目录
一、代理模式
代理模式类似代理商、中介。
代理模式定义:为其他对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问。说白了就是,在一些情况下客户不想或 者不能直接引用一个对象,而代理对象可以在客户和目标对象之间起到中介作用,去掉客户不能看到的内容和服务或者增添客户需要的额外服务。
例子:参考Java 接口
在软件开发中,由于一些原因,客户端不想或不能直接访问一个对象,此时可以通过一个称为"代理"的第三者来实现间接访问。该方案对应的设计模式被称为代理模式。
代理模式(Proxy Design Pattern ) 原始定义是:让你能够提供对象的替代品或其占位符。代理控制着对于原对象的访问,并允许将请求提交给对象前后进行一些处理。
①现实生活中的代理::中介买房,海外代购(顾客-->购买商品--->代购网站--->代购商品--->手机)
②软件开发中的代理:代理模式中引入了一个新的代理对象,代理对象在客户端对象和目标对象之间起到了中介的作用,它去掉客户不能看到的内容和服务或者增加客户需要的额外的新服务。
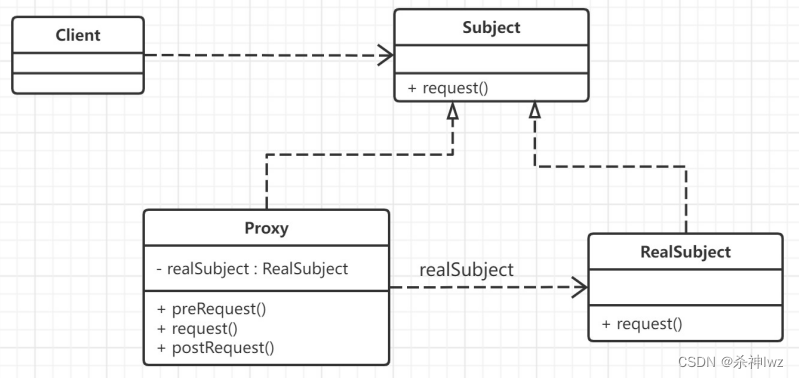
1、代理模式原理
代理(Proxy)模式分为三种角色:
①、抽象主题(Subject)类: 声明了真实主题和代理主题的共同接口,这样就可以保证任何使用真实主题的地方都可以使用代理主题,客户端一般针对抽象主题类进行编程。
②、代理(Proxy)类 : 提供了与真实主题相同的接口,其内部含有对真实主题的引用,它可以在任何时候访问、控制或扩展真实主题的功能。
③、真实主题(Real Subject)类: 实现了抽象主题中的具体业务,是代理对象所代表的真实对象,是最终要引用的对象。
2、静态代理实现
这种代理方式需要代理对象和目标对象实现一样的接口。
优点:可以在不修改目标对象的前提下扩展目标对象的功能。
缺点:
1. 冗余。由于代理对象要实现与目标对象一致的接口,会产生过多的代理类。
2. 不易维护。一旦接口增加方法,目标对象与代理对象都要进行修改。
举例:保存用户功能的静态代理实现
//接口类: IUserDao
public interface IUserDao {
void save();
}
//目标对象:UserDaoImpl
public class UserDaoImpl implements IUserDao {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("保存数据");
}
}
//静态代理对象:UserDaoProxy 需要实现IUserDao接口
public class UserDaoProxy implements IUserDao {
private IUserDao target;
public UserDaoProxy(IUserDao target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("开启事务"); //扩展额外功能
target.save();
System.out.println("提交事务");
}
}
//测试类
public class TestProxy {
@Test
public void testStaticProxy(){
//目标对象
UserDaoImpl userDao = new UserDaoImpl();
//代理对象
UserDaoProxy proxy = new UserDaoProxy(userDao);
proxy.save();
}
}3、JDK动态代理实现
动态代理利用了JDK API,动态地在内存中构建代理对象,从而实现对目标对象的代理功能。动态代理又被称为JDK代理或接口代理。
静态代理与动态代理的区别:
1. 静态代理在编译时就已经实现了,编译完成后代理类是一个实际的class文件
2. 动态代理是在运行时动态生成的,即编译完成后没有实际的class文件,而是在运行时动态生成类字节码,并加载到JVM中。
JDK中生成代理对象主要涉及的类有
//1、java.lang.reflect Proxy,主要方法为
static Object newProxyInstance(
ClassLoader loader, //指定当前目标对象使用类加载器
Class<?>[] interfaces, //目标对象实现的接口的类型
InvocationHandler h //事件处理器
)
//返回一个指定接口的代理类实例,该接口可以将方法调用指派到指定的调用处理程序。
//2、java.lang.reflect InvocationHandler,主要方法为
Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
// 在代理实例上处理方法调用并返回结果。举例:保存用户功能
/**
* 代理工厂-动态生成代理对象
**/
public class ProxyFactory {
private Object target; //维护一个目标对象
public ProxyFactory(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
//为目标对象生成代理对象
public Object getProxyInstance(){
