转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/ywheunji/p/10479019.html。侵删
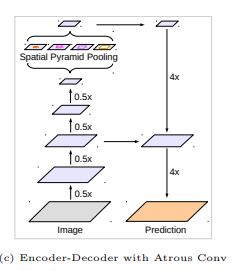
添加了解码模块来重构精确的图像物体边界。对比如图
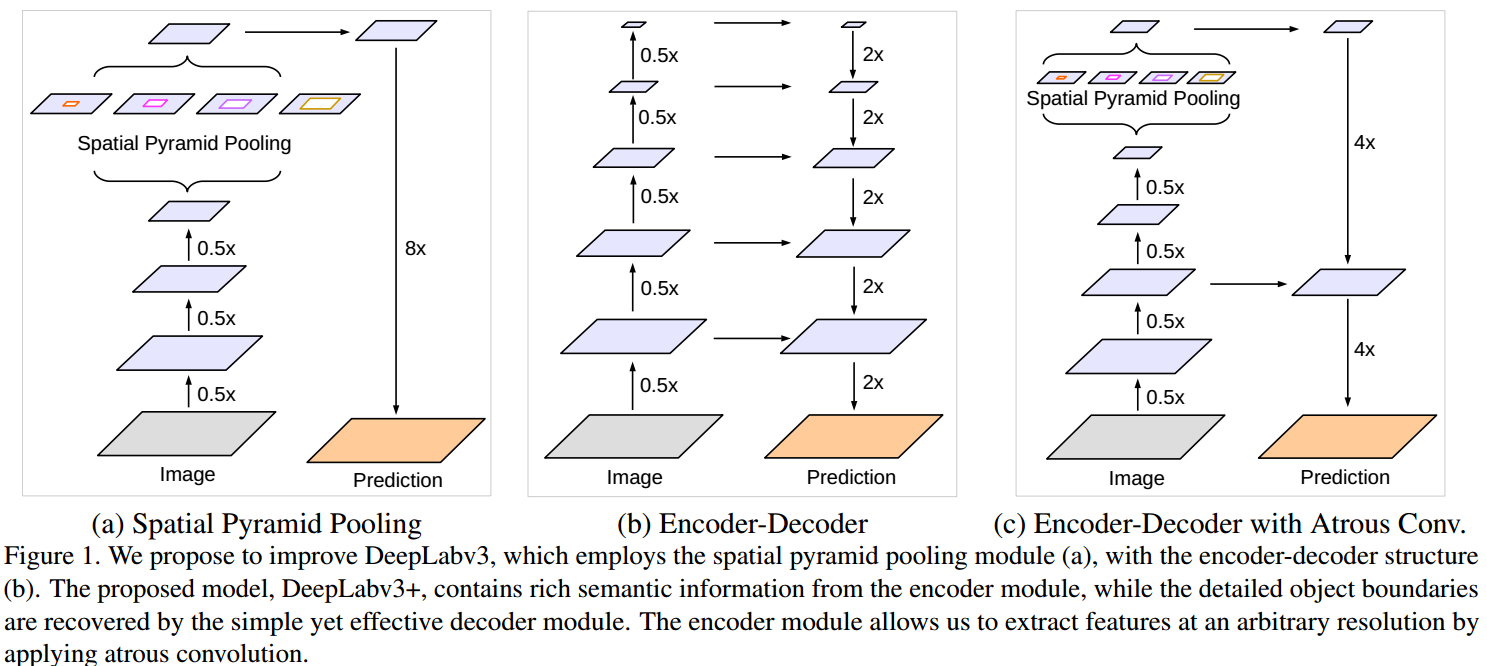
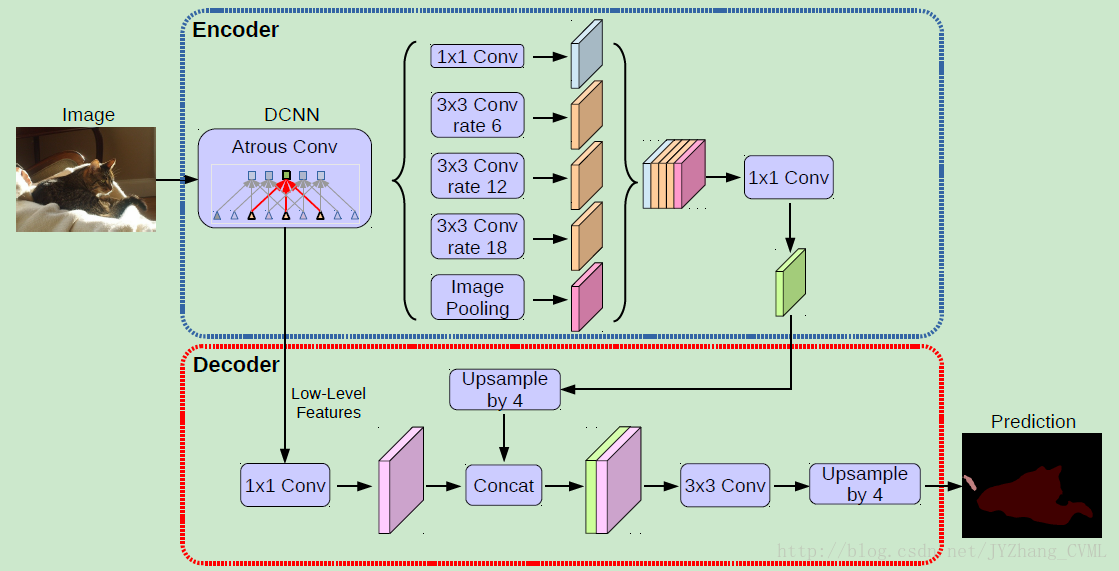
deeplab v3+采用了与deeplab v3类似的多尺度带洞卷积结构ASPP,然后通过上采样,以及与不同卷积层相拼接,最终经过卷积以及上采样得到结果。
deeplab v3:
基于提出的编码-解码结构,可以任意通过控制 atrous convolution 来输出编码特征的分辨率,来平衡精度和运行时间(已有编码-解码结构不具有该能力.).
可以用来挖掘不同尺度的上下文信息
PSPNet 对不同尺度的网络进行池化处理,处理多尺度的上下文内容信息
deeplab v3+以resnet101为backbone

1 import math
2 import torch
3 import torch.nn as nn
4 import torch.nn.functional as F
5 import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
6 from modeling.sync_batchnorm.batchnorm import SynchronizedBatchNorm2d
7
8 BatchNorm2d = SynchronizedBatchNorm2d
9
10 class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
#'resnet网络的基本框架’
11 expansion = 4
12
13 def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, dilation=1, downsample=None):
14 super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
15 self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
16 self.bn1 = BatchNorm2d(planes)
17 self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
18 dilation=dilation, padding=dilation, bias=False)
19 self.bn2 = BatchNorm2d(planes)
20 self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * 4, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
21 self.bn3 = BatchNorm2d(planes * 4)
22 self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
23 self.downsample = downsample
24 self.stride = stride
25 self.dilation = dilation
26
27 def forward(self, x):
28 residual = x
29
30 out = self.conv1(x)
31 out = self.bn1(out)
32 out = self.relu(out)
33
34 out = self.conv2(out)
35 out = self.bn2(out)
36 out = self.relu(out)
37
38 out = self.conv3(out)
39 out = self.bn3(out)
40
41 if self.downsample is not None:
42 residual = self.downsample(x)
43
44 out += residual
45 out = self.relu(out)
46
47 return out
48
49 class ResNet(nn.Module):
50 #renet网络的构成部分
51 def __init__(self, nInputChannels, block, layers, os=16, pretrained=False):
52 self.inplanes = 64
53 super(ResNet, self).__init__()
54 if os == 16:
55 strides = [1, 2, 2, 1]
56 dilations = [1, 1, 1, 2]
57 blocks = [1, 2, 4]
58 elif os == 8:
59 strides = [1, 2, 1, 1]
60 dilations = [1, 1, 2, 2]
61 blocks = [1, 2, 1]
