小白学Pytorch系列–Torch.nn API Non-linear Activations (weighted sum, nonlinearity)(5)

| 方法 | 注释 |
|---|---|
| nn.ELU | 如论文中所述,按元素应用指数线性单元(ELU)函数:通过指数线性单元(ELU)快速准确的深度网络学习。 |
| nn.Hardshrink | 按元素应用硬收缩(Hardshrink)函数。 |
| nn.Hardsigmoid | 按元素应用Hardsigmoid函数。 |
| nn.Hardtanh | 按元素应用HardTanh函数。 |
| nn.Hardswish | 如本文所述,按元素应用Hardswish函数:搜索MobileNetV3。 |
| nn.LeakyReLU | 应用按元素的函数 |
| nn.LogSigmoid | 应用按元素的函数 |
| nn.MultiheadAttention | 允许模型联合关注来自不同表示子空间的信息,如论文所述:Attention Is All You Need。 |
| nn.PReLU | 应用按元素的函数 |
| nn.ReLU | 按元素应用校正的线性单位函数 |
| nn.ReLU6 | 按元素应用校正的线性单位函数 |
| nn.RReLU | 如本文所述,在单元上应用随机化漏校正线性单元函数 |
| nn.SELU | 按元素应用 |
| nn.CELU | 应用按元素的函数 |
| nn.GELU | 应用高斯误差线性单位函数 |
| nn.Sigmoid | 应用按元素的函数 |
| nn.SiLU | 按元素应用Sigmoid线性单元(SiLU)函数。 |
| nn.Mish | 在元素上应用Mish函数。 |
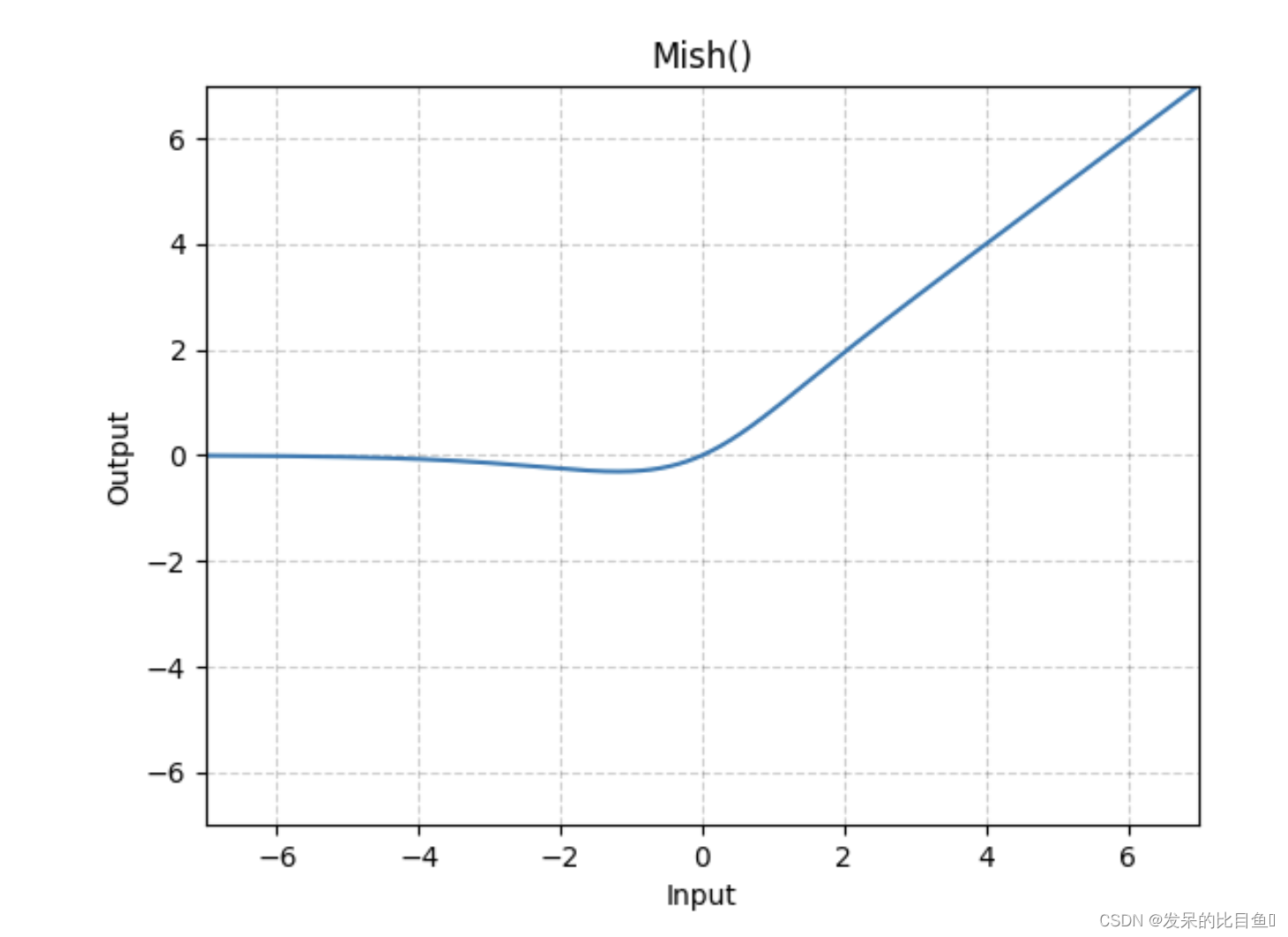
| nn.Softplus | 应用Softplus函数 Softplus ( x ) = 1 β ∗ log ( 1 + exp ( β ∗ x ) ) \operatorname{Softplus}(x)=\frac{1}{\beta} *\log (1+\exp (\beta * x)) Softplus(x)=β1∗log(1+exp(β∗x)) 逐点元素 |
| nn.Softshrink | 按元素应用软收缩函数 |
| nn.Softsign | 应用按元素的函数 |
| nn.Tanh | 按元素应用双曲正切(Tanh)函数。 |
| nn.Tanhshrink | 应用按元素的函数 |
| nn.Threshold | 阈值输入张量的每个元素。 |
| nn.GLU | 应用门控线性单元函数 G L U ( a , b ) = a ⊗ σ ( b ) G L U(a, b)=a \otimes \sigma(b) GLU(a,b)=a⊗σ(b) 其中a是输入矩阵的前一半b是后一半。 |
nn.ELU
如论文中所述,按元素应用指数线性单元(ELU)函数:通过指数线性单元(ELU)快速准确的深度网络学习。

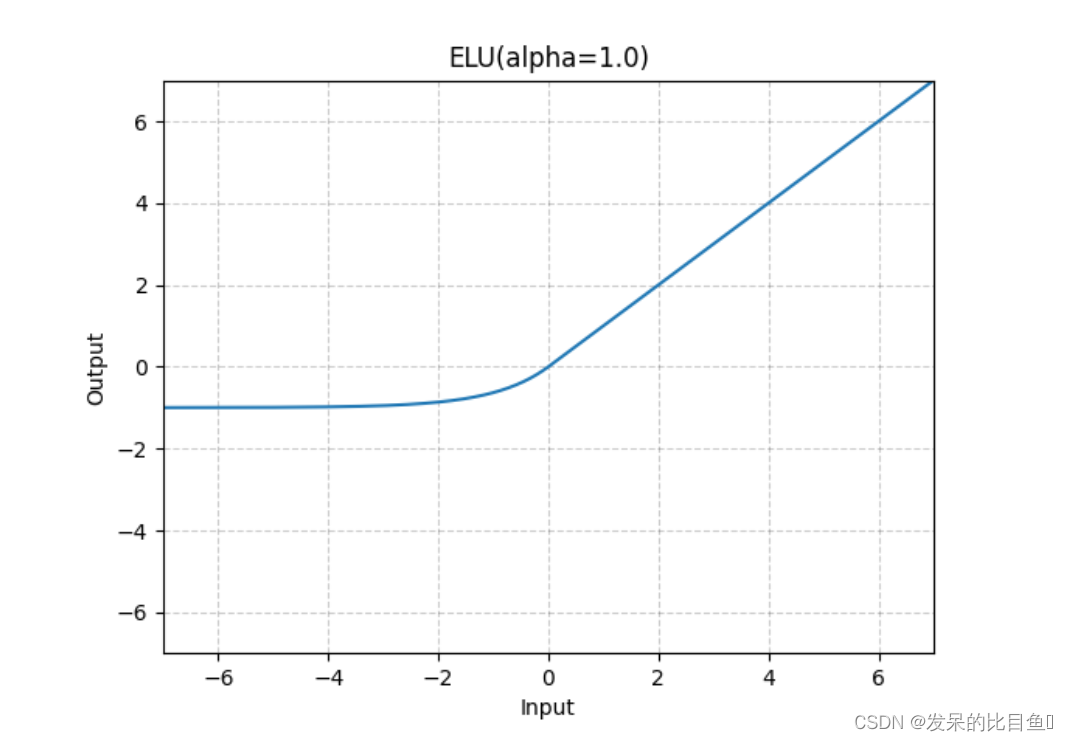
>>> m = nn.ELU()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.Hardshrink
按元素应用Hardsigmoid函数