//使用Proxy获取代理对象
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
target.getClass().getClassLoader(), //目标类使用的类加载器
target.getClass().getInterfaces(), //目标对象实现的接口类型
new InvocationHandler(){ //事件处理器
/**
* invoke方法参数说明
* @param proxy 代理对象
* @param method 对应于在代理对象上调用的接口方法Method实例
* @param args 代理对象调用接口方法时传递的实际参数
* @return: java.lang.Object 返回目标对象方法的返回值,没有返回值就返回null
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("开启事务");
//执行目标对象方法
method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("提交事务");
return null;
}
}
);
}
}
//测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
IUserDao target = new UserDaoImpl();
System.out.println(target.getClass());//目标对象信息
IUserDao proxy = (IUserDao) new ProxyFactory(target).getProxyInstance();
System.out.println(proxy.getClass()); //输出代理对象信息
proxy.save(); //执行代理方法
}3.1、类是如何动态生成的
Java虚拟机类加载过程主要分为五个阶段:加载、验证、准备、解析、初始化。其中加载阶段需要完成以下3件事情:
1. 通过一个类的全限定名来获取定义此类的二进制字节流
2. 将这个字节流所代表的静态存储结构转化为方法区的运行时数据结构
3. 在内存中生成一个代表这个类的 java.lang.Class 对象,作为方法区这个类的各种数据访问入口
由于虚拟机规范对这3点要求并不具体,所以实际的实现是非常灵活的,关于第1点,获取类的二进制字节流(class字节码)就有很多途径:
1.从本地获取
2.从网络中获取
3.运行时计算生成:这种场景使用最多的是动态代理技术,在 java.lang.reflect.Proxy 类中,就是用了 ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass 来为特定接口生成形式为 *$Proxy 的代理类的二进制字节流,所以,动态代理就是想办法,根据接口或目标对象,计算出代理类的字节码,然后再加载到JVM中使用
3.2、代理类的调用过程
我们通过借用阿里巴巴的一款线上监控诊断产品 Arthas(阿尔萨斯) ,对动态生成的代理类代码进行查看
//测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
IUserDao target = new UserDaoImpl();
System.out.println(target.getClass());//目标对象信息
IUserDao proxy = (IUserDao) new ProxyFactory(target).getProxyInstance();
System.out.println(proxy.getClass()); //输出代理对象信息
proxy.save(); //执行代理方法
// 不让程序结束,为了拿出jvm中加载的类
try {
Thread.sleep(10000000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}Arthas(阿尔萨斯)反编译加载在JVM中的类,执行jad jdk.proxy1.$Proxy0 即可查看代理类源码

D:\.m2\java_dev\arthas>java -jar arthas-boot.jar
[INFO] JAVA_HOME: C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-21
[INFO] arthas-boot version: 3.7.1
[INFO] Found existing java process, please choose one and input the serial number of the process, eg : 1. Then hit ENTER.
* [1]: 17844 org.jetbrains.jps.cmdline.Launcher
[2]: 9652
[3]: 12488 com.lwz.p2.CliectTest
[4]: 4472 org.jetbrains.idea.maven.server.RemoteMavenServer36
3
[INFO] local lastest version: 3.7.1, remote lastest version: 3.7.2, try to download from remote.