62 else:
63 raise NotImplementedError
64
65 # Modules
66 self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(nInputChannels, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,
67 bias=False)
68 self.bn1 = BatchNorm2d(64)
69 self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
70 self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
71
72 self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0], stride=strides[0], dilation=dilations[0])
73 self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=strides[1], dilation=dilations[1])
74 self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=strides[2], dilation=dilations[2])
75 self.layer4 = self._make_MG_unit(block, 512, blocks=blocks, stride=strides[3], dilation=dilations[3])
76
77 self._init_weight()
78
79 if pretrained:
80 self._load_pretrained_model()
81
82 def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, dilation=1):
83 downsample = None
84 if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
85 downsample = nn.Sequential(
86 nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
87 kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
88 BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
89 )
90
91 layers = []
92 layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, dilation, downsample))
93 self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
94 for i in range(1, blocks):
95 layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
96
97 return nn.Sequential(*layers)
98
99 def _make_MG_unit(self, block, planes, blocks=[1, 2, 4], stride=1, dilation=1):
100 downsample = None
101 if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
102 downsample = nn.Sequential(
103 nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
104 kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
105 BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
106 )
107
108 layers = []
109 layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, dilation=blocks[0]*dilation, downsample=downsample))
110 self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
111 for i in range(1, len(blocks)):
112 layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride=1, dilation=blocks[i]*dilation))
113
114 return nn.Sequential(*layers)
115
116 def forward(self, input):
117 x = self.conv1(input)
