http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/processors/processor-numbers.html
About Intel® Processor Numbers

The processor number is one of several factors, along with processor brand, specific system configurations, and system-level benchmarks, to be considered when choosing the right processor for your computing needs.
A higher number within a processor class or family generally indicates more features, but it may be more of one and less of another. Once you decide on a specific processor brand and type, compare processor numbers to verify the processor includes the features you are looking for.
View processor specifications and compare processors >
View processor performance benchmarks >
Laptop, Desktop, and Mobile Device Processors
4th generation and 3rd generation Intel® Core™ processor families
Processor numbers for 3rd and 4th generation Intel® Core™ processors use an alphanumeric scheme based on generation and product line following the brand and its modifier. The first digit in the four-number sequence indicates the generation of processor, and the next three digits are SKU numbers. Where applicable, an alpha suffix appears at the end of the processor name, which represents the processor line.
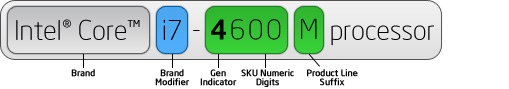
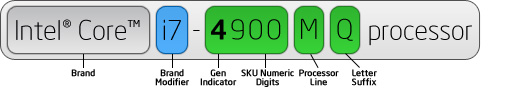
| Alpha Suffix | Correct Trademark Usage |
|---|---|
| MX | Intel® Core™ i7-4900MX processor |
| MQ | Intel® Core™ i7-4900MQ processor Intel® Core™ i7-4702MQ processor |
| M | Intel® Core™ i7-4600M processor Intel® Core™ i5-4300M processor |
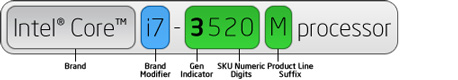
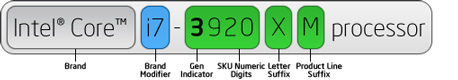
| Alpha Suffix | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| K | Unlocked | Intel® Core™ i7-3770K desktop processor series Intel® Core™ i5-3570K desktop processor series |
| QM | Quad-Core Mobile | Intel® Core™ i7-3820QM mobile processor series |
| S | Performance optimized lifestyle | Intel® Core™ i7-3770S processor Intel® Core™ i5-3550S processor |
| T | Power optimized lifestyle | Intel® Core™ i7-3770T processor Intel® Core™ i5-3570T processor |
2nd generation Intel® Core™ processor family
Processor numbers for the 2nd generation Intel® Core™ processor family have an alpha/numerical identifier followed by a four digit numerical sequence, and may have an alpha suffix depending on the processor. The table below explains the alpha suffixes used for the 2nd generation Intel Core processor family.

| Alpha Suffix | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| K | Unlocked | Intel® Core™ i7-2600K mobile processor series Intel® Core™ i5-2500K mobile processor series |
| S | Performance optimized lifestyle | Intel® Core™ i5-2500S processor Intel® Core™ i5-2400S processor |
| T | Power optimized lifestyle | Intel® Core™ i5-2500T processor Intel® Core™ i5-2390T processor |

Processor numbers for the Previous Generation Intel Core processor family have an alpha/numerical identifier followed by a three digit numerical sequence.

Processor numbers for the Intel® Core™2 processor family brands are categorized with an alpha prefix followed by a four digit numerical sequence. The table below explains the alpha prefixes used for the Intel Core2 processor families.
| Alpha Prefix | Description |
|---|---|
| QX | Desktop or mobile quad-core extreme performance processors |
| X | Desktop or mobile dual-core extreme performance processors |
| Q | Mobile quad-core high performance processors |
| E | Desktop energy efficient dual-core processors with TDP greater than or equal to 55W |
| T | Mobile highly energy efficient processors with TDP 30-39W |
| P | Mobile highly energy efficient processor with TDP 20-29 W |
| L | Mobile highly energy efficient with TDP 12-19W |
| U | Mobile ultra high energy efficient with TDP less than or equal to 11.9W |
| S | Mobile small form-factor with 22x22 BGA package |