[INFO] Start download arthas from remote server: https://arthas.aliyun.com/download/3.7.2?mirror=aliyun
[INFO] File size: 17.84 MB, downloaded size: 6.09 MB, downloading ...
[INFO] File size: 17.84 MB, downloaded size: 13.92 MB, downloading ...
[INFO] Download arthas success.
[INFO] arthas home: C:\Users\Administrator\.arthas\lib\3.7.2\arthas
[INFO] Try to attach process 12488
Picked up JAVA_TOOL_OPTIONS:
[INFO] Attach process 12488 success.
[INFO] arthas-client connect 127.0.0.1 3658
,---. ,------. ,--------.,--. ,--. ,---. ,---.
/ O \ | .--. ''--. .--'| '--' | / O \ ' .-'
| .-. || '--'.' | | | .--. || .-. |`. `-.
| | | || |\ \ | | | | | || | | |.-' |
`--' `--'`--' '--' `--' `--' `--'`--' `--'`-----'
wiki https://arthas.aliyun.com/doc
tutorials https://arthas.aliyun.com/doc/arthas-tutorials.html
version 3.7.2
main_class
pid 12488
time 2024-04-25 23:32:25
[arthas@12488]$ jad jdk.proxy1.$Proxy0
ClassLoader:
+-jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader@36baf30c
+-jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$PlatformClassLoader@2e6005e0
Location:
/*
* Decompiled with CFR.
*
* Could not load the following classes:
* com.lwz.p1.IUserDao
*/
package jdk.proxy1;
import com.lwz.p1.IUserDao;
import java.lang.invoke.MethodHandles;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException;
public final class $Proxy0
extends Proxy
implements IUserDao {
private static final Method m0;
private static final Method m1;
private static final Method m2;
private static final Method m3;
public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler invocationHandler) {
super(invocationHandler);
}
static {
ClassLoader classLoader = $Proxy0.class.getClassLoader();
try {
m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object", false, classLoader).getMethod("hashCode", new Class[0]);
m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object", false, classLoader).getMethod("equals", Class.forName("java.lang.Object", false, classLoader));
m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object", false, classLoader).getMethod("toString", new Class[0]);
m3 = Class.forName("com.lwz.p1.IUserDao", false, classLoader).getMethod("save", new Class[0]);
return;
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException noSuchMethodException) {
throw new NoSuchMethodError(noSuchMethodException.getMessage());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException classNotFoundException) {
throw new NoClassDefFoundError(classNotFoundException.getMessage());
}
}
public final boolean equals(Object object) {
try {
return (Boolean)this.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[]{object});
}
catch (Error | RuntimeException throwable) {
throw throwable;
}
catch (Throwable throwable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable);
}
}
public final String toString() {
try {
return (String)this.h.invoke(this, m2, null);
}
catch (Error | RuntimeException throwable) {
throw throwable;
}
catch (Throwable throwable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable);
}
}
public final int hashCode() {
try {
return (Integer)this.h.invoke(this, m0, null);
}
catch (Error | RuntimeException throwable) {
throw throwable;
}
catch (Throwable throwable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable);
}
}
public final void save() {
try {
this.h.invoke(this, m3, null);
return;
}
catch (Error | RuntimeException throwable) {
throw throwable;
}
catch (Throwable throwable) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable);
}
}
private static MethodHandles.Lookup proxyClassLookup(MethodHandles.Lookup lookup) throws IllegalAccessException {