118 x = self.bn1(x)
119 x = self.relu(x)
120 x = self.maxpool(x)
121
122 x = self.layer1(x)
123 low_level_feat = x
124 x = self.layer2(x)
125 x = self.layer3(x)
126 x = self.layer4(x)
127 return x, low_level_feat
128
129 def _init_weight(self):
130 for m in self.modules():
131 if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
132 n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
133 m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
134 elif isinstance(m, BatchNorm2d):
135 m.weight.data.fill_(1)
136 m.bias.data.zero_()
137
138 def _load_pretrained_model(self):
139 pretrain_dict = model_zoo.load_url('https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth')
140 model_dict = {}
141 state_dict = self.state_dict()
142 for k, v in pretrain_dict.items():
143 if k in state_dict:
144 model_dict[k] = v
145 state_dict.update(model_dict)
146 self.load_state_dict(state_dict)
147
148 def ResNet101(nInputChannels=3, os=16, pretrained=False):
149 model = ResNet(nInputChannels, Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], os, pretrained=pretrained)
150 return model
151
152
153 class ASPP_module(nn.Module):
#ASpp模块的组成
154 def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, dilation):
155 super(ASPP_module, self).__init__()
156 if dilation == 1:
157 kernel_size = 1
158 padding = 0
159 else:
160 kernel_size = 3
161 padding = dilation
162 self.atrous_convolution = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=kernel_size,
163 stride=1, padding=padding, dilation=dilation, bias=False)
164 self.bn = BatchNorm2d(planes)
165 self.relu = nn.ReLU()
166
167 self._init_weight()
168
169 def forward(self, x):
170 x = self.atrous_convolution(x)
171 x = self.bn(x)
172
173 return self.relu(x)
174
175 def _init_weight(self):
176 for m in self.modules():
177 if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
178 n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
179 m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
180 elif isinstance(m, BatchNorm2d):
181 m.weight.data.fill_(1)
182 m.bias.data.zero_()
183
184
185 class DeepLabv3_plus(nn.Module):
#正式开始deeplabv3+的结构组成
186 def __init__(self, nInputChannels=3, n_classes=21, os=16, pretrained=False, freeze_bn=False, _print=True):
187 if _print:
188 print("Constructing DeepLabv3+ model...")