Processor numbers for the Intel® Core™2 Quad family have an alpha prefix followed by a four digit numerical sequence. Additionally, low power Intel Core2 Quad processors are identifiable by an "S" suffix which represents processors having a lower thermal design power.
Intel® Atom™ processors
Processor numbers for the Intel® Atom™ processor family are categorized by a three digit numerical sequence. Netbook class Intel® Atom™ processors have an alpha prefix of N, and Intel Atom processors with an alpha prefix of Z indicate the processor is for Mobile Internet Devices (MIDs).
A higher number within a processor class or family generally indicates more features. A higher processor number may have more of one feature and less of another.


Intel® Pentium® processors
Processor numbers for the Intel Pentium brand have an alpha prefix followed by a four character numerical sequence. All are desktop energy-efficient dual-core processors with TDP that is greater than or equal to 65W.
A higher number within a processor class or family generally indicates more features such as cache, clock speed, Front Side Bus or other Intel technologies¹. A higher number processor may also have more of one feature and less of another.

Intel® Celeron® processors
Processor numbers for the Intel® Celeron® brand are expressed with either a three digit numerical sequence or a five character sequence with an alphabetical prefix and four digits, depending on the processor type.
A higher number within a processor class or family generally indicates more features such as cache, clock speed, Front Side Bus or other Intel technologies¹. A higher number processor may also have more of one feature and less of another.


Server and Workstation Processors
Intel® Xeon® processor E3, E5, and E7 and Intel® Xeon Phi™ families
The latest Intel® Xeon® processor numbering system is an alpha numeric representation of product line, product family, and version. An ‘L’ suffix will be used to identify a low power processor. The version number will not be used in the first processor generation.
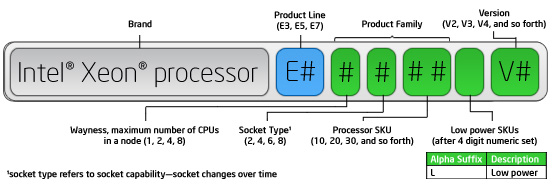

| Processor Family | Product Line | System Type |
|---|---|---|
| Intel® Xeon® processor | E7 | Multi-processor |
| Intel® Xeon® processor | E5 | Multi-processor |
| Intel® Xeon® processor | E3 | Single-processor |
Intel® Xeon® and Intel® Itanium® processors
Intel® Xeon® and Intel® Itanium® processor numbers are categorized in four digit numerical sequences, and may have an alpha prefix to indicate power and performance.

