系列一:利用Field II仿真计算发射声场强度
0. 基本参数定义
c = 1540; % Speed of sound
f0 = 2.5e6; % Transducer center frequency [Hz]
fs = 100e6; % Sampling frequency [Hz]
lambda = c/f0; % Wavelength
element_height = 13/1000; % Height of element [m] (elevation direction)
element_width = 18.5/1000; % Element width [m] (azimuth direction)
kerf = 0;
focus = [0 0 60]/1000; % Fixed emitter focal point [m] (irrelevant for single element transducer)
N_elements = 1; % Number of physical elements in array
N_sub_x = 1; % Element sub division in x-direction
N_sub_y = 1; % Element subdivision in y-direction
1. 定义发射孔径
在Filed II中使用xdc_命令设置换能器的基本参数,xdc_linear_array命令创建一个线阵换能器。
emit_aperture = xdc_linear_array (N_elements, element_width, element_height, kerf, N_sub_x, N_sub_y, focus);
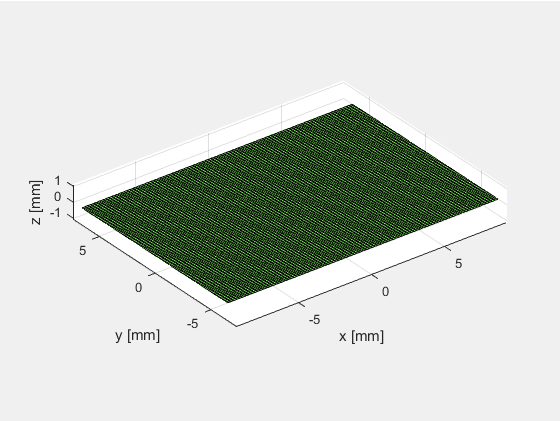
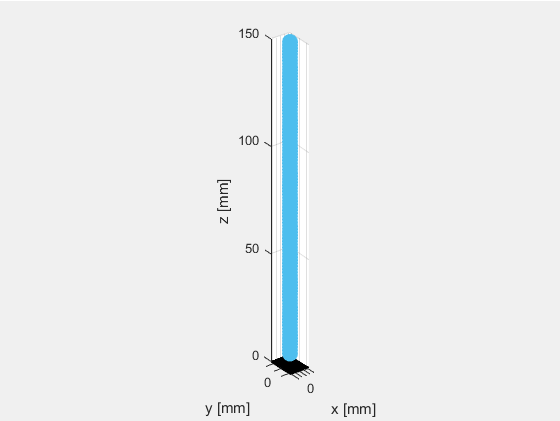
#####1.1 单阵元换能器
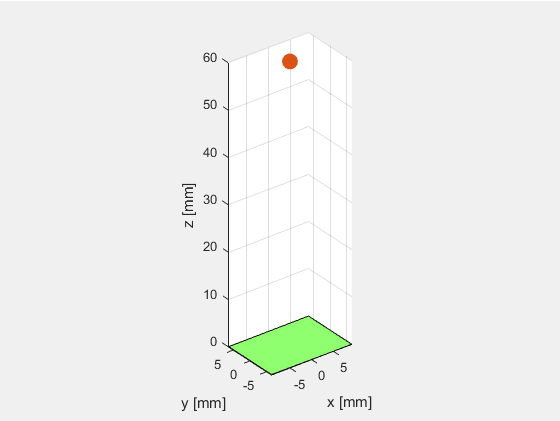
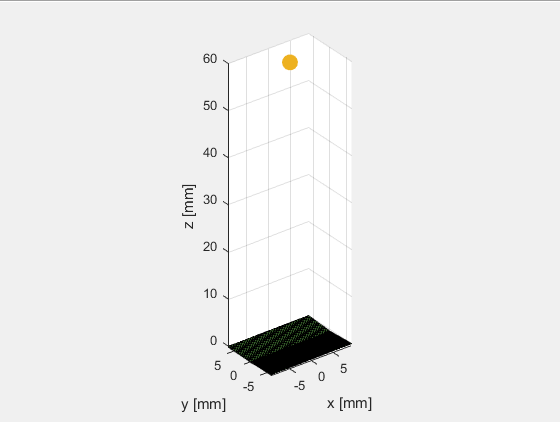
定义单阵元换能器,阵元个数为1,x和y方向上的子阵个数也设置为1:N_elements = 1, N_sub_x=1; N_sub_y=1.
