Arduino ESP32配置静态IP并通过网页控制GPIO引脚
配置静态IP前,需要对当前要进入的wifi网络的基本信息有了解才行,必须知道wifi的网关,网段,尽量配置比较远一点的IP,防止IP相同的冲突。
实例代码
/*ESP32 配置静态IP并通过网页控制GPIO引脚*/
#include <WiFi.h>
// WIFI信息
const char* ssid = "MERCURY_D268G";
const char* password = "pba5ayzk";
// Set web server port number to 80
WiFiServer server(80);
// 变量来存储HTTP请求
String header;
// 用于存储当前输出状态的辅助变量
String output26State = "off";
String output27State = "off";
// 配置输出引脚号
const int output26 = 26;
const int output27 = 27;
// 设置静态IP信息(配置信息前需要对将要接入的wifi网段有了解)
IPAddress local_IP(192, 168, 0, 188);
// 设置静态IP网关
IPAddress gateway(192, 168, 0, 1);
IPAddress subnet(255, 255, 0, 0);
IPAddress primaryDNS(8, 8, 8, 8); //optional
IPAddress secondaryDNS(8, 8, 4, 4); //optional
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize the output variables as outputs
pinMode(output26, OUTPUT);
pinMode(output27, OUTPUT);
// Set outputs to LOW
digitalWrite(output26, LOW);
digitalWrite(output27, LOW);
// Configures static IP address
if (!WiFi.config(local_IP, gateway, subnet, primaryDNS, secondaryDNS)) {
Serial.println("STA Failed to configure");
}
// Connect to Wi-Fi network with SSID and password
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
// Print local IP address and start web server
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected.");
Serial.println("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
server.begin();
}
void loop(){
WiFiClient client = server.available(); // Listen for incoming clients
if (client) { // If a new client connects,
Serial.println("New Client."); // print a message out in the serial port
String currentLine = ""; // make a String to hold incoming data from the client
while (client.connected()) { // loop while the client's connected
if (client.available()) { // if there's bytes to read from the client,
char c = client.read(); // read a byte, then
Serial.write(c); // print it out the serial monitor
header += c;
if (c == '\n') { // if the byte is a newline character
// if the current line is blank, you got two newline characters in a row.
// that's the end of the client HTTP request, so send a response:
if (currentLine.length() == 0) {
// HTTP headers always start with a response code (e.g. HTTP/1.1 200 OK)
// and a content-type so the client knows what's coming, then a blank line:
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
client.println("Content-type:text/html");
client.println("Connection: close");
client.println();
// turns the GPIOs on and off
if (header.indexOf("GET /26/on") >= 0) {
Serial.println("GPIO 26 on");
output26State = "on";
digitalWrite(output26, HIGH);
} else if (header.indexOf("GET /26/off") >= 0) {
Serial.println("GPIO 26 off");