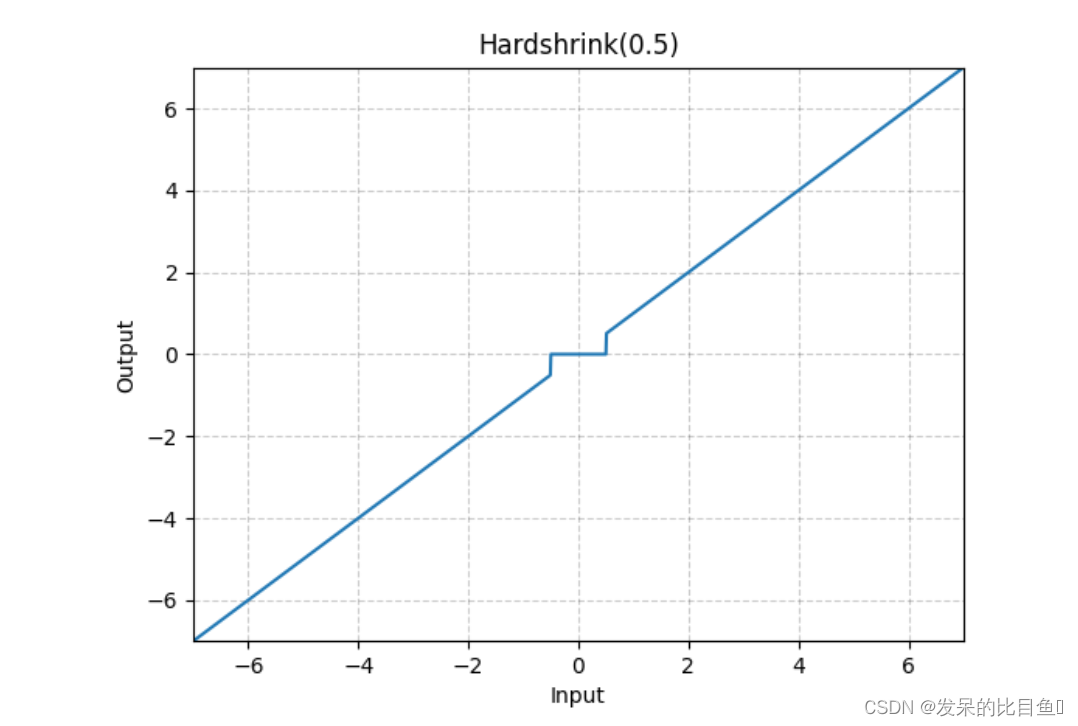
>>> m = nn.Hardshrink()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.Hardsigmoid
按元素应用Hardsigmoid函数。
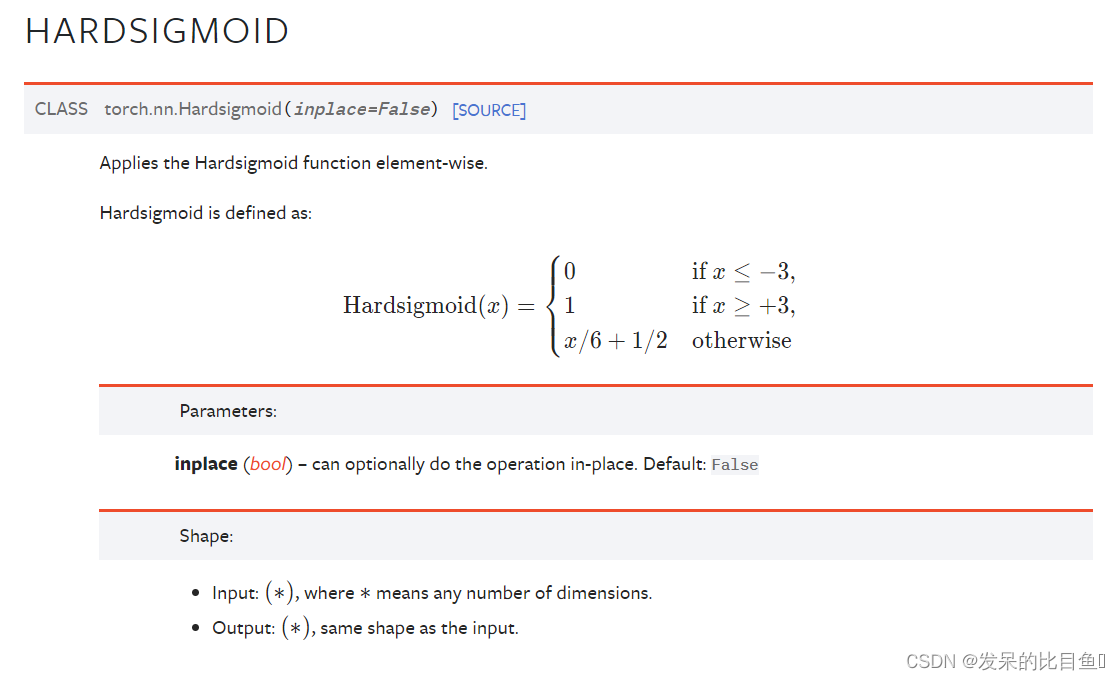
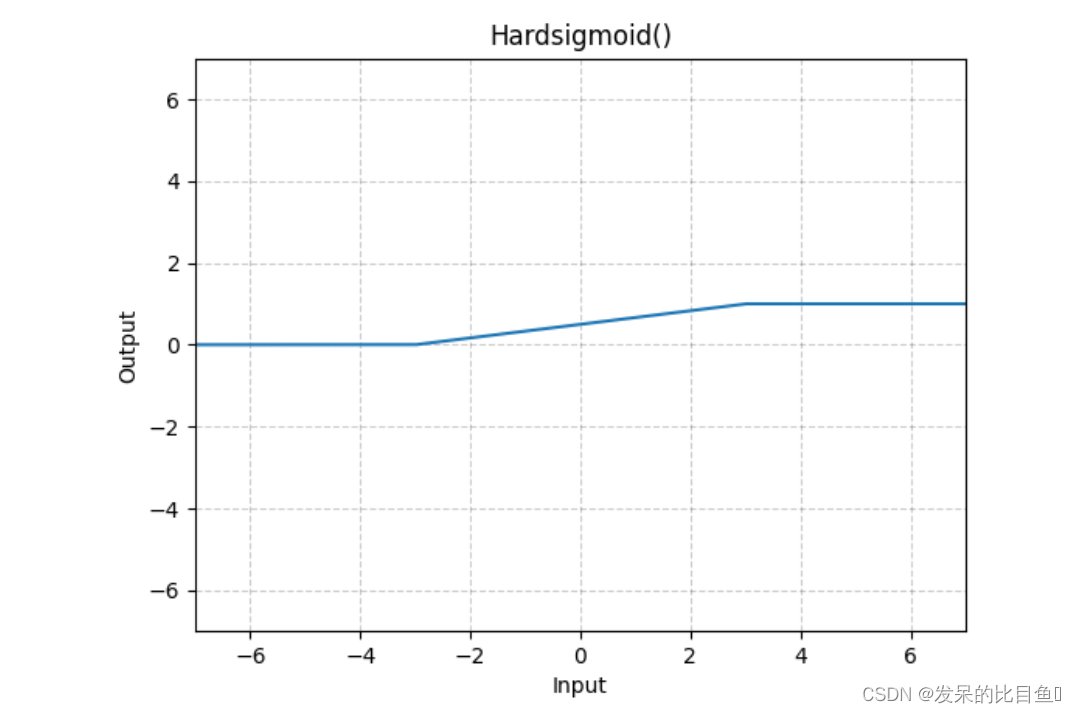
>>> m = nn.Hardsigmoid()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.Hardtanh
按元素应用HardTanh函数。
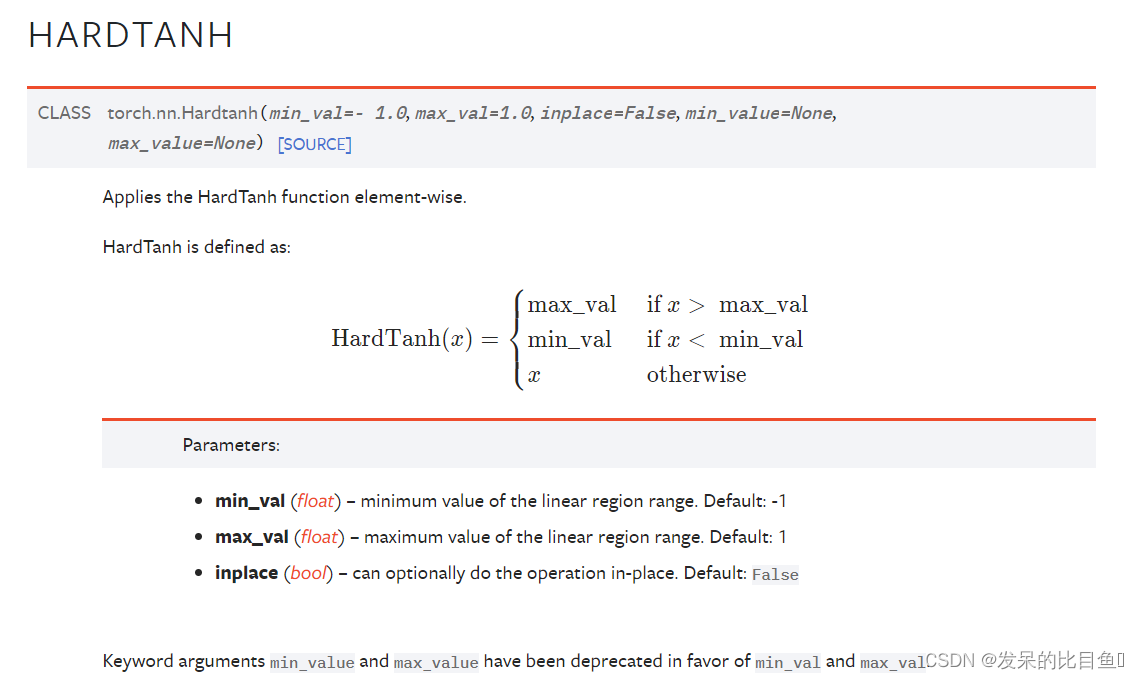
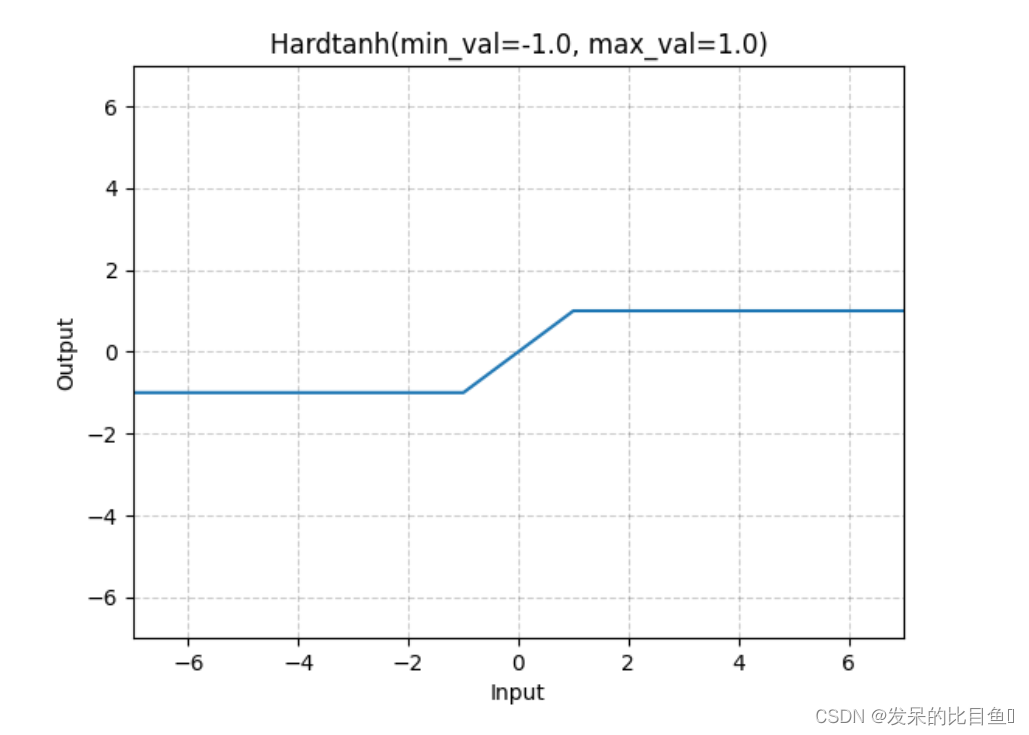
>>> m = nn.Hardtanh(-2, 2)
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.Hardswish
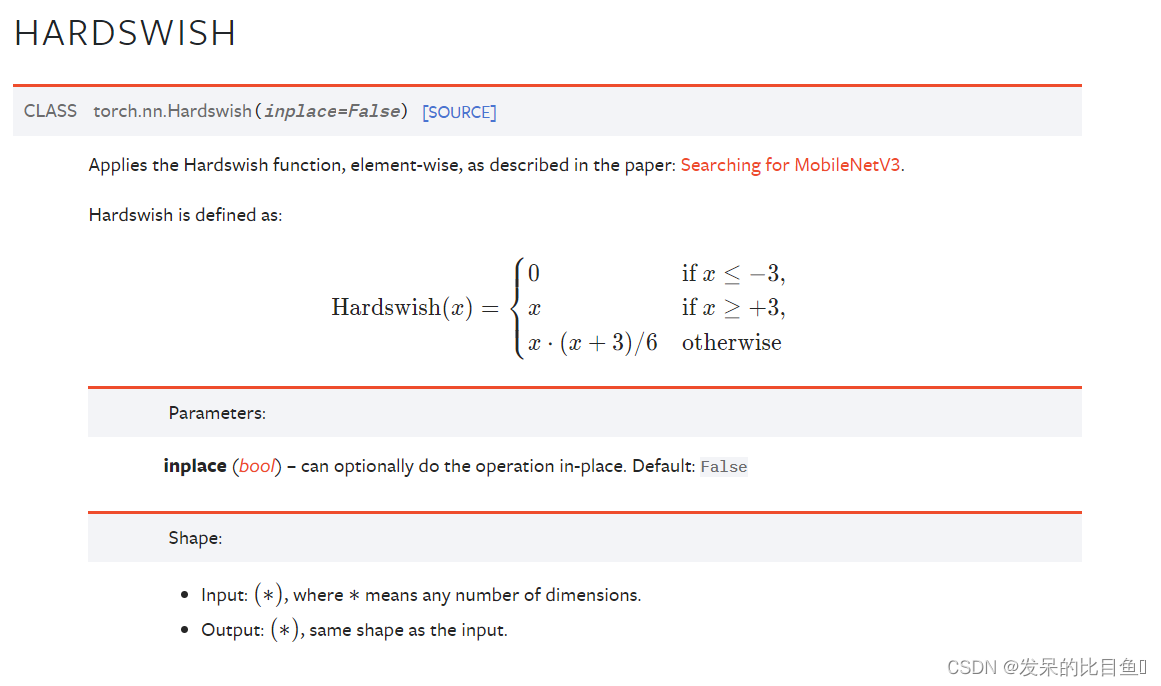
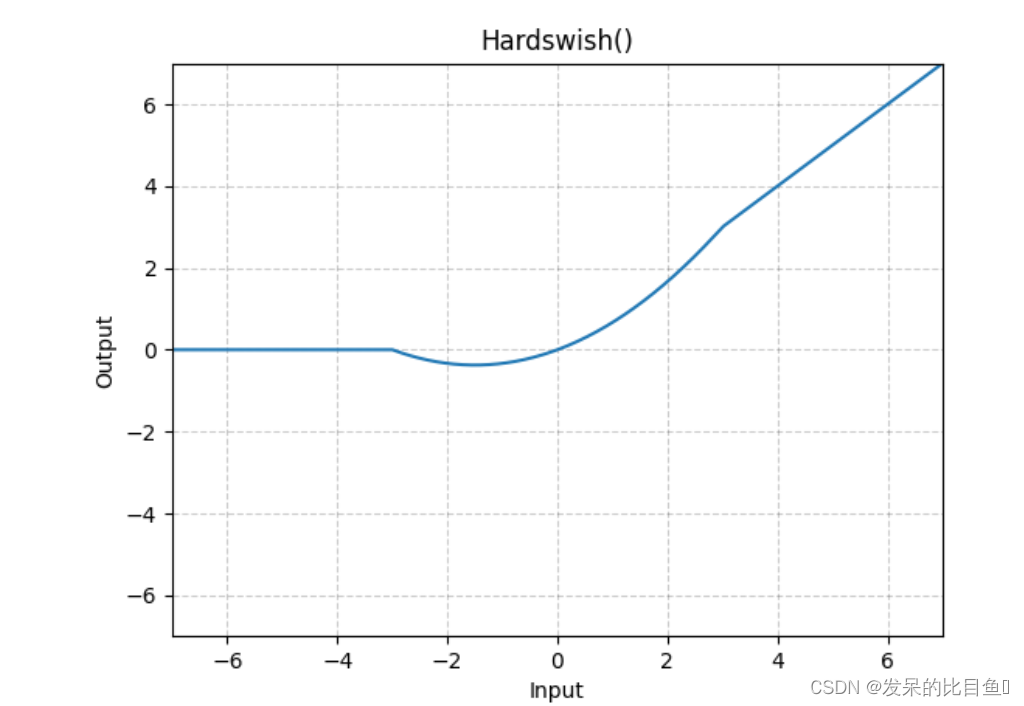
>>> m = nn.Hardswish()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.LeakyReLU
应用按元素的函数
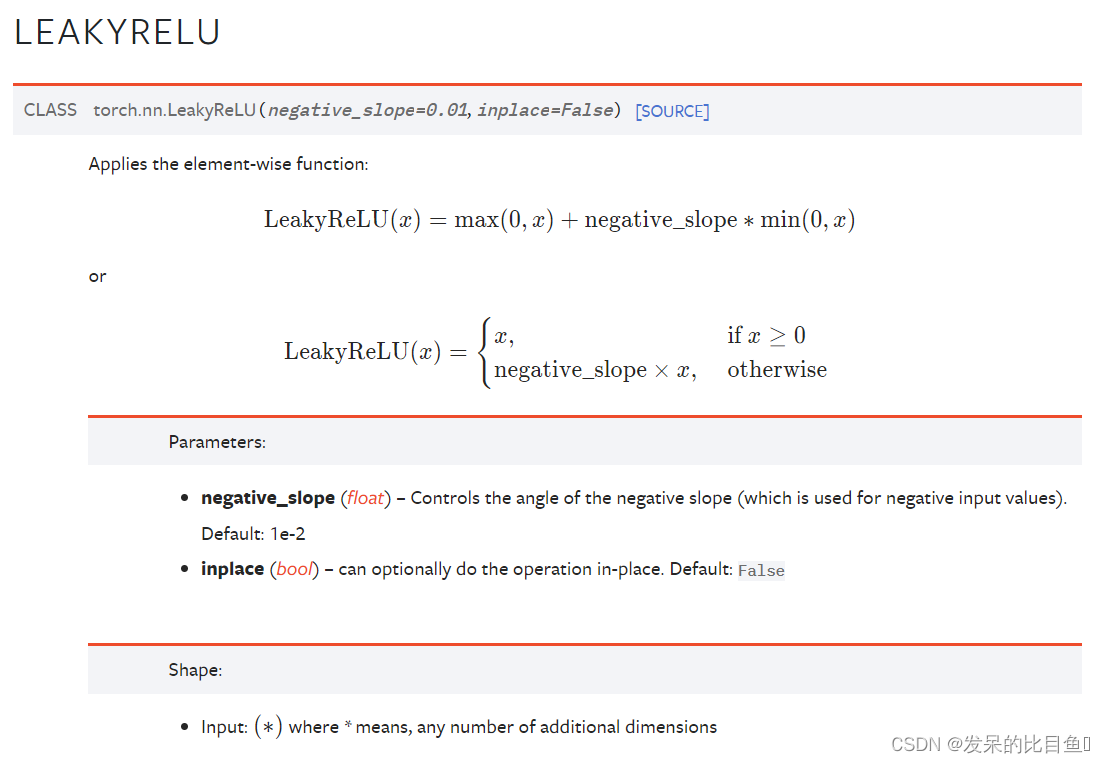
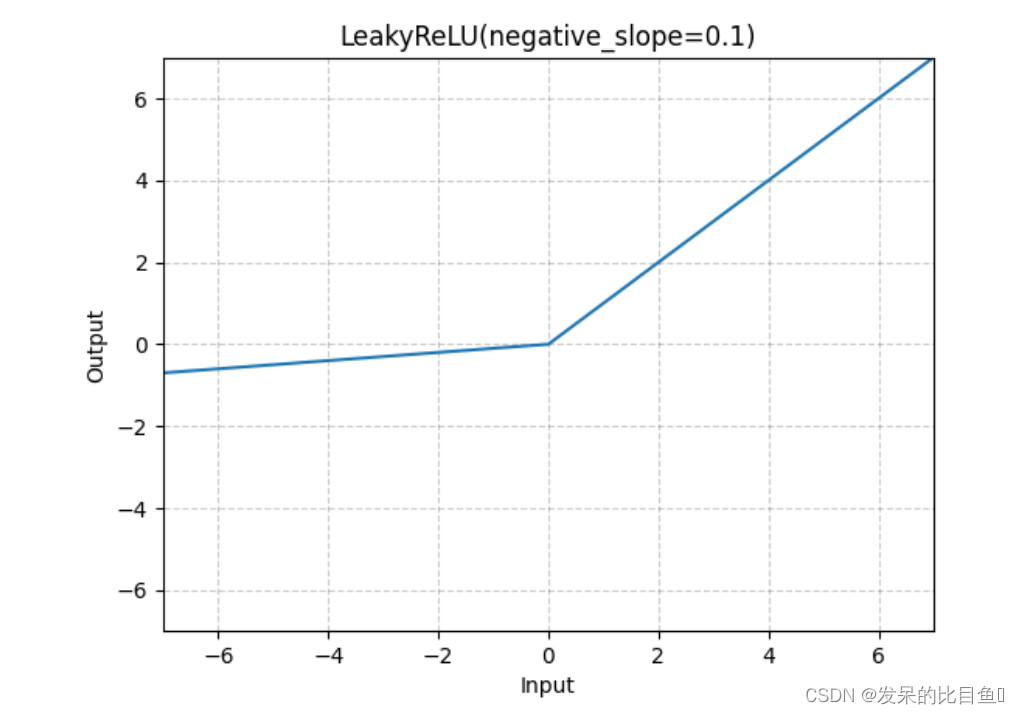
>>> m = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.LogSigmoid
应用按元素的函数
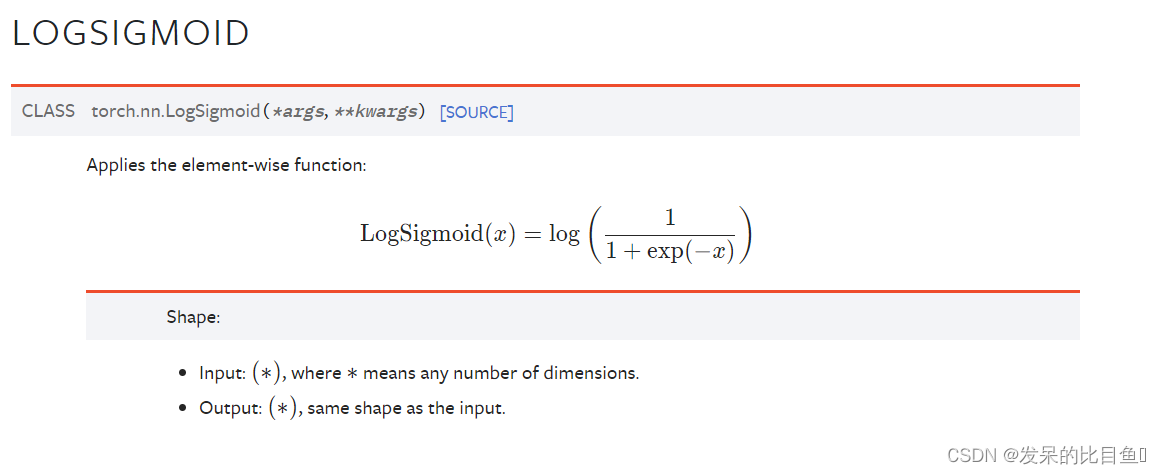
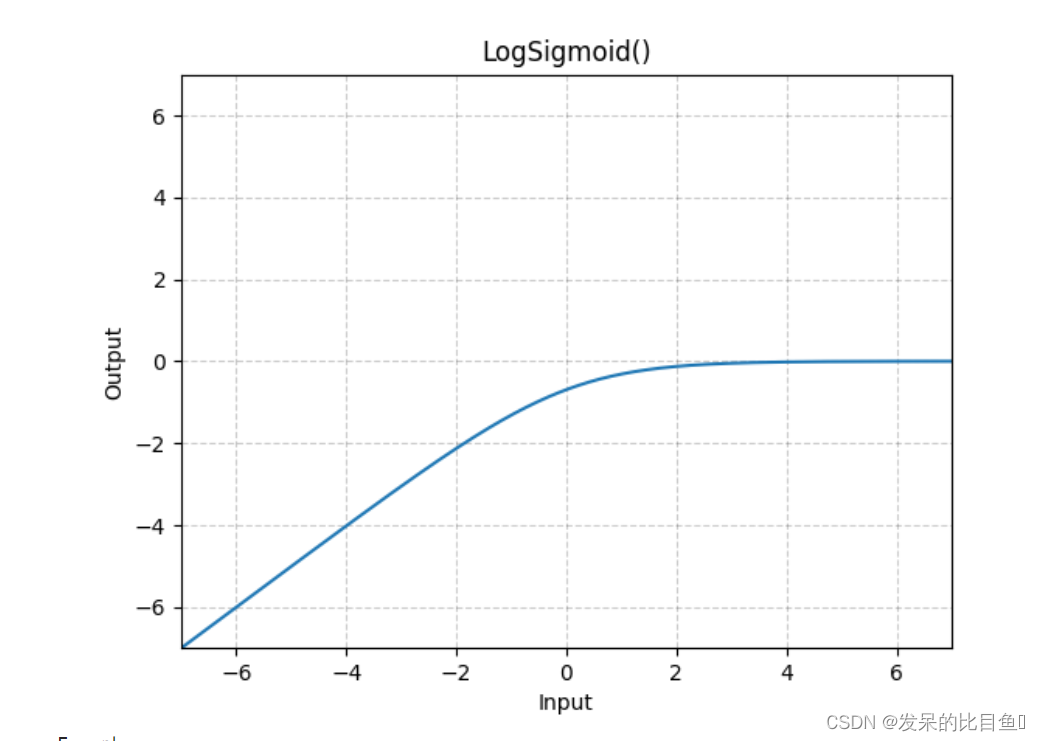
>>> m = nn.LogSigmoid()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
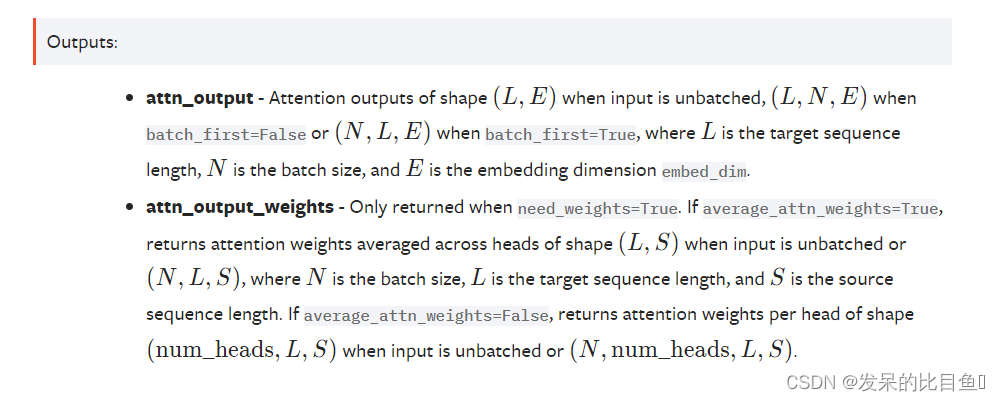
nn.MultiheadAttention



