这篇文章发布于2023年10月nature。通讯作者是来自于 DOE Joint Genome Institute, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA, USA.
背景介绍&目标
作者首先背景介绍了两种主流宏基因组分析方法,包括reads-based reference mapping(eg. MG-RAST)和assembled-based de novo(Integrated Microbial Genomes & Microbiomes (IMG/M) and MGnify)两种.
又提到目前无论哪种方法下游分析中对基因组的功能注释都依赖于现有的库,这种分析方法会去除掉一些未知的基因。所以一个全面的基因组比对以解释未知功能的分析是非常需要的。那这个未知功能作者援引为functional dark matters。
原文:‘
Same major limitation with respect to gene functional annotation, which relies on predicting function by homology searching against reference protein databases, such as COG, Pfam and KEGG Orthology. As a result, any genes predicted in assembled metagenomic data that do not map to reference protein families are typically ignored and dropped from subsequent comparative analysis.
To estimate the breadth of unexplored functional diversity, referred to as the functional dark matter an all-versus-all metagenomic comparison is required.’
这些reference database都是做功能注释非常常用的库。
-
COG-Database: The Clusters of Orthologous Genes (COGs) database
-
Pfam: a complete and accurate classification of protein families and domains.
-
KEGG Orthology: molecular functions represented in terms of functional orthologs.
为了揭示这个位置的dark matters(功能),总结来说这篇文章主要做了以下工作
-
They present a scalable computational approach 他们提出了一种可扩展的计算方法,用于识别和表征宏基因组中发现的功能性暗物质。
-
They identified the novel protein space (after removing all reference matched genes) and clustered them into families首先,在删除与超过 100,000 个参考基因组或 Pfam 的 IMG 数据库匹配的所有基因后,我们确定了 IMG/M 的 26,931 个宏基因组数据集中存在的新蛋白质空间。接下来,我们将剩余的序列聚集到蛋白质家族中。
-
They explored their taxonomic and biome distributions 他们探索了这些未知cluster的分类学和生物群落分布
-
They predicted their three-dimensional (3D) structures他们预测了它们的三维结构
数据来源和数据处理Data source and preprocess of the data
Environmental dataset 来源于:数据来源:来自IMG/M平台托管的所有公共参考基因组和组装的宏基因组和元转录组的所有蛋白质序列(超过35个氨基酸残基)
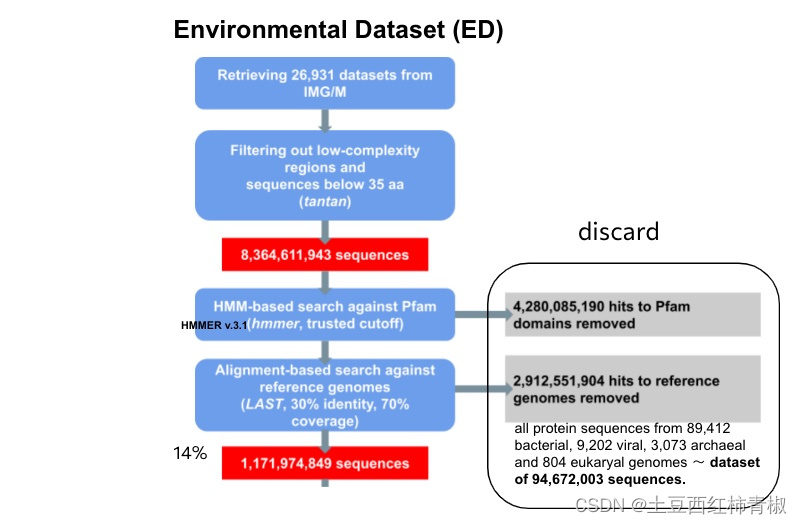
这个来自于supplementary的图片说明整个流程更加的清晰。可以看到首先去除一些低复杂度的序列,拿到>35bp的序列,作者用hmm比对pfam数据库去除map上的hits,后面又使用LAST比对工具再次过滤reference genomes。最后仅仅得到最初序列的14%,即1,171,974,849序列,这些序列被称为novel protein sequences。
tips:
文章中去除低复杂度序列应该是处于低复杂度区域通常包含一些高度重复的序列,这些重复序列可能对分析和解释基因组和转录组数据造成干扰,因此去除它们有助于减少噪音和提高数据的可信度。
文章中提到提取reference genomes方法:
Reference Genomes: In total, we extracted all protein sequences from 89,412 bacterial, 9,202 viral, 3,073 archaeal and 804 eukaryal genomes, resulting in a final dataset of 94,672,003 sequences. The reference genomes included in this study consisted solely of isolate genomes, not MAGs or single-amplified genomes.

那么接下来拿到这些novel protein sequences 之后作者又用LAST对蛋白质序列之间做相似性比较(an all-versus-all similarity matrix was built for each of the two gene catalogues by calculating all significant pairwise sequence similarities.),生成一个相似性矩阵,然后根据相似性矩阵用HipMCL进行聚类得到最后的蛋白质clusters。作者同样对reference genomes也进行了类似的操作,以便后续比较。整个过程结合图1a和supp figure更加清楚
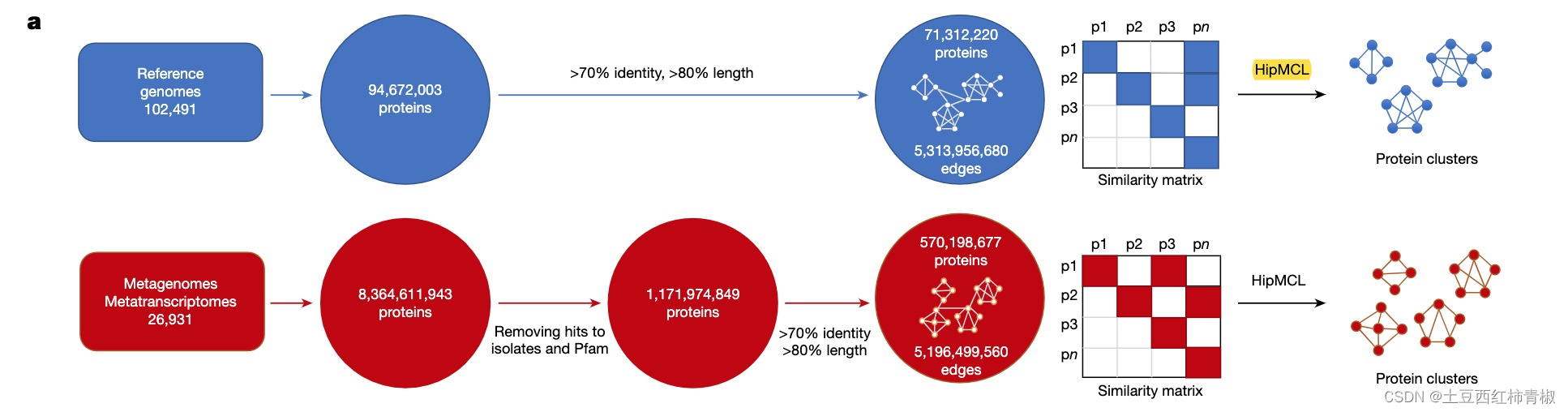

原文细节描述(具体node和edges数目)如下
We next clustered the 1.1 billion ED proteins using a graph-based approach. For comparative purposes, we followed the same approach for the 94 million proteins from reference genomes.