绘制换能器,结果如下图所示。
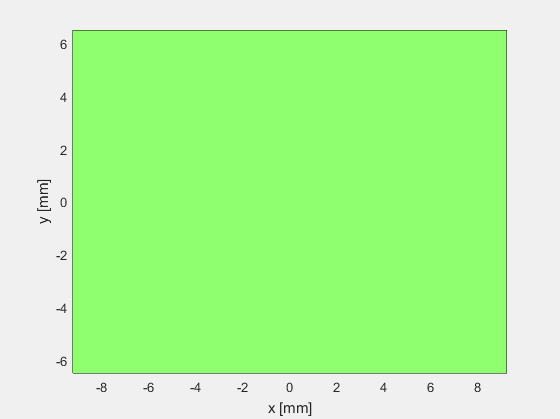
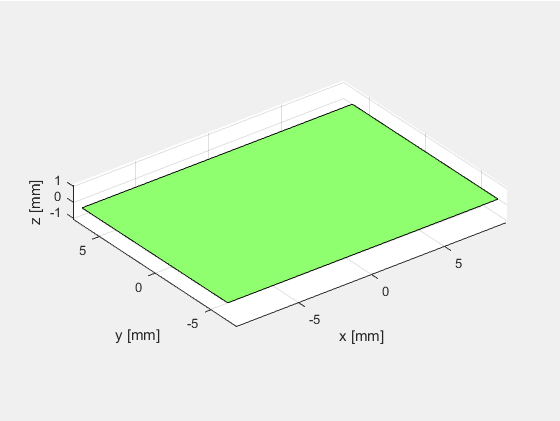
可以看出当阵元数等于1时(N_elements=1),阵元在x轴方向上的长度等于element_width,在y轴方向上的宽度等于element_height。而N_sub_x和N_sub_y只是进行进一步的子阵划分,并不影响仿真计算的结果。
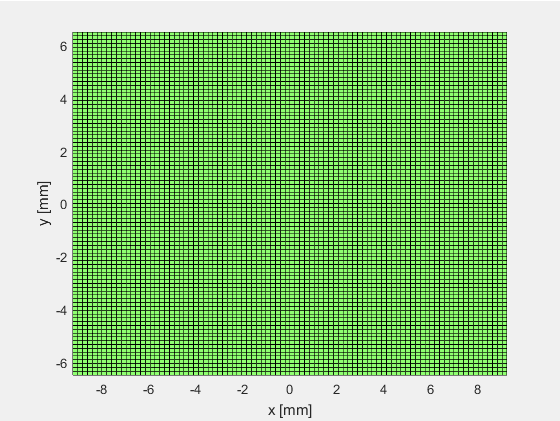
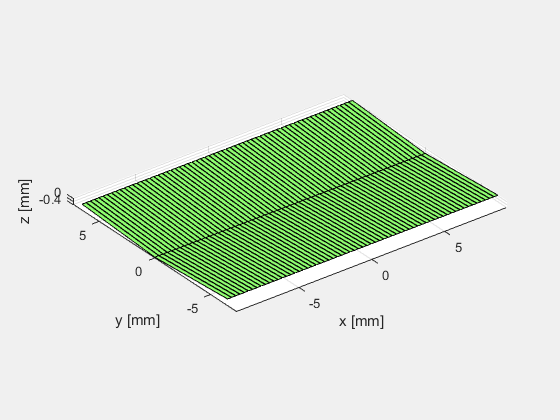
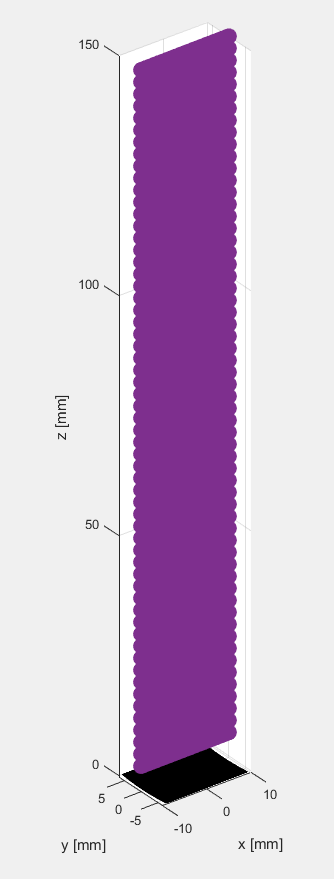
#####1.2 换能器阵列
使用xdc_focus_array指令创建聚焦换能器阵列,如下图所示
element_height = 13/1000; % Height of element [m] (elevation direction)
pitch = 0.290/1000; % Distance between element centers
kerf = 0.025/1000; % Width of fill material between the ceramic elements
element_width = pitch-kerf; % Element width [m] (azimuth direction)
Rfocus = 60/1000; % Elevation lens focus (or radius of curvature, ROC)