import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import math, copy
def clones(module, N):
"""Product N identical layers."""
# print("clones!")
return nn.ModuleList([copy.deepcopy(module) for _ in range(N)])
def attention(query, key, value, mask=None, dropout=None):
"""Compute Scaled Dot Product Attention"""
d_k = query.size(-1)
scores = torch.matmul(query, key.transpose(-2, -1)) / math.sqrt(d_k)
print("scores size: ", str(scores.size()))
if mask is not None:
scores = scores.masked_fill(mask == 0, -1e9)
p_attn = F.softmax(scores, dim = -1)
if dropout is not None:
p_attn = dropout(p_attn)
return torch.matmul(p_attn, value), p_attn
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, h, d_model, dropout=0.1):
"""Take in model size and number of heads."""
super(MultiHeadAttention, self).__init__()
assert d_model % h == 0
# We assume d_v always equals d_k
self.d_k = d_model // h
self.h = h
self.linears = clones(nn.Linear(d_model, d_model), 4) # create 4 linear layers
self.attn = None
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=dropout)
def forward(self, query, key, value, mask=None):
if mask is not None:
# Same mask applied to all h heads
mask = mask.unsqueeze(1)
batch_size = query.size(0)
print('Before transform query: ', str(query.size()))
# (batch_size, seq_length, d_model)
# 1) Do all the linear projections in batch from d_model => h * d_k
query, key, value = [l(x) for l, x in zip(self.linears, (query, key, value))]
query, key, value = [x.view(batch_size, -1, self.h, self.d_k).transpose(1, 2) for x in (query, key, value)]
# (batch_size, h, seq_length, d_k)
print('After transform query: ' + str(query.size()))
# 2) Apply attention on all the projected vectors in batch.
x, self.attn = attention(query, key, value, mask=mask, dropout=self.dropout)
# 3) "Concat" using a view and apply a final linear.
x = x.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(batch_size, -1, self.h * self.d_k)
return self.linears[-1](x)
h = 8
d_model = 512
batch_size = 1024
seq_length = 10
model = MultiHeadAttention(h, d_model)
query = torch.randn([batch_size, seq_length, d_model])
key = query
value = query
print("Input size: ", str(query.size()))
m = model(query, key, value)
print("Output size: " + str(m.size()))
atten = nn.MultiheadAttention(512, num_heads=8)
atten(query, key, value)[0].shape
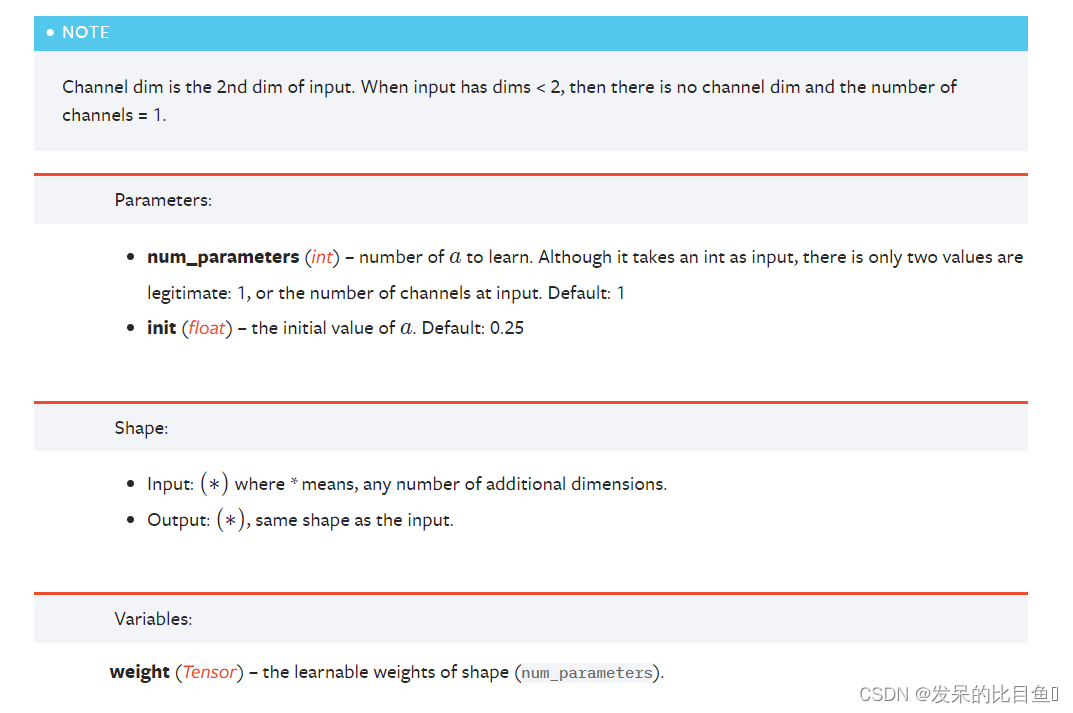
nn.PReLU
应用按元素的函数