First, an all-versus-all similarity matrix was built for each of the two gene catalogues (that is, proteins from reference genomes and those from the ED) by calculating all significant pairwise sequence similarities.
The all-versus-all pairwise alignments were calculated using LAST (70% sequence identity, 80% alignment coverage). The reference genome graph consisted of 71,312,220 nodes (proteins) and 5,313,956,680 edges (pairwise similarities). The graph for the ED proteins consisted of 570,198,677 nodes and 5,196,499,560 edges.
下面作者进一步移走了一些只有少数蛋白序列的cluster以及和pfam有weak hits的cluster,只留下包含有至少100个memeber的cluster,我认为这部是为了保证这个novel。这个部分就是novel protein families,也就是全文通篇在提的NMPFs(novel metagenome protein families)

结果1: ED has more clusters than reference genomes
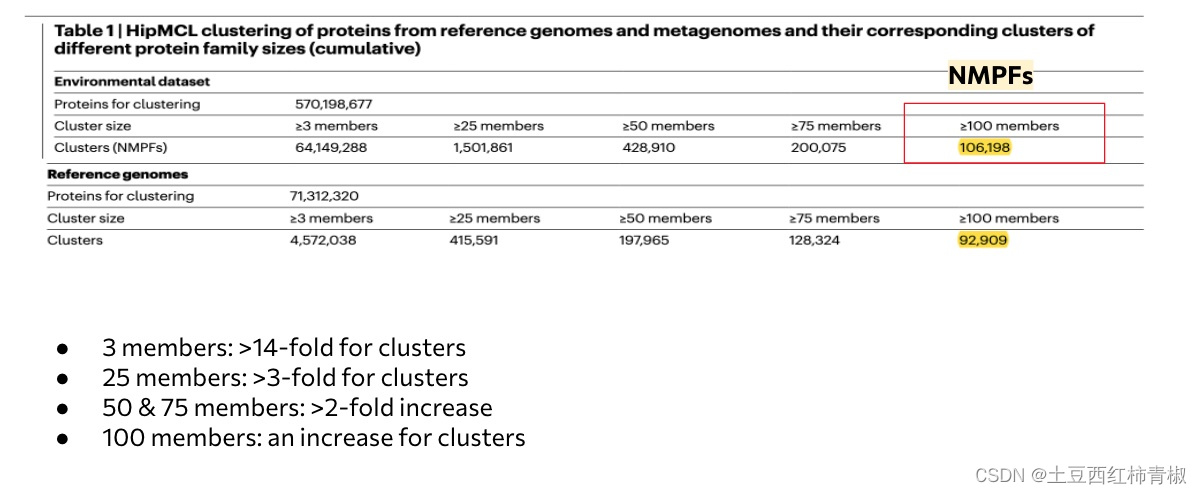
文章这里的图是说明与reference genome的cluster相比,NMPFs包含的蛋白序列更加的多,不仅仅是有3个members的cluster多,从3-100都多。