189 print("Backbone: Resnet-101")
190 print("Number of classes: {}".format(n_classes))
191 print("Output stride: {}".format(os))
192 print("Number of Input Channels: {}".format(nInputChannels))
193 super(DeepLabv3_plus, self).__init__()
194
195 # Atrous Conv 首先获得从resnet101中提取的features map
196 self.resnet_features = ResNet101(nInputChannels, os, pretrained=pretrained)
197
198 # ASPP,挑选参数
199 if os == 16:
200 dilations = [1, 6, 12, 18]
201 elif os == 8:
202 dilations = [1, 12, 24, 36]
203 else:
204 raise NotImplementedError
205 #四个不同带洞卷积的设置,获取不同感受野
206 self.aspp1 = ASPP_module(2048, 256, dilation=dilations[0])
207 self.aspp2 = ASPP_module(2048, 256, dilation=dilations[1])
208 self.aspp3 = ASPP_module(2048, 256, dilation=dilations[2])
209 self.aspp4 = ASPP_module(2048, 256, dilation=dilations[3])
210
211 self.relu = nn.ReLU()
212 #全局平均池化层的设置
213 self.global_avg_pool = nn.Sequential(nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)),
214 nn.Conv2d(2048, 256, 1, stride=1, bias=False),
215 BatchNorm2d(256),
216 nn.ReLU())
217
218 self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1280, 256, 1, bias=False)
219 self.bn1 = BatchNorm2d(256)
220
221 # adopt [1x1, 48] for channel reduction.
222 self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(256, 48, 1, bias=False)
223 self.bn2 = BatchNorm2d(48)
224 #结构图中的解码部分的最后一个3*3的卷积块
225 self.last_conv = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(304, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
226 BatchNorm2d(256),
227 nn.ReLU(),
228 nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
229 BatchNorm2d(256),
230 nn.ReLU(),
231 nn.Conv2d(256, n_classes, kernel_size=1, stride=1))
232 if freeze_bn:
233 self._freeze_bn()
234 #前向传播
235 def forward(self, input):
236 x, low_level_features = self.resnet_features(input)
237 x1 = self.aspp1(x)
238 x2 = self.aspp2(x)
239 x3 = self.aspp3(x)
240 x4 = self.aspp4(x)
241 x5 = self.global_avg_pool(x)
242 x5 = F.upsample(x5, size=x4.size()[2:], mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
243 #把四个ASPP模块以及全局池化层拼接起来
244 x = torch.cat((x1, x2, x3, x4, x5), dim=1)
245 #上采样
246 x = self.conv1(x)
247 x = self.bn1(x)
248 x = self.relu(x)
249 x = F.upsample(x, size=(int(math.ceil(input.size()[-2]/4)),
250 int(math.ceil(input.size()[-1]/4))), mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
251
252 low_level_features = self.conv2(low_level_features)
253 low_level_features = self.bn2(low_level_features)
254 low_level_features = self.relu(low_level_features)
255
256 #拼接低层次的特征,然后再通过插值获取原图大小的结果
257 x = torch.cat((x, low_level_features), dim=1)
258 x = self.last_conv(x)
259 x = F.interpolate(x, size=input.size()[2:], mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
260
261 return x
262
263 def _freeze_bn(self):
264 for m in self.modules():
265 if isinstance(m, BatchNorm2d):
266 m.eval()
267
268 def _init_weight(self):
269 for m in self.modules():
270 if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
271 n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
272 m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
273 elif isinstance(m, BatchNorm2d):
274 m.weight.data.fill_(1)
275 m.bias.data.zero_()
276
277 def get_1x_lr_params(model):
278 """
279 This generator returns all the parameters of the net except for
280 the last classification layer. Note that for each batchnorm layer,
281 requires_grad is set to False in deeplab_resnet.py, therefore this function does not return
282 any batchnorm parameter
283 """
284 b = [model.resnet_features]
285 for i in range(len(b)):
286 for k in b[i].parameters():
287 if k.requires_grad:
288 yield k
289
290
291 def get_10x_lr_params(model):
292 """
293 This generator returns all the parameters for the last layer of the net,
294 which does the classification of pixel into classes
295 """
296 b = [model.aspp1, model.aspp2, model.aspp3, model.aspp4, model.conv1, model.conv2, model.last_conv]
297 for j in range(len(b)):
298 for k in b[j].parameters():
299 if k.requires_grad:
300 yield k
301
302
303 if __name__ == "__main__":
304 model = DeepLabv3_plus(nInputChannels=3, n_classes=21, os=16, pretrained=True, _print=True)
305 model.eval()
306 image = torch.randn(1, 3, 512, 512)
307 with torch.no_grad():
308 output = model.forward(image)
309 print(output.size())





















 1774
1774











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