>>> m = nn.PReLU()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
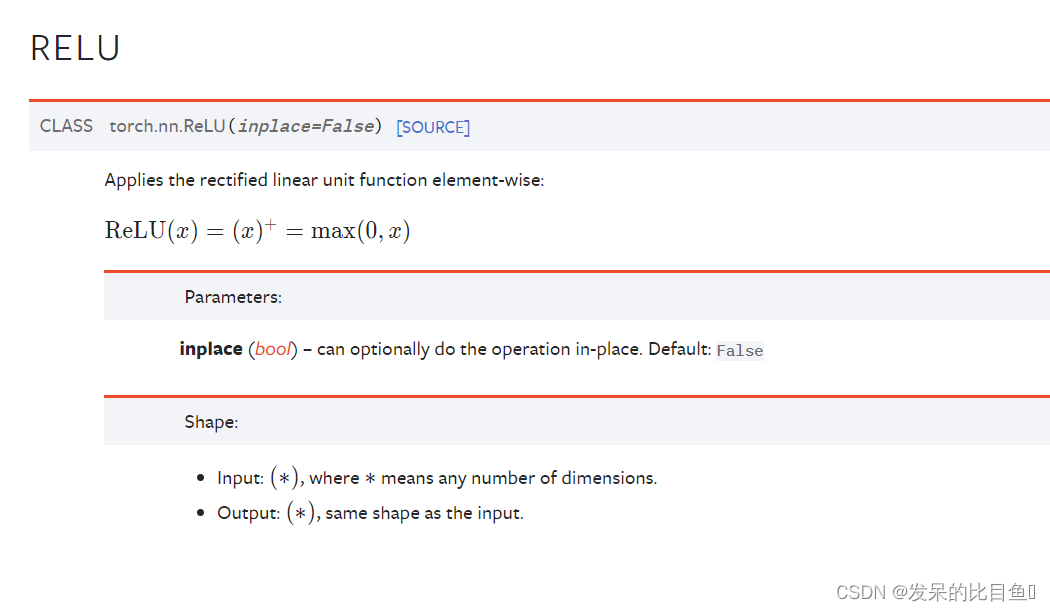
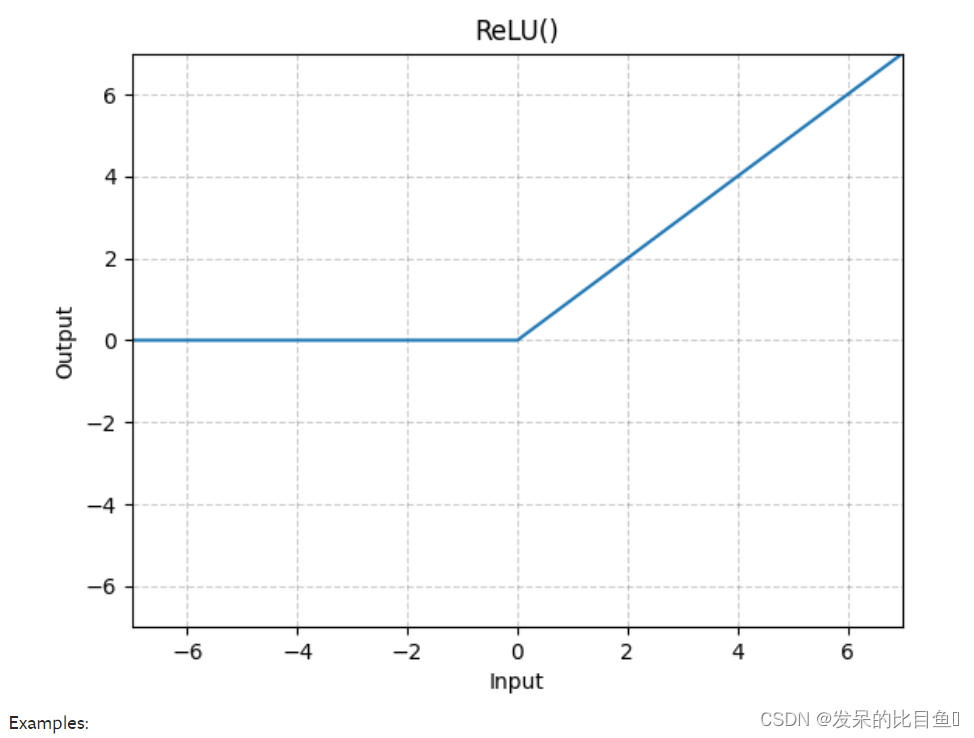
nn.ReLU
按元素应用校正的线性单位函数
>>> m = nn.ReLU()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
An implementation of CReLU - https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.05201
>>> m = nn.ReLU()
>>> input = torch.randn(2).unsqueeze(0)
>>> output = torch.cat((m(input), m(-input)))
nn.ReLU6
应用元素函数

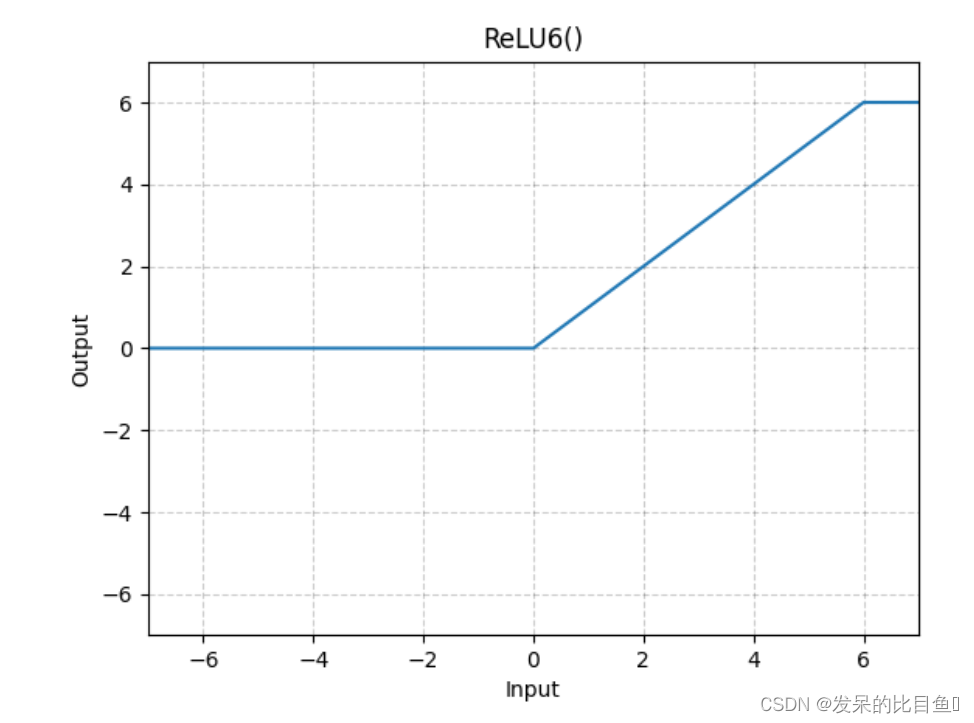
>>> m = nn.ReLU6()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.RReLU
如本文所述,在单元上应用随机化漏校正线性单元函数