In total, we identified 106,198 families with at least 100 members that will be referred to as novel metagenome protein families (NMPFs) (Table 1 (right column)).
For comparison, we identified 92,909 protein clusters in the corresponding set of protein clusters with at least 100 members from reference genomes.
We observed an increase in the ED protein clusters by greater than 14-fold for clusters with at least 3 members, greater than 3-fold for clusters with at least 25 members, around a 2-fold increase for clusters with at least 50 and 75 members as well as an increase for clusters with at least 100 members.
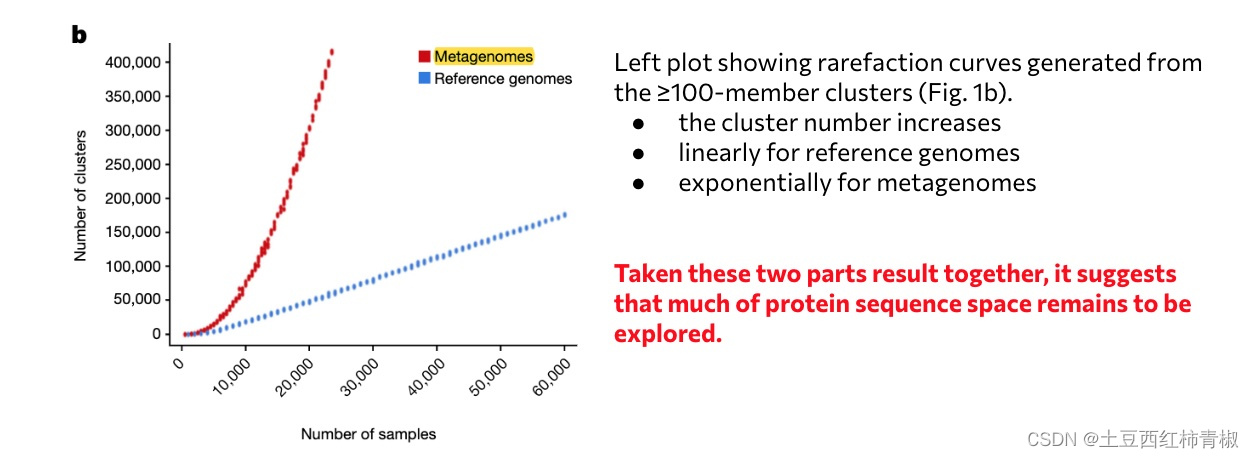
下面作者又做了一个稀释曲线,可以发现ED组相比较reference genomes的斜率更大,说明随着sample数目的增加,还可能有更多的cluster被发现。这进一步说明这些unknown protein sequence是未知的,非常值得探索的,是比reference genomes更多未知的更丰富的功能序列。
结果2:biome distribution生态系统来源
作者收集的这些dataset都有对应的biome distribution,可以在他文章的supp table看到,这些ecosystem的来源(main GOLD ecosystems)被作为biome distribution的定义。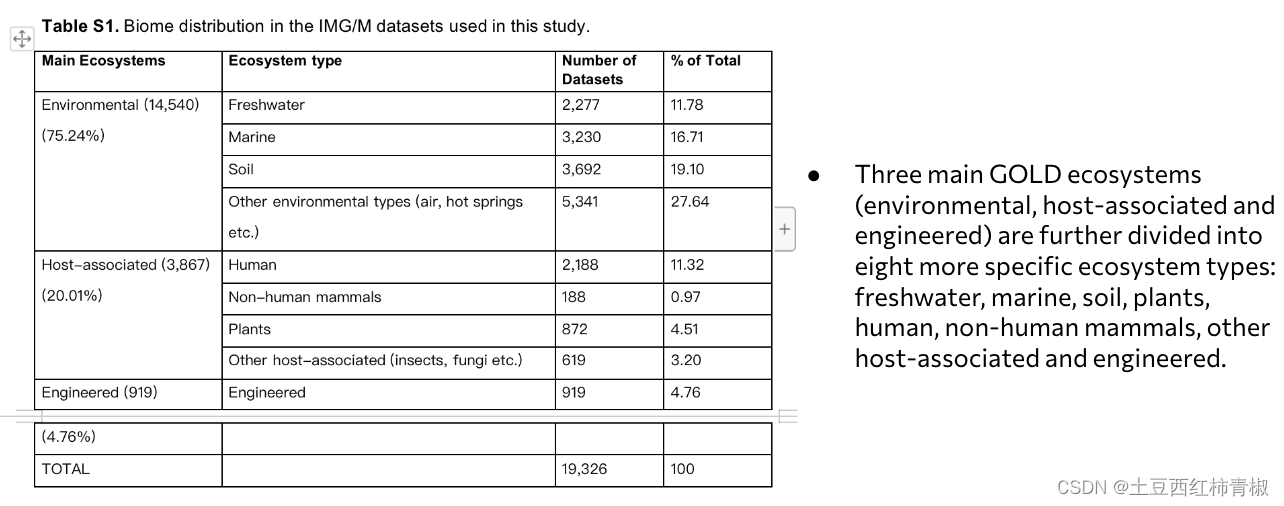