focus = [0 0 60]/1000; % Fixed emitter focal point [m] (irrelevant for single element transducer)
N_elements = 64; % Number of physical elements in array
N_sub_x = 1; % Element sub division in x-direction
N_sub_y = 2; % Element subdivision in y-direction
emit_aperture = xdc_focused_array (N_elements, element_width, element_height, kerf, Rfocus, N_sub_x, N_sub_y, focus);
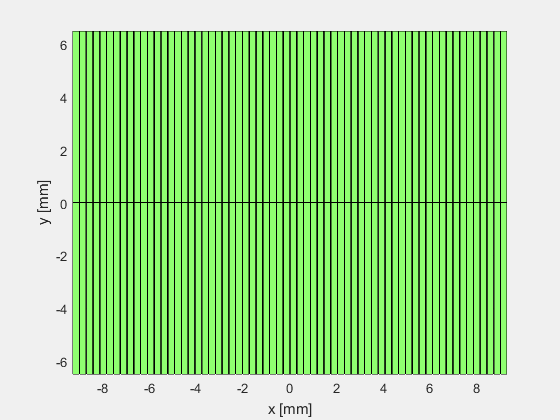
其中,Rfocus定义了换能器的曲率半径。
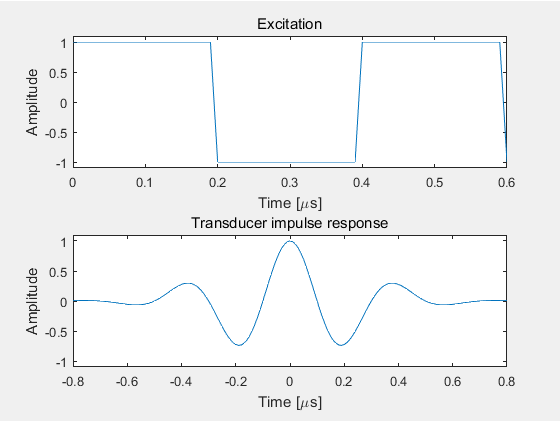
2. 设置换能器的激励和脉冲响应
定义好发射孔径之后,使用xdc_excitation()函数设置发射孔径的激励脉冲Excitation,此处设置激励脉冲的中心频率为2.5MHz,脉冲长度为1.5个周期。
ex_periods = 1.5;
t_ex=(0:1/fs:ex_periods/f0);
excitation=square(2*pi*f0*t_ex);
xdc_excitation (emit_aperture, excitation);
之后,使用xdc_impulse()函数设置换能器发射孔径的脉冲响应Transducer impulse response.