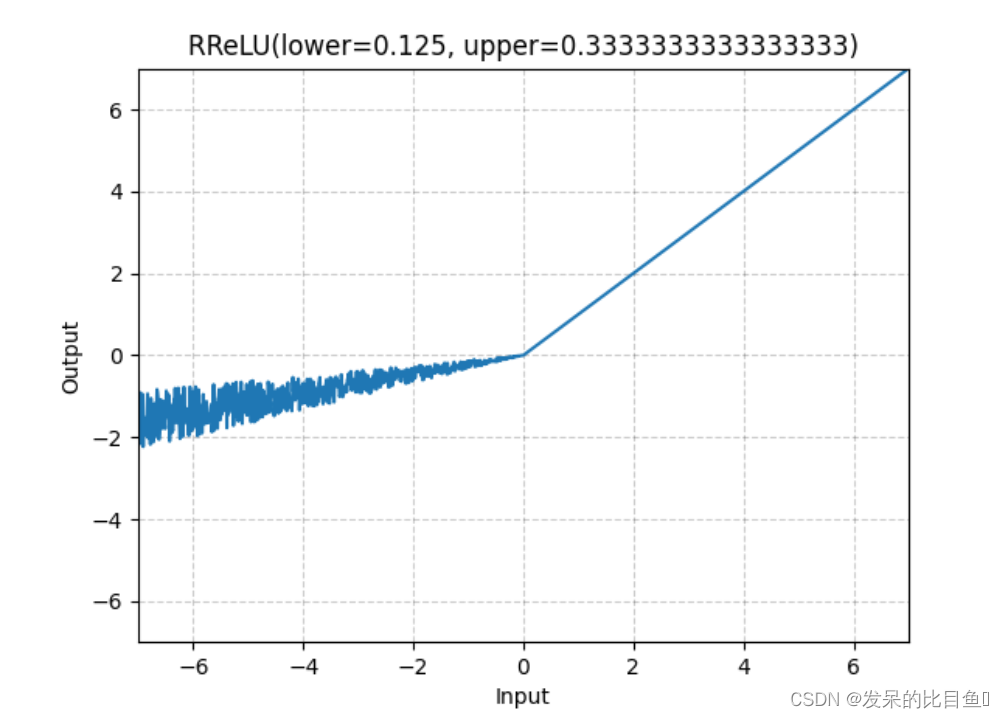
>>> m = nn.RReLU(0.1, 0.3)
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.RReLU
如本文所述,在单元上应用随机化漏校正线性单元函数
Empirical Evaluation of Rectified Activations in Convolutional Network.
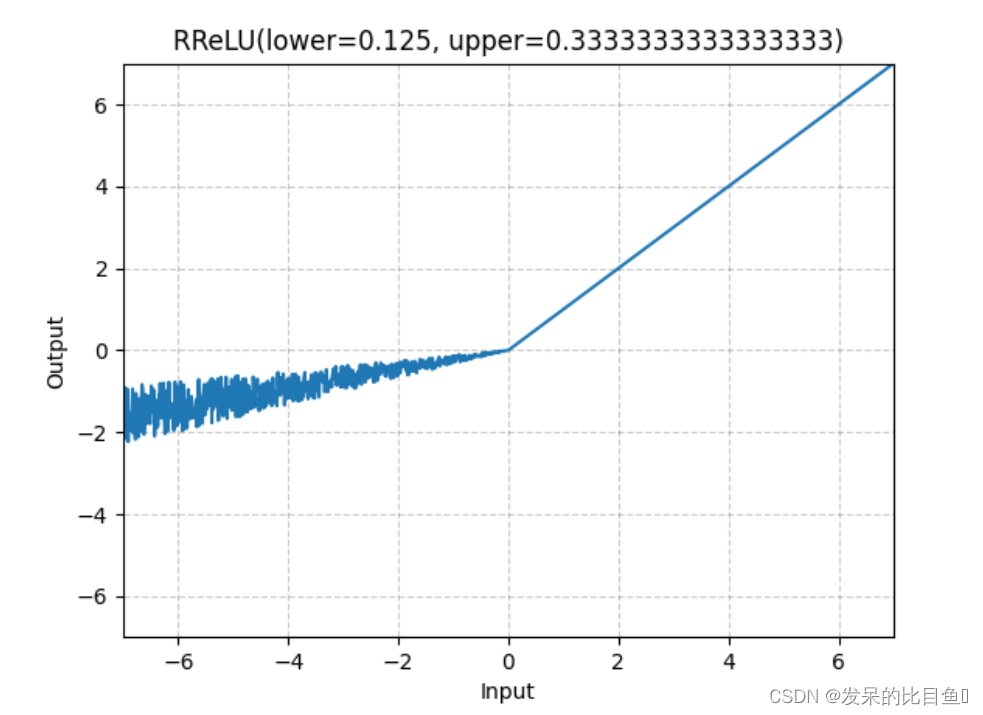
>>> m = nn.RReLU(0.1, 0.3)
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.SELU
按元素应用,如
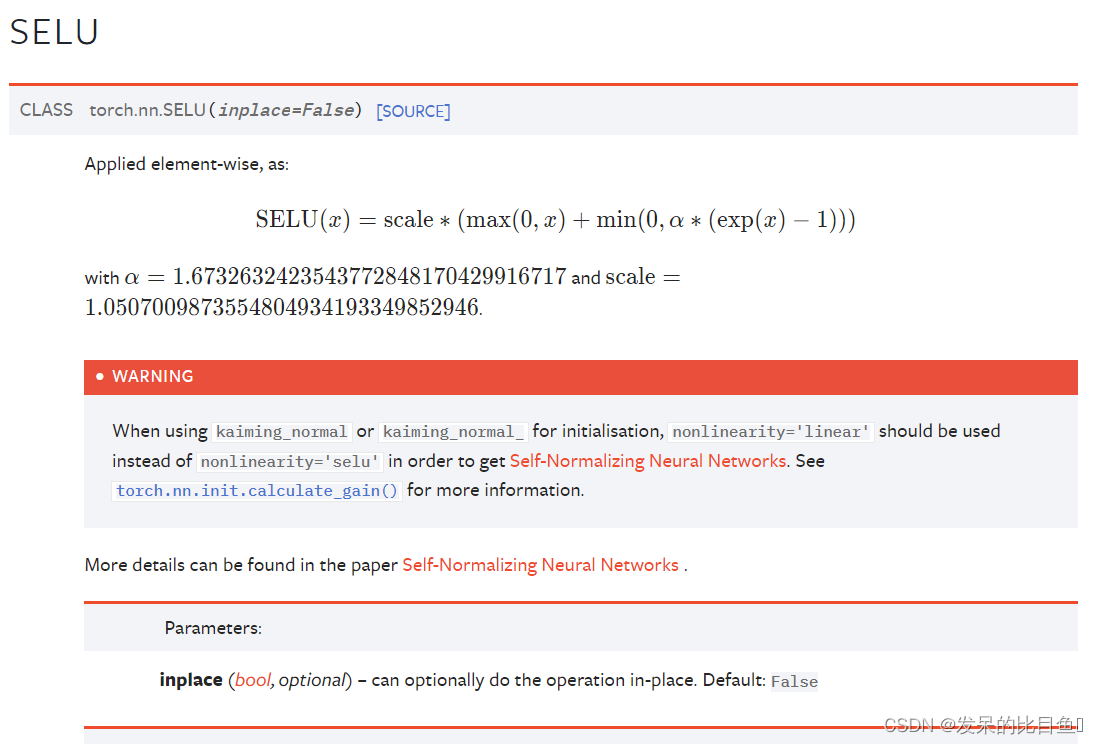
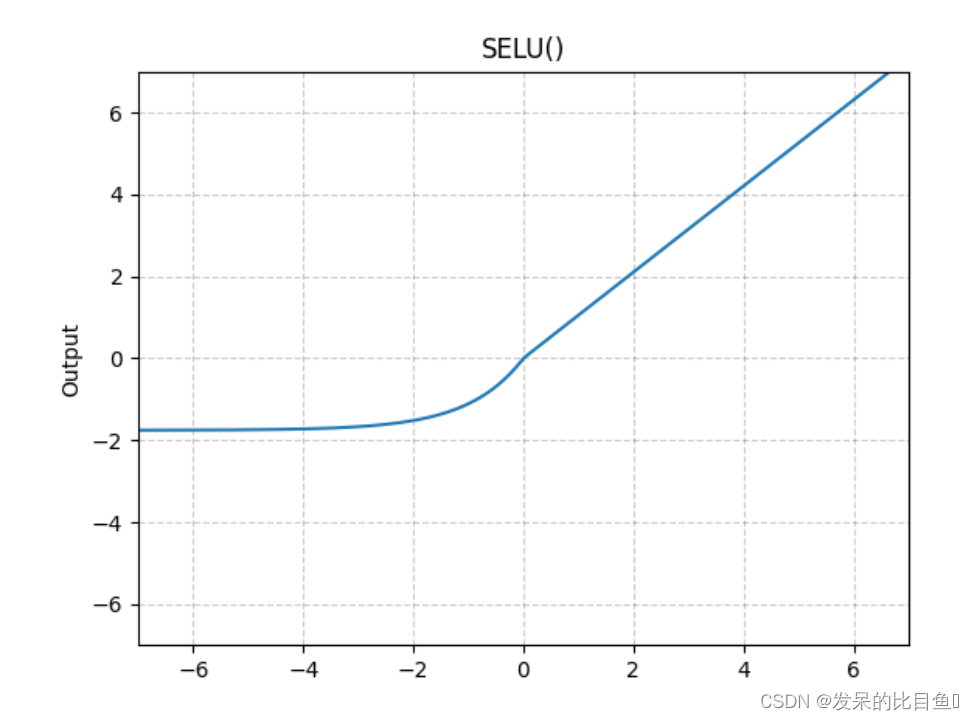
>>> m = nn.SELU()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.CELU
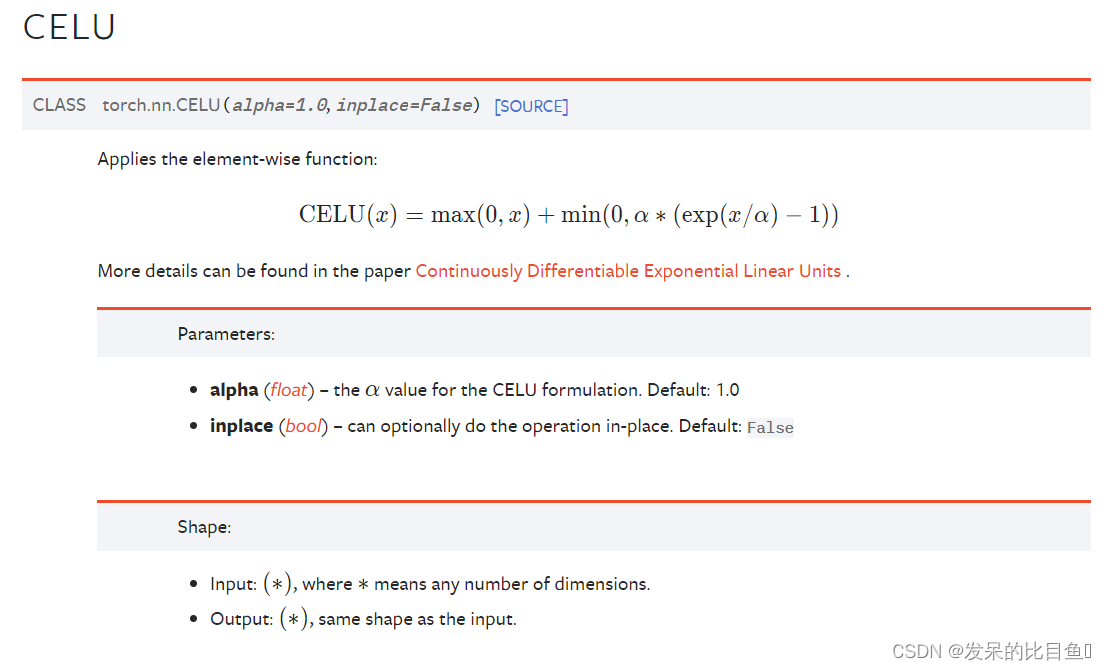
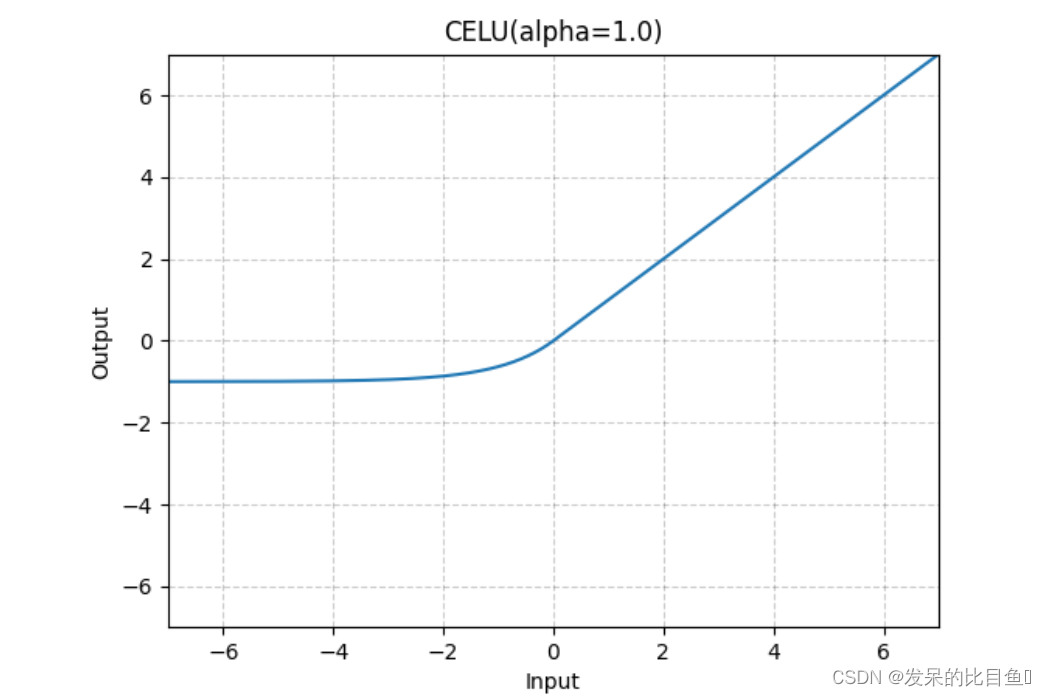
>>> m = nn.CELU()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.GELU
应用高斯误差线性单位函数
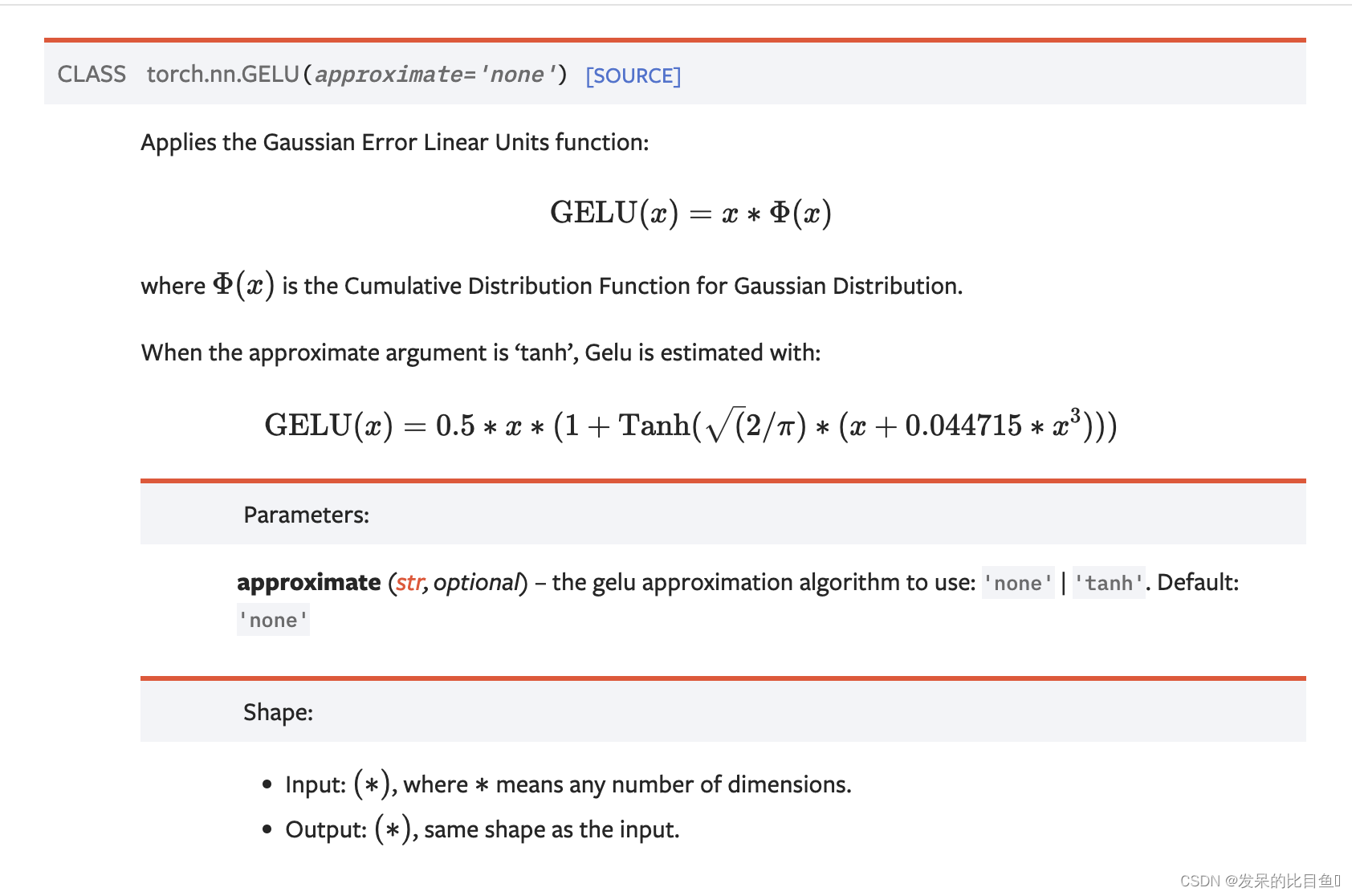
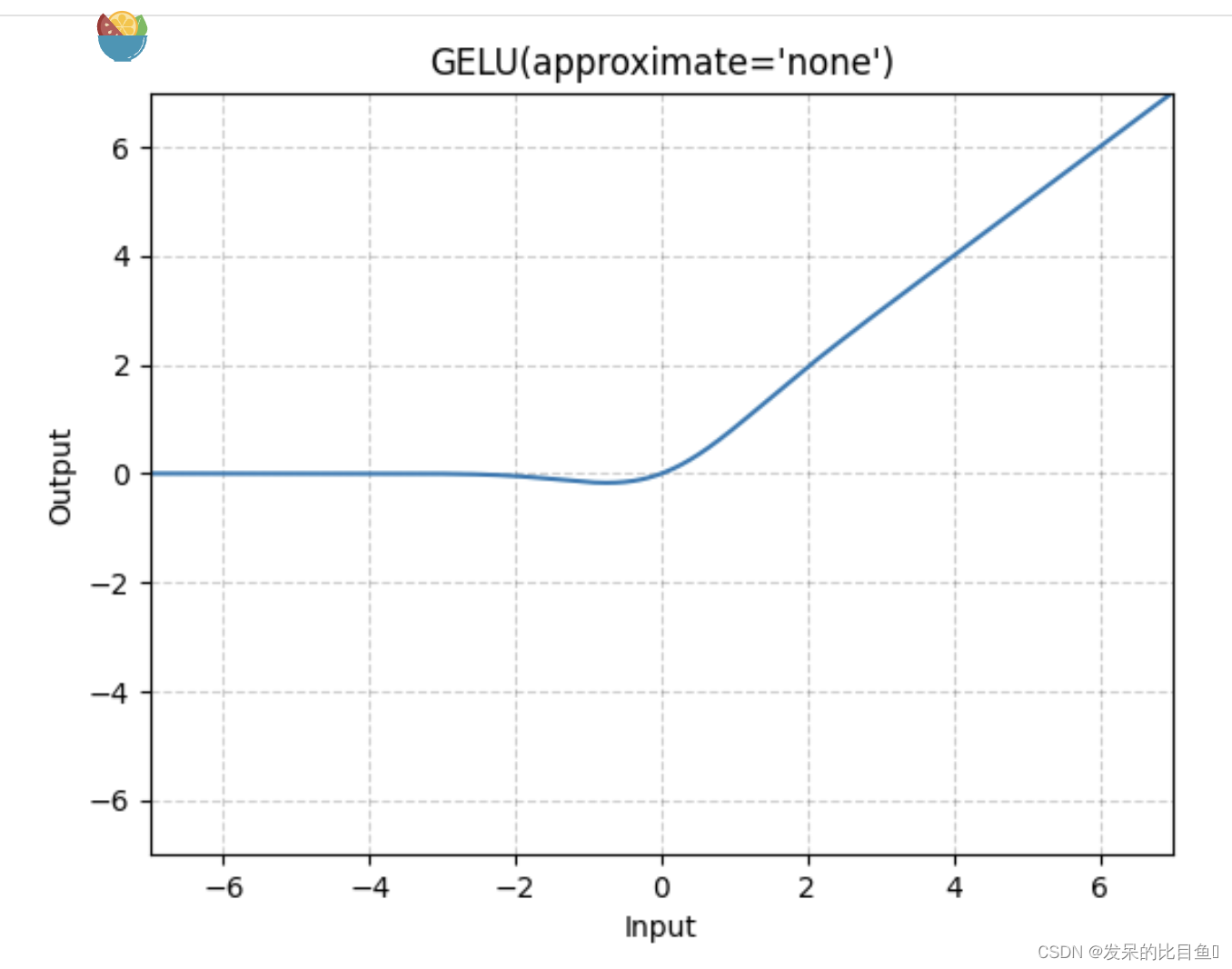
>>> m = nn.GELU()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.SiLU
按元素应用Sigmoid线性单元(SiLU)函数。SiLU函数也称为swish函数。
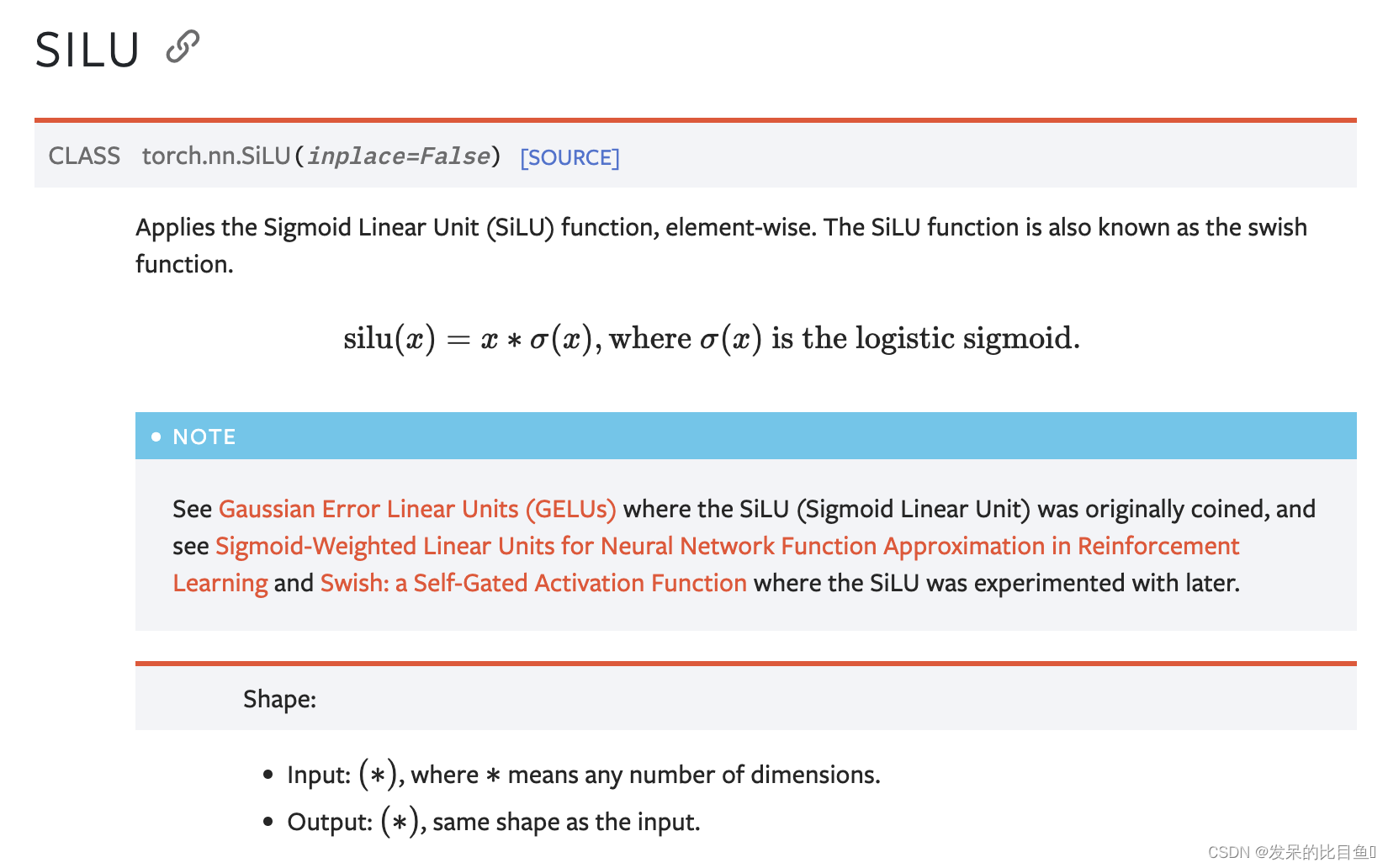
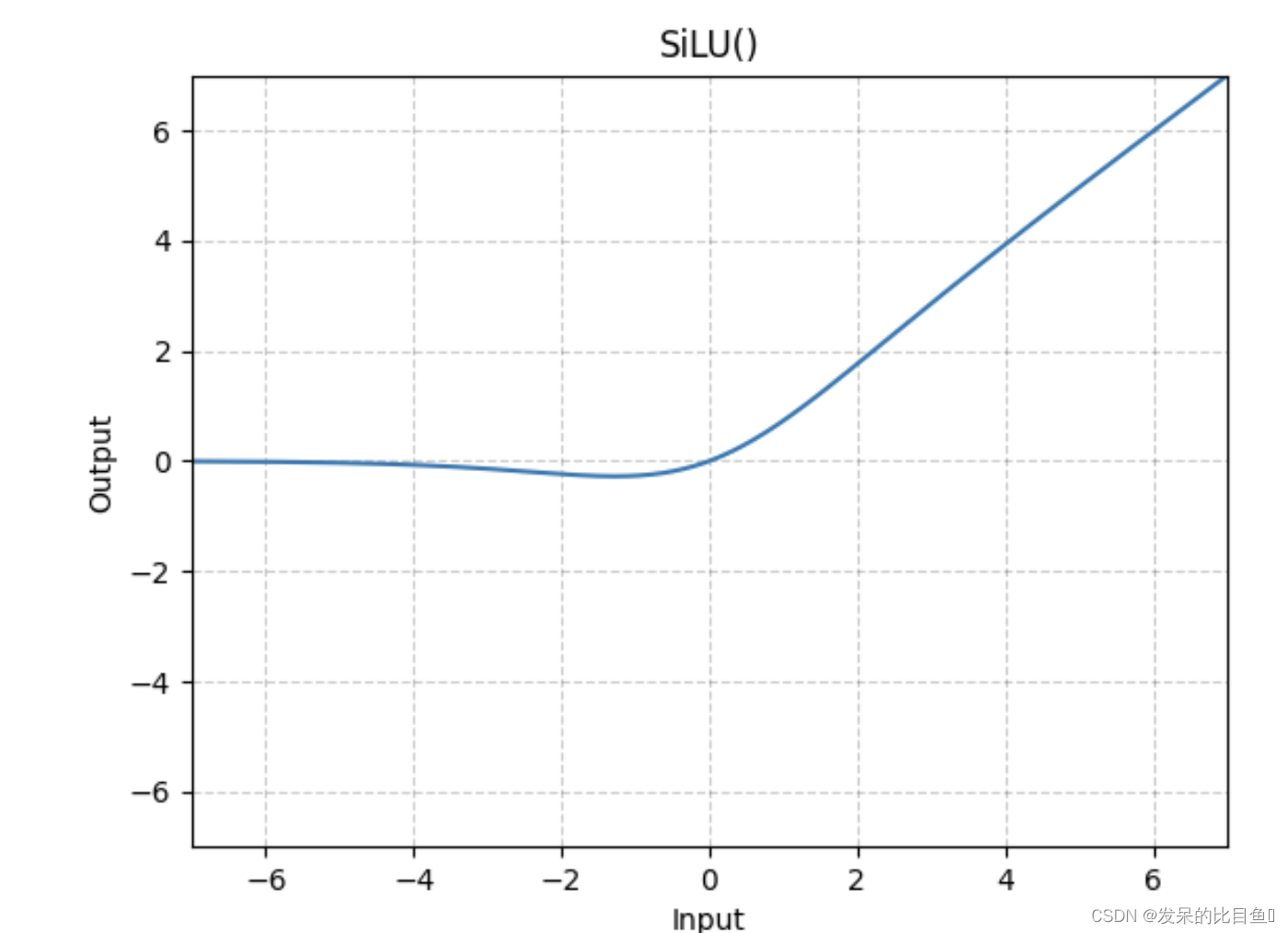
>>> m = nn.SiLU()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.Mish
在元素上应用Mish函数。一个自正则非单调神经激活函数。
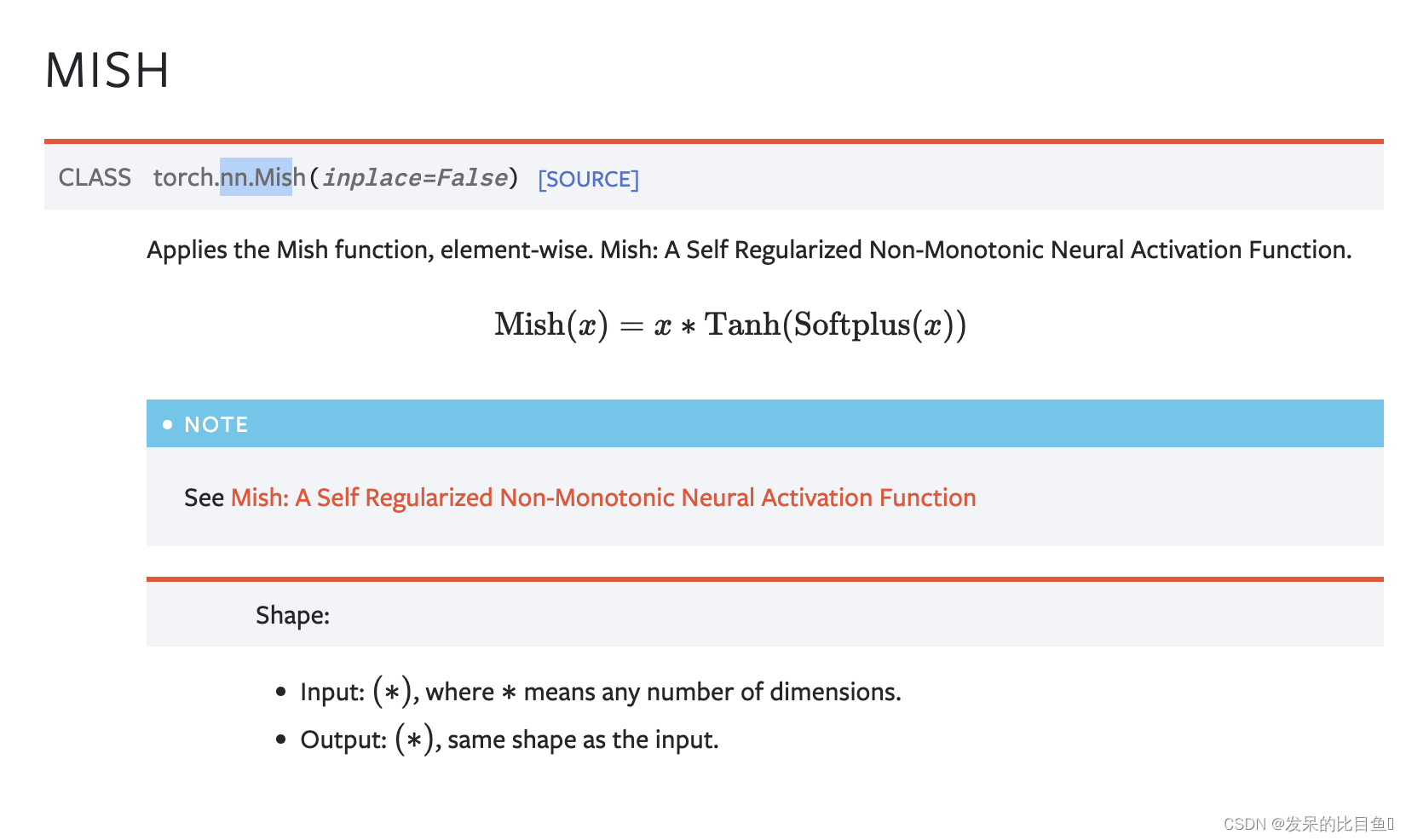
>>> m = nn.Mish()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.Softplus
应用Softplus功能