作者对这些蛋白cluster的来源进行了visualization展示,这里用到的包我们可以借鉴。(Distribution analysis of the protein clusters across ecosystems and NCBI taxa was performed by creating and visualizing networks with Gephi using the Yifan Hu algorithm to generate the layout. )
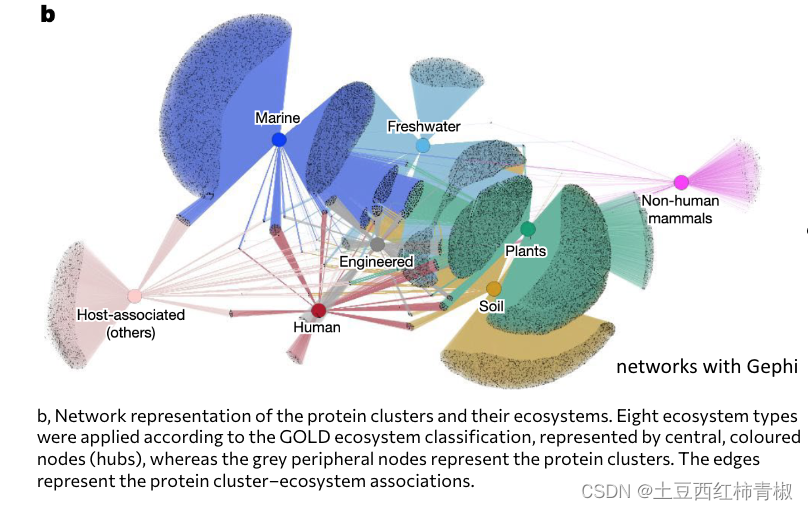
我所理解的就是我们可以直观看到蛋白cluster的生态系统来源。
通过进一步详细的zoom in,我们可以看到NMPFs的主要生态系统来源。
有一些环境共享了一些nmpfs,有一些环境也存在一些比较独特的nmpfs.
这里面我们能看到最主要的overlap存在于土壤和植物的环境,或者土壤和淡水环境,然后是植物和淡水环境,土壤淡水植物环境。
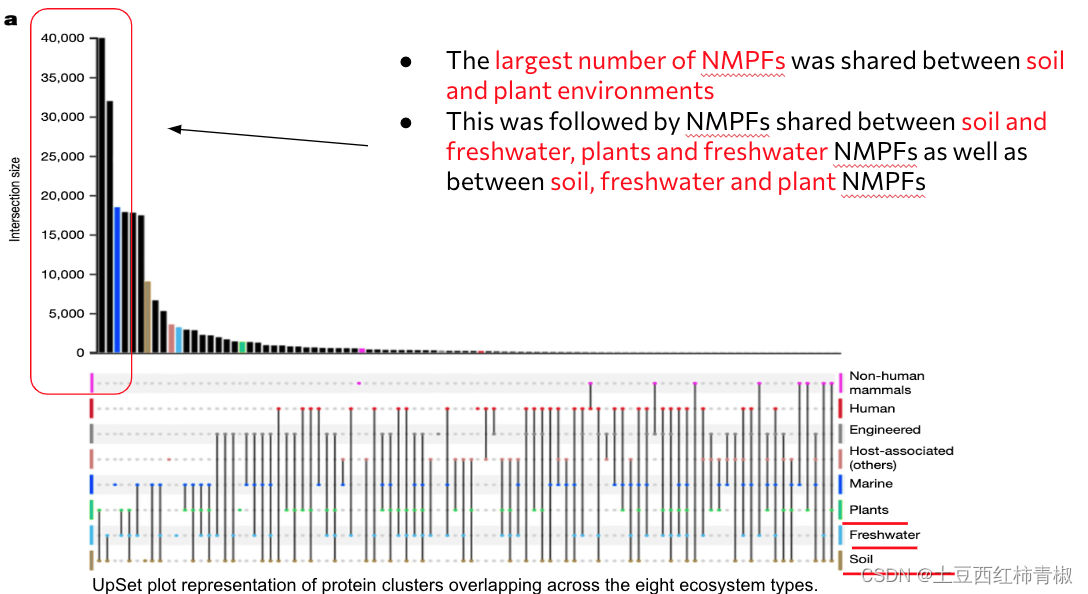
相对比较少在环境之间共享的nmpfs。比如文章中提到的人类,非人类哺乳动物和其他host-associated的,文章中还提到大量的overlap存在于人类和工业环境(这里虽然提到了大量,但是其共享的nmpfs数目还是比之前的human和host-associated要少。)

文章的supp figure里面还对具体的overlap的数目进行了展示,比如这里淡水和宿主相关环境的共享的nmpfs。这里说明相同的微生物功能团体是可以存在于不同的环境中的。
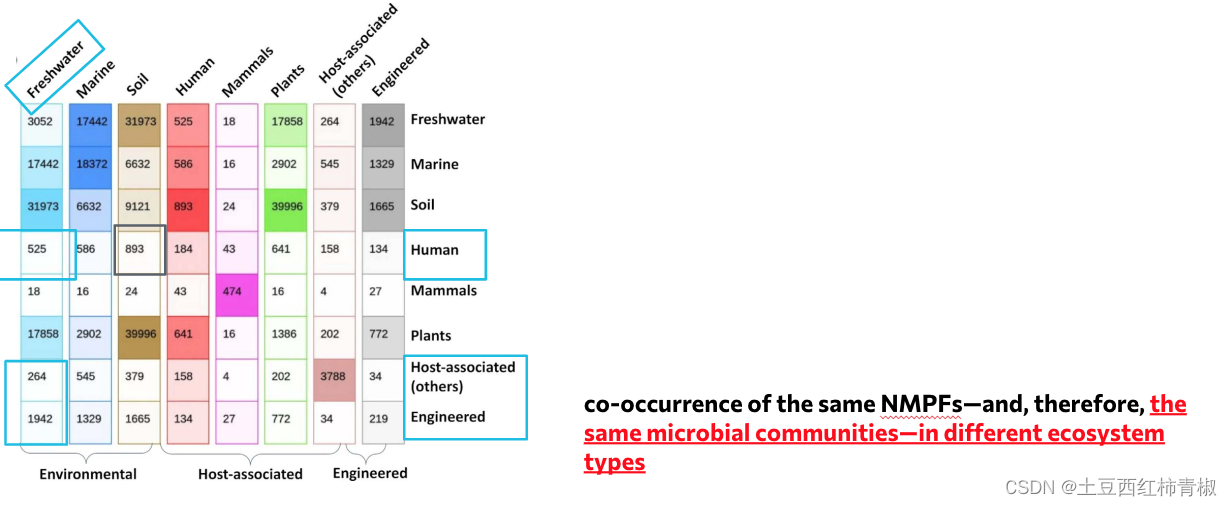
文章同样也具体展示了特异的nmpfs,其中比较深色部分是环境特异的nmpfs
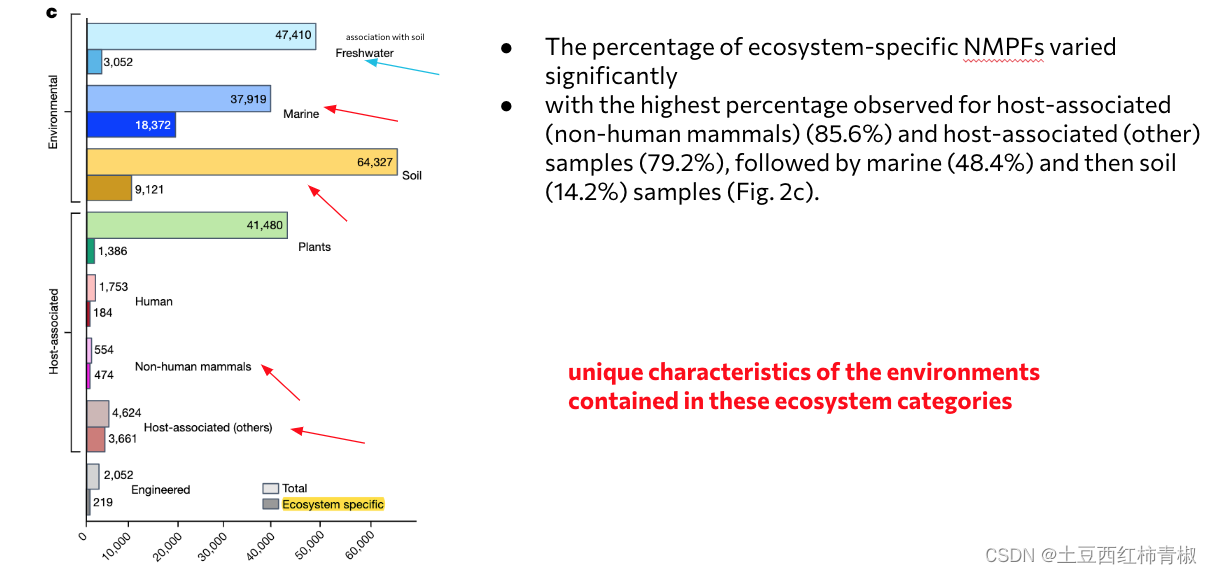
至此这些nmpfs的生态系统来源研究结束。
结果3:taxonomic distribution 分类学分布
在注释方法上,作者用了非常多的方法来尽可能得到分类学信息。