t_ir = -2/f0:1/fs:2/f0;
Bw = 0.6; %带宽设为0.6
impulse_response=gauspuls(t_ir,f0,Bw);
set_sampling(fs);
xdc_impulse (emit_aperture, impulse_response);
3. 计算发射声场强度
#####3.1 一个点处的声场强度
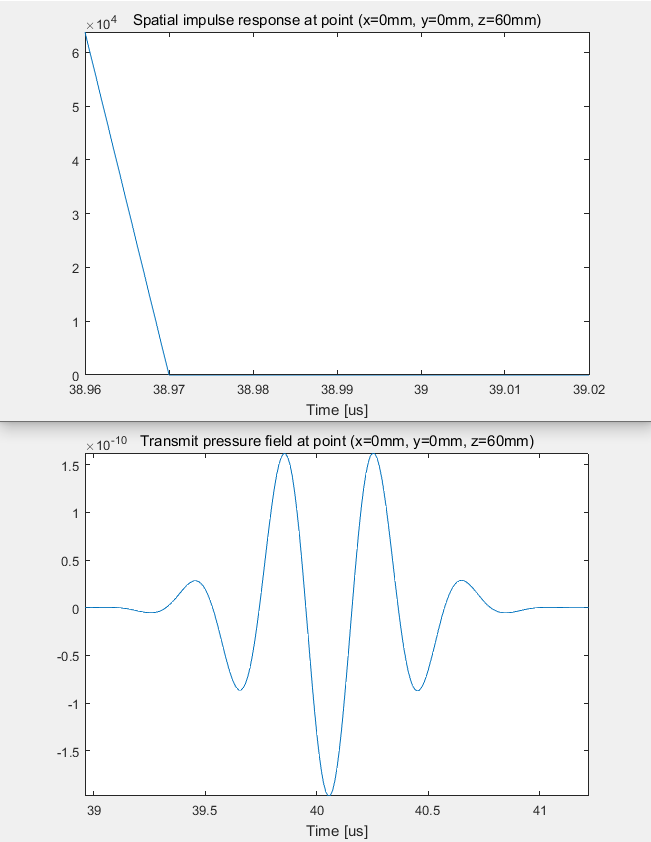
比如,选择(0, 0, 60)mm处为测量点。
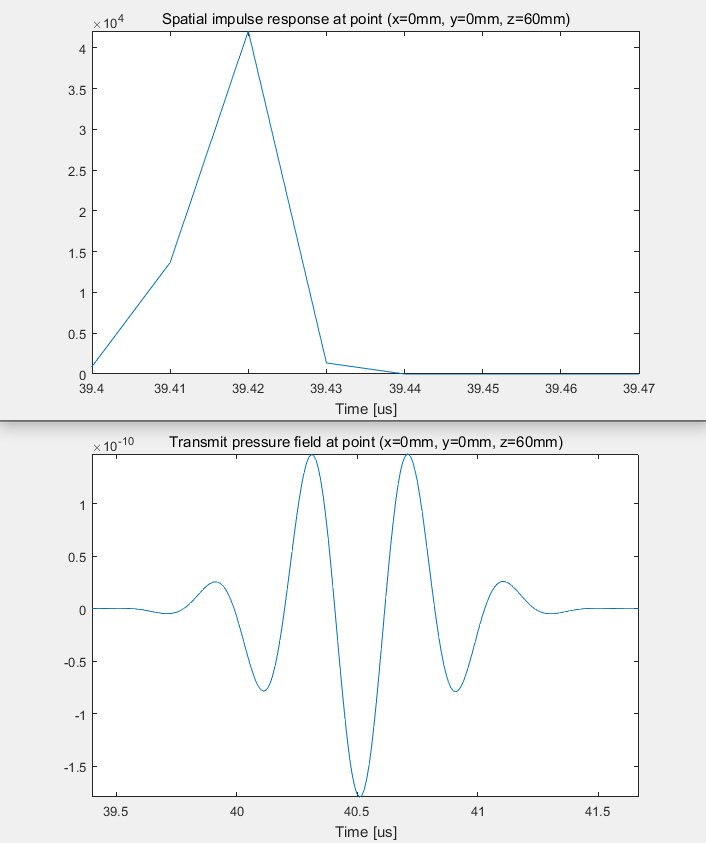
使用calc_h()函数计算该点处的空间脉冲响应Spatial impulse response.
