Pedestrian Attribute Recognition(PAR): A Survey
Abstract
本文目的:回顾一下最近的行人属性工作
1、研究背景?相关概念 and 挑战
2、现存的benchmark?
3、multi-task and multi-label learning
4、popular solutions for this task
5、some applications:考虑到这些行人属性之后,识别结果更好?
6、给出possible research directions
本文结构
 主要包括:
主要包括:
2、introduction
2.1、 PAR概念
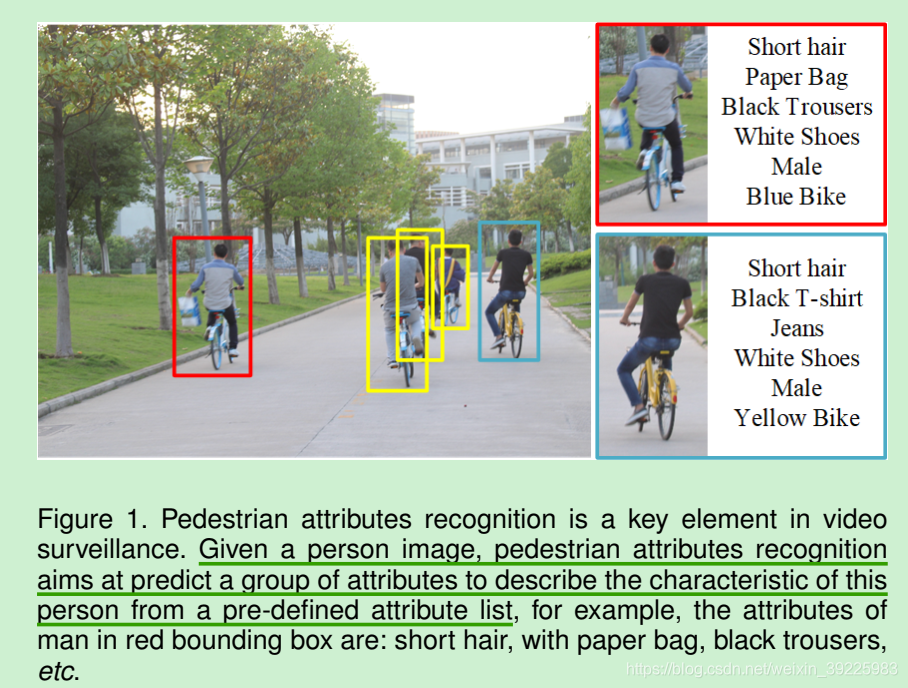
predict a group of attributes to describe the characteristic of this person from a pre-defined attribute list ;
**行人属性识别,从预定义的属性列表中预测一组属性来描述该人的特征;**下面是文中的一张图,比如,红框框中识别出来这个人的属性有:短发,纸袋子,黑裤子,白鞋子,男性,蓝色自行车等
2.2、why attribute?
传统的比如HOG、SIFT等可称为一些低水平的特征,而属性可以被认为是高水平信息,面对视角转换等变化时鲁棒性更强
Different from low-level features, such as HOG, LBP or deep features, attributes can be seen as high-level semantic information which is more robust to viewpoint changes and viewing condition diversity.
所以,比如在行人重识别,行人检测这些研究中,都会把属性考虑进去, to achieve better performance
2.3、challenging factors of PAR
(1) Multi-views
由于摄像机用过不同角度进行采样导致的视角问题;
(2) Occlusion
行人密集导致一些人体被遮挡;
(3) Unbalanced Data Distribution
没个行人都有一些不同的属性,所以个体属性个数的不一致会导致样本不平衡的问题;
(4) Low Resolution
由于好的摄像机成本比较大,现实场景中低分辨率的图片占大多数;
(5) Illumination
光照问题,不同时间段采集到的图片样本光照








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