注释方法: NMPF 的分类学注释是根据 IMG 中相应支架的可用分类信息对簇的每个成员进行的。 在没有此类注释的情况下,他们使用了其他方法的组合来通过计算推断支架的分类。 eg. DeepVirFinder (v.1.0), Whokaryote, EukRep, Tara Oceans collection of eukaryotic MAGs, MMseqs2 taxonomy tool, LCA of best hits from UniRef50.
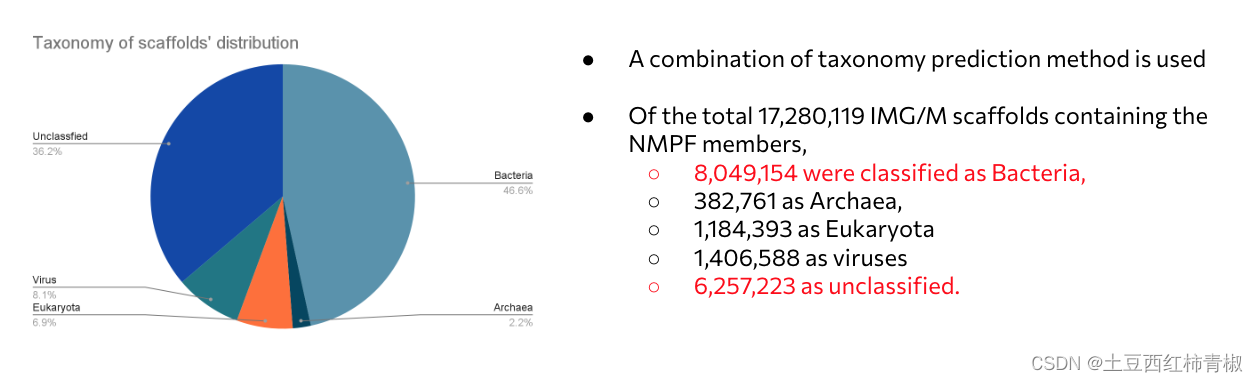
首先可以确定的是这些nmpfs可以来自于多个的生物学分类。比如细菌和unclassified,或者细菌和病毒。尽管作者尝试了很多方法注释,仍然有一些未知的序列。
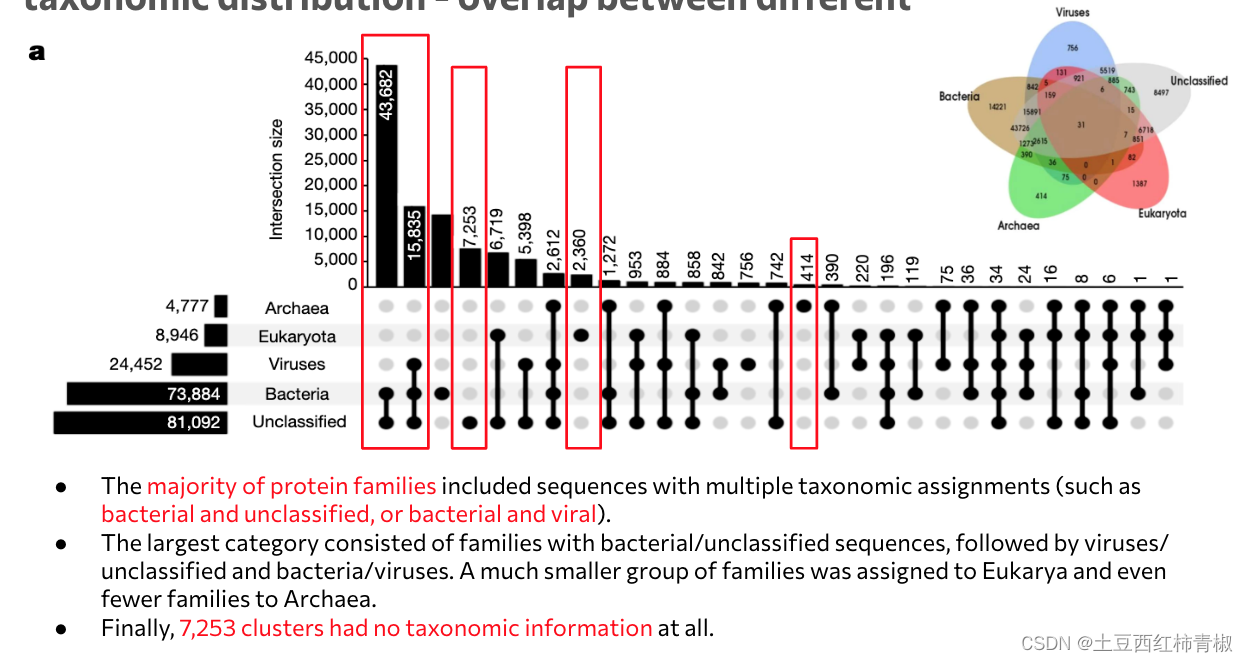
随后作者将这些nmpfs和之前非常大的地球微生物组分析相结合比较。具体来讲‘Subsequently, we evaluated whether any of the NMPF proteins (and their corresponding families) were found in any of the recently identified MAGs from the Genomes from Earth’s Microbiomes (GEM) catalogue20. Specifically, we examined whether any of the scaffolds containing genes of the NMPFs were binned in any of the 52,515 MAGs of the GEM catalogue.’
结论是只能发现非常少的与地球微生物组重合的发现few overlap with Earth’s microbiome
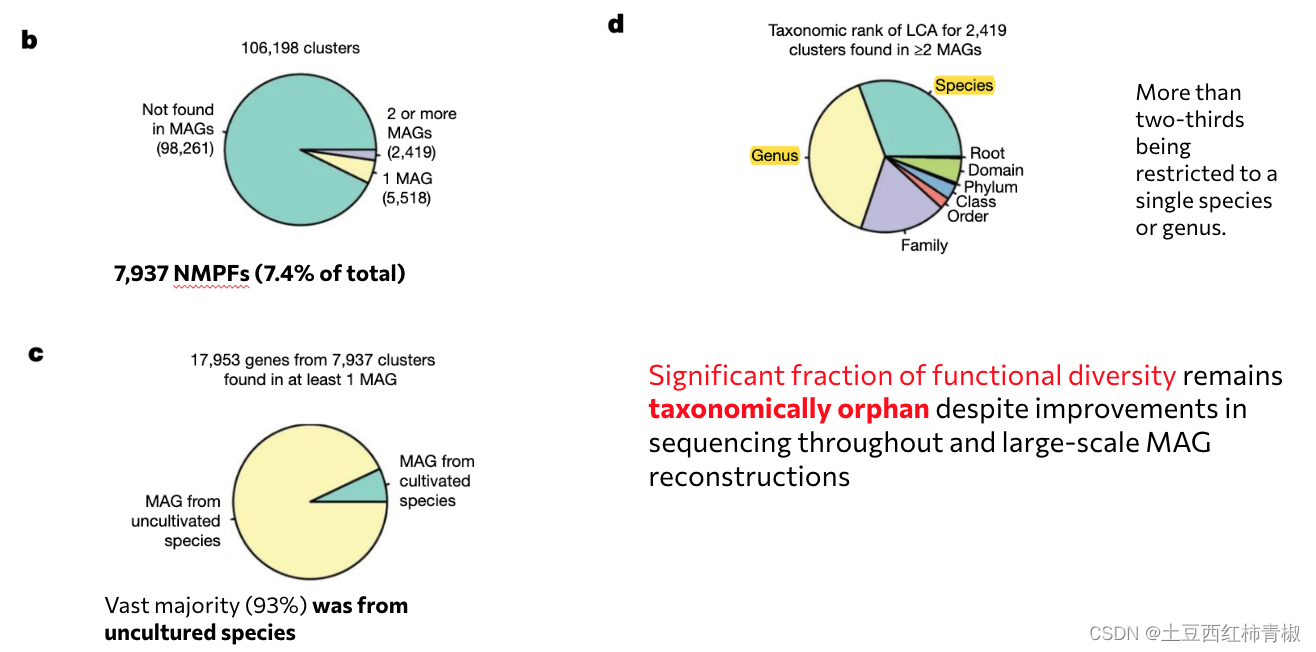
可以发现仅仅7.4%的可以在gem里面发现,并且大部分是来自于未培养过的物种,对于那些存在于两个或多个 MAG 中的nmpfs,其分类分布非常狭窄,其中三分之二以上仅限于单一物种或属,只有极少数分布在多个科、纲或门中。 图3d)。所以大部分nmpfs的分类学注释仍然是未知的。
结果4:这些 NMPF 的地理分布是什么?
