个。 这是一个缓慢的实现,因为它花费的时间是线性的,因此最好保持尾变量保存对最后一个Node的引用,这将花费恒定的时间。
if head is null
then, assign the new Node to head, i.e head references the new Node.
else
tranverse the linked list till the last Node
then assign the new Node to the next of the last Node.Psuedo Code to add the New Node to the last by maintaining a reference to the last Node.
伪代码,通过维护对最后一个节点的引用来将新节点添加到最后一个节点。

if head or tail is null
then, assign the new Node to both head and tail
else
assign the new Node to the next of tail
assing the new Node to tailCode Examples in python for addition to the beginning and also add to the end, both in constant time!
python中的代码示例可在固定时间内添加到开头,也可以添加到结尾!
class Node:
def __init__(self,data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
def addToFront(self,data):
newNode = Node(data)
if(self.head):
newNode.next = self.head
self.head = newNode
else:
self.head = newNode
self.tail = newNode
def addToLast(self,data):
newNode = Node(data)
if(self.tail):
self.tail.next = newNode
self.tail = newNode
else:
self.head = None
self.tail = NoneCongratulations! We have built our Linked List from Scratch.
恭喜你! 我们从头开始建立了链接列表。
Time Complexity of a Linked List
链表的时间复杂度
Variants of Linked List
链表的变体
1.Singly Linked List
1.单链表

2.Doubly Linked List
2.双向链表

A doubly linked list not only holds a reference to the next node but also holds a reference to the previous node, which makes it possible to traverse the list in both directions.
双链表不仅保留对下一个节点的引用,而且还保留对前一个节点的引用,这使得可以在两个方向上遍历该列表。
3.Circular Linked List
3,循环链表

http://www.c4learn.com/data-structure/linked-list-advantages/
http://www.c4learn.com/data-structure/linked-list-advantages/
https://medium.com/basecs/whats-a-linked-list-anyway-part-1-d8b7e6508b9d
https://medium.com/basecs/whats-a-linked-list-anyway-part-1-d8b7e6508b9d
数据结构单向链表线性结构





















 302
302

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