>>> m = nn.Softplus()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
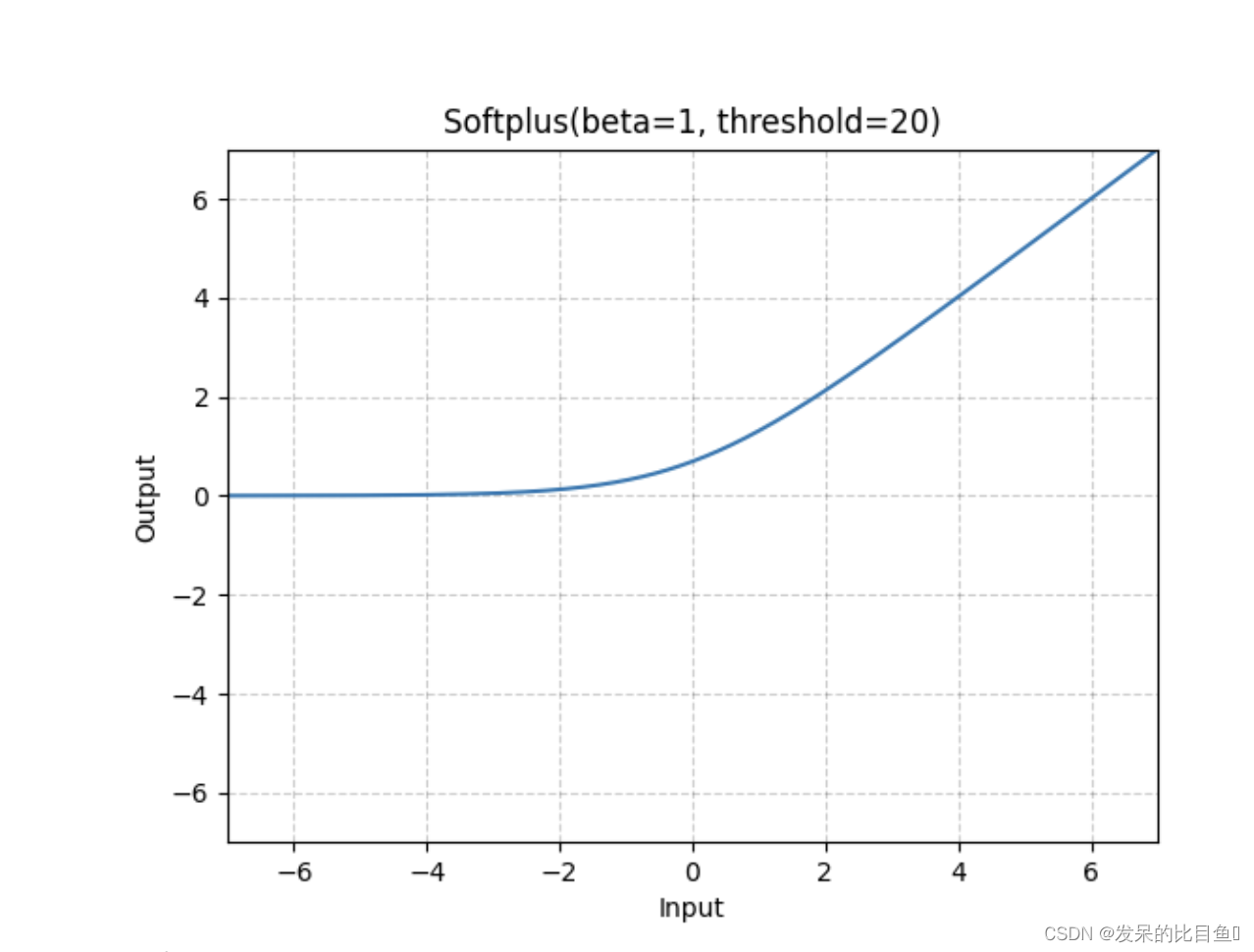
nn.Softshrink
按元素应用软收缩函数