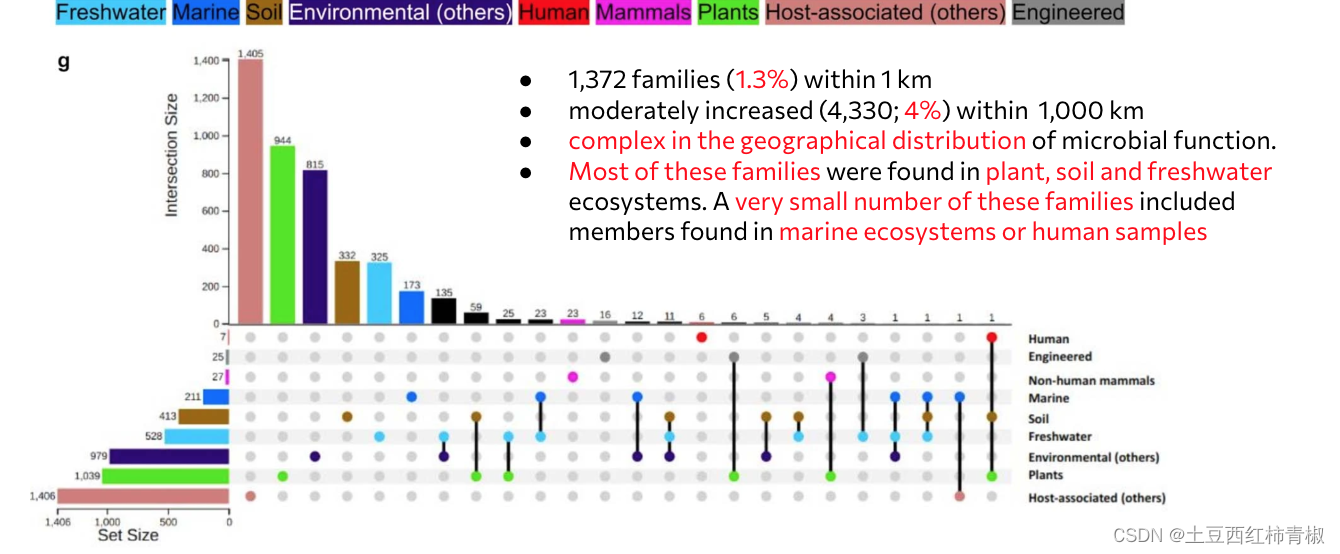
作者有这些nmpfs的地理坐标,这里可以发现只有1.3%的nmpfs他们的地理位置来源集中在1km之内。4%的集中在1000km之内。这说明这些聚类的nmpfs有着非常广泛复杂的地理位置分布。
下面这里是一个1000km的地理分布来源示意图,大部分来自于植物,土壤和淡水生态系统。
(g) UpSet plot showing the distribution of the geographically-isolated NMPF clusters, based on a cut-off distance of 1000 Km (as shown in panel f).
结果5:功能预测(co-occurrence of neighbouring genes & 3D structure)
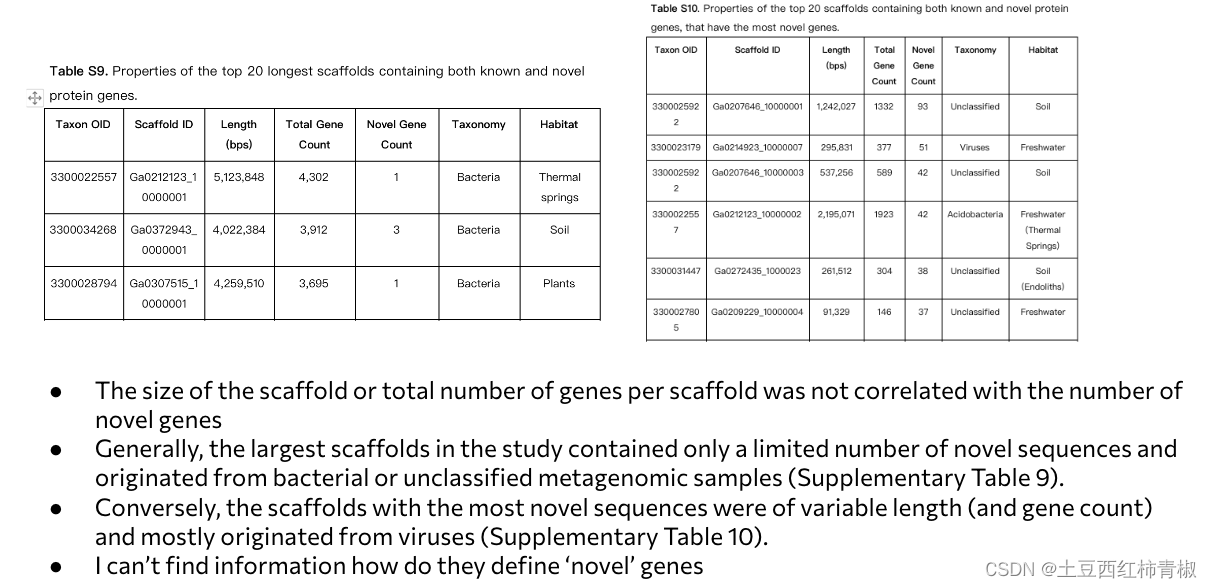
我们知道nmpfs里面由很多scaffold聚类而来的,那么这些scaffold都包含有已知和未知的基因。这个scaffold长度并不与未知基因数目成正比。这些特别长的序列只还有比较有限的新序列,并且大部分来自于细菌或者unclassified的宏基因组样本。(这里怎么定义新基因的,我没有找到。)
下面是对这些nmpfs的未知基因功能进行了一个预测
先是用比较传统的方法 co-occurrence of neighbouring genes
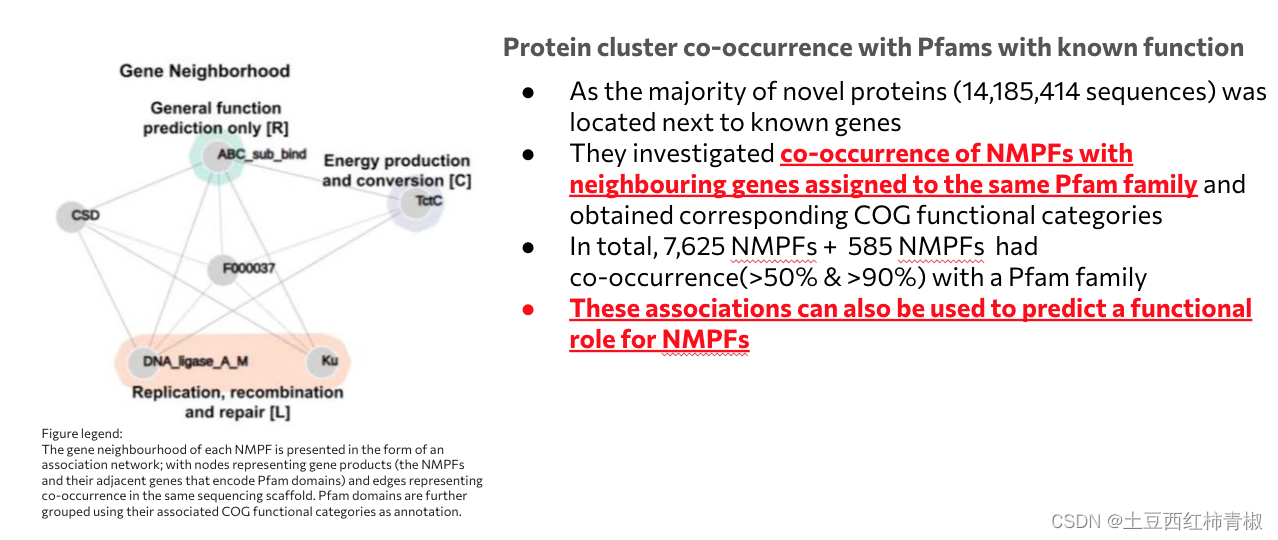
简单来说就是通过与之距离相近的已知基因的pfam的功能来预测nmpfs功能
具体方法如下:
通过在包含新的和已知的蛋白质编码基因的分析支架中搜索 Pfam 蛋白质结构域的存在来确定 NMPF 与已知蛋白质结构域的共现。
使用 HMMER 和 HMM 配置文件的默认可信截止值,针对 Pfam 的 HMM 配置文件搜索每个支架的已知基因的翻译序列。 所有阳性命中都分配给各自的支架,然后分配给包含来自这些支架的新序列的 NMPF,作为潜在的共存结构域。 计算每个 NMPF 的每个 Pfam 结构域的共现频率百分比,定义为包含该结构域的支架数量占与 NMPF 相关的支架总数的比例。 Pfam 结构域随后被映射到 COG7 结构域及其功能类别。 7,885 个 NMPF 中未观察到与 Pfam 的关联; 对于其余集群,补充数据 1 中报告了基于频率的前 5 个 Pfam 和 COG 命中。
原文
The co-occurrence of NMPFs with known protein domains was determined by performing searches for the existence of Pfam protein domains in the analysed scaffolds containing both novel and known protein-coding genes.