| Alpha Prefix | Description |
|---|---|
| X | Performance |
| E | Mainstream (rack-optimized) |
| L | Power-Optimized |
Intel® Xeon® and Intel® Itanium® processor families and their number sequence
| Processor Family | Number Sequence | System Type |
|---|---|---|
| Intel® Itanium® processor | 9000 | Multi-processor and dual-processor |
| Intel® Xeon® processor | 7000 | Multi-processor |
| Intel® Xeon® processor | 5000 | Dual-processor |
| Intel® Xeon® processor | 3000 | Single-processor |
http://www.cpu-world.com/info/Intel/processor-number.html
Intel processor numbers (model numbers) of desktop CPUs
This page lists processor numbers of all desktop Intel microprocessors. If you want to identify a processor number and cannot find it on this page then please see processor numbers of mobile CPUs and server CPUspages, or use the tool on the right to identify the processor number.
Intel processor number (model number) represents processor's relative performance within the same processor family. The processor number depends on processor's speed, front bus speed, L2 cache size, architecture and other processor features. The processors with larger numbers within the same family and within the same range have greater performance than processors with smaller numbers. Processor numbers cannot be used to compare CPUs from different families, even if the numbers reside in the same range. For example, Core 2 Duo E7xxx CPUs cannot be compared to Xeon E7xxx processors using processor numbers. Also, the numbers in different ranges cannot be used for performance comparison, even if the numbers belong to the same family. For example, processor (model) numbers cannot be used to compare Core 2 Duo E4xxx and Core 2 Duo E6xxx microprocessors. Even for processors within the same family and the range, the numbers can only tell which processor is faster or slower, but they cannot be used to tell how much faster or slower the processor is.
Older Intel families, like Pentium 4 or Celeron D, used numerical processors numbers. The first digit in this number signified processor family, and remaining digits represented relative CPU performance. Newer processors families, starting from Core 2 Duo, in addition to a number also used one letter prefix that indicated processor's maximum power consumption:
- E - from 50 to 74 Watt.
- X - 75 Watt and higher.
With introduction of quad-core CPUs, this numbering scheme was modified by adding new prefixes and re-defining existing ones:
- E - desktop dual-core CPU with TDP 55 Watt or higher.
- Q - desktop quad-core processor.
- X - desktop / mobile dual-core extreme-performance CPU.
- QX - desktop / mobile quad-core extreme-performance CPU.
The latest generation of Intel Core ix-branded processors uses yet different processor numbers, that consist of "i3-", "i5-" or "i7-" prefix, and a number.
Along with various prefixes, Intel processor numbers make use of a few suffixes, that indicate specific processor features:
- K - Unlocked clock multiplier.
- P - Processor without integrated graphics controller.
- S - Energy efficient version.
- T - Low power version.
- X - Extreme version. This suffix is used only on Core ix-branded CPUs.
The first digit, or the prefix letters and the first digit in the processor number, can be used to identify Intel processor family:
- 3xx - Celeron D
- 4xx - Celeron
- 5xx - Pentium 4
- 6xx - Pentium 4
- 8xx - Pentium D and Pentium Extreme Edition
- 9xx - Pentium D and Pentium Extreme Edition
- E1xxx - Celeron Dual-Core
- E2xxx - Pentium Dual-Core
- E3x00 - Celeron Dual-Core
- E4xxx - Core 2 Duo
- E5x00 - Pentium Dual-Core
- E6xxx - Core 2 Duo
- E6x00 - Pentium Dual-Core
- E7x00 - Core 2 Duo
- E8xxx - Core 2 Duo
- G6xxx - Pentium Dual-Core
- i3-5xx - Core i3
- i5-6xx - Core i5 (dual-core)
- i5-7xx - Core i5 (quad-core)
- i7-8xx - Core i7
- i7-9xx - Core i7 and Core i7 Extreme Edition
- Q6xxx - Core 2 Quad
- Q8xxx - Core 2 Quad
- Q9xxx - Core 2 Quad
- QX6xxx - Core 2 Extreme
- QX9xxx - Core 2 Extreme
- X6xxx - Core 2 Extreme
http://www.cpu-world.com/info/Intel/server-processor-number.html
Intel processor numbers (model numbers) of server CPUs
