虚函数
虚函数是C++的运行时多态,可以在基类中将被重写的成员函数设置为虚函数。
虚函数的作用是:当通过基类的指针或引用调用该成员函数时,将根据指针指向的对象类型确定调用的函数,而非指针的类型。
例子如下所示:
- 我们定义一个基类Shape,令Rectangle类继承自Shape。
- 我们写两个函数:
outputType和outputTypeWithoutVirtual,在子类中对其进行重写。 - 在测试类中,我们创建一个Rectangle对象,然后使用Shape指针获取Rectangle对象的引用,然后分别调用虚函数和非虚函数。
#include<iostream>
namespace dcp{
class Shape{
public:
virtual int getArea(){
return 0;
}
//虚函数
virtual void outputType(){
std::cout<<"this is shape?"<<std::endl;
}
//非虚函数
void outputTypeWithoutVirtual(){
std::cout<<"this is shape!"<<std::endl;
}
};
class Rectangle:public Shape{
public:
int getArea(){
return length*width;
}
//继承后重写虚函数
void outputType(){
std::cout<<"this is rectangle"<<std::endl;
}
//继承非虚函数后重写函数
void outputTypeWithoutVirtual(){
std::cout<<"this is rectangle!"<<std::endl;
}
int length;
int width;
};
class Test{
public:
static void runTestMain(){
Rectangle rectangle;
Shape* shape = &rectangle;
shape->outputType();
shape->outputTypeWithoutVirtual();
}
};
}
在main.cpp调用,
#include <iostream>
#include"dynamic_cast_principle.cpp"
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
dcp::Test::runTestMain();
}
得到如下结果:带有virtual关键字的函数被重写后,最终调用的是子类函数,不带有virtual调用的是父类本身的函数。
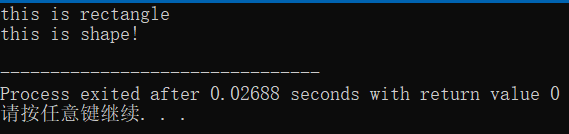
所以虚函数的作用是:当通过基类的指针或引用调用该成员函数时,将根据指针指向的对象类型确定调用的函数,而非指针的类型。
纯虚函数
纯虚函数通常需要在类声明的后面加上关键字"=0"。
有纯虚函数的类是抽象类,只能被继承,不能用来声明对象。
简单的修改一下上面的例子,将Shape中的getArea改成如下纯虚函数的形式:
virtual int getArea()=0;
然后编译以下的代码会报错:
Shape shape;
报错信息如下,意思是Shape是抽象函数不能实例化(如果Rectangle这时没有实现getArea函数,那么Rectangle也不能实例化,因为没有实现所有基类纯虚函数的Rectangle也被认为抽象函数)。

虚继承
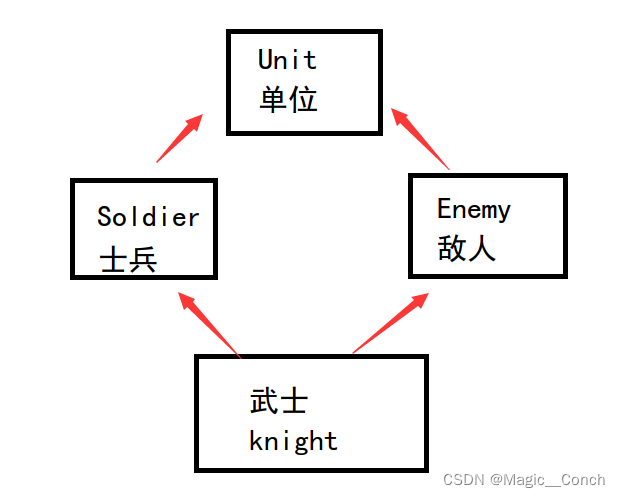
有时候会出现一个类被继承两次的情况,如下是一种多继承关系,Unit的属性在Knight中出现了2次:
#include<iostream>
namespace vt{
class Unit{
public:
int x,y;
};
class Enemy:public Unit{
public:
int hp;
};
class Soldier:public Unit{
public:
int atk;
};
class Knight:public Enemy,public Soldier{
public:
int def;
void Attack(){
std::cout<<x<<","<<y<<"attack!"<<std::endl;
}
};
class Test{
public:
static void RunTestMain(){
Knight knight;
knight.x=1;
}
};
}
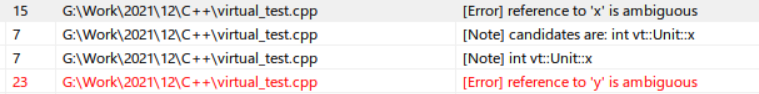
上面Attack()函数中使用了Unit的属性x、y,但是由于这个x、y可能来自于两个基类,所以无法编译成功,如下所示。这就是二义性。
想要解决这个问题,只要进行虚继承即可,如下所示。
class Unit{
public:
int x,y;
};
class Enemy:virtual public Unit{
public:
int hp;
};
class Soldier:virtual public Unit{
public:
int atk;
};
class Knight:public Enemy,public Soldier{
public:
int def;
void attack(){
std::cout<<x<<","<<y<<"attack!"<<std::endl;
}
};
简而言之,虚基类可以使得从多个类(它们继承自一个类)中派生出的对象只继承一个对象。






















 2112
2112











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