>>> m = nn.Softshrink()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.Softsign
应用按元素的函数

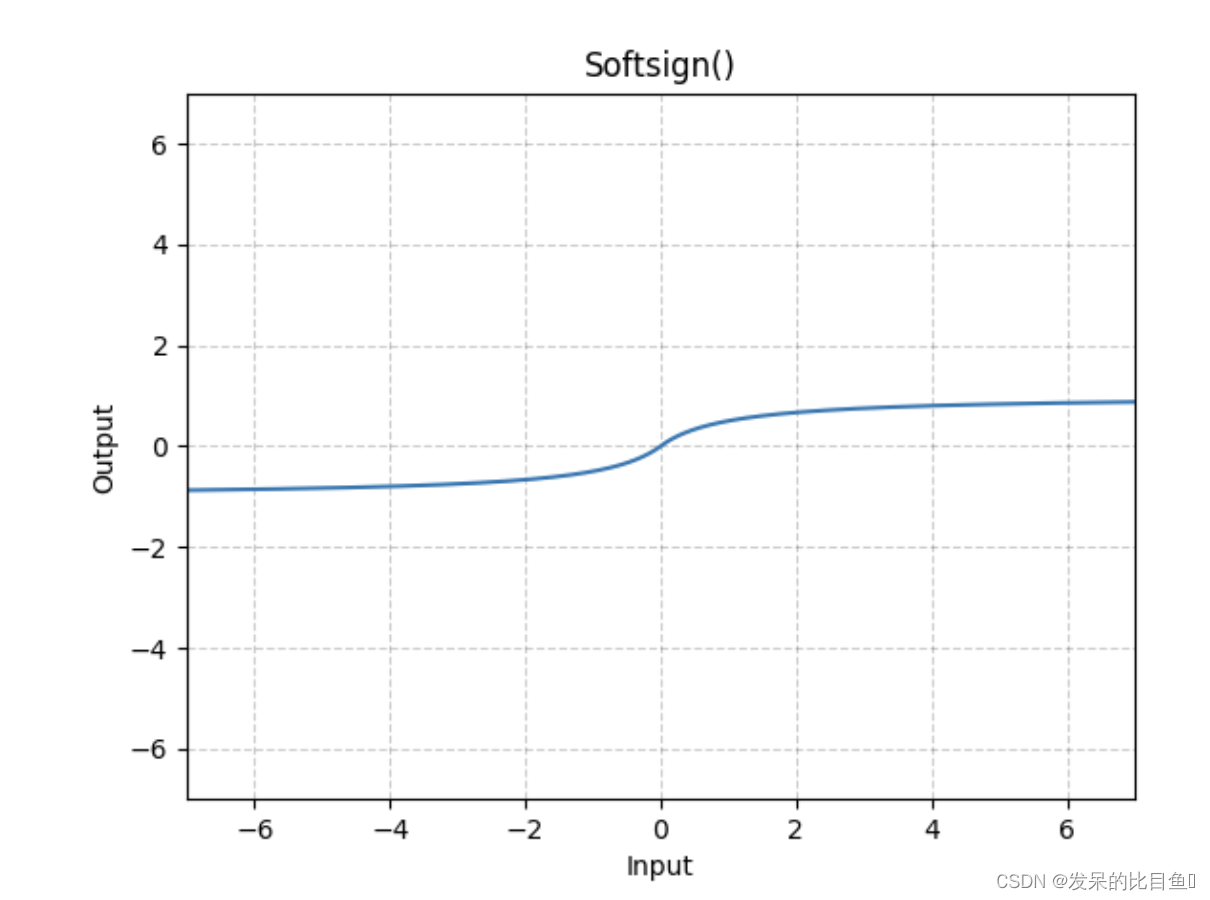
>>> m = nn.Softsign()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.Tanh
按元素应用双曲正切(Tanh)函数。

