本系列文章由 @yhl_leo 出品,转载请注明出处。
文章链接: http://blog.csdn.net/yhl_leo/article/details/52185581
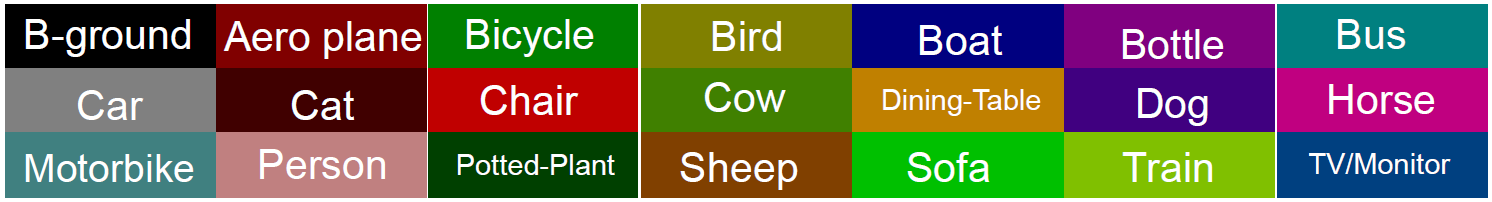
PASCAL VOC图像分割数据集中,图像中各个类别以不同的颜色进行区分,即Ground Truth中,每种颜色都对应着相应的类别:
可以看出这个颜色表既好看又容易区分开。下面来看,这个color map是如何产生的。
先附上Matlab版本的代码:
% VOCLABELCOLORMAP Creates a label color map such that adjacent indices have different
% colors. Useful for reading and writing index images which contain large indices,
% by encoding them as RGB images.
%
% CMAP = VOCLABELCOLORMAP(N) creates a label color map with N entries.
function cmap = labelcolormap(N)
if nargin==0
N=256
end
cmap = zeros(N,3);
for i=1:N
id = i-1; r=0;g=0;b=0;
for j=0:7
r = bitor(r, bitshift(bitget(id,1),7 - j));
g = bitor(g, bitshift(bitget(id,2),7 - j));
b = bitor(b, bitshift(bitget(id,3),7 - j));
id = bitshift(id,-3);
end
cmap(i,1)=r; cmap(i,2)=g; cmap(i,3)=b;
end
cmap = cmap / 255;其中,N就是类别数,而bitor(),bitshift(),bitget()这些位运算的函数,可以在Matlab中查询其功能,很容易理解(源码就不做分析了)。
对于VOC 20类的分割问题,我们调用:labelcolormap(21),可以得到如下输出(这里把结果乘以255,使用整数表示):
0 0 0
128 0 0
0 128 0
128 128 0
0 0 128
128 0 128
0 128 128
128 128 128
64 0 0
192 0 0
64 128 0
192 128 0
64 0 128
192 0 128
64 128 128
192 128 128
0 64 0
128 64 0
0 192 0
128 192 0
0 64 128|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 0 | (0,0,0) | |
| 1 | (128,0,0) | |
| 2 | (0,128,0) | |
| 3 | (128,128,0) | |
| 4 | (0,0,128) | |
| 5 | (128,0,128) | |
| 6 | (0,128,128) | |
| 7 | (128,128,128) | |
| 8 | (64,0,0) | |
| 9 | (192,0,0) | |
| 10 | (64,128,0) | |
| 11 | (192,128,0) | |
| 12 | (64,0,128) | |
| 13 | (192,0,128) | |
| 14 | (64,128,128) | |
| 15 | (192,128,128) | |
| 16 | (0,64,0) | |
| 17 | (128,64,0) | |
| 18 | (0,192,0) | |
| 19 | (128,192,0) | |
| 20 | (0,64,128) |
我将Matlab代码转为python版本:
def uint82bin(n, count=8):
"""returns the binary of integer n, count refers to amount of bits"""
return ''.join([str((n >> y) & 1) for y in range(count-1, -1, -1)])
def labelcolormap(N):
cmap = np.zeros((N, 3), dtype = np.uint8)
for i in range(N):
r = 0
g = 0
b = 0
id = i
for j in range(7):
str_id = uint82bin(id)
r = r ^ ( np.uint8(str_id[-1]) << (7-j))
g = g ^ ( np.uint8(str_id[-2]) << (7-j))
b = b ^ ( np.uint8(str_id[-3]) << (7-j))
id = id >> 3
cmap[i, 0] = r
cmap[i, 1] = g
cmap[i, 2] = b
return cmap这里,我并没有将cmap保存成float型,而是无符号整型,不过这是小事。执行labelcolormap(21)后,得到输出如下:
[[ 0 0 0]
[128 0 0]
[ 0 128 0]
[128 128 0]
[ 0 0 128]
[128 0 128]
[ 0 128 128]
[128 128 128]
[ 64 0 0]
[192 0 0]
[ 64 128 0]
[192 128 0]
[ 64 0 128]
[192 0 128]
[ 64 128 128]
[192 128 128]
[ 0 64 0]
[128 64 0]
[ 0 192 0]
[128 192 0]
[ 0 64 128]]与Matlab版本的结果一致。





















 212
212











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