if (lookup.lookupClass() == Proxy.class && lookup.hasFullPrivilegeAccess()) {
return MethodHandles.lookup();
}
throw new IllegalAccessException(lookup.toString());
}
}代理类简化后的代码
package jdk.proxy1;
import com.lwz.p1.IUserDao;
import java.lang.invoke.MethodHandles;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException;
public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements IUserDao {
private static final Method m3;
public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler invocationHandler) {
super(invocationHandler);
}
static {
ClassLoader classLoader = $Proxy0.class.getClassLoader();
try {
m3 = Class.forName("com.lwz.p1.IUserDao", false, classLoader).getMethod("save", new Class[0]);
return;
}
}
public final void save() {
try {
this.h.invoke(this, m3, null);
return;
}
}
}- 动态代理类对象 继承了 Proxy 类,并且实现了被代理的所有接口,以及equals、hashCode、toString等方法
- 代理类的构造函数,参数是InvocationHandler实例,Proxy.newInstance方法就是通过这个构造函数来创建代理实例的
- 类和所有方法都被 public final修饰,所以代理类只可被使用,不可以再被继承
- 每个方法都有一个 Method 对象来描述,Method 对象在static静态代码块中创建,以m + 数字 的格式命名
- 调用方法的时候通过this.h.invoke(this, m3, null));实际上 h.invoke就是在调用ProxyFactory中我们重写的invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("开启事务");
//执行目标对象方法
method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("提交事务");
return null;
}4、cglib动态代理
cglib (Code Generation Library ) 是一个第三方代码生成类库,运行时在内存中动态生成一个子类对象从而实现对目标对象功能的扩展。cglib 为没有实现接口的类提供代理,为JDK的动态代理提供了很好的补充。
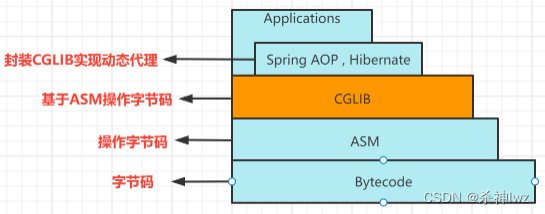
最底层是字节码
ASM是操作字节码的工具
cglib基于ASM字节码工具操作字节码(即动态生成代理,对方法进行增强)
Spring AOP基于cglib进行封装,实现cglib方式的动态代理
使用cglib 需要引入cglib 的jar包,如果你已经有spring-core的jar包,则无需引入,因为spring中包含了cglib 。
cglib 的Maven坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>3.2.5</version>
</dependency>示例代码
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}public class UserServiceImpl {
public List<User> findUserList(){
return Collections.singletonList(new User("tom",18));
}
}cglib代理类,需要实现MethodInterceptor接口,并指定代理目标类target
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
public class UserLogProxy implements MethodInterceptor {
private Object target;
public UserLogProxy(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
public Object getLogProxy(){
//增强器类,用来创建动态代理类
Enhancer en = new Enhancer();
//设置代理类的父类字节码对象
en.setSuperclass(target.getClass());
//设置回调: 对于代理类上所有的方法的调用,都会调用CallBack,而Callback则需要实现intercept()方法进行拦截
en.setCallback(this);
//创建动态代理对象并返回
return en.create();
}
/**
* 实现回调方法
* @param o 代理对象
* @param method 目标对象中的方法的Method实例
* @param args 实际参数
* @param methodProxy 代理对象中的方法的method实例
* @return: java.lang.Object
*/
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(formatter.format(calendar.getTime()) + " [" +method.getName() + "] 查询用户信息...]");
Object result = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, args);
return result;
}
}
测试类
public class ClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//目标对象
UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl();
System.out.println(userService.getClass());
//代理对象
UserServiceImpl proxy = (UserServiceImpl) new UserLogProxy(userService).getLogProxy();
System.out.println(proxy.getClass());
List<User> userList = proxy.findUserList();
System.out.println("用户信息: "+userList);
}
}cglib代理流程
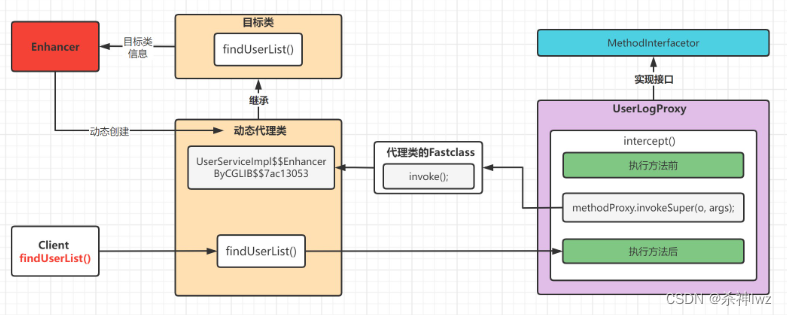
Arthas(阿尔萨斯)反编译加载在JVM中的类,执行jad com.lwz.p3.UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd 即可查看代理类源码
D:\.m2\java_dev\arthas>java -jar arthas-boot.jar
[INFO] JAVA_HOME: C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-21
[INFO] arthas-boot version: 3.7.1
[INFO] Found existing java process, please choose one and input the serial number of the process, eg : 1. Then hit ENTER.