output26State = "off";
digitalWrite(output26, LOW);
} else if (header.indexOf("GET /27/on") >= 0) {
Serial.println("GPIO 27 on");
output27State = "on";
digitalWrite(output27, HIGH);
} else if (header.indexOf("GET /27/off") >= 0) {
Serial.println("GPIO 27 off");
output27State = "off";
digitalWrite(output27, LOW);
}
// 访问显示页面
client.println("<!DOCTYPE html><html>");
client.println("<head><meta name=\"viewport\" content=\"width=device-width, initial-scale=1\">");
client.println("<meta charset=\"UTF-8\">");
client.println("<link rel=\"icon\" href=\"data:,\">");
// CSS to style the on/off buttons
// Feel free to change the background-color and font-size attributes to fit your preferences
client.println("<style>html { font-family: Helvetica; display: inline-block; margin: 0px auto; text-align: center;}");
client.println(".button { background-color: #4CAF50; border: none; color: white; padding: 16px 40px;");
client.println("text-decoration: none; font-size: 30px; margin: 2px; cursor: pointer;}");
client.println(".button2 {background-color: #555555;}</style></head>");
// Web Page Heading
client.println("<body><h1>ESP32 Web Server</h1>");
// Display current state, and ON/OFF buttons for GPIO 26
client.println("<p>GPIO 26 - 状态 " + output26State + "</p>");
// If the output26State is off, it displays the ON button
if (output26State=="off") {
client.println("<p><a href=\"/26/on\"><button class=\"button\">开</button></a></p>");
} else {
client.println("<p><a href=\"/26/off\"><button class=\"button button2\">关</button></a></p>");
}
// Display current state, and ON/OFF buttons for GPIO 27
client.println("<p>GPIO 27 - 状态 " + output27State + "</p>");
// If the output27State is off, it displays the ON button
if (output27State=="off") {
client.println("<p><a href=\"/27/on\"><button class=\"button\">开</button></a></p>");
} else {
client.println("<p><a href=\"/27/off\"><button class=\"button button2\">关</button></a></p>");
}
client.println("</body></html>");
// The HTTP response ends with another blank line
client.println();
// Break out of the while loop
break;
} else { // if you got a newline, then clear currentLine
currentLine = "";
}
} else if (c != '\r') { // if you got anything else but a carriage return character,
currentLine += c; // add it to the end of the currentLine
}
}
}
// Clear the header variable
header = "";
// Close the connection
client.stop();
Serial.println("Client disconnected.");
Serial.println("");
}
}
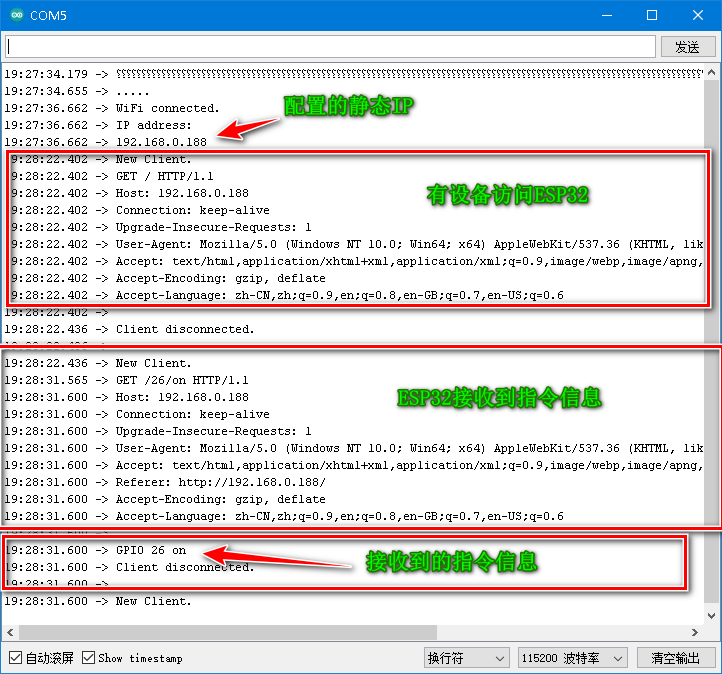
- 串口打印信息
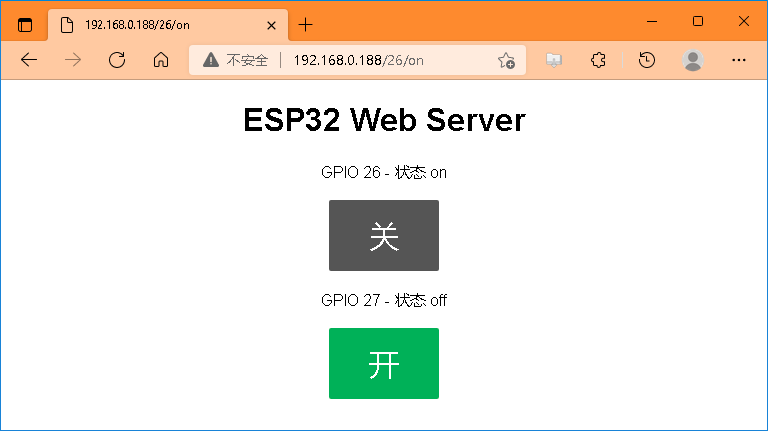
- 控制页面






















 3824
3824











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








