在C++中没有垃圾回收机制,必须自己释放分配的内存,否则就会造成内存泄露。解决这个问题最有效的方法是使用智能指针(smart pointer)。智能指针是存储指向动态分配(堆)对象指针的类,用于生存期的控制,能够确保在离开指针所在作用域时,自动地销毁动态分配的对象,防止内存泄露。智能指针的核心实现技术是引用计数,每使用它一次,内部引用计数加1,每析构一次内部的引用计数减1,减为0时,删除所指向的堆内存。
C++11中提供了三种智能指针,使用这些智能指针时需要引用头文件 < memory >:
std::shard_ptr : 共享的智能指针
std::unique_ptr : 独占的智能指针
std::weak_ptr : 弱引用的智能指针,它不共享指针,不能操作资源,是用来监视shared_ptr的。
shared_ptr的初始化
共享智能指针是指多个智能指针可以同事管理同一块有效内存,共享智能指针shared_ptr是一个模板类,如果要进行初始化有三种方式:构造函数,std::make_shared辅助函数,reset方法。共享智能指针对象初始化完毕后,就指向了要管理的那块内存,如果想要查看当前有多少个智能指针同时管理这块内存,可以使用use_count。
通过构造函数初始化
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//使用智能指针管理一块int型的堆内存
shared_ptr<int>ptr1(new int(520));
cout << "ptr1 use count : " << ptr1.use_count() << endl;
//使用智能指针管理一块字符数组对应的堆内存
shared_ptr<char> ptr2(new char[12]);
cout << "ptr2 use count : " << ptr2.use_count() << endl;
//创建智能指针对象,不管理任何内存
shared_ptr<int> ptr3;
cout << "ptr3 use count : " << ptr3.use_count() << endl;
//创建智能指针对象,不管理任何内存
shared_ptr<int> ptr4(nullptr);
cout << "ptr4 use count : " << ptr4.use_count() << endl;
return 0;
}

注:如果智能指针被初始化了一块有效内存,那么这块内存的引用计数+1;如果智能指针没有被初始化或者被初始化为nullptr空指针,引用计数不会+1。另外,不要一个原始指针初始化多个shared_ptr.
下面代码运行会报错:
int* p = new int;
shared_ptr<int> p1(p);
shared_ptr<int> p2(p);
通过拷贝和移动构造函数初始化
当一个智能指针被初始化之后,就可以通过这个智能指针初始化其他新对象。在创建新对象的时候,对应的拷贝构造函数或者移动构造函数就被自动调用了。
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//使用智能指针管理一块int型的堆内存
shared_ptr<int>ptr1(new int(520));
cout << "ptr1 use count : " << ptr1.use_count() << endl;
//调用拷贝构造函数
shared_ptr<int>ptr2(ptr1);
cout << "ptr2 use count : " << ptr2.use_count() << endl;
shared_ptr<int>ptr3 = ptr2;
cout << "ptr3 use count : " << ptr3.use_count() << endl;
//调用移动构造函数
shared_ptr<int>ptr4(move(ptr3));
cout << "ptr4 use count : " << ptr4.use_count() << endl;
shared_ptr<int>ptr5 = move(ptr4);
cout << "ptr5 use count : " << ptr5.use_count() << endl;
return 0;
}
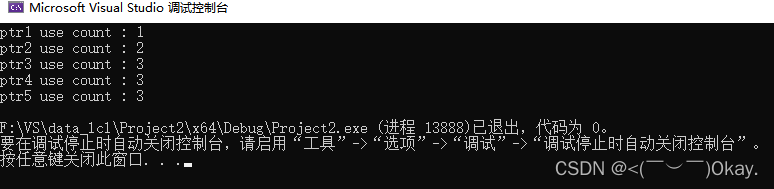
move移动语义只是转让内存的所有权,因此引用计数不会变化。
通过std::make_shared初始化
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
public:
Test()
{
cout << "consturct Test" << endl;
}
Test(int x)
{
cout << "consturct Test,x = " << x << endl;
}
Test(string str)
{
cout << "consturct Test,str = " << str << endl;
}
~Test()
{
cout << "desturct Test..." << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
//使用智能指针管理一块int型的堆内存,内存引用计数为1
shared_ptr<int> ptr1 = make_shared<int>(520);
shared_ptr<Test>ptr2 = make_shared<Test>();
shared_ptr<Test>ptr3 = make_shared<Test>(520);
shared_ptr<Test>ptr4 = make_shared<Test>("lllllllllllll");
return 0;
}
通过reset方法初始化
reset()函数通常与智能指针(如std::shared_ptr、std::unique_ptr等)一起使用。对于智能指针来说,reset()函数的作用是将指针重新指向另一个对象或者将指针置为空。当调用reset()函数时,智能指针会释放原来指向的对象(如果有,引用计数减一),然后重新指向新的对象或者置为空。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//使用智能指针管理一块int型的堆内存,内存引用计数为1
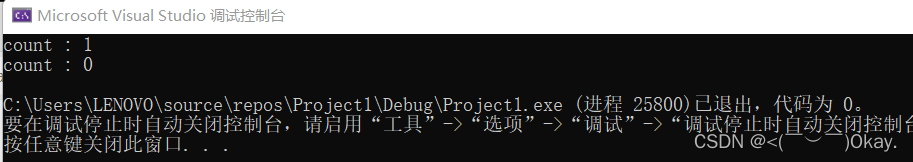
shared_ptr<int> ptr1 = make_shared<int>(100);
ptr1.reset(new int(100)); //使用reset()函数将指针重新指向另一个整数对象
cout << "count : " << ptr1.use_count() << endl;
ptr1.reset(); //将指针置为空
cout << "count : " << ptr1.use_count() << endl;
return 0;
}
获取原始指针
通过智能指针可以管理一个普通变量或者对象的地址,此时原始地址就不可见了。当我们想要修改变量或者对象中的值的时候,就需要从智能指针对象中先取出数据的原始内存的地址再操作,解决方案是调用共享智能指针类提供的get()方法,其函数原型如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
shared_ptr<int> p(new int);
*p = 100;
cout << *p.get() << " " << *p << endl;
return 0;
}
























 1539
1539











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