* [1]: 10212 org.jetbrains.idea.maven.server.RemoteMavenServer36
[2]: 4740
[3]: 11240 com.lwz.p3.ClientTest
[4]: 15496 org.jetbrains.jps.cmdline.Launcher
3
[INFO] arthas home: C:\Users\Administrator\.arthas\lib\3.7.2\arthas
[INFO] Try to attach process 11240
Picked up JAVA_TOOL_OPTIONS:
[WARN] Current VM java version: 21 do not match target VM java version: 1.8, attach may fail.
[WARN] Target VM JAVA_HOME is C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_202\jre, arthas-boot JAVA_HOME is C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-21, try to set the same JAVA_HOME.
[WARN] It seems to use the higher version of JDK to attach the lower version of JDK.
[WARN] This error message can be ignored, the attach may have been successful, and it will still try to connect.
[INFO] Attach process 11240 success.
[INFO] arthas-client connect 127.0.0.1 3658
,---. ,------. ,--------.,--. ,--. ,---. ,---.
/ O \ | .--. ''--. .--'| '--' | / O \ ' .-'
| .-. || '--'.' | | | .--. || .-. |`. `-.
| | | || |\ \ | | | | | || | | |.-' |
`--' `--'`--' '--' `--' `--' `--'`--' `--'`-----'
wiki https://arthas.aliyun.com/doc
tutorials https://arthas.aliyun.com/doc/arthas-tutorials.html
version 3.7.2
main_class
pid 11240
time 2024-04-27 00:40:43
[arthas@11240]$ jad com.lwz.p3.UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd
ClassLoader:
+-sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
+-sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@e2144e4
Location:
/D:/WorkSpace/GitWorkSpace/lwz_workspace/05_DesignPatterns/design_patterns/dp-05-proxy/target/classes/
/*
* Decompiled with CFR.
*
* Could not load the following classes:
* com.lwz.p3.UserServiceImpl
*/
package com.lwz.p3;
import com.lwz.p3.UserServiceImpl;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.List;
import net.sf.cglib.core.ReflectUtils;
import net.sf.cglib.core.Signature;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Callback;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Factory;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
public class UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd
extends UserServiceImpl
implements Factory {
private boolean CGLIB$BOUND;
public static Object CGLIB$FACTORY_DATA;
private static final ThreadLocal CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS;
private static final Callback[] CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS;
private MethodInterceptor CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
private static Object CGLIB$CALLBACK_FILTER;
private static final Method CGLIB$findUserList$0$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$findUserList$0$Proxy;
private static final Object[] CGLIB$emptyArgs;
private static final Method CGLIB$equals$1$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$equals$1$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$toString$2$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$toString$2$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$hashCode$3$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$hashCode$3$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$clone$4$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy;
public UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd() {
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd userServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd = this;
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(userServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd);
}
static {
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$STATICHOOK1();
}
public final boolean equals(Object object) {
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (methodInterceptor == null) {
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if (methodInterceptor != null) {
Object object2 = methodInterceptor.intercept(this, CGLIB$equals$1$Method, new Object[]{object}, CGLIB$equals$1$Proxy);
return object2 == null ? false : (Boolean)object2;
}
return super.equals(object);
}
public final String toString() {
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (methodInterceptor == null) {
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if (methodInterceptor != null) {
return (String)methodInterceptor.intercept(this, CGLIB$toString$2$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$toString$2$Proxy);
}
return super.toString();
}
public final int hashCode() {
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (methodInterceptor == null) {
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if (methodInterceptor != null) {
Object object = methodInterceptor.intercept(this, CGLIB$hashCode$3$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$hashCode$3$Proxy);
return object == null ? 0 : ((Number)object).intValue();
}
return super.hashCode();
}
protected final Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (methodInterceptor == null) {
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if (methodInterceptor != null) {
return methodInterceptor.intercept(this, CGLIB$clone$4$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy);
}
return super.clone();
}
public Object newInstance(Callback[] callbackArray) {
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(callbackArray);
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd userServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd = new UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd();
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(null);
return userServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd;
}
public Object newInstance(Callback callback) {
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(new Callback[]{callback});
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd userServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd = new UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd();
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(null);
return userServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd;
}
public Object newInstance(Class[] classArray, Object[] objectArray, Callback[] callbackArray) {