This page lists processor numbers of all server Intel microprocessors. If you cannot find processor number on this page then please see processor numbers of desktop CPUs and mobile CPUs pages, or use the tool on the right to identify the processor number.
Intel processor number represents relative performance of a microprocessor within the same processor family. The processor number depends on the core and FSB frequencies, cache sizes, microarchitecture and other processor features. The processors with larger numbers within the same family and within the same range have greater performance than processors with smaller numbers. Processor numbers cannot be used to compare CPUs from different families, even if the numbers reside in the same range. For example, Core 2 Duo E7xxx CPUs cannot be compared to Xeon E7xxx processors using processor numbers. Also, the numbers in different ranges cannot be used to compare CPU performance, even if the numbers belong to the same family. For example, Core 2 Duo E4xxx and E6xxx model numbers can't be compared because they belong to different ranges. Even for processors within the same family and range, the numbers can only tell which processor is faster or slower, but they don't tell how much faster or slower the processor is.
Older Intel server CPUs had numerical processor numbers. The first digit in this number signified scalability:
- 3xxx - 1-way
- 5xxx - 2-way
- 7xxx - 4-way or more
The second digit in the number identified CPU generation, and the last two digits represented relative processor performance. Eventually Intel added a prefix letter, that indicated power requirements:
- E - mainstream CPUs with standard TDP.
- L - low-power CPUs.
- W - workstation-class microprocessors.
- X - high-performance models with 75 Watt and higher.
The latest generation of Intel Xeon microprocessors uses different naming convention. New processor numbers have "E3-", "E5-" or "E7-" prefix, a 4-digit number, and an optional suffix. The prefix signifies server market segment:
- E3-xxxx - microprocessors for workstations
- E5-xxxx - CPUs for mid-class servers or high-performance workstations
- E7-xxxx - processors for enterprise computing
The first digit in the 4-digit number is a CPU scalability. The second digit specifies microprocessor socket, and the last two digits vary depending on processor performance. The suffix can be "L" for low-power products, and "W" for workstation-only products.
The first digit in the processor number, or the prefix letters and the first digit, can be used to identify the family and some of the features of the CPU:
- 14xx - Pentium Dual-Core, 1-way processing
- 3xxx - Xeon
- 5xxx - Xeon
- 7xxx - Xeon
- 9xxx - Itanium 2
- E31xx - Xeon
- E5xxx - Quad-core Xeon
- E7xxx - Xeon MP
- L3xxx - Low-power Xeon (uni-processing)
- L5xxx - Low-power Xeon (dual-processing)
- L7xxx - Low-power Xeon (multi-processing)
- QX9xxx - Xeon
- Wxxxx - Xeon
- X3xxx - Xeon
- X5xxx - Xeon
- X7xxx - Xeon
http://www.cpu-world.com/info/Intel/mobile-processor-number.html
Intel processor numbers (model numbers) of mobile CPUs
This page lists processor numbers of all mobile Intel microprocessors. If you cannot find Intel processor number on this page then please see processor numbers of desktop CPUs and server CPUs pages, or use the "Identify Part" tool in the top right corner of the page to identify the processor number.
Intel processor number (model number) represents processor's relative performance within the same processor family. The processor number depends on processor's speed, front bus speed, L2 cache size, architecture and other processor features. The processors with larger numbers within the same family and within the same range have greater performance than processors with smaller numbers. Processor numbers cannot be used to compare CPUs from different families, even if the numbers reside in the same range. For example, Celeron M 5xx CPUs cannot be compared to mobile Pentium 4-M 5xx processors using processor numbers. Also, the numbers in different ranges cannot be used for performance comparison, even if the numbers belong to the same family. For example, processor (model) numbers cannot be used to compare Celeron M 3xx and Celeron M 4xx microprocessors. Even for processors within the same family and the range, the numbers can only tell which processor is faster or slower, but they cannot be used to tell how much faster or slower the processor is.