The translated sequences of the known genes for each scaffold were searched against the HMM profiles of Pfam using HMMER and the HMM profiles’ default trusted cut-off. All positive hits were assigned to their respective scaffolds and, in turn, to NMPFs containing novel sequences from these scaffolds, as potential co-occurring domains. The co-occurrence frequency percentage of each Pfam domain for each NMPF was calculated, defined as the number of scaffolds containing this domain over the total number of scaffolds associated with the NMPF. The Pfam domains were subsequently mapped to COG7 domains and their functional categories. No associations to Pfam were observed for 7,885 NMPFs; for the rest of the clusters, the top five Pfam and COG hits based on their frequency are reported in Supplementary Data 1.
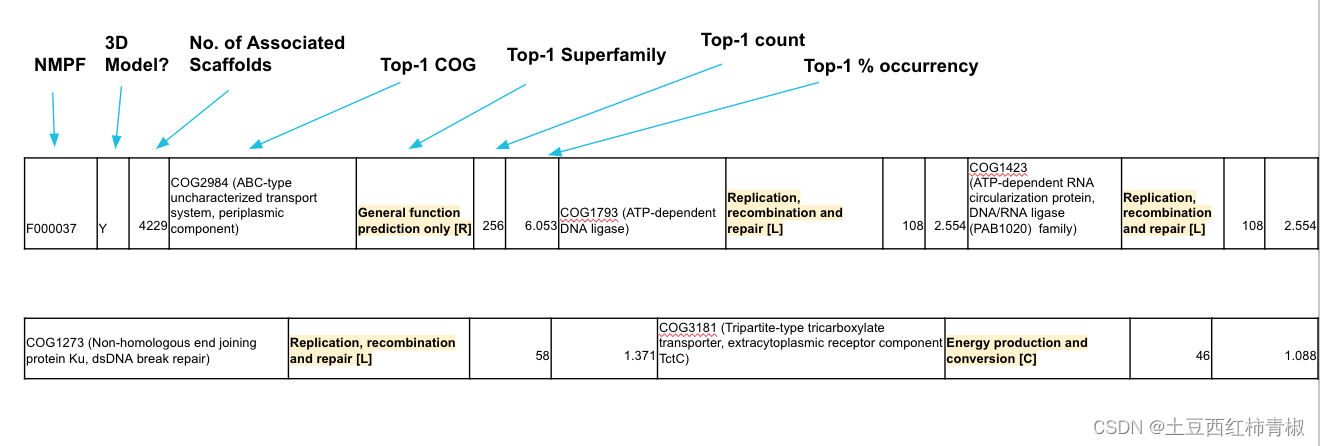
下面是这个示意图的表格。比如这里的nmpfs f0000037,与它相关的scaffold有256个和general function prediction only 比对,有108个scaffold和replication,recombination and repair 比对。所以就会呈现出图示的几个可能的功能。当然这里具体如何操作的,还是需要自己去仔细研究,这里只是大概理解所表达的意思。
 我认为接下来是文章的华点之一,使用结构信息预测功能
我认为接下来是文章的华点之一,使用结构信息预测功能
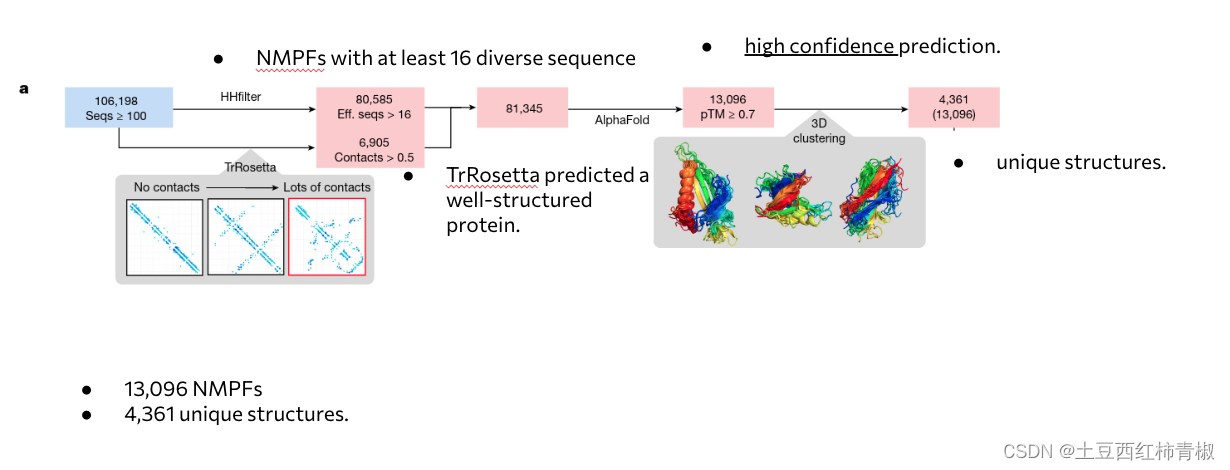
首先作者筛选了至少含有16个序列的nmpfs,然后运行 hhfilter,或者 TrRosetta 筛选出那些可能会产生结构良好的蛋白质的nmpfs。
再用这些符合标准的nmpfs,运行 AlphaFold2预测结构。预测了 80,585 个 3D 模型,其中 13,096 个 NMPF 具有高置信度(预测 TM (pTM) 得分 > 0.700)预测。 在结构聚类的基础上,这些高置信度预测代表了 4,361 个独特的结构。
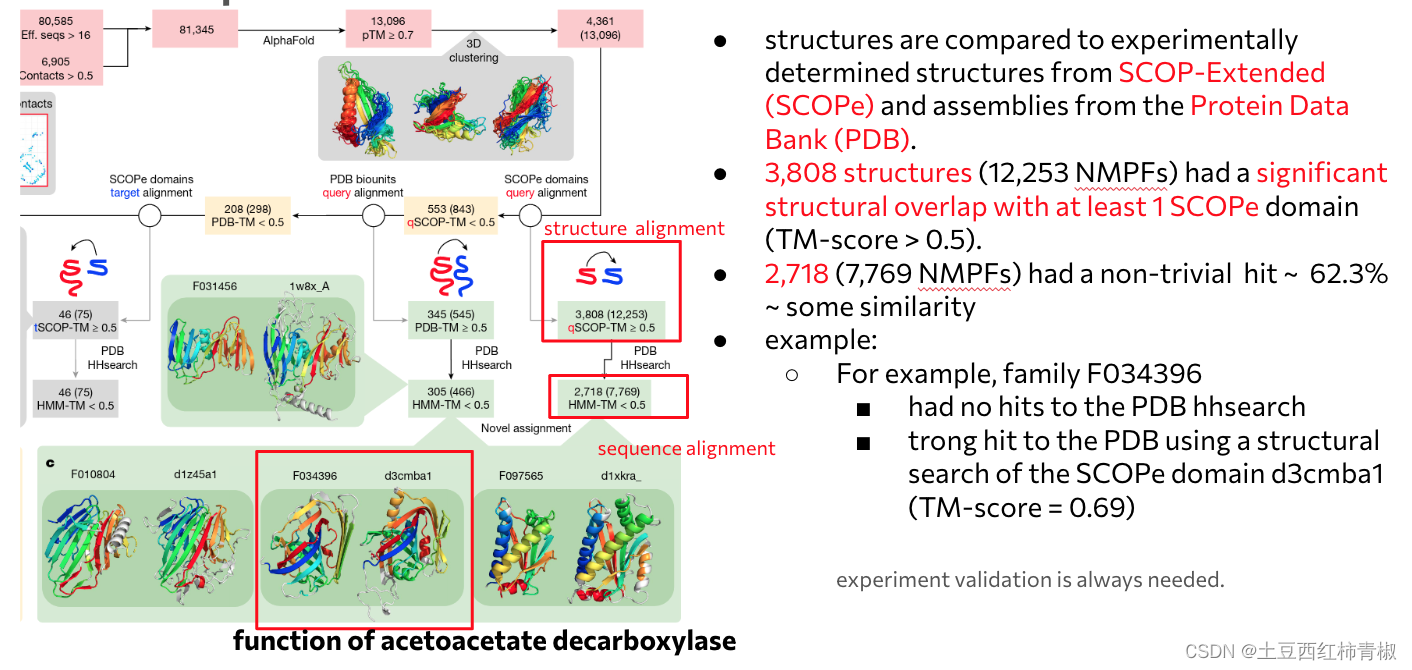
在这些4361个独特结构中, 为了检查这些结构的新颖性或功能,作者将它们与 SCOP-Extended (SCOPe) 中实验确定的结构和蛋白质数据库 (PDB) 中的assembles进行了比较。总共有 3,808 个结构(12,253 个 NMPF)与至少 1 个 SCOPe 结构域(TM 得分 > 0.5)具有显着的结构重叠。其中,2,718 个(7,769 个 NMPF)具有不平凡/显着的命中,表明 62.3% 的高质量预测与至少一个 SCOPe 域或 PDB 组件具有一定的相似性。通俗地讲,我理解是这些具有结构相似性的nmpf然后他们序列上并没有被发现。所以这里预测他们的功能集于结构是具有一定新颖性的。
举例
例如,家族 F034396 使用 HHsearch 没有命中 PDB-第二步sequence alignment那里(e 值的最高命中 = 12),但使用 SCOPe 域 d3cmba1 的结构搜索第一步那里(TM-score = 0.69)却有有强烈命中,具有乙酰乙酸脱羧酶的功能。
对于那些没有命中SCOPe的结构阈
为了确认没有 SCOPE 命中的剩余 553 个蛋白质是新折叠,对所有 PDB 生物组件(包括所有可能的链排列)进行了更彻底的搜索。
总共有 345 个模型至少命中了一个 PDB 条目,其中 305 个模型代表了新的比对。这个和之前的逻辑是类似的,也是结构类似,序列新颖,可以用来预测功能。