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd userServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd;
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(callbackArray);
Class[] classArray2 = classArray;
switch (classArray.length) {
case 0: {
userServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd = new UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd();
break;
}
default: {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Constructor not found");
}
}
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(null);
return userServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd;
}
public final List findUserList() {
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (methodInterceptor == null) {
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
if (methodInterceptor != null) {
return (List)methodInterceptor.intercept(this, CGLIB$findUserList$0$Method, CGLIB$emptyArgs, CGLIB$findUserList$0$Proxy);
}
return super.findUserList();
}
public void setCallback(int n, Callback callback) {
switch (n) {
case 0: {
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 = (MethodInterceptor)callback;
break;
}
}
}
public void setCallbacks(Callback[] callbackArray) {
Callback[] callbackArray2 = callbackArray;
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd userServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd = this;
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 = (MethodInterceptor)callbackArray[0];
}
public static void CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(Callback[] callbackArray) {
CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS.set(callbackArray);
}
public static void CGLIB$SET_STATIC_CALLBACKS(Callback[] callbackArray) {
CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS = callbackArray;
}
public Callback[] getCallbacks() {
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd userServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd = this;
return new Callback[]{this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0};
}
public Callback getCallback(int n) {
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor;
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
switch (n) {
case 0: {
methodInterceptor = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
break;
}
default: {
methodInterceptor = null;
}
}
return methodInterceptor;
}
public static MethodProxy CGLIB$findMethodProxy(Signature signature) {
String string = ((Object)signature).toString();
switch (string.hashCode()) {
case -1938190956: {
if (!string.equals("findUserList()Ljava/util/List;")) break;
return CGLIB$findUserList$0$Proxy;
}
case -508378822: {
if (!string.equals("clone()Ljava/lang/Object;")) break;
return CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy;
}
case 1826985398: {
if (!string.equals("equals(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z")) break;
return CGLIB$equals$1$Proxy;
}
case 1913648695: {
if (!string.equals("toString()Ljava/lang/String;")) break;
return CGLIB$toString$2$Proxy;
}
case 1984935277: {
if (!string.equals("hashCode()I")) break;
return CGLIB$hashCode$3$Proxy;
}
}
return null;
}
static void CGLIB$STATICHOOK1() {
CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS = new ThreadLocal();
CGLIB$emptyArgs = new Object[0];
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.lwz.p3.UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd");
Class<?> clazz2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object");
Method[] methodArray = ReflectUtils.findMethods(new String[]{"equals", "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z", "toString", "()Ljava/lang/String;", "hashCode", "()I", "clone", "()Ljava/lang/Object;"}, clazz2.getDeclaredMethods());
CGLIB$equals$1$Method = methodArray[0];
CGLIB$equals$1$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(clazz2, clazz, "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z", "equals", "CGLIB$equals$1");
CGLIB$toString$2$Method = methodArray[1];
CGLIB$toString$2$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(clazz2, clazz, "()Ljava/lang/String;", "toString", "CGLIB$toString$2");
CGLIB$hashCode$3$Method = methodArray[2];
CGLIB$hashCode$3$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(clazz2, clazz, "()I", "hashCode", "CGLIB$hashCode$3");
CGLIB$clone$4$Method = methodArray[3];
CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(clazz2, clazz, "()Ljava/lang/Object;", "clone", "CGLIB$clone$4");
clazz2 = Class.forName("com.lwz.p3.UserServiceImpl");
CGLIB$findUserList$0$Method = ReflectUtils.findMethods(new String[]{"findUserList", "()Ljava/util/List;"}, clazz2.getDeclaredMethods())[0];
CGLIB$findUserList$0$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(clazz2, clazz, "()Ljava/util/List;", "findUserList", "CGLIB$findUserList$0");
}
final List CGLIB$findUserList$0() {
return super.findUserList();
}
private static final void CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(Object object) {
block2: {
Object object2;
block3: {
UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd userServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd = (UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd)object;
if (userServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$BOUND) break block2;
userServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$BOUND = true;
object2 = CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS.get();
if (object2 != null) break block3;
object2 = CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS;
if (CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS == null) break block2;
}
userServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$6a2159dd.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 = (MethodInterceptor)((Callback[])object2)[0];
}
}
final String CGLIB$toString$2() {
return super.toString();
}
final int CGLIB$hashCode$3() {
return super.hashCode();
}
final boolean CGLIB$equals$1(Object object) {
return super.equals(object);
}
final Object CGLIB$clone$4() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
Affect(row-cnt:2) cost in 1006 ms.