First Intel processor numbers, used for Celeron M and Pentium microprocessors, were numeric ones. The first digit in these numbers signified processor family, and remaining digits represented relative CPU performance. To distinguish two processors with identical performance, but different features, Intel began to append one-letter suffix to the number. With introduction of Core Solo and Core Duo families, all new processor numbers included one-letter prefix, that indicated maximum Thermal Design Power:
- T - from 25 to 49 Watt.
- L - from 15 to 24 Watt.
- U - less than 15 Watt.
Later this numbering scheme was modified to add more prefixes, and to re-define the meaning of existing ones:
- L - mobile low-power processor with TDP in the range of 12 - 19 Watt.
- P - mobile power-optimized processor with TDP in the range of 20 - 29 Watt.
- Q - desktop / mobile quad-core processor.
- QX - desktop / mobile quad-core CPU with extreme performance.
- S - mobile processor in small form-factor package.
- T - mobile microprocessor with TDP in the range of 30 - 39 Watt.
- U - mobile ultra low-power CPU with TDP less than 12 Watt.
- X - desktop / mobile dual-core extreme-performance CPU.
Processor numbers were changed once again when Intel released mobile Core i7 CPU family. The new numbers included "i3-", "i5-" or "i7-" prefix, and a number followed by one or more suffix letters. The suffix was used to signify microprocessor type, mobile or embedded, as well as to highlight certain CPU features. Below is a list of suffixes used in the Core ix and earlier CPUs:
- E - Embedded microprocessor.
- G - Unlocked clock multiplier.
- J - Processor has NX (No-execute, or Execute disable, bit) feature.
- L - Low power processor.
- M - Mobile microprocessor.
- P - Different package type (Atom).
- Q - High performance version.
- T - Extended temperature range (Atom).
- U - Ultra-low power processor.
- X - Extreme version.
The optional letters at the beginning of the processor number, and the following digit identify Intel processor family:
- 2xx - Atom / Celeron M
- 3xx - Atom / Celeron M
- 4xx - Celeron M
- 5xx - Celeron M
- 5xx - Mobile Pentium 4
- 7xx - Low-power Celeron M
- 7xx - Pentium M
- 9xx - Mobile Celeron
- Axxx - Atom
- Dxxx - Atom
- E8xxx - Core 2 Duo Mobile
- i3-xxx - Core i3 Mobile
- i5-xxx - Core i5 Mobile
- i7-xxx - Core i7 Mobile
- L2xxx - Low-voltage Core Duo
- L7xxx - Low-voltage Core 2 Duo Mobile
- Nxxx - Atom
- P4xxx - Power-optimized dual-core Mobile Celeron
- P6xxx - Power-optimized dual-core Pentium Mobile
- P7xxx - Power-optimized Core 2 Duo Mobile
- P8xxx - Power-optimized Core 2 Duo Mobile
- P9xxx - Power-optimized Core 2 Duo Mobile
- Q9xxx - Core 2 Quad Mobile
- QX9xxx - Core 2 Extreme Mobile
- SL9xxx - Low-power Core 2 Duo Mobile CPUs in Small Form Factor package
- SP9xxx - Power-optimized Core 2 Duo Mobile CPUs in Small Form Factor package
- SU2xxx - Ultra low-power Celeron Dual-Core Mobile and Pentium Mobile
- SU3xxx - Ultra low-power Core 2 Solo CPUs in Small Form Factor package
- SU4xxx - Ultra low-power Pentium Mobile
- SU7xxx - Ultra low-power Core 2 Duo Mobile CPUs in Small Form Factor package
- SU9xxx - Ultra low-power Core 2 Duo Mobile CPUs in Small Form Factor package
- T1xxx - Core Solo
- T1xxx - Mobile Celeron Dual-Core
- T2xxx - Core Duo
- T2xxx - Pentium Dual-Core Mobile
- T3xxx - Mobile Celeron Dual-Core and Pentium Dual-Core Mobile
- T4xxx - Pentium Dual-Core Mobile
- T5xxx - Core 2 Duo Mobile
- T6xxx - Core 2 Duo Mobile
- T7xxx - Core 2 Duo Mobile
- T8xxx - Core 2 Duo Mobile
- T9xxx - Core 2 Duo Mobile
- U1xxx - Ultra low-power Core Solo
- U2xxx - Ultra low-power Core Duo
- U2xxx - Ultra low-power Core 2 Solo
- U3xxx - Ultra low-power Mobile Celeron Dual-Core
- U5xxx - Ultra low-power Pentium Dual-Core Mobile
- U7xxx - Ultra low-power Core 2 Duo Mobile
- X7xxx - Core 2 Extreme Mobile
- X9xxx - Core 2 Extreme Mobile
- Z5xx - Atom





















 1458
1458

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