最后再对剩下的 208 个进行了进一步过滤,删除了 50% 的结构与 SCOPe 域匹配的预测。这里与之前不同的是我们的query是SCOPe的domain而不是之前输入的那些nmpf了。通过示意图可以发现,这样可以获取一些仅是原nmpf序列一部分的蛋白序列的比对,这部分也认为是类似结构具有类似功能。(这里有46个序列被去掉)
最后,剩下的这223 个 NMPF 中的 162就是完完全全新颖的未知功能的,因为没有被任何搜索/库被涵盖了。

当然对于结构功能预测这部分作者并没有包含有配套的实验。可以肯定是作者真的做了非常多的工作在这篇文章里,从他们使用的方法以及长达80多页的supp还有无尽的extendedfigure可以一窥。
总结下作者主要工作
-
26,931 metagenomes
-
1.17 billion protein sequences with no similarity to any sequences from 102,491 reference genomes or the Pfam database.
-
106,198 novel sequence clusters with more than 100 members, doubling the number of protein families from the reference genomes.
-
taxonomic, habitat, geographical and gene neighbourhood distributions
-
protein three-dimensional models, revealing novel structures
他们分析了 26,931 个宏基因组,并鉴定了 11.7 亿个长度超过 35 个氨基酸的蛋白质序列,与 102,491 个参考基因组或 Pfam 数据库中的任何序列没有相似性。
他们使用基于大规模graph-based的聚类,将这些蛋白质分组为 106,198 个具有 100 多个成员的新序列簇,从而使从使用相同方法聚类的参考基因组中获得的蛋白质家族数量增加了一倍。
他们根据这些家族的分类、栖息地、地理和基因邻域分布对这些家族进行注释,并且在有足够的序列多样性的情况下,预测蛋白质三维模型,揭示新的结构。
总的来说,他们的结果揭示了一个极其多样化的功能空间,凸显了进一步探索微生物功能暗物质的重要性。
总结下来,我认为他们的优越点,当然只是个人意见,毕竟没有发过这重量级的文章。大部分缺点是总结文章自己提到的诸如scaffold长度不是特别长,包括真核序列也比较多。

我还总结了之前有哪些工作类似的被做了,简单的(没有细看)总结了它们的不足之处。仅供参考。

有一些可以被后面我们用到的资源
-
IMG/M platform: analysis and annotation of genome and metagenome datasets
-
clustering method for sequence similarity : hipMCL
-
unknown functional prediction : combination of structural similarity alignment and sequence similarity alignment
-
The database provided by this paper 数据库资源这篇文章总结整理的
Home - NMPFamsDB: Fotis A Baltoumas, et al, NMPFamsDB: a database of novel protein families from microbial metagenomes and metatranscriptomes, Nucleic Acids Research, 2023;, gkad800, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad800
example: https://bib.fleming.gr/NMPFamsDB/family?id=F000037
download option: Downloads
IMG/M
个人分享,能力有限,有问题欢迎指正。
reference
Unraveling the functional dark matter through global metagenomics | Nature






















 1889
1889











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