使用calc_hp()函数计算该点处的声场强度Transmit pressure.
(1) 单阵元测量结果
(2) 聚焦换能器阵列测量结果
#####3.2 一条线上的声场强度
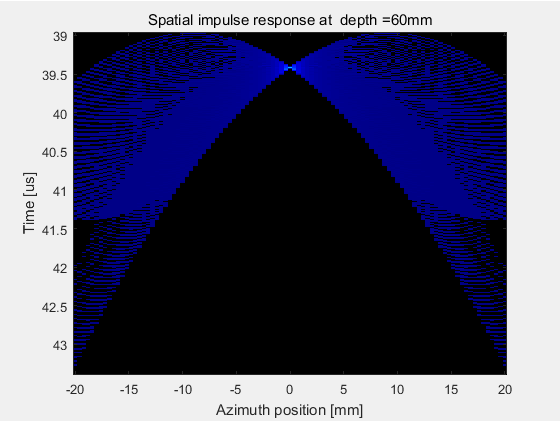
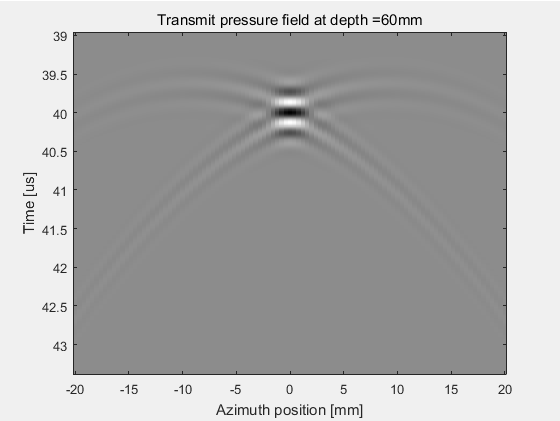
(1) 横向计算结果
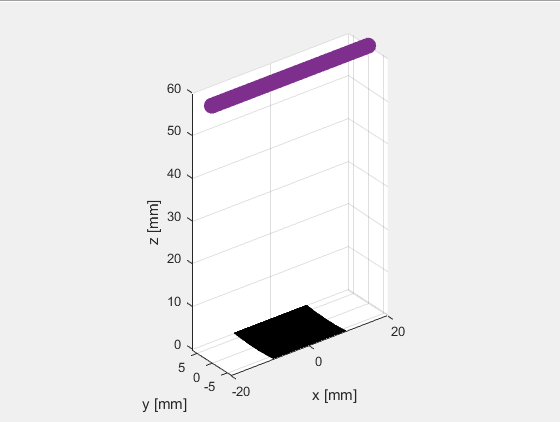
若干点可以组成一条线,在(-20,0,60)mm到(20,0,60)mm处选择101个测量点形成一条线,计算聚焦换能器阵列在60mm深度处的空间脉冲响应和声场强度。
(2) 径向计算结果:计算声轴上声压分布
在(0,0,5)mm到(0,0,150)mm处选择101个测量点形成一条测量线
![Rfocus = 60mm; focus = [0 0 60]mm; 声轴上声压分布](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/e877fee86437fa51b88e47fcfc7fd508.png)
改变焦点位置
Rfocus = 60/1000; % Elevation lens focus (or radius of curvature, ROC)
focus = [0 0 30]/1000; % Fixed emitter focal point [m] (irrelevant for single element transducer)