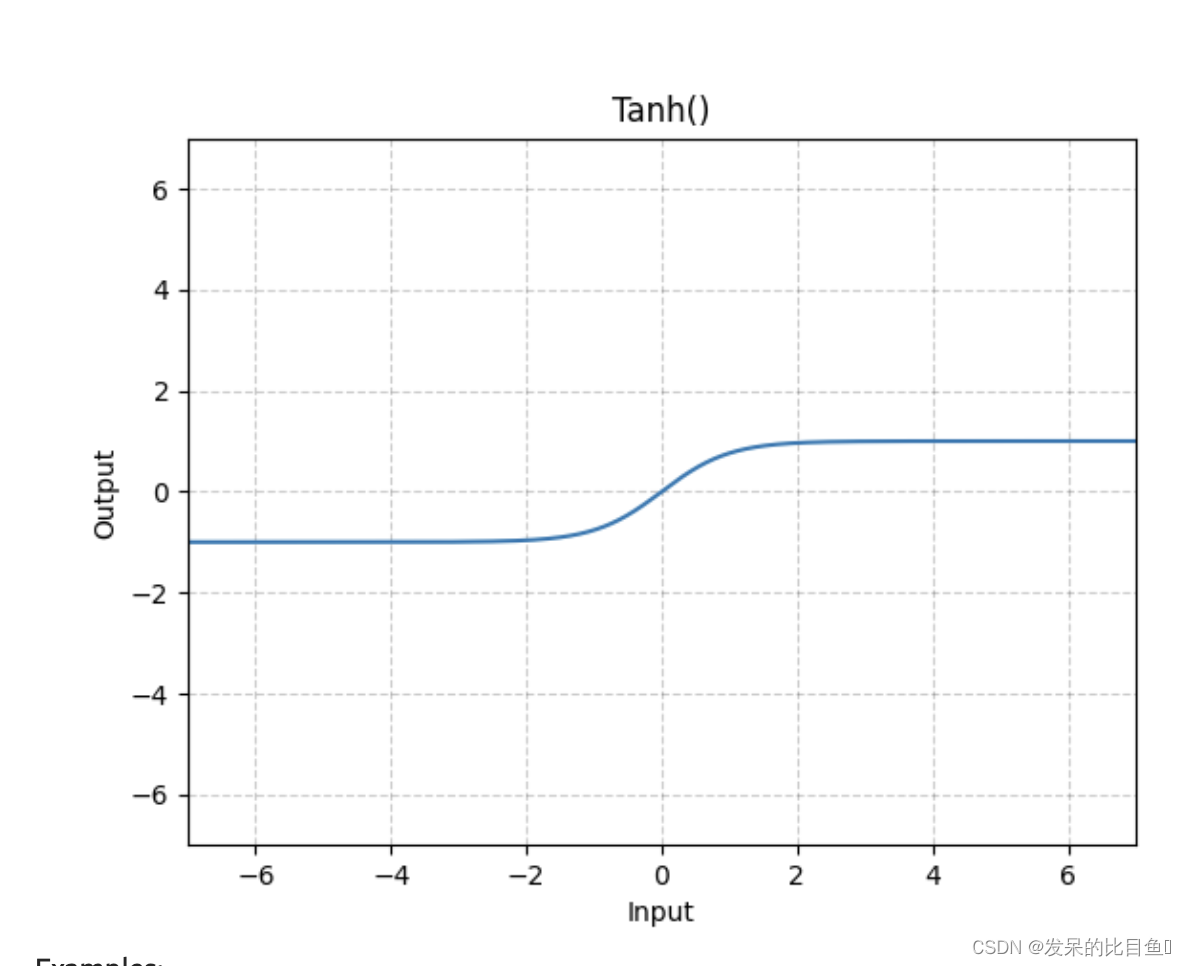
>>> m = nn.Tanh()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.Tanhshrink

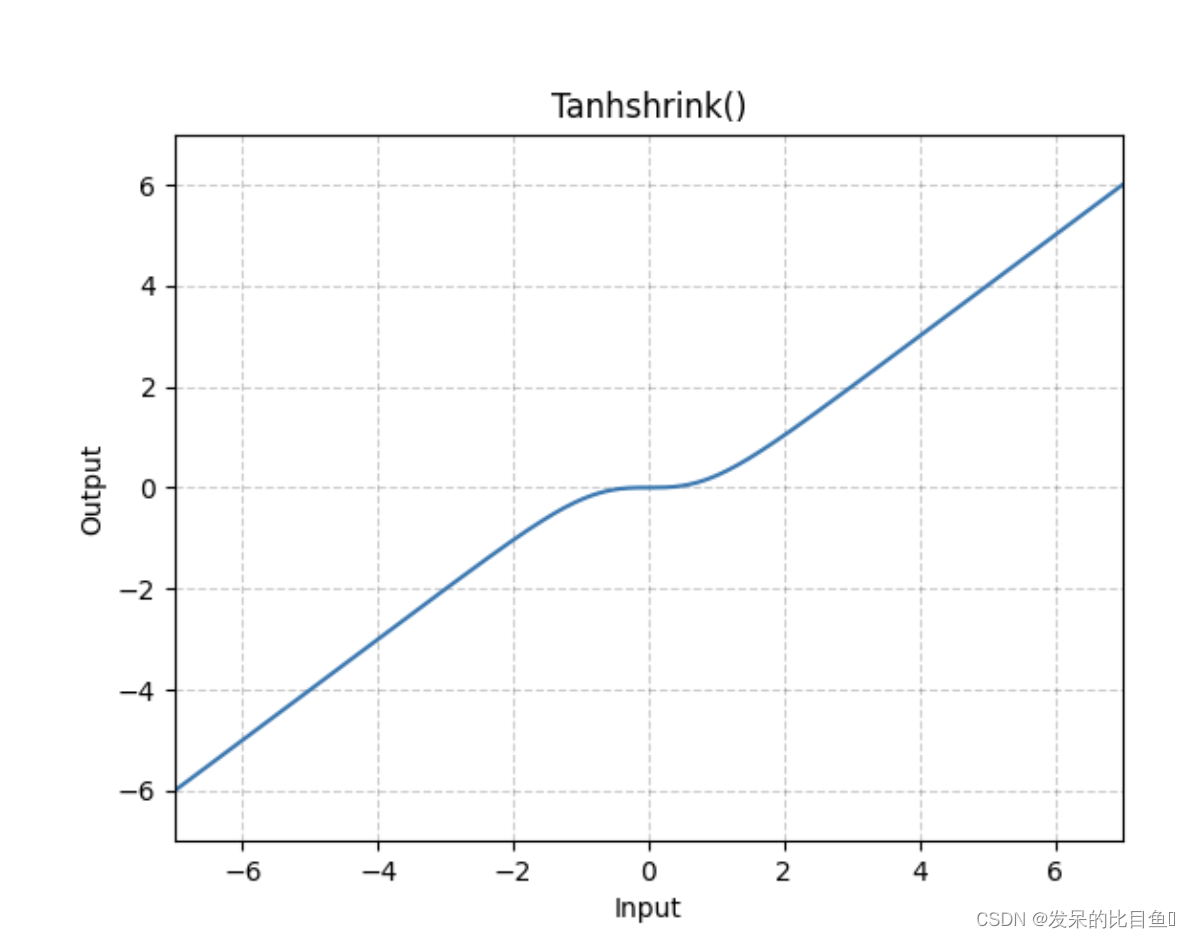
>>> m = nn.Tanhshrink()
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.Threshold
阈值输入张量的每个元素。
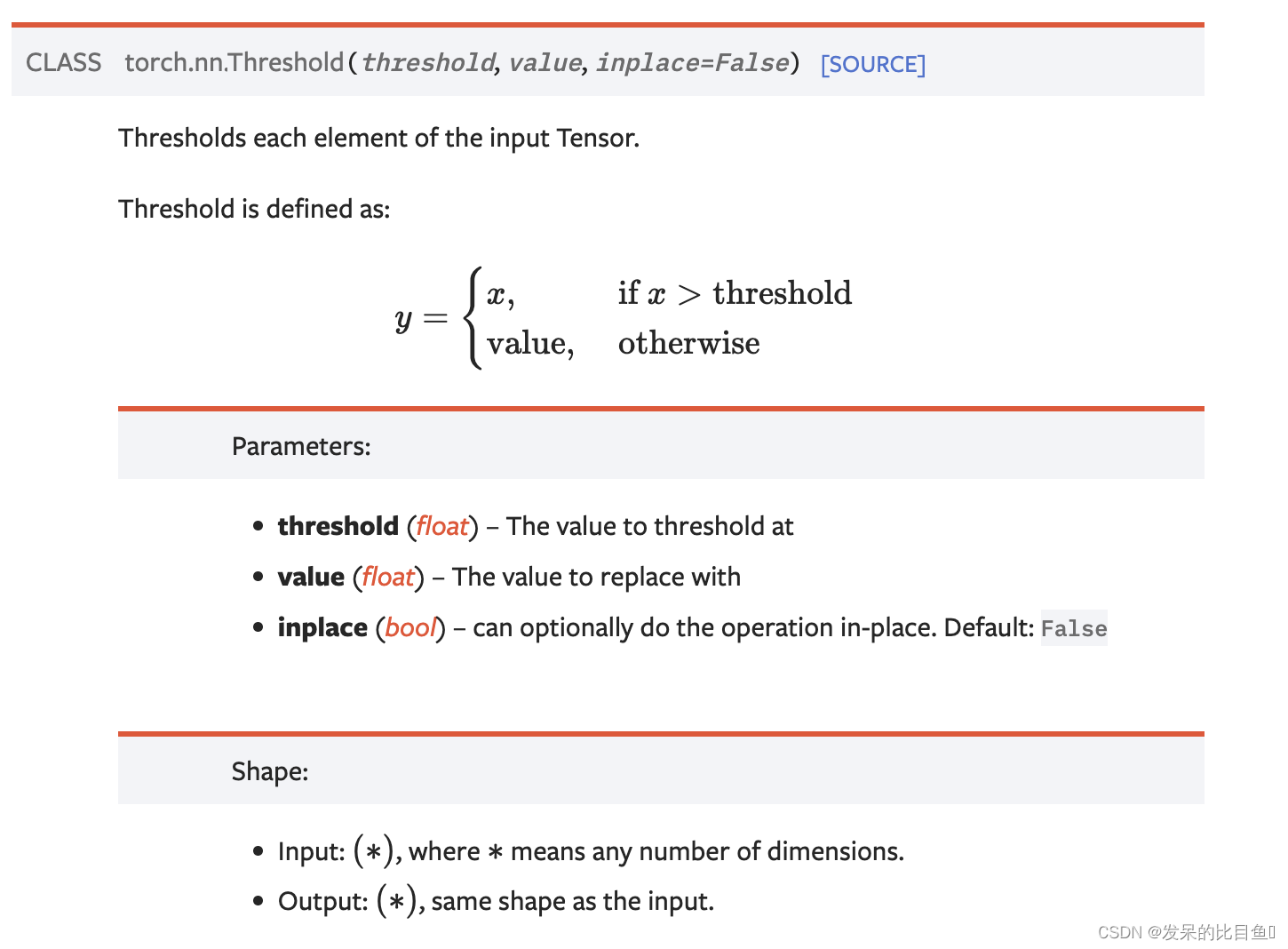
>>> m = nn.Threshold(0.1, 20)
>>> input = torch.randn(2)
>>> output = m(input)
nn.GLU
应用门控线性单元函数
G
L
U
(
a
,
b
)
=
a
⊗
σ
(
b
)
G L U(a, b)=a \otimes \sigma(b)
GLU(a,b)=a⊗σ(b)其中a是输入矩阵的前一半 b是后一半。

>>> m = nn.GLU()
>>> input = torch.randn(4, 2)
>>> output = m(input)























 2923
2923











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