[arthas@11240]$5、代理模式总结
5.1、三种代理模式实现方式的对比
jdk代理和CGLIB代理
使用CGLib实现动态代理,CGLib底层采用ASM字节码生成框架,使用字节码技术生成代理类,在JDK1.6之前比使用Java反射效率要高。唯一需要注意的是,CGLib不能对声明为final的类或者方法进行代理,因为CGLib原理是动态生成被代理类的子类。
在JDK1.6、JDK1.7、JDK1.8逐步对JDK动态代理优化之后,在调用次数较少的情况下,JDK代理效率高于CGLib代理效率,只有当进行大量调用的时候,JDK1.6和JDK1.7比CGLib代理效率低一点,但是到JDK1.8的时候,JDK代理效率高于CGLib代理。所以如果有接口使用JDK动态代理,如果没有接口使用CGLIB代理。
动态代理和静态代理
动态代理与静态代理相比较,最大的好处是接口中声明的所有方法都被转移到调用处理器一个集中的方法中处理(InvocationHandler.invoke)。这样,在接口方法数量比较多的时候,我们可以进行灵活处理,而不需要像静态代理那样每一个方法进行中转。
如果接口增加一个方法,静态代理模式除了所有实现类需要实现这个方法外,所有代理类也需要实现此方法。增加了代码维护的复杂度。而动态代理不会出现该问题
5.2、代理模式优缺点
优点:
- 代理模式在客户端与目标对象之间起到一个中介作用和保护目标对象的作用;
- 代理对象可以扩展目标对象的功能;
- 代理模式能将客户端与目标对象分离,在一定程度上降低了系统的耦合度;
缺点:
- 增加了系统的复杂度;
5.3、代理模式使用场景
1、功能增强
当需要对一个对象的访问提供一些额外操作时,可以使用代理模式
2、远程(Remote)代理
实际上,RPC 框架也可以看作一种代理模式,GoF 的《设计模式》一书中把它称作远程代理。通过远程代理,将网络通信、数据编解码等细节隐藏起来。客户端在使用 RPC 服务的时候,就像使用本地函数一样,无需了解跟服务器交互的细节。除此之外,RPC 服务的开发者也只需要开发业务逻辑,就像开发本地使用的函数一样,不需要关注跟客户端的交互细节。
3、防火墙(Firewall)代理
当你将浏览器配置成使用代理功能时,防火墙就将你的浏览器的请求转给互联网;当互联网返回响应时,代理服务器再把它转给你的浏览器。
4、保护(Protect or Access)代理
控制对一个对象的访问,如果需要,可以给不同的用户提供不同级别的使用权限。
无论你是年轻还是年长,所有程序员都需要记住:时刻努力学习新技术,否则就会被时代抛弃!
一个程序员最重要的能力是:写出高质量的代码!!
有道无术,术尚可求也,有术无道,止于术。
























 1174
1174











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