![Rfocus = 60mm; focus = [0 0 30]mm; 声轴上声压分布](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/df00ba49e70af5513b6e7cd358bff6f6.png)
改变换能器阵元数,从64减少至32
![Rfocus = 60mm; focus = [0 0 60]mm; N_elements=32; 声轴上声压分布](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/22c1870c3ccc3b722b9665ee06f23fae.png)
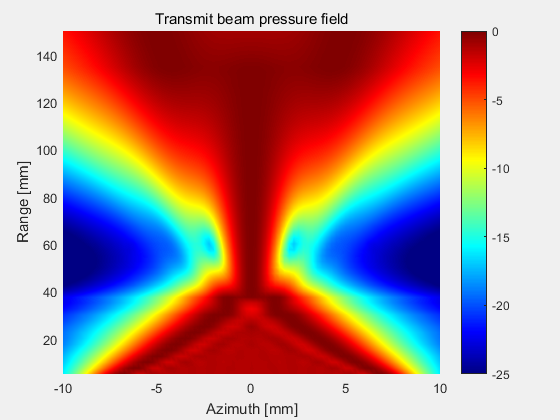
3.3 一个平面的声场强度(xz平面)
选择81x59个测量点,计算xz切面方向上的声场强度,其中x的变化范围为-15mm至15mm,z的变化范围为5mm至150mm。
4. 增加变迹函数
4.1 boxcar变迹函数
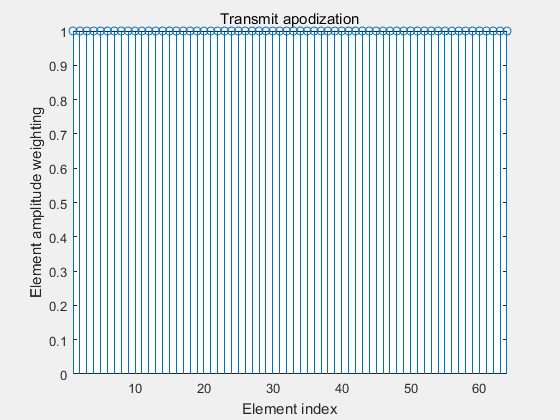
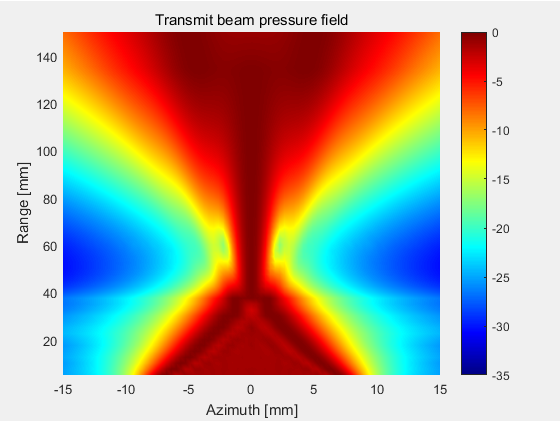
4.2 Hanning变迹函数
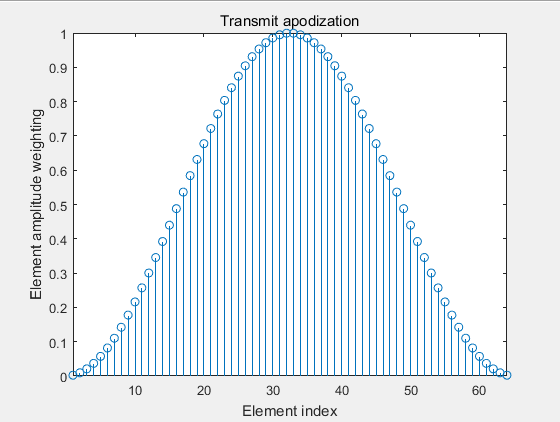
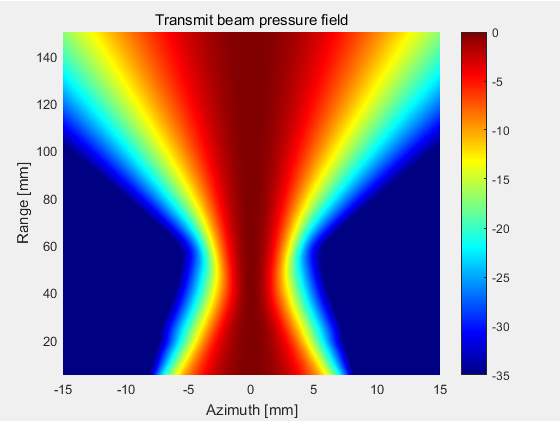
代码请加QQ:2971319104





















 3375
3375











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








